
Abstract
Aims: Percutaneous transcatheter device closure of left atrial appendage (LAA), patent foramen ovale (PFO) and atrial septal defect (ASD) are usually performed with unfractionated heparin anticoagulation. We report a first experience using intravenous (IV) enoxaparin without anticoagulation monitoring in transcatheter structural heart interventions performed in the left atrium (LA).
Methods and results: This retrospective, non-controlled study included all consecutive and unselected patients who underwent percutaneous LAA, PFO or ASD closure at a tertiary care centre using IV enoxaparin anticoagulation. The primary composite endpoint was the occurrence of in-hospital death, embolic complications (stroke, transient ischaemic attack, and peripheral arterial embolism) and bleedings defined as type 3a or more according to the BARC definitions. We enrolled 198 patients (mean age 60±18 years, 55% male) with an indication for LAA (40.4%), PFO (34.3%) or ASD closure (25.3%). The majority of patients (n=163, 82%) received a single IV enoxaparin dose of 0.5 mg/kg. The composite endpoint occurred in six (3%) patients including four (2%) type 3a bleedings, one (0.5%) transient ischaemic attack and one (0.5%) death from sepsis.
Conclusions: IV enoxaparin without monitoring appears to be a potentially safe and easy-to-use anticoagulation regimen in percutaneous LA cardiac interventions. Further investigations with larger cohorts of patients are warranted.
Abbreviations
ASD: atrial septal defect
GFR: glomerular filtration rate
IQR: interquartile range
IV: intravenous
LA: left atrium
LAA: left atrial appendage
PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
PFO: patent foramen ovale
UFH: unfractionated heparin
Introduction
Percutaneous transcatheter closure of the left atrial appendage (LAA)1-3, patent foramen ovale (PFO)4-6 and atrial septal defect (ASD)4,7,8 have become common structural heart procedures. Although these interventions are aimed at different types of patients and diseases, they share similar thromboembolic and haemorrhagic periprocedure-related risks. Anticoagulation is achieved by the administration of intravenous (IV) unfractionated heparin (UFH) with a target activated clotting time of >250 s1,3,6,8,9. Due to non-specific binding to plasma proteins10, UFH bears a complex pharmacokinetic profile with a non-linear dose response at therapeutic dose, resulting in great inter- and intra-individual variations. As a consequence, close monitoring including baseline ACT measurement is needed11. Enoxaparin, the most widely used low-molecular-weight heparin presents more reliable pharmacology properties, resulting in a better bioavailability and a more predictable anticoagulant response12-14. Hence, an IV bolus of 0.5 mg/kg achieves a maximal anticoagulation level within a few minutes12,15 and provides effective levels of anti-Xa activity without the need for biological monitoring13. In the field of coronary artery disease, IV enoxaparin has been successfully compared to UFH in elective percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI)14 and in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients undergoing scheduled or primary PCI16-18.
In contrast to the evidence which has accumulated with IV enoxaparin for PCI, there is no information available on structural heart interventions. However, interventions in the left atrium (LA) are at high thrombotic risk, as multiple risk factors including atrial fibrillation, history of stroke, heart failure, blood stasis, atrial septal aneurysm, large LA and spontaneous echocardiographic contrast19 may accumulate at the time of implanting large metallic devices. Periprocedural anticoagulation is paramount to prevent thrombus formation on wires, sheaths, catheters, devices, or in the LA. However, periprocedural anticoagulation may also be held accountable for the bleeding complications that may occur during these transseptal procedures. We report the feasibility and safety of IV enoxaparin use in percutaneous structural cardiac procedures in the LA.
Material and methods
STUDY DESIGN AND ANTICOAGULATION MANAGEMENT
In this retrospective, non-controlled, single-centre study, all patients who underwent LAA, PFO or ASD closure procedures at the Institut de Cardiologie of the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, from January 2006 to December 2016, were considered. We excluded patients on UFH or exposed to vitamin K antagonists with an international normalised ratio ≥2 at the time of the procedure. All the other patients underwent the procedures on IV enoxaparin without further selection. When patients were on direct oral anticoagulant agents, administration was interrupted before the intervention and the same regimen of enoxaparin was used.
