Abstract
Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) is increasingly used as a valuable intervention to prevent cardioembolic stroke among patients with atrial fibrillation who are poor candidates for long-term anticoagulation. The safety of the procedure has significantly improved over time; nevertheless, device embolisation remains a severe complication that still occurs in around 0.1% of cases. Its management must be rapid and effective in order to reduce mortality. The anatomical location of the embolised device dictates the technical approach for retrieval and has a major impact on the clinical outcome of patients. Percutaneous recapture is the main approach in case of an aortic or left atrial embolisation, while emergent surgery should be performed if the device becomes entangled in the mitral apparatus with poor haemodynamics unsolved by transcatheter device mobilisation into the left ventricular (LV) cavity. In cases of LV embolisation and stable haemodynamics, a transfemoral or transseptal retrieval may be attempted. The equipment for retrieval is key to success: all cath labs performing LAAC procedures should be equipped with minimum 16 Fr sheaths, steerable sheaths, single-loop snares and grasping tool devices. This paper includes a summary of the European Left Atrial Appendage Closure Club consensus recommendations for LAAC device embolisation management.
Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) is increasingly used as a valuable intervention to prevent cardioembolic stroke among patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) who are poor candidates for long-term anticoagulation. The safety of the procedure has significantly improved over time, due to operator experience and optimised design of closure devices, with a rate of major periprocedural adverse events around 2-3% in recent series12. Among these, device embolisation is a severe complication, occurring mainly (65-70% of cases) in the acute (within 24 hours) and early (<30 days) phases34. Using modern devices, better computed tomography-/transoesophageal echocardiography-based sizing, and better implantation techniques, this problem has become exceedingly rare. Although the incidence of this complication has been reduced from 1% to 0.1%, its management must be rapid and effective in order to reduce mortality, which has been reported as high as 20%, particularly in patients requiring surgery to remove the embolised device5.
Mis-sizing (under- and oversizing), off-axis device orientation, too proximal implantation, shallow-shaped appendages, and rhythm cardioversion have been identified as risk factors for device embolisation during LAAC procedures6.
The anatomical location of the embolised device dictates the technical approach for retrieval and has a major impact on the clinical outcome of patients. In the case of a device entangled in the mitral apparatus with poor haemodynamics, a rapid attempt at transcatheter mobilisation of the device into the left ventricular cavity can be performed; in case of failure, emergent surgery should be performed. In all other cases, a percutaneous recapture may be attempted for retrieval of the embolised device.
The aim of this manuscript is to describe the possible techniques for handling the embolisation of specific LAAC devices in specific clinical scenarios, from a practical point of view. The Central illustration summarises the European Left Atrial Appendage Closure Club (ELAACC) consensus recommendations for LAAC device embolisation management.
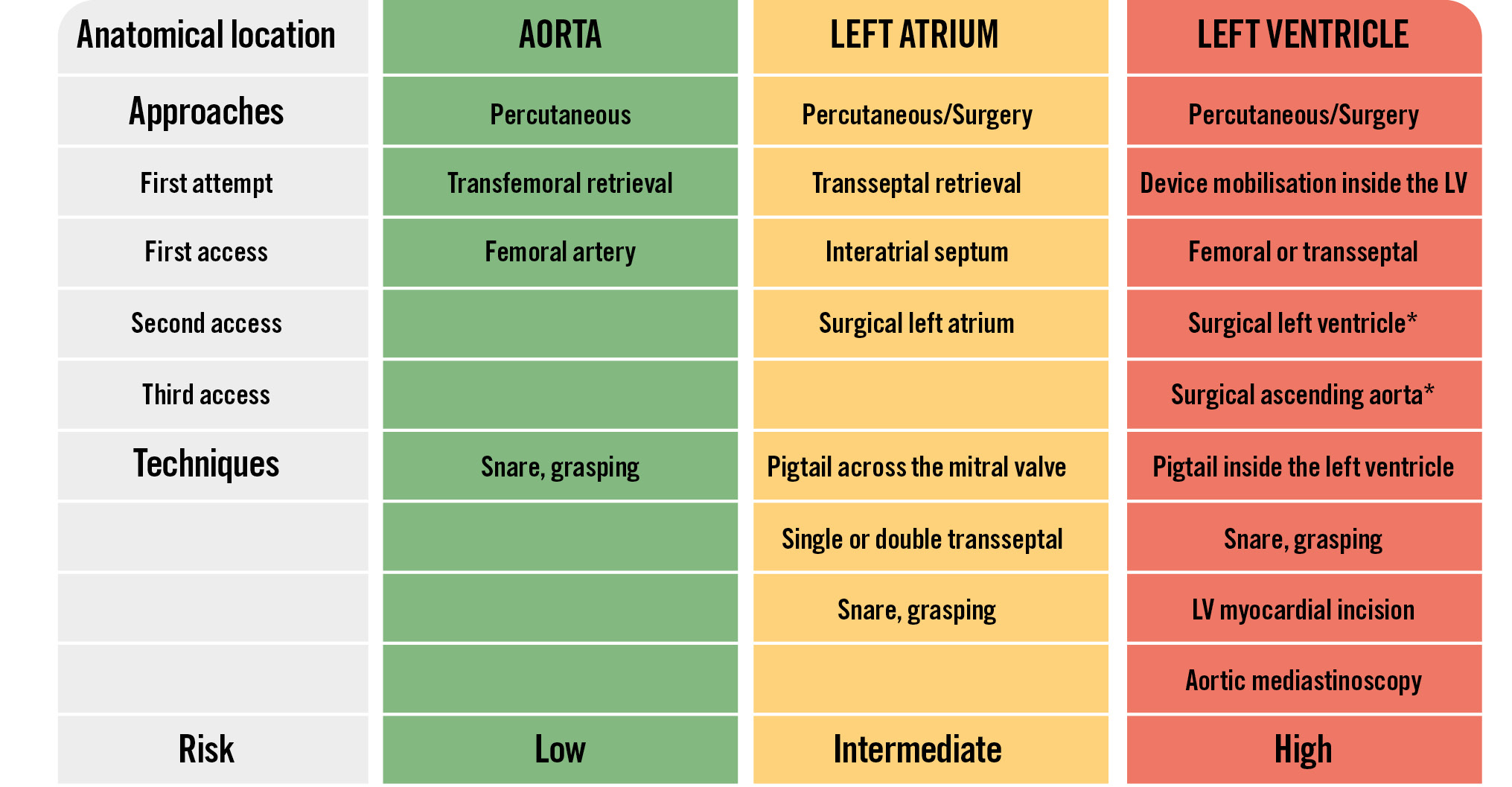
Central illustration. Management of LAAC device embolisation: ELAACC consensus. *Should be used emergently in cases where the device is entangled in the mitral apparatus and if haemodynamic compromise is not resolved by device mobilisation. ELAACC: European Left Atrial Appendage Closure Club; LAAC: left atrial appendage closure; LV: left ventricle
Dedicated material and specific techniques for LAAC device embolisation management
The design of the dislodged device has an impact on the recapture manoeuvre.
