
Abstract
Aims: The goal of the study was to compare long-term outcomes of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) versus coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), accounting for the clinical impact of individual components in the composite endpoints and prioritising these using the win ratio (Rw).
Methods and results: The win ratio was compared with conventional methods of analyses (hazard ratio [HR] and relative risk) in the SYNTAX trial (n=1,800). For the composite of death/stroke/myocardial infarction (MI), the win ratio favoured CABG and was 1.37 (95% CI: 1.10-1.77) for matched analysis, 1.28 (95% CI: 1.11-1.53) for unmatched analysis, while the conventional HR was 1.29 (95% CI: 1.11-1.53). The largest number of winners in favour of CABG over PCI were based on MI (n=39 vs. n=19, respectively). Death was significantly reduced with CABG in matched (Rw=1.39, 95% CI: 1.04-1.86) and unmatched win ratio analyses (Rw=1.27, 95% CI: 1.01-1.42) as compared with non-significant conventional analysis (HR 1.19, 95% CI: 0.92-1.56). In subgroups, matched win ratio analyses had a larger treatment effect in favour of CABG compared with conventional analyses, especially in patients with three-vessel disease and intermediate SYNTAX scores, while unmatched win ratios had a smaller point estimate, but with narrower confidence intervals than matched analyses findings.
Conclusions: This re-analysis of the SYNTAX trial using the win ratio shows that the most important benefit of CABG treatment is the reduction of hard clinical endpoints such as mortality and MI. Future trials using this approach can expect to maintain similar statistical power with smaller sample sizes, and thereby reduce the cost of a trial. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00114972
Abbreviations
DM: medically treated diabetes mellitus
HR: hazard ratio
LM: left main
MACCE: major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events
MI: myocardial infarction
PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
Rw: win ratio
3VD: three-vessel disease
Introduction
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) have been compared in many randomised clinical trials1. These trials often used composite endpoints to obtain higher event rates and provide more statistical power, thus requiring smaller sample sizes, shorter follow-up, or both2,3. However, composite endpoints are often criticised for having an intrinsic weakness, combining events with a very different impact on a patient’s quality of life or life expectancy. The reporting of composite endpoints in clinical trials also has an inherent limitation in that it emphasises each patient’s first event, which is often the outcome of lesser clinical importance.
The SYNTAX trial assessed the optimum revascularisation treatment for patients with de novo left main (LM) coronary disease and/or three-vessel disease (3VD), by randomly assigning patients to either CABG or PCI with a first-generation drug-eluting stent (DES). The primary endpoint was powered on non-inferiority of PCI versus CABG for the endpoint of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), which is the composite of all-cause death, stroke, myocardial infarction (MI), and repeat revascularisation4. The difference in MACCE between PCI and CABG was largely driven by higher rates of repeat revascularisation with PCI, which is thought to be a softer, less important endpoint, while rates of all-cause death were not significantly different between CABG and PCI5,6.
To overcome this weakness of putting the same emphasis on individual components with a clinically different impact in the composite endpoint, a recent novel approach, the win ratio, has been introduced7. Based on clinical priorities, the win ratio methodology applies a hierarchical weighting to individual components in MACCE. This approach is also designed to combat two fundamental difficulties that may be present in typical efficacy studies: study population heterogeneity and important events that are censored. The method uses risk score stratification to select and match pairs with similar risk profiles from both treatment groups and provides a more patient-specific interpretation of composite endpoints in clinical trials.
The objective of this re-analysis of the SYNTAX trial was to compare PCI with CABG using different methods of analysis, accounting for the severity of the individual components and prioritising these using the win ratio approach as an informative estimate of treatment difference. Moreover, this paper evaluates the impact of applying the win ratio on the design of future trials.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN
The design and methods of the SYNTAX trial have been reported previously8. In SYNTAX, 1,800 patients with de novo LM or three-vessel coronary artery disease were randomly assigned to undergo CABG or PCI with a paclitaxel-eluting stent (TAXUS® Express™; Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA). Patients with anticipated clinical revascularisation equipoise through PCI and CABG were randomised (CABG n=897, PCI n=903). Five-year follow-up was 89.7% for CABG and 96.5% for PCI.
This study was carried out in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and registered on the National Institutes of Health website with identifier NCT00114972.
