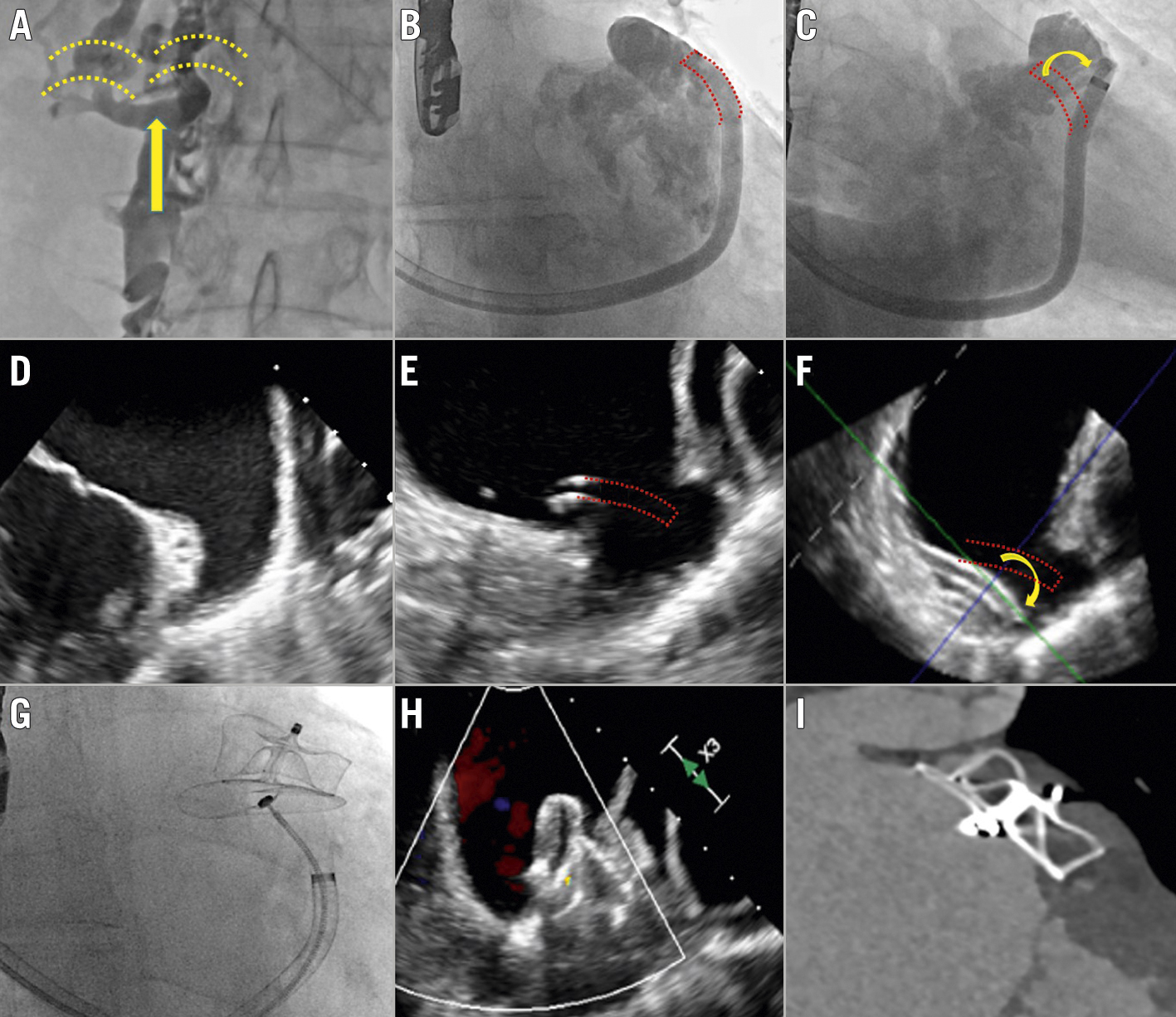
Figure 1. LAAC with superior vascular access. LAAC completed in a patient with agenesis of the inferior vena cava (A) by means of superior vascular access with a steerable sheath. B-F)The wrong initial delivery system position (red dotted lines), a direct consequence of the superior vascular access, was corrected by using the new Amplatzer steerable delivery sheath (C, F), with a good degree of LAA sealing before device release (G-H) and at 45 days (I). LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAC: LAA closure
Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) is an alternative therapeutic option for preventing stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. However, the procedure cannot be completed in a small but sizeable percentage of cases due to several factors, such as challenging left atrial appendage (LAA) anatomies, delivery sheath LAA misalignment, or inferior venous system anomalies.