In the case of the Amplatzer Cardiac Plug (Abbott), the distal end screw is the preferred snare point because the device’s hooks point away from the sheath when it is pulled into the retrieval sheath. The proximal end screw is still a feasible snare point but requires a greater withdrawal force.
With the Amplatzer Amulet device (Abbott), the proximal end screw is recessed (for a lower thrombogenicity), and therefore, only the distal end screw remains available for snaring. The waist between the lobe and the disc of the Amplatzer Amulet could be snared as well, but it requires very large sheaths. Figure 1 illustrates the recapture of an Amplatzer Amulet device using a single-loop snare and a large sheath (bench test).
The percutaneous retrieval of a dislodged WATCHMAN FLX device (Boston Scientific) has been reported to be more challenging than that of Amplatzer Cardiac Plug/Amulet devices7, requiring larger sheaths and snares. Although it may be possible to snare the treaded insert, it is too short to be pulled into the sheath. Snaring a strut of the WATCHMAN FLX could be attempted in order to pull the device into the sheath with a firm force for complete collapse. Snaring the device in the centre or from the sides is also possible but requires more withdrawal force (Figure 2, Figure 3). A mother-in-child technique using a steerable sheath (e.g., Agilis 8.5 Fr [Abbott]) inside a large-bore sheath could be used for snaring.
Another possible technique involves using a stiff coronary wire guided through the device using a 6 Fr guiding catheter, capturing it with a lasso, and then pulling back both the lasso and the guiding catheter into the same large-bore sheath. Table 1 summarises the peculiarities of Amplatzer Amulet and WATCHMAN FLX devices and tips and tricks for retrieval manoeuvres after embolisation.