Medical data including procedural characteristics with the administered dose of enoxaparin were collected. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was calculated according to the Cockcroft-Gault formula. All patients had a follow-up visit three months after the procedure.
IMPLANTATION TECHNIQUE
All indications were discussed by our structural Heart Team and written informed consent was obtained from all patients. All interventions were carried out under general anaesthesia using a femoral vein approach. All procedures were guided with transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) and fluoroscopy. Periprocedural anticoagulation was obtained by a single 0.5 mg/kg IV dose of enoxaparin16. A second loading dose of 0.25 to 0.5 mg/kg was considered when interventions were prolonged (≥1 hour)13,14. Catheter flushes were performed using isotonic saline solution with enoxaparin at a final concentration of 6 IU/mL of anti-Xa. There was no coagulation monitoring14. There was no subcutaneous administration of enoxaparin after the procedure. Procedural technical failure was defined as no device implanted.
For PFO and ASD closure, patients not already under antiplatelet therapy received a loading dose of 300 mg of clopidogrel and 250 mg of aspirin the day before the procedure, followed by a prescription of aspirin 75 mg and clopidogrel 75 mg for three months. Antithrombotic treatment regimen before and after LAA closure was a case-by-case decision made according to the risk profile of each patient. A clinical follow-up was scheduled at three months.
STUDY ENDPOINTS
The primary composite endpoint (net clinical benefit) was the occurrence during hospitalisation of all-cause death, embolic complications such as stroke, transient ischaemic attack (TIA) or peripheral arterial embolism and major bleedings. Major bleedings were defined as type 3a or above according to the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium definitions20, including overt bleeding with haemoglobin drop of at least 3 g/dL, any transfusion with overt bleeding, cardiac tamponade, bleeding requiring surgical intervention for control and/or intravenous vasoactive agent, intracranial, intraocular and fatal bleeding. Any other significant adverse events during the hospitalisation such as air embolism, inhalation pneumonia, and pericardial effusion without tamponade were also collected. The same primary composite endpoint was evaluated after successful device implantation at three-month follow-up.