
The established mechanisms of long-term adverse events related to coronary stenting include thrombosis, neointimal hyperplasia, and persistent inflammation/neoatherosclerosis, which could be closely related to the persistent presence of metallic stents in the vessel wall (Figure 1). Fully bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) have been developed to overcome the shortcomings of metallic coronary stents that are persistently present with or without polymer in the vessel wall. However, the Absorb™ BVS (Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was demonstrated to be inferior to new-generation metallic drug-eluting stents (DES) due to a higher rate of device thrombosis before complete resorption of the scaffold in several randomised controlled trials1. The DynamX™ Novolimus-Eluting Coronary Bioadaptor System (Elixir Medical Corporation, Milpitas, CA, USA) is a novel coronary device in which the sinusoidal rings of metallic DES are designed to be separated at the uncaging segments at around six months after implantation, allowing the artery to be circumferentially “uncaged”.
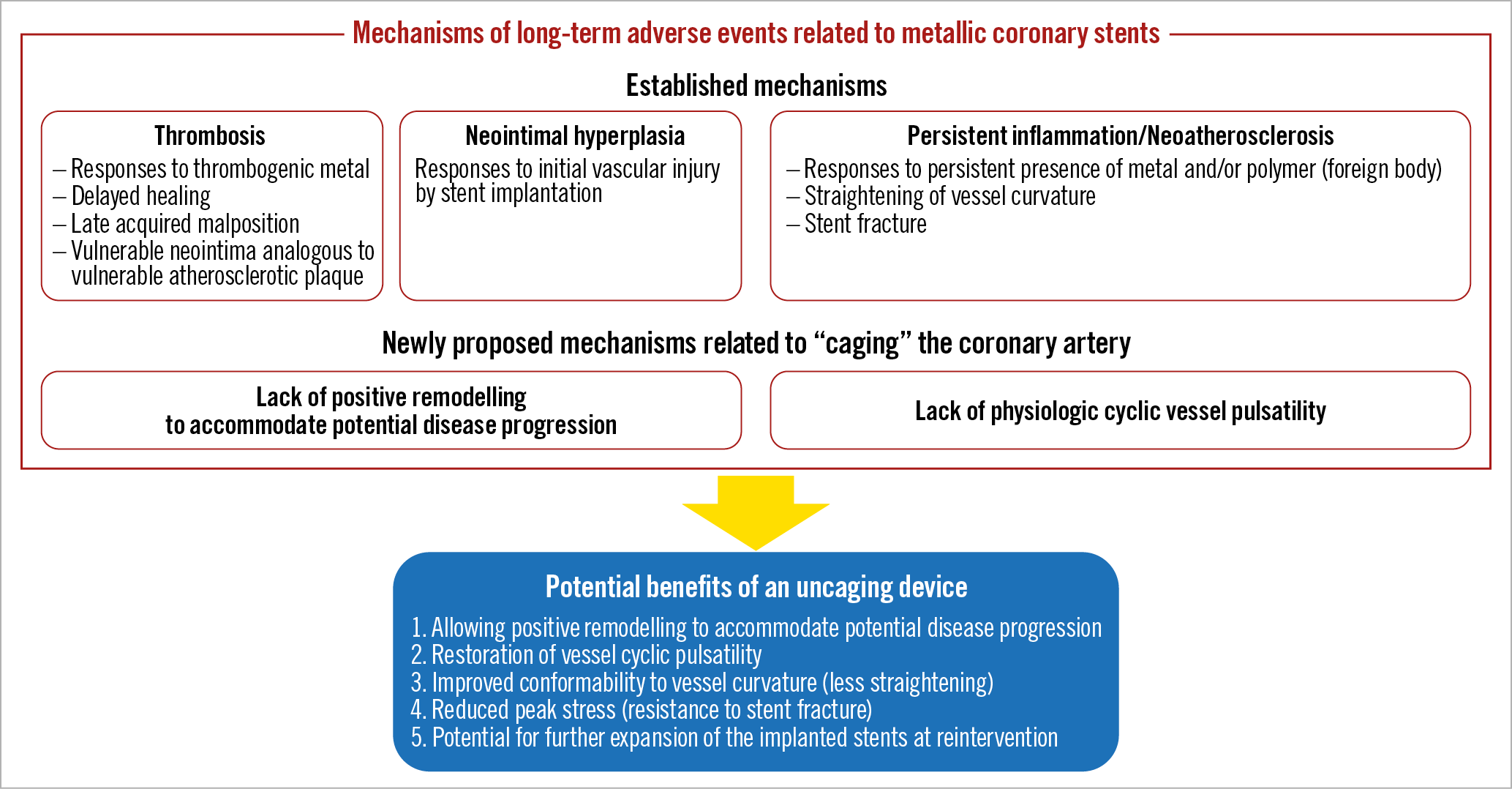
Figure 1. Mechanisms of long-term adverse events related to metallic coronary stents and potential benefits of an uncaging device.