DEFINITIONS
The primary endpoint of the trial was MACCE, which included all-cause death, stroke, MI, or repeat revascularisation (subsequent CABG or PCI)9. Secondary endpoints consisted of: i) a composite safety endpoint of death/stroke/MI, and ii) the individual endpoint of all-cause death. Definitions of these endpoints have been published elsewhere8.
Medically treated diabetes was defined as treatment with oral hypoglycaemic agents or insulin at the time of enrolment.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
All analyses were carried out according to the intention-to-treat principle. Conventional analyses were performed using: i) Cox proportional hazard analyses to provide hazard ratios (HRs), and ii) estimates of relative risk (RR) associated with PCI versus CABG treatment. The proportional hazards assumption was estimated using Schoenfeld’s test and was found to have been met. Relative risks were calculated by dividing the Kaplan-Meier estimated rate of an event at five years in the PCI group by the event rate in the CABG group. The 95 percent confidence interval (CI) for the relative risk was calculated with the use of the standard errors from the Kaplan-Meier curve10. The significance of differences in event rates between treatment groups was assessed with the use of the log-rank test. Conventional analyses were performed using SPSS software, Version 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Win ratio analyses were performed for all-cause death, the composite safety endpoint of death/stroke/MI, and for the composite of MACCE7. The hierarchy of events within MACCE was as follows: all-cause death, stroke, MI, repeat CABG, repeat PCI.
The win ratio can be used in a matched or unmatched fashion, depending on how the patients are compared. As recommended, priority was given to a matched approach versus an unmatched approach that dilutes the win ratio7. In the matched approach, each patient in the CABG group was matched to a patient in the PCI group based on a similar risk of death. A risk score to predict death was developed using 18 pre-selected baseline variables that are known to be associated with prognosis (Table 1). A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was generated to assess the ability of the scoring system model to predict mortality, 0.71 (95% CI: 0.67-0.75; p<0.0001). From the Cox proportional model’s coefficients, a risk score was calculated for each patient in the trial. Patients in the two treatment groups formed matched pairs based on their risk profiles and ranks. For each pair, the new treatment is a “winner” or “loser” according to who had died first (Figure 1). If no deaths occurred, a “winner” or “loser” was designated based on who first had a stroke, and so forth using the hierarchy of events. If one patient had an event but the follow-up period of the matched patient was shorter or if there were pairs without an event, they were considered “tied”. A “winner” patient had a more favourable outcome than his matched pair. The “win ratio” is the number of winners in the CABG group divided by the number of winners in the PCI group (Figure 1). An estimated win ratio >1 indicates a positive outcome of the CABG treatment compared to PCI while a win ratio <1 indicates a difference between treatment groups in favour of PCI. A corresponding 95% CI and p-values were calculated using dedicated statistical methods, as described by Pocock and co-authors7.
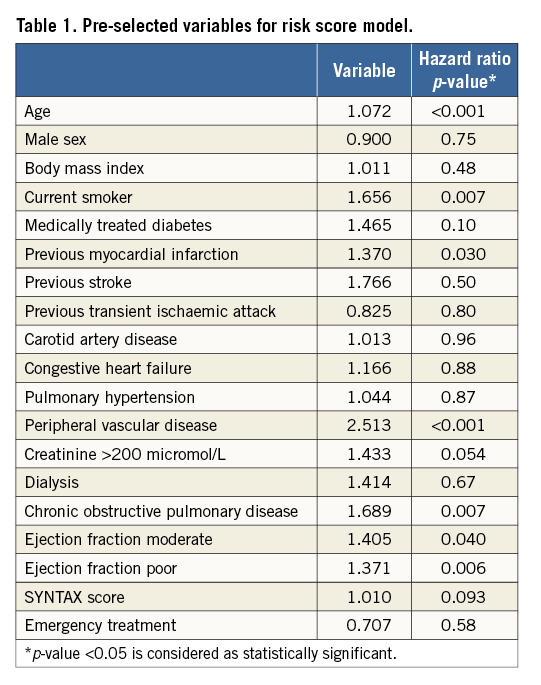
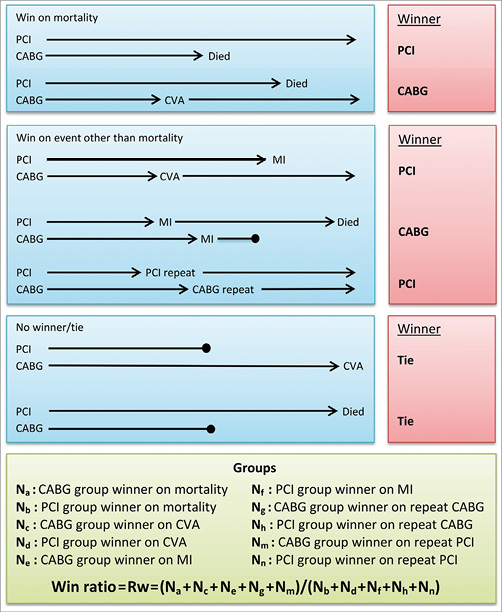
Figure 1. A conceptual diagram illustrating possible scenarios for the win ratio method. The determination of a “winner” is made using a predefined hierarchical outcome scheme. In the SYNTAX trial, mortality is considered the most important outcome followed by stroke, MI, repeat CABG revascularisation and repeat PCI revascularisation. The length of each arrow presents the duration of patient follow-up. Arrows ending in a solid circle denote either incomplete or shorter duration of follow-up.