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Normal distribution of continuous variables was evaluated using the Shapiro-Wilk normality test. Descriptive statistics are reported as mean±standard deviation (SD), median and interquartile range (IQR) or number and percentage when appropriate. Categorical measures were compared by chi-square or Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Kaplan-Meier estimates of the secondary endpoint between device implantation and follow-up evaluation were calculated. All statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, Inc, La Jolla, CA, USA); p-values <0.05 were considered significant.
Results
A total of 220 patients were considered for the study of whom 198 were finally included (Figure 1). The most frequent transcatheter intervention was LAA closure (40.4%) followed by PFO closure (34.3%) and ASD closure (25.3%). The clinical characteristics of the study population differed according to the type of procedure performed (Table 1). Patients with LAA closure were older than those undergoing ASD or PFO closure. Renal failure defined as GFR <60 mL/min was observed in one quarter of patients (n=42, 23%) and severe renal failure was rare (n=10, 5%).
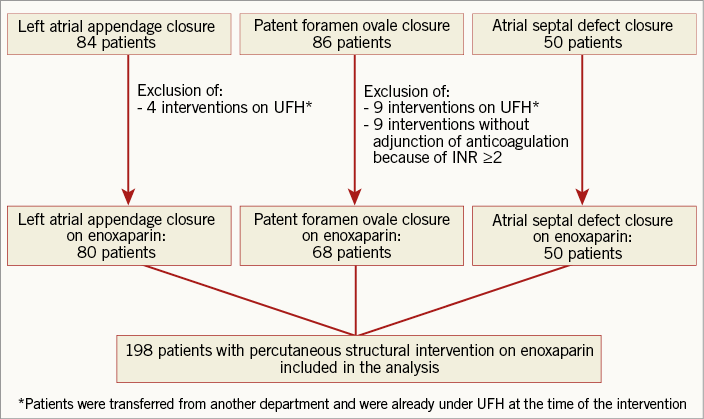
Figure 1. Flow chart of the study. INR: international normalised ratio; UFH: unfractionated heparin
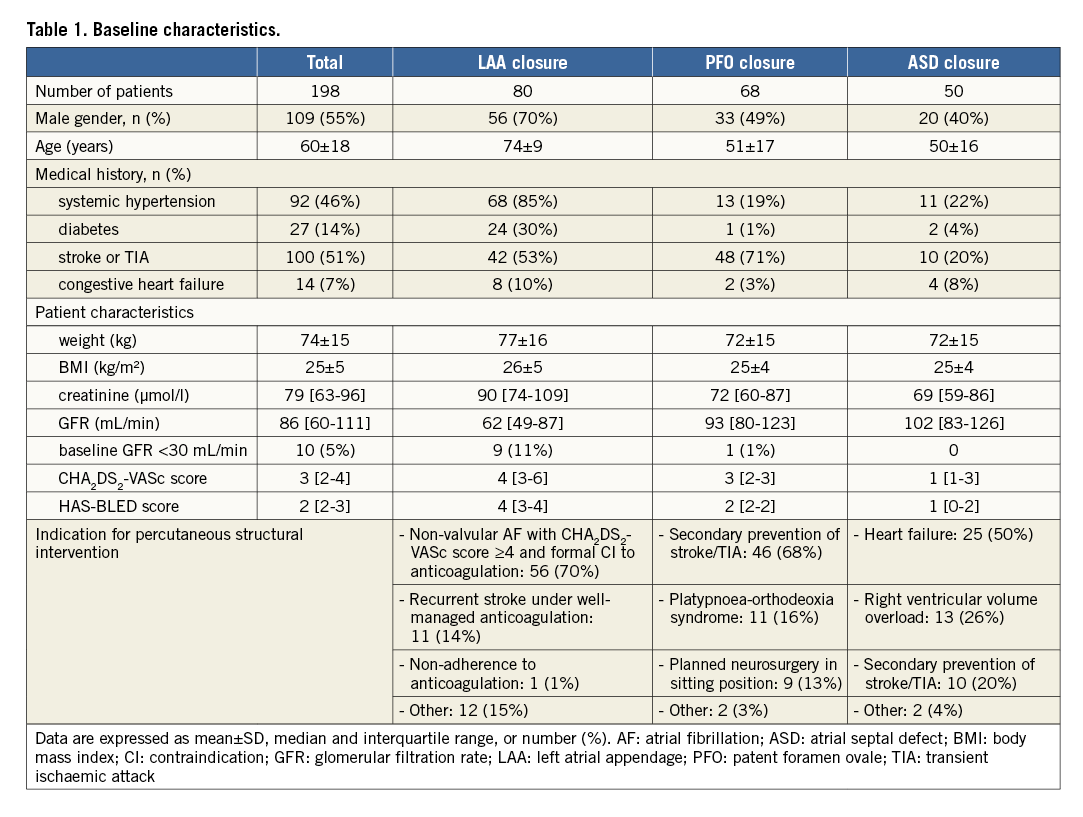
The procedure was successfully performed in 191 (96.5%) patients and was combined in six patients including PFO and ASD closure (n=4), ASD and LAA closure (n=1) and all procedures at once (n=1). Procedure characteristics are described in Table 2. A single intravenous bolus of 0.5 mg/kg of enoxaparin was used in the vast majority of patients (n=163, 82%). A few received one (n=34) or two additional (n=1) boluses with a cumulative median dose of 0.8 mg/kg (IQR, 0.8-0.8). The additional enoxaparin injection was related to prolonged procedure (≥1 hour) in 33 (16.7%) patients and to the appearance of thrombus in the LA in two (1%) patients.