Restenosis after coronary angioplasty occurs predominantly within six months after the procedure, driven mainly by negative remodelling of the treated artery2,3. Indeed, metallic coronary stents reduced restenosis by preventing negative remodelling at the expense of greater neointimal hyperplasia within six months after the procedure. However, the persistent presence of metallic stents in the artery may not be necessary, because lumen diameter after coronary angioplasty is generally maintained without stents beyond six months after the procedure2. The DynamX was developed based on the novel hypothesis that “caging” the artery might lead to long-term stent-related adverse events through lack of positive remodelling and lack of physiologic cyclic vessel pulsatility. Potential benefits of an uncaging device might include the following: 1) allowing positive remodelling to accommodate potential disease progression; 2) restoration of physiologic cyclic vessel pulsatility; 3) improved conformability to vessel curvature (less straightening); 4) reduced peak stress (resistance to stent fracture); and 5) potential for further expansion of the implanted stents at reintervention (Figure 1).
In this issue of EuroIntervention, Verheye et al report the results from the first-in-man (FIM) study of the DynamX, enrolling 50 patients with single de novo coronary lesions4.
The investigators should be congratulated on the accomplishment of this important clinical study of an innovative coronary device with extensive imaging evaluation. Over a period of 12 months, there were only two target lesion failures without definite or probable device thrombosis. Mean late lumen loss was 0.12±0.18 mm in-device and 0.11±0.16 mm in-segment, which is comparable to those of the cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent in the ABSORB Japan trial (0.16±0.33 mm in-device and 0.12±0.32 mm in-segment, respectively)5. Fourteen patients with a post-procedural change in angulation of ≥9° showed a return towards baseline angulation at follow-up (from a mean of 157.5±14.5° post procedure to 149.7±16.1° at follow-up). Furthermore, the detailed intravascular imaging data analyses in the FIM study have provided some proof of concept for “uncaging” the artery with the DynamX. Serial intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) from post procedure to 10.3±1.5 months follow-up in 38 patients demonstrated increased mean device area from 7.39±1.20 mm2 to 7.74±1.46 mm2 (Δ=5%, p=0.0005), and increased mean vessel area from 14.11±2.99 mm2 to 14.54±3.12 mm2 (Δ=3%, p=0.02). Optical coherence tomography (OCT) in 28 patients confirmed disengagement of the uncaging elements in all imaged segments. Stationary co-registered OCT in seven patients demonstrated pulsatility of the treated vessel segment during systole and diastole, with a lumen area change of 11% and a device area change of 7.3%.
Despite some proof of concept provided by the FIM study, there remain many issues to be discussed on the true benefits of the DynamX. First, the single-arm study design of the FIM study without a concurrent control group of contemporary DES precluded any argument on the superiority of DynamX over conventional DES in terms of positive remodelling, pulsatility, and conformability. Second, positive vessel remodelling has historically been recognised as the compensatory mechanism for atherosclerotic plaque progression6. However, positive remodelling at the site of conventional metallic DES implantation has been reported to occur in association with late acquired incomplete stent apposition, persistent inflammation/neoatherosclerosis, and/or very late stent thrombosis7. Therefore, positive remodelling could occur even in the presence of “caging” metallic DES. Moreover, positive remodelling after DES implantation might not always represent a compensatory phenomenon. Third, vessel distensibility was reported to be impaired in the atherosclerotic segments8,9. Therefore, highly atherosclerotic stented segments might perhaps not have enough room for restoration of pulsatility to provide a meaningful reduction in stent-related adverse events. Fourth, stent fracture was reported in 1-8% of patients after DES implantation and was associated with higher risk for target lesion revascularisation and/or stent thrombosis10. The present FIM study did not provide any data on stent fracture, and it is unknown whether the use of DynamX as compared with conventional DES is associated with fewer stent fractures. Furthermore, the most potent risk factor for stent fracture is reported to be “hinge motion” at the lesion site. Therefore, it is also unknown whether the culprit for the stent-related adverse events is stent fracture or “hinge motion”. Despite these potential limitations, the DynamX has taken a promising first step. A large clinical trial with intracoronary imaging evaluation would be needed to demonstrate the true benefits of the concept of “uncaging” the artery with an innovative device.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