Unmatched analyses were performed for subgroups according to diabetes, LM disease and SYNTAX score to compare this result with the matched approach. Due to the fact of unequal treatment groups in subgroups, some patients had to be excluded randomly to provide equal numbers for matching. In smaller subgroups within pre-specified subgroups of patients, up to 17% had to be excluded. To determine the impact of randomly excluding patients, a repeated analysis was performed 10 times to examine whether the obtained results were affected: this was performed in the subgroup of patients with LM disease and an intermediate SYNTAX score (n=190). The results of the 10 analyses were very different, with the win ratio ranging from 0.31-0.50 with p-values ranging from 0.0050-0.1052 for all-cause death, and, respectively, 0.64-0.96 and 0.13-0.90 for MACCE. Therefore, only unmatched analyses were performed for the smaller SYNTAX score subgroups within subgroups of patients with LM/3VD and diabetes; no patients needed to be excluded for the unmatched analyses11. In the unmatched approach, a CI for the win ratio cannot be directly calculated: the bootstrap method with 1,000 samples was performed to determine significance and CIs, using R software version 3.2.4 (Institute for Statistics and Mathematics of WU, Vienna, Austria). A p-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant for all analyses.
While originally the win-ratio code for unmatched analyses was designed for composite endpoints that include two components (death and re-hospitalisation), in order to analyse the SYNTAX trial data with five endpoints, the statistical code was rewritten, tested and validated according to the original statistical software provided directly by the authors of the win ratio approach7, when we requested and as they recommended. Now, this code can be used to calculate the win ratio with any number of components in the composite endpoint (for the code contact [email protected]).
Results
OVERALL COHORT
Of the 1,800 patients randomly assigned to PCI or CABG, 880 matched pairs were computed based on the risk score.