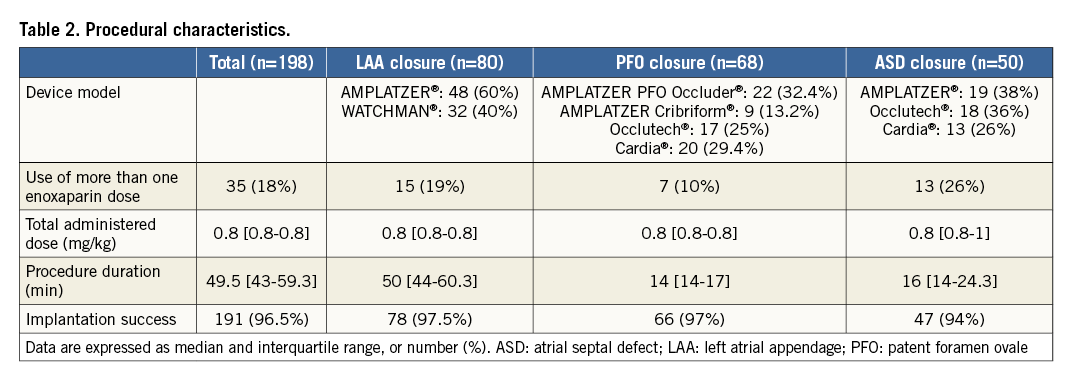
SAFETY OF PERIPROCEDURAL USE OF ENOXAPARIN
The primary composite endpoint occurred in six (3%) patients (Table 3). The only in-hospital death occurred in a comatose patient with severe platypnoea-orthodeoxia syndrome who underwent a successful large PFO closure, and was attributed to a non-procedure-related sepsis. There were four (2%) type 3a bleedings and a single embolic complication with TIA after PFO closure.
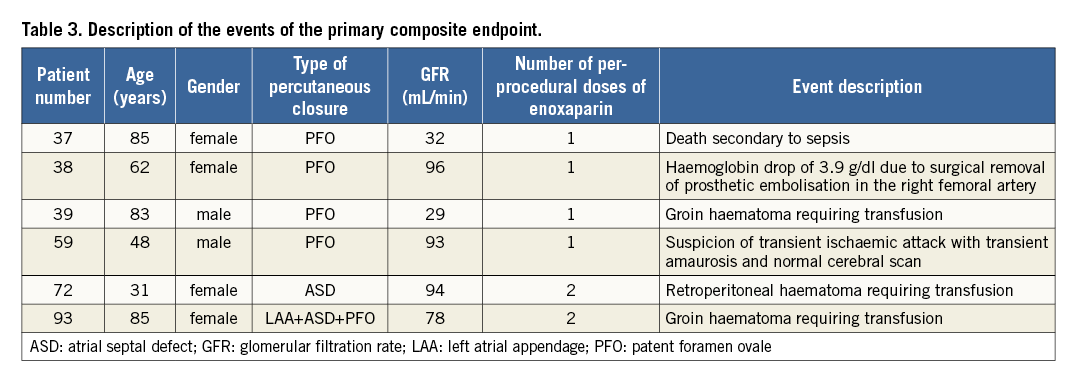
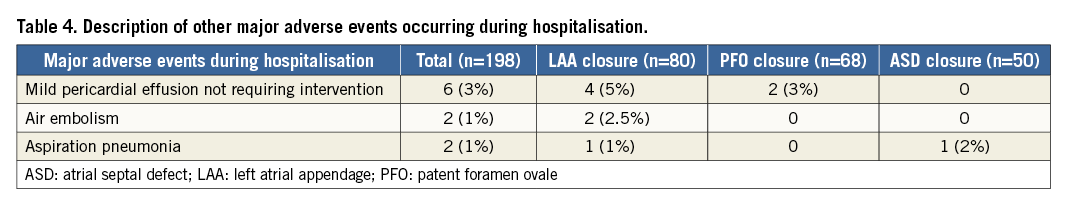
The use of more than one dose of enoxaparin tended to be associated with more severe bleeding complications as compared to single bolus administration - two (5.7%) and two (0.6%) patients, respectively, p=0.08. GFR below 60 mL/min was associated neither with more frequent primary composite endpoints (4.8% vs. 2.6%) nor with more frequent bleeding complications (2.4% vs. 1.9%) as compared to patients with normal renal function, respectively. There was no significant association between the HAS-BLED and CHA2DS2-VASc scores and bleeding complications. The other periprocedural and in-hospital adverse events are described in Table 4.