Large-bore sheaths with a minimum lumen diameter of 2-4 Fr greater than the delivery catheter used during the LAAC procedure are needed to accommodate device retrieval, ranging from 14 Fr up to 26 Fr (Table 2).
Single-loop snares are more appropriate than multiple-loop snares for grasping the embolised devices with a minimum diameter of 20 mm, up to 35 mm. In addition to snares, a bioptome or vascular forceps can be used, but it must be borne in mind that the high withdrawal force required to pull the device into the sheath can lead to failures with these materials, as illustrated in Moving image 1.
The Raptor grasping device (STERIS) is an endoscopic instrument designed for gastrointestinal applications that combines alligator and rat tooth capabilities, increasing the withdrawal force applied for recapture of the embolised LAAC device7. A coaxial alignment of the jaws of the Raptor with the centre of the disc of the Amplatzer Amulet or WATCHMAN FLX prosthesis allows successful grasping and retraction of the disc into the sheath (Figure 4A)8.
The ŌNŌ retrieval device (B. Braun)9 has a basket flare design that can be used in addition to snares and/or grasping tools to enhance the retrieval capability of large embolised LAAC devices (Figure 4B).
The main advantage of the grasping devices is the significant withdrawal force that can be applied when the grasper is advanced to clamp the trabeculae or struts of the umbrella. This provides a much greater strength than a snare embracing a part of the embolised device. The risk of damaging the surrounding structures is lower during snaring manoeuvres than when using grasping devices.
During these manoeuvres, the entire device should be retracted into the lumen of the retrieval sheath in order to reduce the risk of vascular damage while removing all the material from the patient’s body. Figure 5 lists the snares and grasping devices available for LAAC device recapture.
