Abstract
Aims: The long-term clinical performance of drug-eluting stents (DES) coated with biodegradable polymers is poorly known.
Methods and results: A total of 274 coronary patients were randomly allocated to paclitaxel-eluting stents, sirolimus-eluting stents, or bare metal stents (2:2:1 ratio). The two DES used the same biodegradable polymers and were identical except for the drug. At three years, the pooled DES population had similar rates of cardiac death or myocardial infarction (9.0% vs. 7.1; p=0.6), but lower risk of repeat interventions (10.0% vs. 29.9%; p<0.01) than controls with bare stents. The cumulative 3-year incidence of definite or probable stent thrombosis in the pooled DES group was 2.3% (first year: 1.8%; second year: 0.4%; third year: zero). There were no significant differences in outcomes between paclitaxel- and sirolimus-eluting stents.
Conclusions: The biodegradable-polymer coated DES releasing either paclitaxel or sirolimus were effective in reducing the 3-year rate of re-interventions.
Biodegradable polymeric coatings have been proposed as drug carriers for new formulations of drug-eluting stents (DES), in an attempt to enhance biocompatibility and ultimately improve clinical safety. Nevertheless, ideally, any improvement in safety should not be achieved at the expense of a compromise in efficacy. The “Percutaneous intervention with biodegradable-polymer based paclitaxel-eluting or sirolimus-eluting versus bare stents for de novo coronary lesions” – PAINT randomised trial showed that two novel formulations of DES coated with the same biodegradable polymeric coating (but releasing different drugs, either paclitaxel or sirolimus) were effective in reducing neointimal growth at nine months compared with bare metal stents (BMS).1 Currently, little is known regarding the very long-term clinical performance of DES coated with biodegradable polymers, especially after the second year, when the degradation process of the coating is expected to be completed.2,3 In the present study, therefore, we analysed the 36-month clinical outcomes of patients included in the PAINT trial.
Methods
The study protocol and the 1-year results of the PAINT trial have been detailed elsewhere.1,4 In brief, the PAINT was a multicentre 3-arm randomised trial which allocated patients to coronary intervention of de novo lesions with: I) Infinnium® paclitaxel-eluting stent, II) Supralimus® sirolimus-eluting stent, or III) control Milennium Matrix® bare metal stent (all by Sahajanand Medical Technologies Pvt. Ltd., India) in a 2:2:1 ratio, respectively. The primary endpoint of the present pre-defined substudy was the 3-year incidence of major adverse cardiac events defined as the composite of cardiac death, myocardial infarction or target vessel revascularisation. An independent Adverse Events Committee adjudicated all adverse events.
The stents were built with the same 316L stainless metallic platform and delivery system. The drug carrier (thickness 4-5 μm) for both DES was a blend of biodegradable polymers that included Poly L-Lactide, 50/50 Poly DL-Lactide-co-Glycolide, 75/25 Poly L-Lactide-co-Caprolactone, and Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone. The polymeric matrix is ultimately eliminated as water and carbon dioxide. Both DES formulations released approximately 50% of the drug content in the first 9-11 days, 90% in 38 days and 100% in 48 days. Complete polymer degradation occurred after seven months.
The incidence of clinical adverse events was estimated with the Kaplan-Meier method, and the outcomes of the study arms were compared using Cox regression analysis. In order to evaluate the impact of the biodegradable polymeric coating on long-term outcomes, the clinical results of both DES were pooled together and compared to the control arm with bare metal stents.