For the primary outcome of MACCE at five years, 274 patients who underwent CABG won versus 170 patients who underwent PCI, corresponding to a matched win ratio of 1.61 (95% CI: 1.34-1.96; p<0.0001) (Table 2, Figure 2). In comparison with matched analyses, unmatched analyses tended to have a smaller ratio between CABG and PCI (Figure 2).
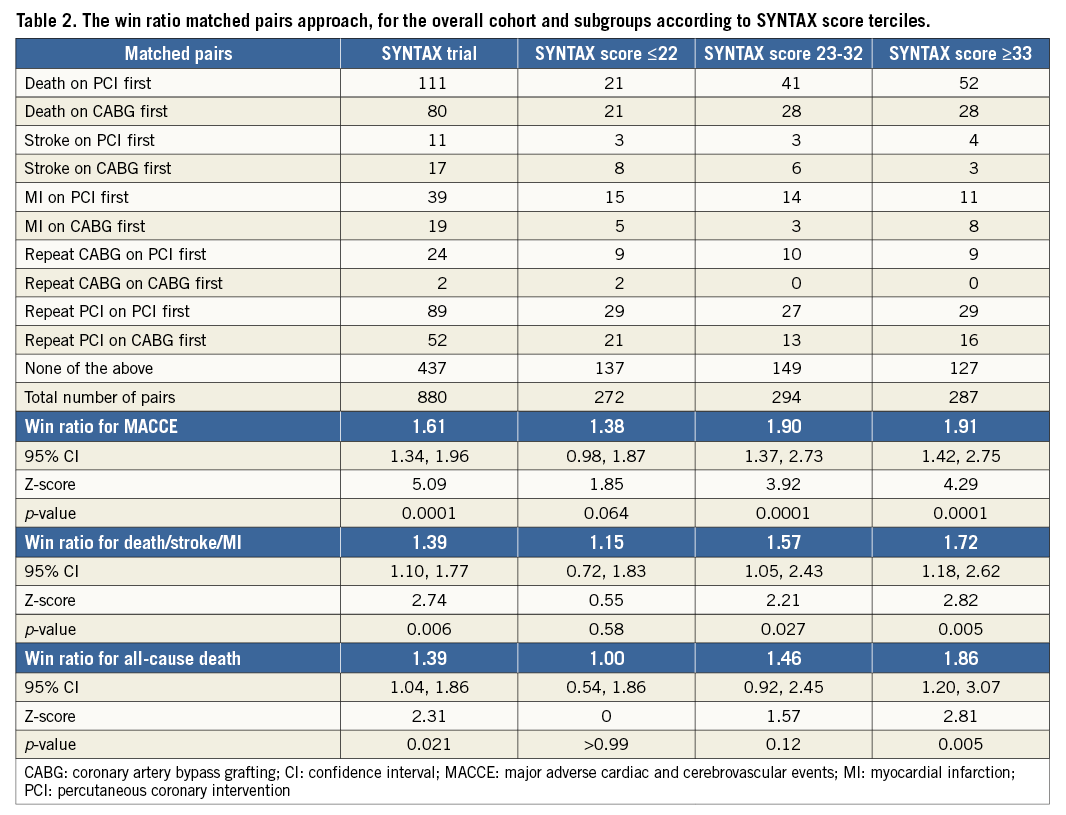
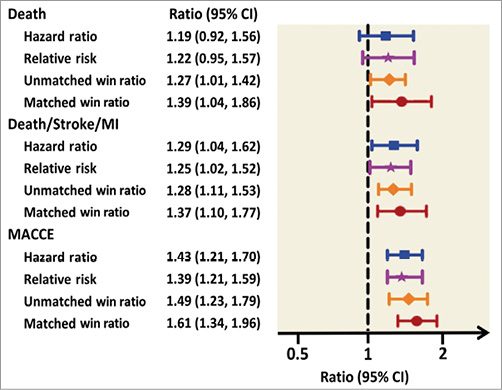
Figure 2. Win ratio approach vs. conventional analyses for the overall SYNTAX randomised cohort. Different colours represent conventional time-to-event hazard ratio analyses (blue), relative risk (purple), unmatched win ratio (orange), matched win ratio (red), approaches with 95% CIs. MACCE: major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events
For the composite safety endpoint of death/stroke/MI, the win ratios and the conventional result were similar. The matched win ratio for the composite safety endpoint of death/stroke/MI was the analysis with the largest relative difference between CABG versus PCI in favour of CABG (n=116 vs. n=161, respectively; Rw=1.37, 95% CI: 1.10-1.77; p=0.006). Out of 578 (65.7%) matched pairs that were tied for the composite of death/stroke/MI, 552 pairs did not have an event of death/stroke/MI during follow-up, and 26 patients were tied because of a different length of follow-up (Table 2, Figure 2).
Death occurred first after CABG in 80 patients and first after PCI in 111 patients; the unmatched win ratio for all-cause death was 1.27 (95% CI: 1.01-1.42) and the matched win ratio was 1.39 (95% CI: 1.04-1.86), which was statistically significant unlike conventional analyses that resulted in an HR of 1.19 (95% CI: 0.92-1.56) (Table 2, Figure 2).
SUBGROUP ANALYSES
SYNTAX SCORE
In patients with intermediate and high SYNTAX scores, the matched win ratio for MACCE at five years confirmed statistically significant better outcomes with CABG (Rw=1.90, 95% CI: 1.37-2.73 and Rw=1.91, 95% CI: 1.42-2.75, respectively) (Figure 3, Table 2). Nevertheless, the magnitude of the treatment effect was larger with the matched win ratio; even in the group of patients with a low SYNTAX score, there was a trend towards a difference.