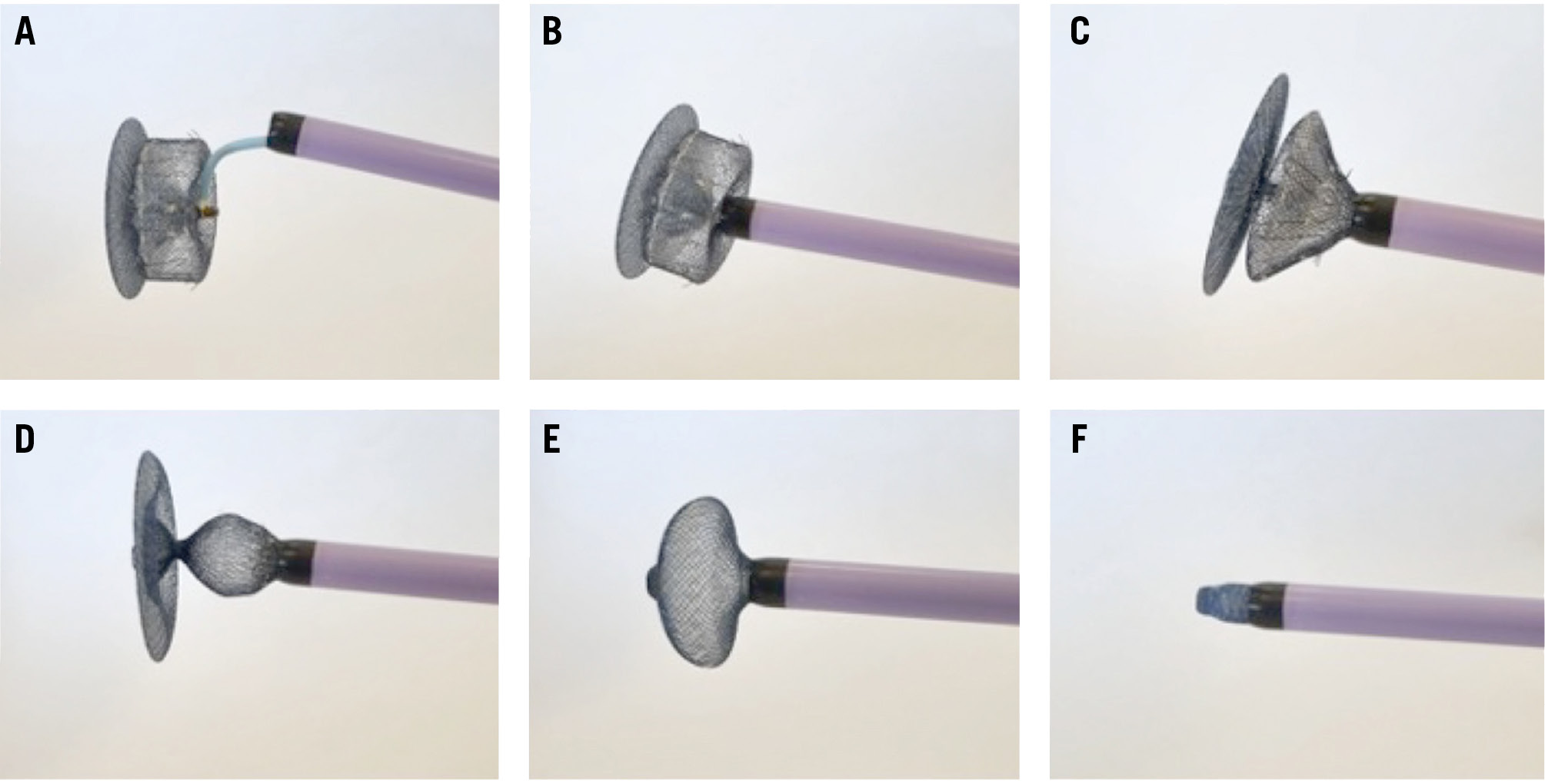
Figure 1. Recapture of an Amplatzer Amulet device into a large-bore sheath using a single-loop snare, step-by-step (bench test). A) A single-loop snare captures the distal end screw of an Amplatzer Amulet device, using a 6 Fr multipurpose catheter inside a 16 Fr sheath. B) A 16 Fr sheath is advanced close to the lobe of the Amplatzer Amulet device. C,D) Withdrawal force is applied to the snare, allowing a partial collapse of the lobe of the Amplatzer Amulet device. E) Complete collapse of the lobe and partial collapse of the disc of the Amplatzer Amulet device. F) Complete collapse of the entire Amplatzer Amulet device, recaptured inside the 16 Fr sheath.
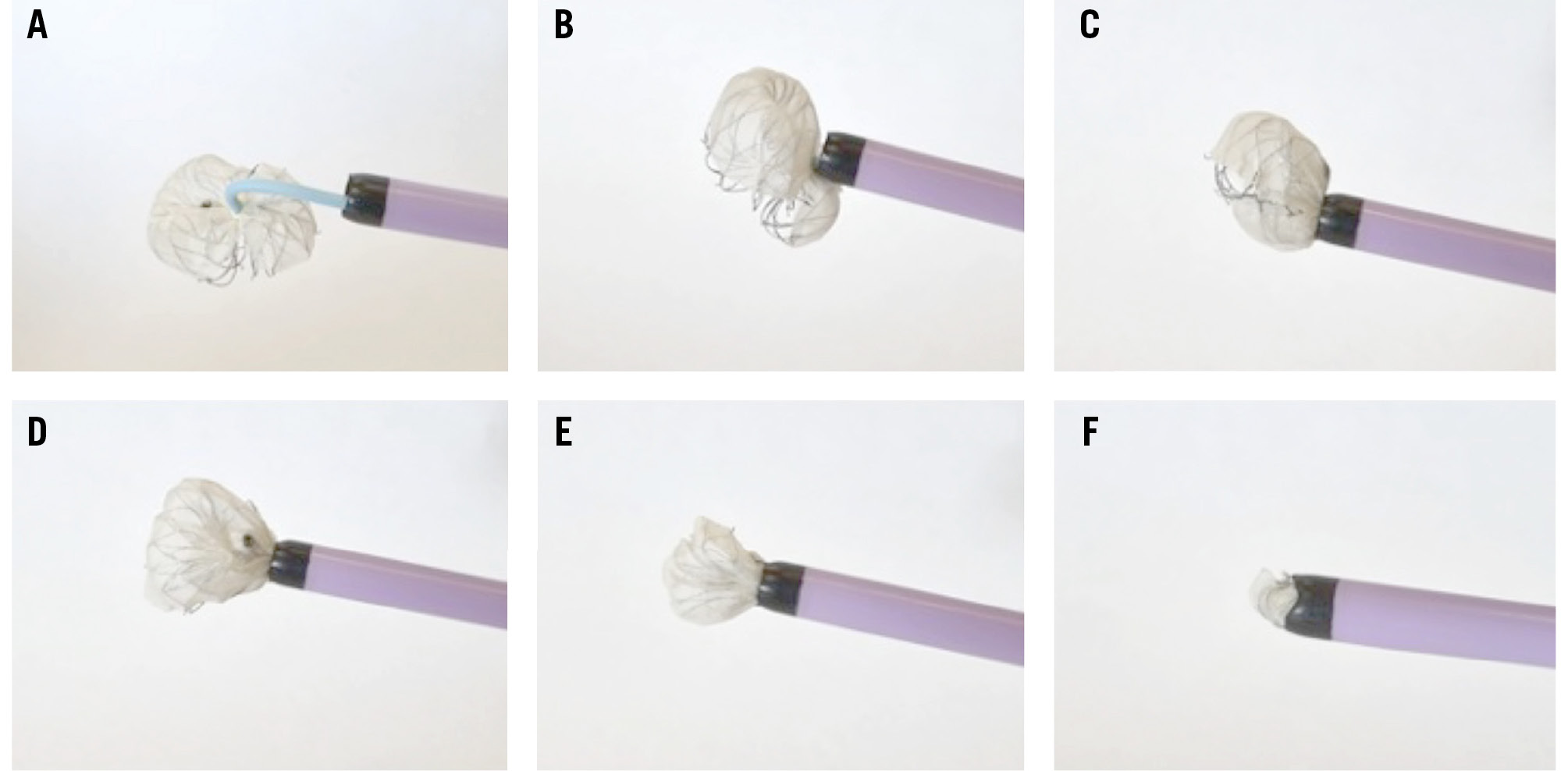
Figure 2. Recapture of a WATCHMAN FLX device into a large-bore sheath using a single-loop snare, step-by-step (bench test). A) A single-loop snare captures the centre of the WATCHMAN FLX device, using a 6 Fr multipurpose catheter inside a 16 Fr sheath. B) A 16 Fr sheath is advanced close to the WATCHMAN FLX device. C-E) Withdrawal force is applied to the snare, allowing a partial collapse of the WATCHMAN FLX device. F) Complete collapse of the entire WATCHMAN FLX device, recaptured inside the 16 Fr sheath. Fr: French
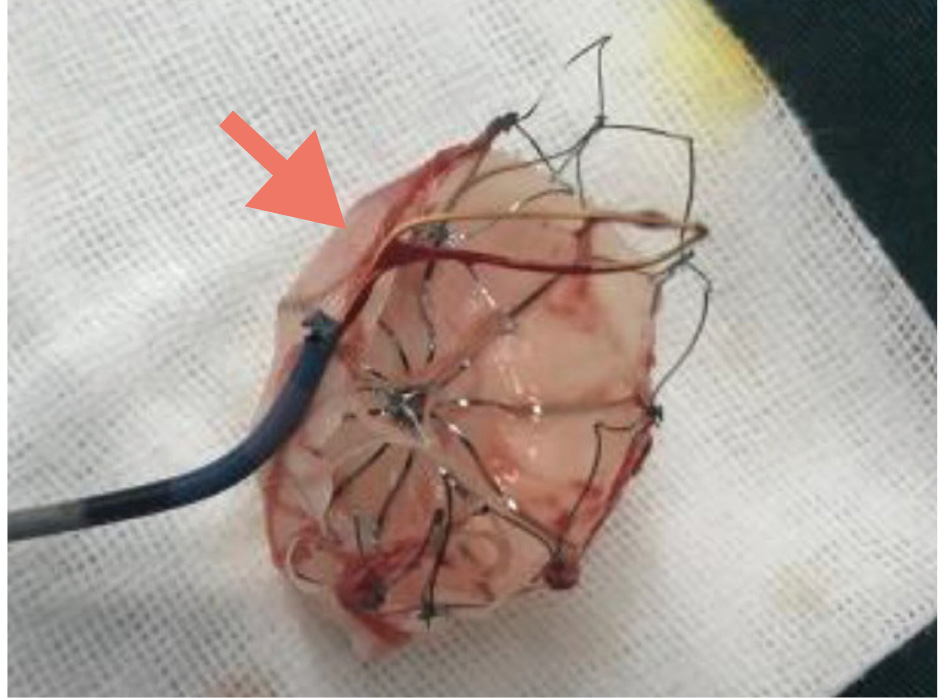
Figure 3. A WATCHMAN device after recapture using a single-loop snare. The aspect of a 33 mm WATCHMAN device (Boston Scientific) after retrieval using a Amplatz Goose Neck snare (Medtronic). Adapted with permission from8.
Table 1. Peculiarities of the LAAC devices and tips and tricks for retrieval after embolisation.
|
Retrieval manoeuvre |
Amplatzer Amulet |
WATCHMAN FLX |
|---|---|---|
|
Snaring |
Distal end screw |
Centre of the device |
|
Connecting waist |