FOLLOW-UP AT THREE MONTHS
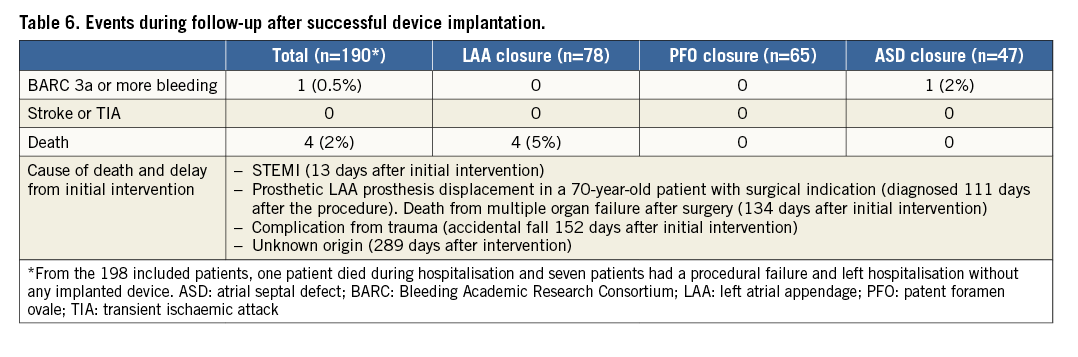
The antithrombotic regimen at discharge is described in Table 5. Systematic follow-up clinical evaluation was performed in patients with successful device implantation at a median of 3.7 months (IQR, 3.2-4.4). Four patients died during follow-up after LAA closure, and cumulated composite endpoints occurred in 11 (5.8%) patients (Table 6, Figure 2).
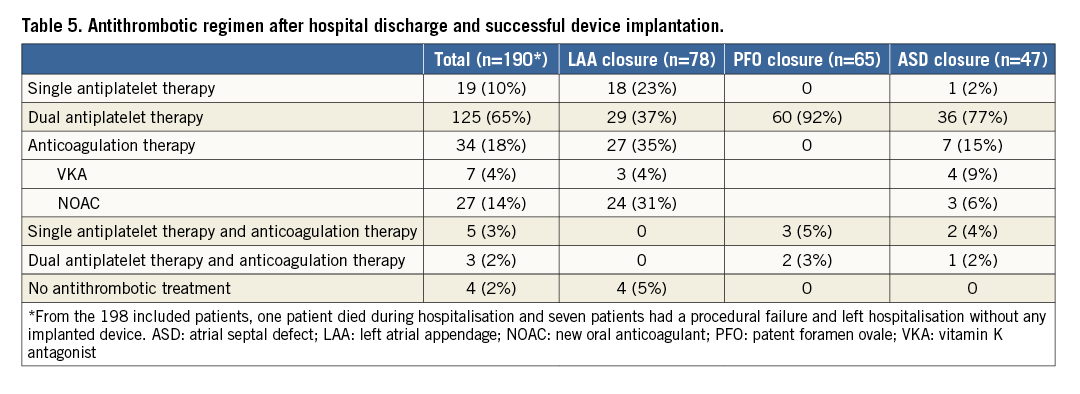

Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier curve of cumulated composite endpoint.
Type 3a or above BARC bleeding: bleeding responsible for haemoglobin drop of at least 3 g/dl, any transfusion with overt bleeding, cardiac tamponade, bleeding requiring surgical intervention for control and/or intravenous vasoactive agent, intracranial, intraocular and fatal bleeding. BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium
Discussion
The present study is the first large experience obtained with IV enoxaparin for periprocedural anticoagulation of percutaneous structural heart procedures. The rates of both bleeding and ischaemic events were low, suggesting IV enoxaparin to be a potentially safe and easy-to-use anticoagulation strategy for structural heart interventions.
As opposed to UFH, biological monitoring is not needed with enoxaparin and the use of a single dose of IV enoxaparin in the majority of the patients (82% of the current study population) results in a simpler protocol than the one typically used with UFH, which requires repeated activated clotting time controls and dose adjustments. One potential advantage of the use of UFH over enoxaparin is the possibility of complete antagonisation when the latter can only be partially antagonised using protamine sulfate21. However, protamine sulfate was never used in the present study. Moreover, enoxaparin has demonstrated its benefit in numerous situations including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism22,23, fibrinolysis for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction24,25, medical management of non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction17, and elective and primary PCI14,16. It has been given a class IIa recommendation for both elective and primary PCI in the European guidelines26,27. The use of enoxaparin as bridging therapy after mechanical heart valve replacement was also reported as safe and effective with a significantly higher proportion of patients within the target range of anticoagulation compared to UFH28. Hence, the results of the present study, in a field where this strategy of anticoagulation has never been tested, are coherent with those of the literature. However, our results represent a first experience and must be considered as exploratory; additional studies with larger cohorts of patients and hopefully randomised or at least comparative studies are warranted.