Results
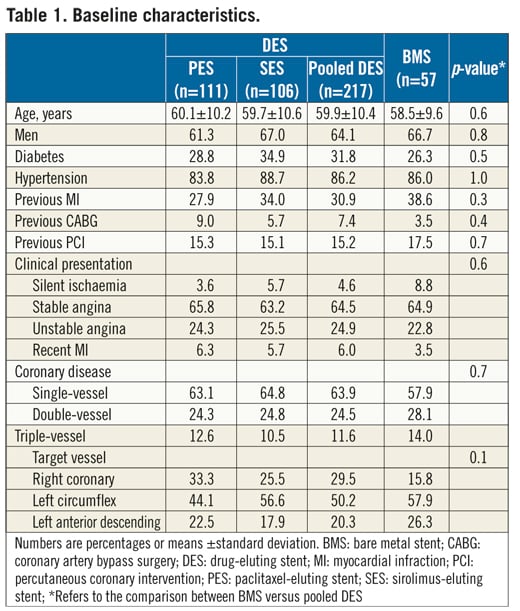
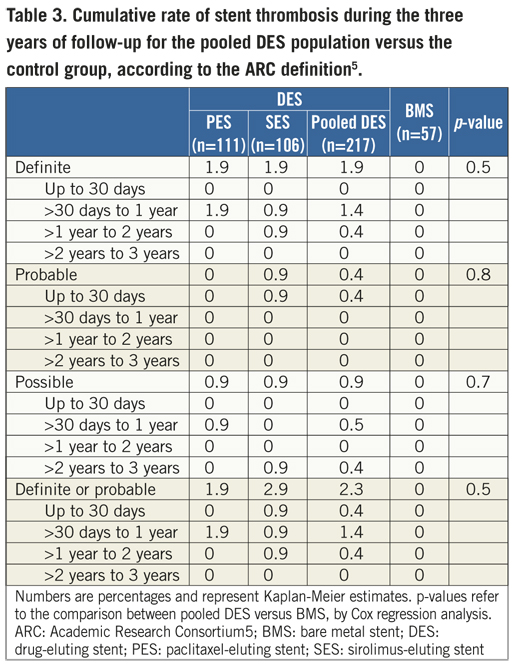
The final study population included 274 patients (111 in the paclitaxel, 106 in the sirolimus, and 57 in the bare stent groups) and 3-year clinical outcomes were assessed for 261 patients (95.2%). The study groups did not differ in terms of their baseline demographic, clinical, angiographic, and procedural characteristics (Table 1). At three years, the rates of cardiac death and of myocardial infarction were not significantly different between the pooled DES and the control groups (Table 2). However, patients treated with drug-eluting stents had significantly fewer repeat interventions than controls (Table 2). There were no stent thromboses in patients treated with BMS, while 2.3% of patients receiving DES had a definite or probable thrombotic event during follow-up (p=0.3) (1.8% in the first year, 0.4% in the second year, and zero in the third year) (Table 3). There were no significant differences in the incidence of 3-year clinical endpoints between paclitaxel- and sirolimus-eluting stents (p>0.05 for all comparisons) (Table 2 and Table 3).
Discussion
The present study shows that, in comparison to bare stents, the two tested formulations of DES using biodegradable coatings were associated with a significant improvement in clinical outcomes that was sustained over the 36-month period of observation. There were no differences in clinical outcomes between sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents. The analysis of the safety profile of the two biodegradable-coated DES was limited by the small sample size and is merely speculative. However, it is curious to observe that, after the second year, no definite or probable stent thrombosis was detected among patients treated with the DES.
Funding
Sahajanand Medical Technologies Pvt. (India) and CMS Medical (Brazil) provided the study stents and the funds to cover the expenses with the angiographic core laboratory.
Conflict of interest statement
P. Lemos, B. Moulin, J.A. Arruda, V.C. Lima, E.E. Ribeiro are members of the advisory board for Scitech Medical. P. Lemos is member of the advisory board for Boston Scientific Latin America. P. Lemos is on the speaker’s bureau for Boston Scientific, Cordis, Sahajanand, and Scitech. E.E. Ribeiro is on the speaker’s bureau for Boston Scientific, CMS, Cordis, and Sanofi-Aventis. F.S. Brito Jr is on the speaker’s bureau for Cordis, Boston Scientific, CMS Medical, and Biotronik. No other authors reported financial relationships with the industry.