Strut |
|
|
0.014 inch wire through the trabeculae |
0.014 inch wire through the strut |
|
|
Grasping |
Trabeculae of the lobe |
Lateral side of the device |
|
Trabeculae of the disc |
Strut |
|
|
Combination of both techniques |
Snaring distal end screw and grasping the lobe |
Snaring centre of the device and grasping the lateral side |
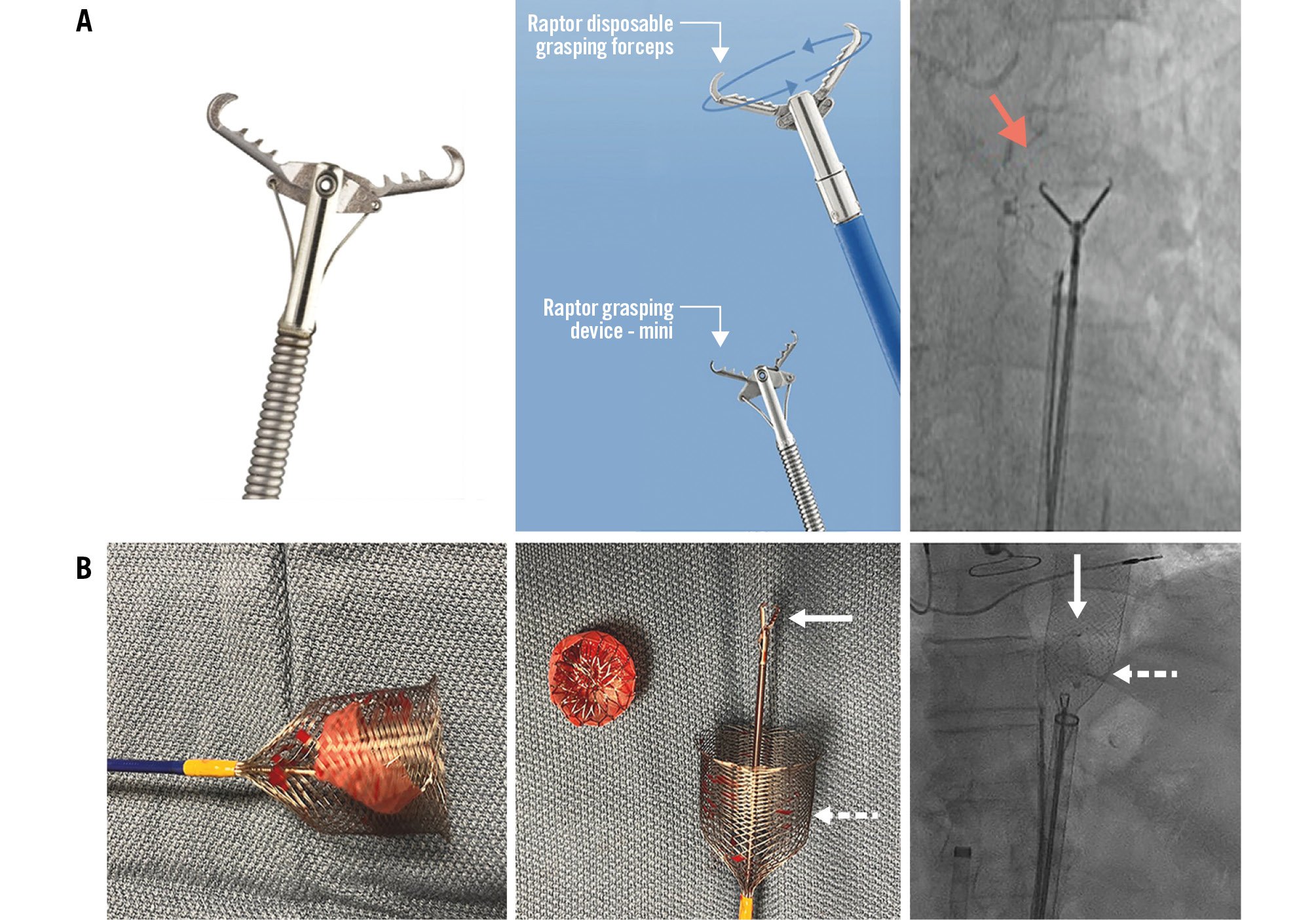
Figure 4. The Raptor grasping tool and the ŌNŌ retrieval device. A) The Raptor grasping tool with alligator and rat tooth capabilities, oriented coaxially to the device for successful retrieval. A 33 mm WATCHMAN embolisation into the aorta recaptured (red arrow) using a combination of a single-loop snare, 7 Fr guiding catheter in a 16 Fr sheath and Raptor forceps. Adapted with permission from8. B) The basket flare design of the ŌNŌ device improves its ability to retrieve large LAAC devices. A 27 mm WATCHMAN FLX embolisation into the left ventricular outflow tract recaptured using Raptor forceps (white solid arrow) and an ŌNŌ device (white dotted arrow). Adapted with permission from9. LAAC: left atrial appendage closure
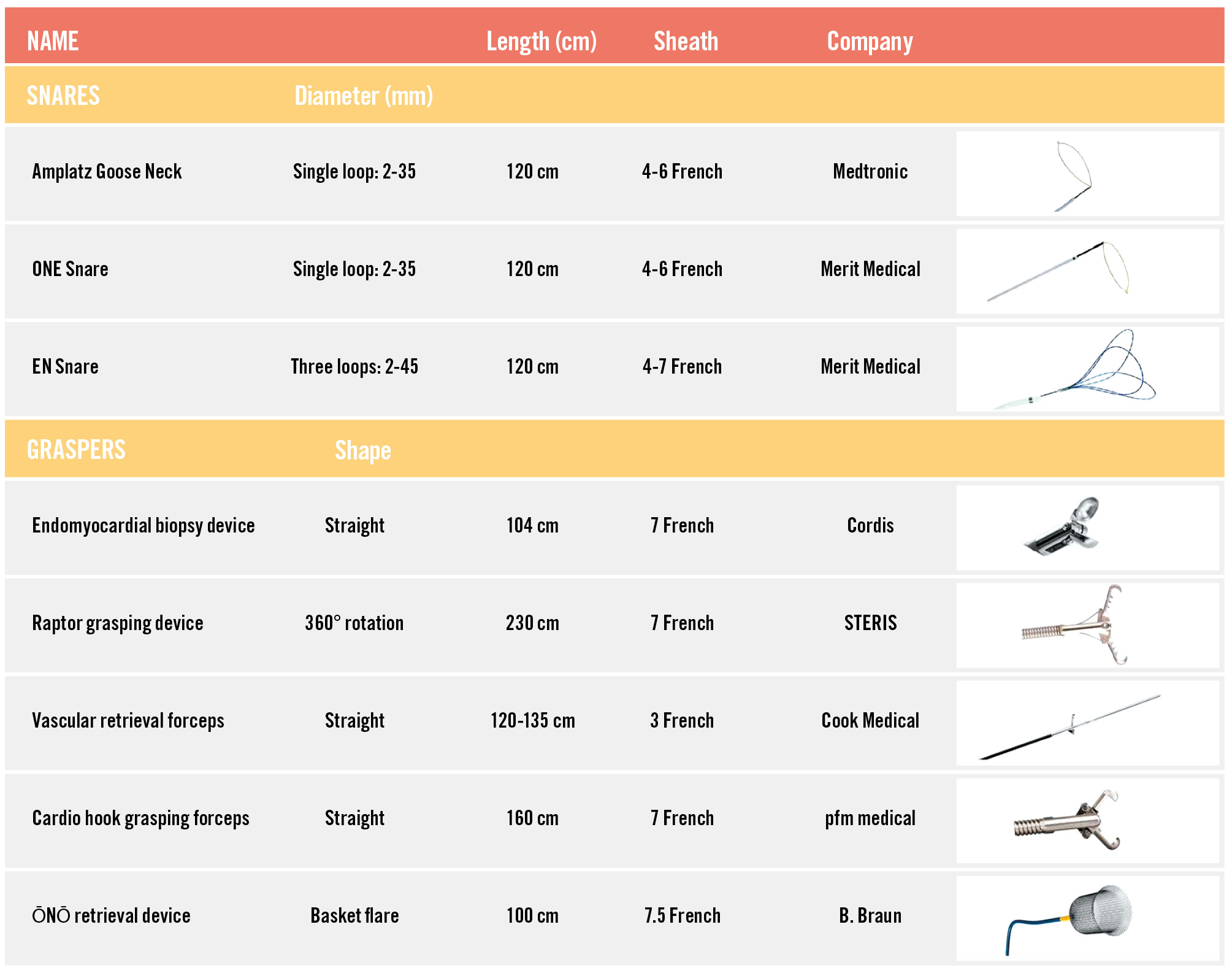
Figure 5. List of snares and grasping devices available for LAAC device recapture. The display provides a list of snares and grasping devices for LAAC device recapture and an image of each item is shown at the end of each row, illustrating their technical features. LAAC: left atrial appendage closure
LAAC device embolisation into the aorta
Most of the time, embolisation into the aorta is an incidental finding among an asymptomatic patient undergoing a systematic imaging follow-up. Smaller devices (≤25 mm) are more likely to embolise through the mitral and then the aortic valve to finally migrate into the aorta, while bigger devices (>25 mm) usually remain inside the left-sided heart cavities.