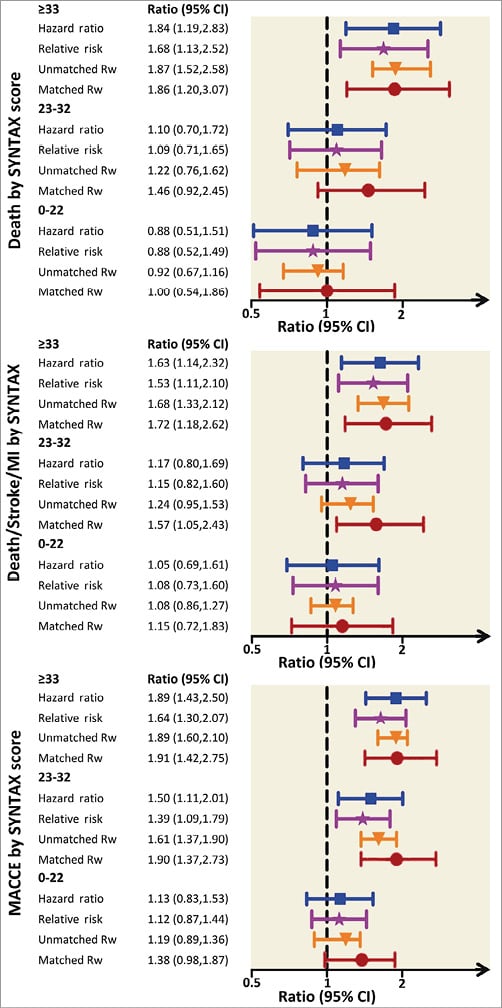
Figure 3. Win ratio approach vs. conventional analyses by baseline SYNTAX score terciles. MACCE: major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events
For the composite endpoint of death/stroke/MI, the matched win ratio increased significantly in favour of CABG from low to intermediate to high SYNTAX scores (Rw=1.15 vs. Rw=1.57 vs. Rw=1.72) as well as for all-cause death (Rw=1.00 vs. Rw=1.46 vs. Rw=1.86) (Figure 3, Table 2). However, the treatment effect of PCI versus CABG was strongest with the matched win ratio, and particularly for subgroups of patients with intermediate SYNTAX scores where there was a clear increase in the treatment effect. In comparison with conventional analyses, the findings from the unmatched analyses were similar in patients with low and high SYNTAX scores, but were stronger in favour of CABG for patients with intermediate SYNTAX scores (Figure 3).
LM/3VD
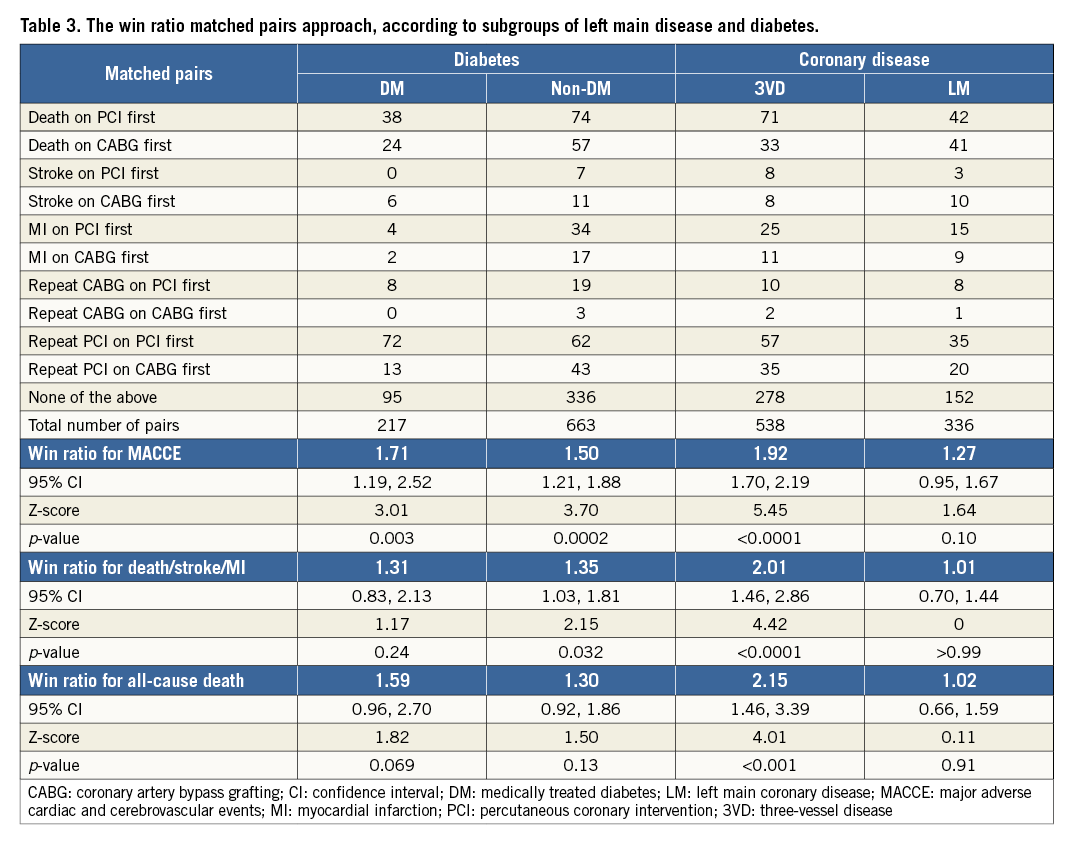
In patients with LM disease, the matched win ratio was not significantly different between CABG versus PCI: 1.27 (95% CI: 0.95-1.67) for MACCE, 1.02 (95% CI: 0.66-1.59) for the composite safety endpoint of death/stroke/MI, and 1.00 (95% CI: 0.70-1.44) for all-cause death (Figure 4, Table 3). In contrast, in patients with three-vessel disease, the matched win ratio for MACCE (Rw=1.92, 95% CI: 1.70-2.19), the composite safety endpoint of death/stroke/MI (Rw=2.00, 95% CI: 1.46-2.86), and all-cause death (Rw=2.15, 95% CI: 1.46-3.39) were all in favour of CABG. The unmatched approach supports the findings derived from conventional analyses in patients with LM, while unmatched analyses were stronger in favour of CABG among patients with three-vessel disease (Figure 4).
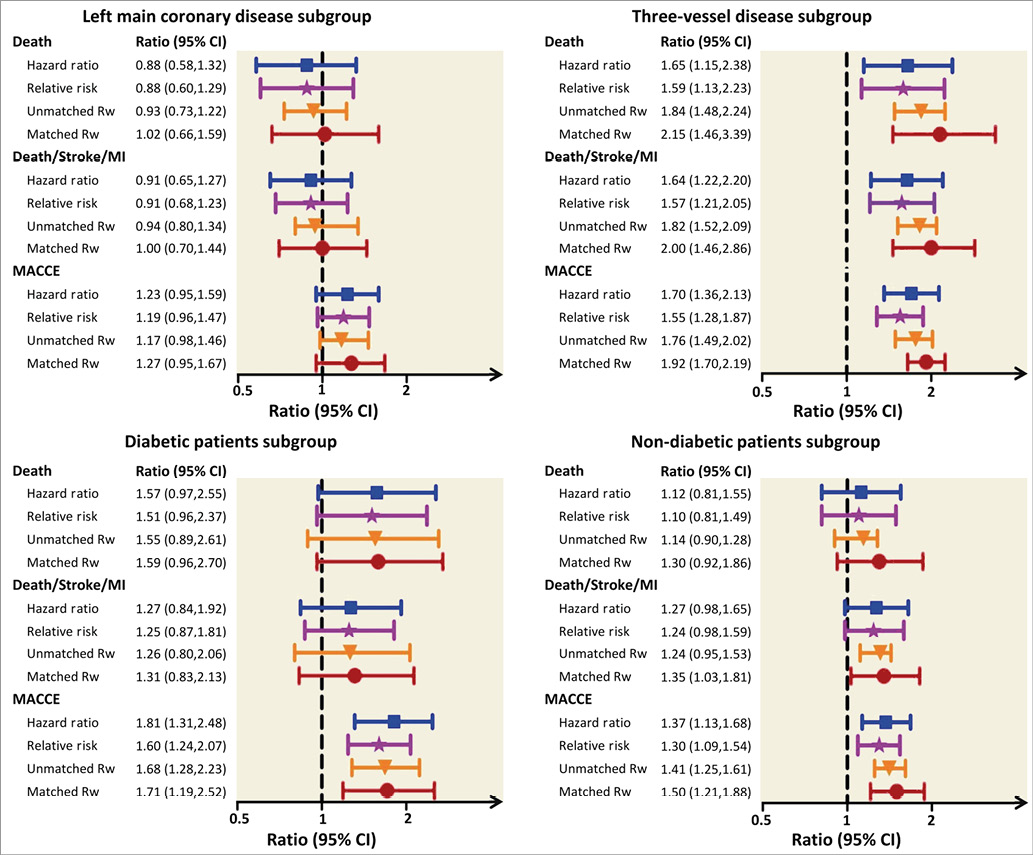
Figure 4. Win ratio approach vs. conventional analyses by baseline subgroups. MACCE: major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events