Below, we present the case of a 62-year-old man referred to our centre for LAAC due to recurrent strokes despite being on anticoagulation. The procedure was aborted due to agenesis of the inferior vena cava with no possibility to access the right atrium, despite several attempts (Figure 1A, Figure 1D). We therefore decided to attempt a new LAAC using superior vascular access (using a vein flowing into the superior vena cava).
We percutaneously gained vascular access through the left axillary vein in order to have a better alignment of the delivery sheath with the LAA axis. The transseptal puncture was performed at the inferoposterior part of the fossa ovalis with the SupraCross RF Wire and Sheath (Baylis Medical), a transseptal puncture system consisting of a steerable sheath and radiofrequency wire with a flexible, spiral tip, to obtain access to the left atrium. After gaining left atrial access, an Amplatzer steerable delivery sheath (ASDS; Abbott) was delivered into the left atrium. However, due to the superior access used in this procedure, the alignment of the ASDS with the main axis of the LAA was possible only after deflecting the distal articulation of the ASDS (Figure 1B, Figure 1C, Figure 1D, Figure 1E, Figure 1F). A 31 mm Amplatzer Amulet device (Abbott) was then successfully released after confirming proper device placement using both fluoroscopy (Figure 1G, Moving image 1) and echocardiography (Figure 1H, Moving image 2). Finally, pericardial tamponade, a probable consequence of the high force applied on the ASDS during the device delivery, was successfully aspirated without sequelae. The vascular access site was then closed with a Z-shaped suture. At 45 days, no events were reported and the computed tomography scan showed a good position of device with good LAA-device alignment (Figure 1I, Moving image 3).
In summary, coaxial alignment of the delivery sheath with the LAA axis is crucial to achieve good LAA sealing and device stability during percutaneous LAAC. However, this goal can be challenging in complex LAA morphologies or with non-femoral vascular access. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first percutaneous LAAC with superior vascular access ever reported. The procedure was completed only by using a steerable sheath for both the transseptal puncture and device deployment. The availability of the new ASDS may reduce the number of failed LAAC in the future, and may even, in some select cases, allow LAAC to be performed using a non-femoral vascular access. However, the high degree of tension developed by the delivery system during this kind of procedure might require further measures (e.g., partial release of the lobe device [the so called “ball shape”] in left atrium and subsequent alignment of the delivery sheath with the LAA) to prevent potential complications.
Conflict of interest statement
L. Roten reports speaker/consultation fees from Abbott and Medtronic. S. Windecker reports research and educational grants to the institution from Abbott, Amgen, BMS, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Cardinal Health, CSL Behring, Daiichi Sankyo, Edwards Lifesciences, Johnson&Johnson, Medtronic, Querbet, Polares, Sanofi, Terumo, and Sinomed. L. Räber reports research grants to institution from Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Biotronik, Heartflow, Infraredx, Sanofi, and Regeneron and speaker/consultation fees from Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, CSL Behring, Canon, Occlutech, Sanofi, and Vifor. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to the contents of this paper.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Images related to the fluoroscopy.
Moving image 2. Images related to the intraprocedural transoesophageal echocardiography.
Moving image 3. Images related to the 45-day computed tomography follow-up.