In case of migration into the aorta, a percutaneous retrieval technique should be used as a first attempt. The femoral artery is the most appropriate vascular access for insertion of the large-bore sheath, using an echo-guided puncture. A combination of snares and graspers (Table 2) allows, in the majority of cases, a safe and successful retrieval manoeuvre. Particular attention should be paid to achieving a full collapse of the embolised device into the large sheath before removing it from the iliofemoral vessels, in order to avoid injury to the vascular wall. Femoral haemostasis should be achieved using a percutaneous vascular closure device (i.e., Perclose ProGlide or ProStyle suture-mediated closure system [both Abbott] or MANTA device [Teleflex]).
Table 2. Available sheaths for LAAC device recapture.
|
Name |
Diameter (Fr) |
Length (cm) |
Shape |
Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Check-Flo sheaths |
14-20 |
40-100 |
Straight |
Cook Medical |
|
Braidin L sheaths |
14 |
90 |
Straight |
APT Medical |
|
DrySeal sheaths |
14-26 |
65 |
Straight |
Gore Medical |
|
Micra delivery catheter |
23 |
105 |
Steerable |
Medtronic |
|
MitraClip/TriClip 24 Fr steerable guide catheter |
24 |
131 |
Steerable |
Abbott Vascular |
|
Agilis NxT |
8.5 |
61 |
Steerable |
Abbott Vascular |
|
FlexCath Advance |
12 |
65 |
Steerable |
Medtronic |
|
Oscor Destino |
12 |
71 |
Steerable |
Integer Holdings |
|
Fustar sheath |
14 |
80 |
Steerable |
Lifetech Scientific |
LAAC device embolisation into the aorta: key messages
• Incidence: 40% of cases
• Symptoms: mostly asymptomatic
• Strategies for retrieval:
• Approach: percutaneous
• First attempt: transfemoral retrieval
• Access: transfemoral
• Material: large-bore sheaths, snares, graspers, vascular closure system
• Clinical outcome: low risk
LAAC device embolisation into the left atrium
Embolisation of an LAAC device into the left atrium (LA) occurs intraoperatively in two-thirds of cases, is delayed postoperatively in one-third of cases, and is usually associated with symptoms such as arrhythmia, dyspnoea or chest pain. A transseptal (TS) approach for a percutaneous retrieval should be performed as a first attempt. A pigtail catheter should be placed across the mitral valve to prevent the embolised device from crossing the mitral valve and travelling into the left ventricle (LV). Then, the recapture manoeuvre can be carried out using steerable sheaths, large-bore sheaths, mother-in-child technique, snares and/or graspers.
Some operators67 have reported the use of specific protection devices for stroke prevention like SENTINEL (Boston Scientific) or the WATCHMAN in ascending aorta for stroke prevention (WAASP) technique.
Particular attention should be paid to the pericardium, and equipment for pericardiocentesis should be ready in case of tamponade.
A single or a double TS puncture can be used. The double TS technique10 is particularly helpful in case of a hypermobile whirling device, to stabilise it against the free wall of the LA with a large three-loop snare from the first TS access, while the retraction of the device into the retrieval sheath (≥16 Fr) is made possible via the second TS access using a single-loop snare and/or a grasping tool, as illustrated in Figure 6.
