Device description
Name and manufacturer: Axxess™; Biosensors International, Morges, Switzerland.
Approval status: CE approved. Not available in USA and certain other countries.
Platform: Nitinol.
Strut thickness: 150 micrometres.
Coating: Biolimus A9™, a highly lipophilic, semi-synthetic sirolimus analogue, immersed in the biodegradable polylactic acid (PLA) and applied abluminally. The Biolimus elution half-life is 21 days. PLA dissolves after nine months.
Specific stent design: Conically shaped, self-expanding stent, with three radiopaque markers at the distal stent edge (asterisks, Figure 1A), and a single marker at the proximal edge (arrowhead, Figure 1A).
Guiding: 7 Fr, but radial 6.5 Fr sheathless is possible with one guidewire.
Classification according to MADS: “M” category. Axxess in main proximal first (PM stenting), post-dilatation if needed (skirt), and additional stents: skirt+distal main (DM), skirt+side branch (SB) or extended V. Bifurcation angle should be ≤70°.
Delivery system: Single rapid exchange delivery system with hydrophilic coating and markers outside the Axxess stent (asterisks and arrowhead, Figure 1B). The cover sheath with a radiopaque distal marker (arrow, Figure 1B) is gradually retracted to deploy the stent (arrow, Figure 1B).
Stent sizes: 3.0 and 3.5 mm, accommodating vessels from 2.75 to 4.25 mm (Figure 1C).
Stent length: 11 and 14 mm.
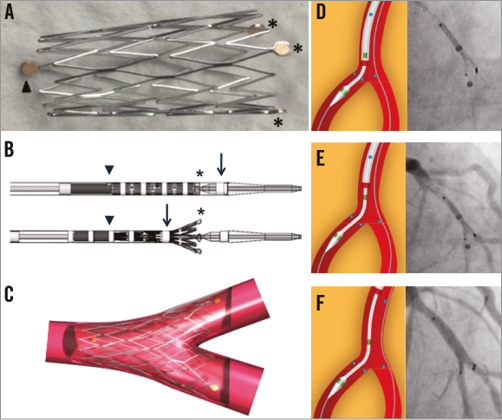
Figure 1. Axxess design and crucial procedural steps.
Procedural details
After wiring both distal branches, predilatation is recommended to facilitate lesion crossing and optimal flaring of the Axxess stent. For tight lesions with few calcifications, compliant balloons can be used with a 0.8 to 1.0 balloon-to-artery ratio. A non-compliant balloon should be preferred for severely calcified lesions. The delivery catheter is preferably advanced on the wire towards the most angulated branch, or the most severely diseased or dissected branch. Once the distal stent markers are at the carina, the stent is progressively unsheathed (Figure 1D). Two of the distal stent markers should be seen in one distal branch and the third marker in the other one. The partially flared stent should be gently advanced over the carina (Figure 1E). As long as the cover sheath has not released more than half of the Axxess stent (point of no return indicated by a radiopaque marker), the stent can be repositioned. Once in optimal position, the cover sheath is further retracted to release the Axxess stent (Figure 1F). The jailed wire can be repositioned and optimal stent deployment can be enhanced by single or kissing balloon inflation. Additional drug-eluting stents (DES) can be implanted in distal branches, considering a 1 to 2 mm overlap with the Axxess stent. Final kissing balloon inflation is recommended in this overlap region. An animation of the implantation sequence is available in the Online data supplement (Moving image 1).
Clinical data
The first-in-man study with the current biolimus-eluting Axxess stent was the AXXESS Plus study enrolling 139 patients1. The majority (77.7%) were true bifurcation lesions2, involving the left anterior descending (LAD) - diagonal (D) bifurcation (73.4%). The device success rate was 93.5% (stent delivery failure 6.5%), and 80.9% of the patients received additional stents in the main vessel (MV) and/or SB, with a majority (77.1%) being CYPHER® stents (Cordis, Johnson & Johnson, Warren, NJ, USA). The angiographic late loss of the Axxess stent at six months, the primary endpoint, was 0.09±0.56 mm. Treatment of the SB varied according to the degree of involvement: 51.5% received a stent, and 29% had balloon angioplasty only. Stenting of the SB resulted in a restenosis rate of only 9.2% at six months, while balloon angioplasty had 25% restenosis and untreated SB had 12%. The overall rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), consisting of cardiac death, myocardial infarction (MI) and ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation (id-TLR) at six months was 11.2% (0.7% death, 6% MI and 7.5% id-TLR). There were no cases of acute or subacute stent thrombosis (ST). Late ST was confirmed in 2.2% of the patients. A limited number of patients (46) underwent intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) interrogation at six months, confirming effective lesion coverage along with significant neointimal suppression3.
Based on these promising results, a second larger study was designed, the DIVERGE study, with a total of 302 patients4. Learning from AXXESS Plus which showed that additional DES in the SB provided better procedural outcomes and better late results, DIVERGE mandated stricter protocol obligations for lesion treatment, such as the use of only CYPHER stents as additional stents if the residual diameter stenosis of the distal branches exceeded 30%. A majority of the lesions were true bifurcations (77.4%), involving the LAD-D bifurcation (80.8%). Most patients underwent additional implantation of CYPHER stents (64.7% in both distal MV and SB; 17.7% in MV only; 4.0% in SB only). Stent delivery failure was 1.7%. Procedural success rate (angiographic success rate in the absence of any in-hospital MACE) was 96.7%. The nine-month MACE rate, the primary endpoint, was 7.7% (composite of 0.7% any death, 4.3% MI, 4.3% id-TLR). Subacute and late ST occurred in 0.7% and 0.3% of patients, respectively. The first 140 patients received angiographic follow-up at nine months, showing a total restenosis rate of 6.4%. In addition, the first 68 patients had baseline and nine-month IVUS5, demonstrating a minimal amount of neointima throughout the Axxess stent segment (0.4±0.6 mm3/mm), and an 18.0% enlargement of the minimum lumen area (MLA) at nine months.
The three-year clinical data have been published for DIVERGE, with MACE rates of 16.0% at three years, and 2.3% of the patients with ST6. Longer-term clinical follow-up has been completed for both the AXXESS Plus and the DIVERGE trials up to five years.
Ongoing studies
The five-year clinical follow-up results of AXXESS Plus and DIVERGE have been presented and are expected, as well as the results of the COBRA trial, which assessed the healing response by optical coherence tomography (OCT) in 40 patients with true and complex bifurcation lesions treated either with Axxess and additional BioMatrix™ (Biosensors International, Morges, Switzerland) or culotte with XIENCE PRIME™ (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA)7.
Unique features
– Second-generation DES with self-expanding nitinol.
– Symmetry of the device respecting the polygon of confluence and equal access to both distal branches, without the need for stent crossing to access branches for additional stenting.
– Axxess can be operated on a single wire.
Potential improvements
Reducing the profile of both Axxess and delivery catheter will improve delivery, especially in very tortuous or calcified vessels. Increase in commercialised stent sizes, including a 4.0 mm device suitable for left main. Extend flaring capacity for bifurcation angles >70°.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Online data supplement
Moving image 1. Animation of the deployment sequence of the Axxess stent and additional stent.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Animation of the deployment sequence of the Axxess stent and additional stent.