Interventions in the LA are at high risk for several reasons. First, there are the procedure-related bleedings, which include vascular access, cardiac tamponade and transseptal puncture-related bleeding events. Second, thromboembolic events are favoured by LA enlargement, atrial fibrillation and septal aneurysm, factors that are associated with blood stasis. Finally, there are the device-related complications, which comprise LA trauma, and contact phase-induced thrombus formation. Anticoagulation during these procedures is therefore critical; data with IV enoxaparin are scarce29. We report the first large experience on this topic with reassuring results.
As percutaneous structural cardiac procedures in the LA have become more frequent and operators more experienced, the rate of procedural success has increased while serious procedure-related complications have decreased over time. The rate of procedural success that we report here was 96.5% and compares favourably with that of the literature where it ranges from 92 to 99.5%1-8. Conversely, major bleeding complication and stroke rates were 2% and 0.5%, which are aligned with those of previous registries which ranged from 0.15 to 4.4% and from none to 0.5%, respectively1-8. However, the non-controlled nature of this study prevents any further conclusions on the value of IV enoxaparin in comparison to UFH in these procedures.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. Firstly, it is retrospective. Secondly, it is non-controlled and the number of procedures for each type of intervention is relatively small, although it is the largest cohort described to date in this particular field. Hence, no conclusion may be drawn on the value of IV enoxaparin compared to UFH and these results ought to be considered only as exploratory. The variety of interventions reflects different patient risk profiles and procedure duration. However, all were structural LA heart procedures in patients with frequent concomitant atrial fibrillation with or without prior stroke, and the low rate of thromboembolic complications is very encouraging. Further studies with larger cohorts of patients would be of interest.
Conclusions
The present study demonstrates that IV enoxaparin without monitoring appears to be a potentially safe and easy-to-use anticoagulation regimen in percutaneous left atrial cardiac interventions. This anticoagulation strategy deserves further investigation with larger cohorts of patients.
| Impact on daily practice Intravenous enoxaparin, at the dose of 0.5 mg/kg, without anticoagulation monitoring appears to be a potentially safe and easy-to-use anticoagulation strategy in percutaneous left atrial interventions such as left atrial appendage closure, patent foramen ovale and atrial septal defect. |
Funding
This study was funded by the ACTION Study Group.
Conflict of interest statement
G. Montalescot reports the following disclosures during the past two years of research: grants to the institution or consulting/lecture fees from ADIR, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Berlin Chimie AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical, Brigham Women’s Hospital, Cardiovascular Research Foundation, Celladon, CME Resources, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Europa, Elsevier, Fédération Française de Cardiologie, Fondazione Anna Maria Sechi per il Cuore, Gilead, ICAN, Janssen, Lead-Up, Menarini, Medtronic, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, The Medicines Company, TIMI Study Group, and WebMD. P. Guedeney reports receiving a research grant from Fédération Française de Cardiologie. J. Silvain reports the following disclosures during the past two years: research grants to the institution from the Fondation de France and the Institute of Cardiometabolism (ICAN); consulting fees from Actelion, Amed, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences and Sanofi-Aventis; speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Algorythm, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Iroko Cardio, and travel support from Amgen, AstraZeneca and St. Jude Medical. J. Collet reports the following disclosures during the past two years: research grants to the institution or honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Fédération Française de Cardiologie, Lead-Up, Medtronic, MSD, Sanofi-Aventis, and WebMD. G. Duthoit reports the following disclosures during the past two years: research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, proctoring fees from St. Jude Medical, lecture fees from the European Society of Cardiology, Boston Scientific and Bristol-Myers Squibb. M. Kerneis reports the following disclosures during the past two years: research grants to the institution or honoraria from AstraZaneca, Bayer, Fédération Française de Cardiologie, and Sanofi-Aventis. R. Isnard reports the following disclosures during the past two years: research grants or honoraria from Novartis, Servier, Daiichi Sankyo, Menarini, Sanofi, Vifor, Bayer, AstraZeneca, BMS, Abbott, ResMed, and Zoll. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