In case of failure of these percutaneous techniques, surgery should be considered.
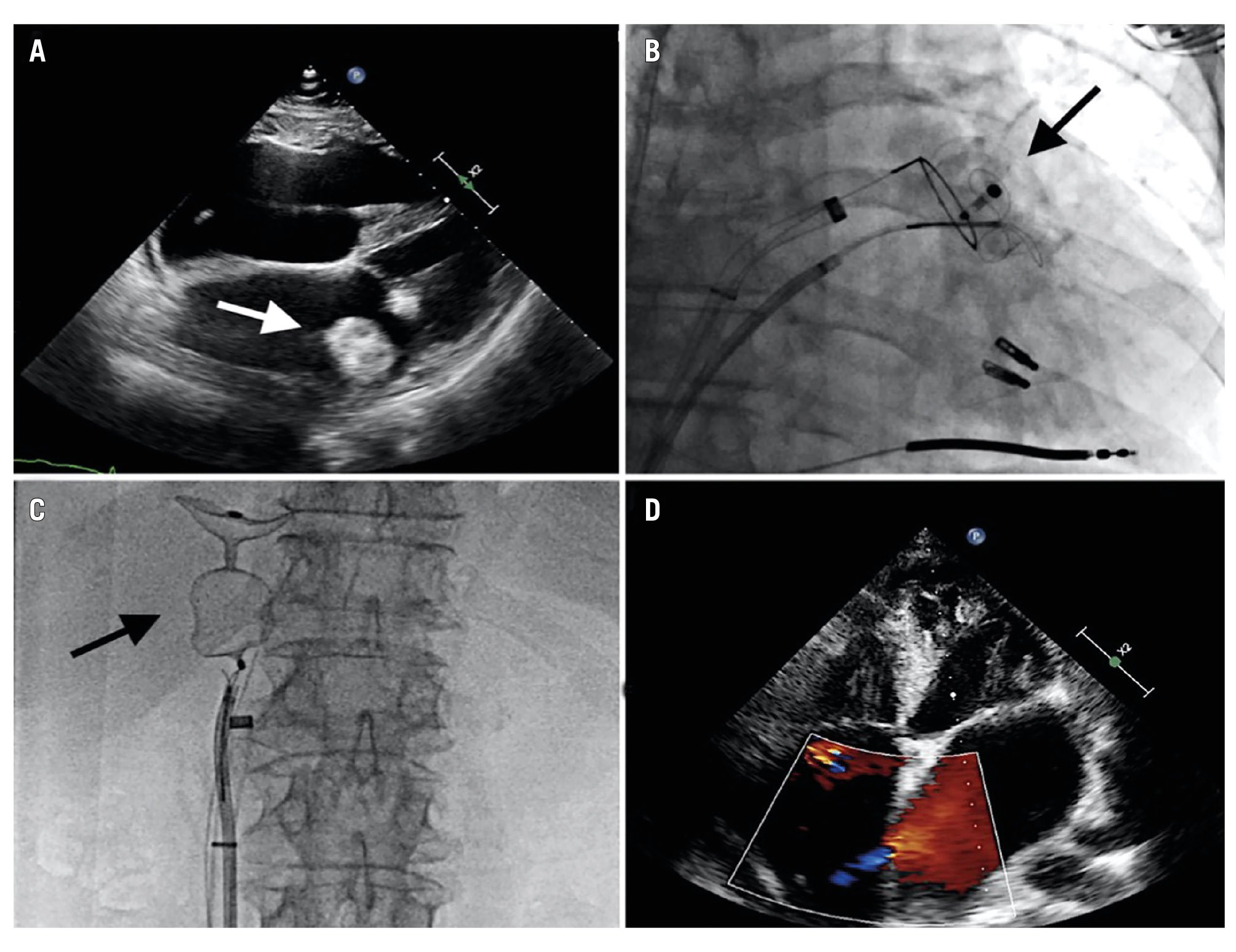
Figure 6. The double transseptal technique for LAAC device recapture in the left atrium. A 34 mm Amplatzer Amulet device (Abbott) embolisation to the left atrium (A) recaptured by a double transseptal technique, using a three-loop snare (B); a 16 Fr sheath into a 24 Fr Mitraclip/Triclip steerable guide catheter (Abbott) and forceps (C). Minimal residual shunt over the interatrial septum after the retrieval manoeuvre (D). Adapted with permission from10. Fr: French; LAAC: left atrial appendage closure
LAAC device embolisation into the left atrium: key messages
• Incidence: 30% of cases
• Symptoms: arrhythmia, dyspnoea, chest pain
• Strategies for retrieval:
• Approach: mainly percutaneous, rarely surgical
• First attempt: transseptal retrieval
• Access: transseptal, often 2 transseptal accesses
• Material: large-bore sheaths, snares, graspers, tamponade kit
• Clinical outcome: intermediate risk
LAAC device embolisation into the left ventricle
LAAC device embolisation into the LV is the most serious situation, usually requiring surgical removal. If the device becomes entangled in the mitral valve apparatus, urgent surgery should be performed. In case of haemodynamic compromise, a rapid attempt to mobilise the device into the LV cavity using a pigtail catheter should be performed to stabilise the patient. In case of failure, emergent surgery should be performed. Some surgeons have reported the use of mediastinoscopy technique11 in order to avoid an LV myocardium incision, leading to a successful mini-invasive surgical retrieval.
In stable haemodynamic conditions, a pigtail catheter placed retrogradely from the femoral artery into the LV cavity can be used to pull the device into the LV outflow tract, just below the aortic valve. The discs should be oriented parallel to the axis of the opening of the valve to mitigate the risk of damage to the leaflets12. Then, an exchange for a large-bore sheath placed in the ascending aorta and the use of snaring and grasping techniques could allow retrograde recapture of the embolised device across the aortic valve, followed by percutaneous closure of the femoral artery, as illustrated in Figure 7.
In case of a large embolised device and/or failure of transfemoral retrieval, a transseptal recapture can be attempted13. A pigtail catheter should be placed retrogradely from the femoral artery into the LV cavity to stabilise the prosthesis and keep it away from the mitral apparatus. A large-bore sheath is advanced by the TS access in the LA, then through the mitral valve up to the LV cavity, allowing snares and graspers for a full recapture of the device into the retrieval sheath, which can then be taken safely back across the mitral apparatus and the interatrial septum, as illustrated in Figure 8.
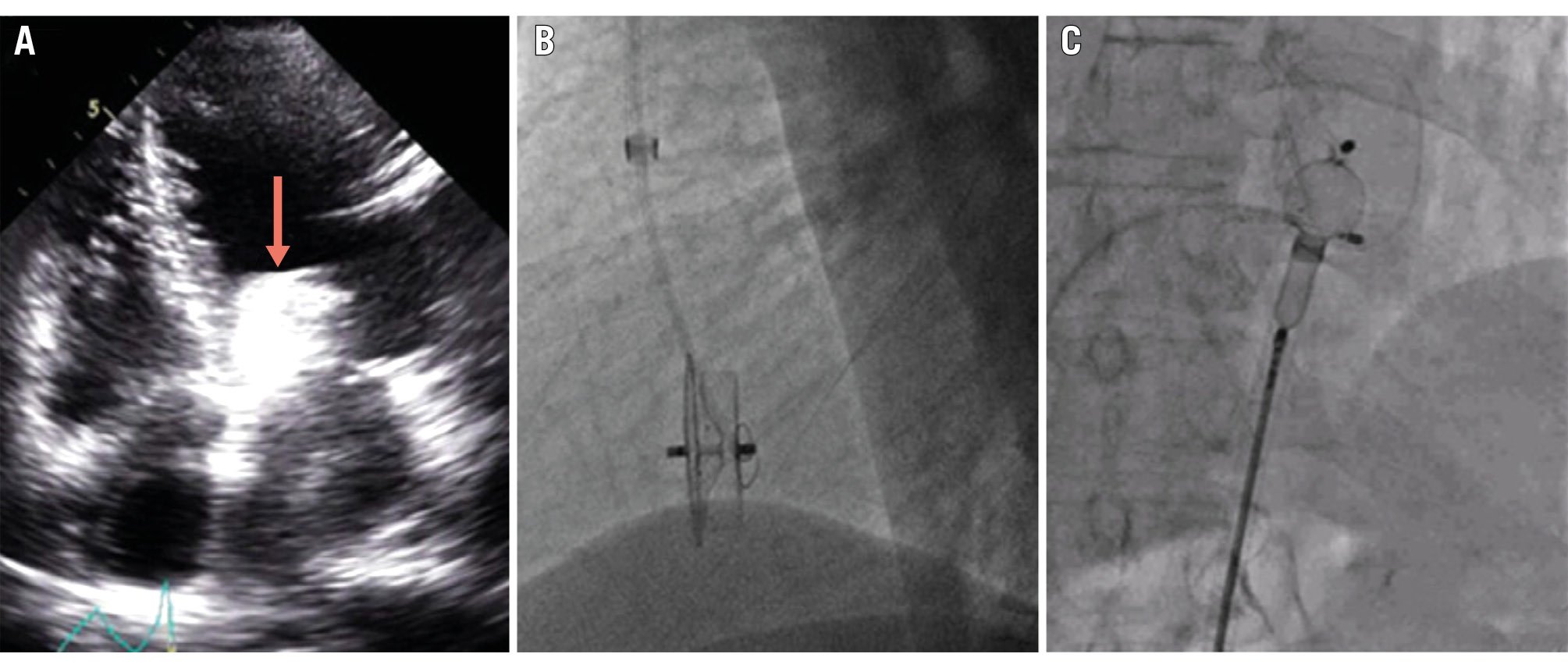
Figure 7. Transfemoral recapture after LAAC device embolisation into the left ventricle. A 28 mm Amplatzer Cardiac Plug device embolisation into the left ventricular outflow tract (A; red arrow) recaptured using a combination of a single-loop snare (B), a biopsy bioptome, a Judkins right catheter and a 14 Fr sheath (C). Adapted with permission from12. Fr: French; LAAC: left atrial appendage closure