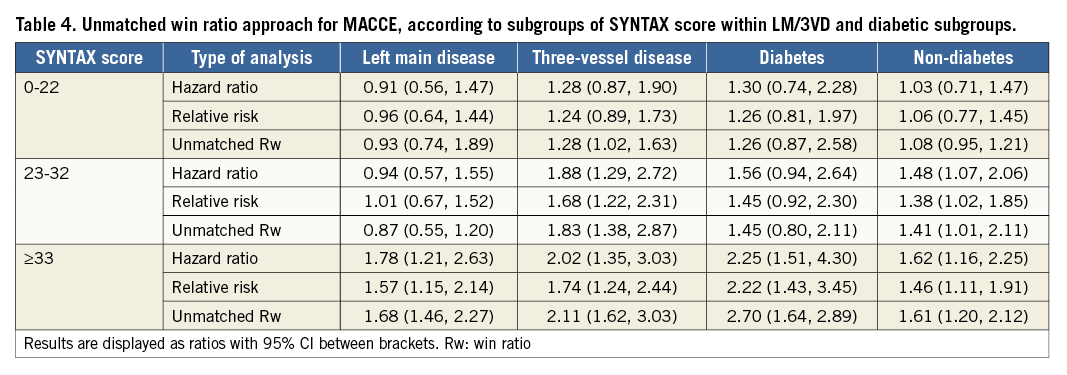
When separately analysing SYNTAX score subgroups for MACCE, differences between conventional analyses, the unmatched analyses, and matched analyses were only minimal (Table 4). Of note, there was no consistency in changes in PCI versus CABG treatment effects choosing conventional or any win ratio analyses, although CIs appeared smaller when using win ratio analyses.
DIABETES
In diabetic as well as non-diabetic patients, results using matched and unmatched win ratio approaches were comparable to those from conventional analyses (Figure 4, Table 3). In diabetic patients, MACCE was significantly lower in favour of CABG with a matched win ratio of 1.71 (95% CI: 1.19-2.52; p=0.003), while all-cause death and the composite of death/stroke/MI were not significantly different between CABG and PCI. In non-diabetic patients, results with the matched win ratio approach slightly favoured CABG in comparison to conventional analyses, although these differences were minimal.
In separate analyses applying the unmatched win ratio approach to SYNTAX score terciles, the overall results of diabetics and non-diabetics were consistent with conventional analyses (Table 4). There was no consistency in increasing or decreasing the treatment effect of PCI versus CABG when using the win ratio approach.
Discussion
The current analysis demonstrates that, by hierarchically prioritising events in the composite of MACCE, the treatment effect of CABG versus PCI is larger than with conventional analyses. In smaller subgroups of patients, for which unmatched win ratio analyses are necessary, differences between the win ratio approach and conventional analyses are minimal. These results provide additional insights into the SYNTAX trial results and have several important implications for future trial conduct.