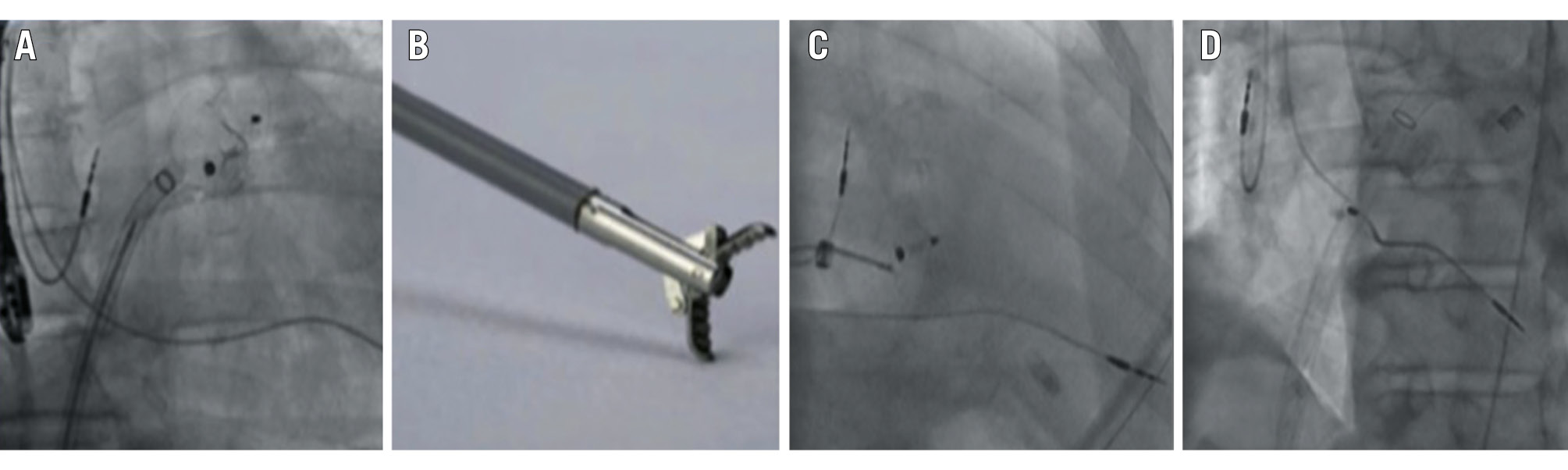
Figure 8. Transseptal recapture after LAAC device embolisation into the left ventricle. A 28 mm Amplatzer Amulet device (Abbott) embolisation into the left ventricle (A) recaptured using grasping forceps (B) and a 24 Fr MitraClip/TriClip steerable guide catheter (Abbott; C,D). Adapted with permission from13. Fr: French; LAAC: left atrial appendage closure
LAAC device embolisation into the left ventricle: key messages
• Incidence: 30% of cases
• Symptoms: shock, arrhythmia, dyspnoea, chest pain
• Strategies for retrieval:
• Approach: percutaneous or surgical*
• First attempt: device mobilisation inside the LV
• Access: transfemoral, transseptal, LV, aorta
• Material: large-bore sheaths, snares, graspers, mediastinoscopy camera
• Clinical outcome: high risk
*Emergent surgery in cases where the device is entangled in the mitral apparatus and if haemodynamic compromise is unsolved by device mobilisation.
Conclusions
LAAC device embolisation is rare but can potentially be a fatal complication. The anatomical location of the migrated device determines the technical approach for device retrieval. Percutaneous recapture is the main approach in case of an aortic or left atrial embolisation, while emergent surgery should be performed if the device becomes entangled in the mitral apparatus with poor haemodynamics unsolved by transcatheter device mobilisation into the LV cavity. In cases of left ventricular embolisation and stable haemodynamics, a transfemoral or transseptal retrieval may be attempted.
The equipment for retrieval is key to success: all cath labs performing LAAC procedures should be equipped with minimum 16 French sheaths, steerable sheaths, single-loop snares and grasping tool devices.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Rudy Lechantre for the visual elements and the main graphic.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Aminian: proctor and consultant for Abbott and Boston Scientific. S. Berti: proctor for Boston Scientific. I. Cruz-Gonzalez: proctor and consultant for Abbott, Boston Scientific, Lifetech, IHT, Quanta, and Eclipse Medical. O. De Backer: institutional research grants and consulting fees from Abbott and Boston Scientific. X. Freixa: proctor for Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Lifetech. P. Garot: fees from Abbott, Biosensors, Boston Scientific, Cordis, GE HealthCare, and Terumo; and shareholder and Medical Co-Director at CERC. J. Kefer: proctor and consultant for Abbott. J.E. Nielsen-Kudsk: proctor and institutional research grants from Abbott and Boston Scientific. L. Räber: research grants to the institution from Abbott and Boston Scientific; speaker fees from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Occlutech; and is a proctor of Abbott. N. Wunderlich: honoraria/consultant fees: Abbott, Boston Scientific, Lifetech, GE HealthCare, and Philips.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Recapture manoeuvre of an Amplatzer Cardiac Plug embolised to the abdominal aorta using a 14 Fr sheath and an endomyocardial biopsy device. Failure to grasp the proximal end screw of the device due to the significant withdrawal force needed.