PCI VERSUS CABG
The use of composite endpoints in trials is problematic because it may provoke controversy regarding their suitability12. Components are often unreasonably combined12,13, results are difficult to interpret14-16, and favourable outcomes or combinations of outcomes are cherry picked6,17. The criticism of the PCI versus CABG trials is that the superiority of CABG is primarily driven by repeat revascularisation which has less of a clinical impact than all-cause death, stroke and MI5. When repeat revascularisation is not part of the composite endpoint, there is no statistically significant difference between PCI and CABG in many trials. A meta-analysis of four trials comparing PCI with stents versus CABG also did not show a difference in rates of death/stroke/MI between CABG and PCI18. However, overall MACCE rates at five years were significantly lower in CABG patients as a result of persistently lower repeat revascularisation rates in those patients18.
The win-ratio approach addresses the limitations of softer clinical components in a composite endpoint by putting more emphasis on events with greater clinical importance. The win-ratio analysis takes into account not only the number of events, but also the timing of the event. While there was no statistically significant difference in survival at longest follow-up in the SYNTAX study, the Kaplan-Meier curves showed a continuous higher all-cause mortality rate after PCI. In a conventional time-to-event analysis with log-rank testing, this difference is not reflected. The win-ratio analysis of the SYNTAX trial shows that the benefit of CABG over PCI is evident in terms of both lower MACCE and lower all-cause mortality rates (p=0.021). Using the win ratio, this is the first time that a difference in all-cause mortality between PCI and CABG has been shown.
In patients with low SYNTAX scores, the win ratio for MACCE was not statistically different between treatment groups, but there was a considerable difference between the win-ratio and conventional analysis, suggesting that CABG may be favourable even in this subgroup of patients with a low SYNTAX score. This can be explained by the three times higher MI rates and the necessity for repeat CABG revascularisation in the PCI group. However, these findings are hypothesis-generating, and the preferred revascularisation method in the group with a low SYNTAX score remains a matter of debate that will need evaluation in future clinical trials.
FUTURE CLINICAL TRIAL DESIGN
The win ratio proves to be an important method for analysing future randomised clinical trial data. The unmatched win ratio substantially increases statistical power, while the matched win ratio showed an even larger increase in treatment effect19,20. Using the win ratio for sample size calculations may therefore reduce the number of patients in a trial, with the obvious advantages of shorter enrolment and lower costs. Expanding the number of components and including components with a wide range of impact severity will increase event rates and reduce the sample size further. While this would be considered inappropriate for conventional analyses21, this is not an issue when applying the win ratio since events are prioritised based on their impact severity.
When using the win ratio, however, it is important to alternate between the matched and unmatched approaches. Although the matched approach is favoured, our subgroup analysis that was performed 10 times suggests that exclusion of patients from an analysis in order to produce matched pairs can create a selection bias, causing an incorrect estimate of the true treatment effect on the outcome of interest. Therefore, it is recommended to use the unmatched approach when matching two treatment groups for which a substantial number of patients (arbitrarily >10%) should be excluded for matching.
Study limitations
Applying the win ratio has some limitations. First, there is no clear consensus on ranking the severity of the events in MACCE. In this study, we used the weighting scheme as proposed by Tong and co-authors17. In addition, a repeat CABG was rated as having more impact than repeat PCI. One may also argue that repeat CABG may have more impact than MI, due to its invasiveness and potential complications. Secondly, even within a single event, there are different degrees of severity, such as major MI with subsequent left ventricular dysfunction versus MI in the smaller branches of the coronary arteries, with less impact on a patient’s quality of life and prognosis. Likewise, a severe MI may have more consequences than a minor stroke. Future validation and verifications of the win ratio should be conducted before it becomes widely used in clinical trials. Moreover, the use of TAXUS stents in clinical practice was superseded by second-generation DES, which has been shown to improve long-term outcomes significantly. Therefore, the presented analyses must be considered observational and “hypothesis-generating”.
It should be acknowledged that a hazard ratio (HR), relative risk (RR) and the win ratio (Rw) are different outcome measures, and it is therefore unclear whether they can be compared directly.
Conclusions
The win ratio is a new method to analyse composite endpoints within clinical trials. It can be used effectively and provides a stronger estimate of a treatment effect than conventional analyses. Furthermore, it can easily be extended to analyse composite endpoints with multiple components and with a wider range of impact severity, while maintaining integrity. Based on these advantages, future trials adopting this approach can expect similar statistical power with smaller sample sizes, and lower trial costs.
In case of PCI versus CABG in the SYNTAX trial, this re-analysis bolstered the results of the conventional analysis and strengthened the finding in favour of CABG treatment for patients with complex coronary disease. This provides evidence that hard clinical outcomes in particular (e.g., death and MI) after CABG are less frequent as compared with PCI. It is important to emphasise that this analysis does not undermine the findings of the original conventional analysis based on a traditional pre-specified design; it does, however, more appropriately estimate the treatment effect of PCI versus CABG by prioritising hard clinical endpoints over softer endpoints.
| Impact on daily practice This study demonstrates that the win ratio approach can be simply and efficiently used to analyse composite outcomes in clinical trials that have combined several components with different clinical importance into a single measure. The obtained results provide a valuable framework to clinicians for meaningful outcome analysis following percutaneous coronary intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting. The win ratio has several advantages over conventional analyses and may be pre-specified in future trial designs. |
Guest Editor
This paper was guest edited by William Wijns, MD, PhD; The Lambe Institute for Translational Medicine and Curam, National University of Ireland, Galway and Saolta University Healthcare Group, Galway, Ireland.
Funding
The SYNTAX trial was supported by funds from Boston Scientific Corporation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. The Guest Editor has no conflicts of interest to declare.

