
Abstract
Aims: We aimed to examine the impact of three different radiation protection devices in a real-world setting of radial artery catheterisation.
Methods and results: In an all-comer randomised trial, consecutive coronary radial diagnostic and intervention procedures were assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to shield-only protection (shield group), shield and overlapping 0.5 mm Pb panel curtain (shield+curtain group) or shield, curtain and additional 75x40 cm, 0.5 mm Pb drape placed across the waist of the patient (shield+curtain+drape group). A total of 614 radial procedures were randomised (n=193 shield, n=220 shield+curtain, n=201 shield+curtain+drape). There were no differences among the groups in patient or procedural characteristics. The primary endpoint (relative exposure ratio between the operators’ exposure in μSv and the patient’s exposure, dose area product in cGy·cm2) was significantly lower in the shield+curtain+drape group for both the first operator (20% reduction vs shield, 16% vs shield+curtain, p=0.025) and the assistant (39% reduction vs shield, 25% vs shield+curtain, p=0.009).
Conclusions: The use of an additional drape reduced the radiation exposure of both the first operator and the second operator during routine radial procedures; a shield-attached curtain alone was only partially effective. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03634657
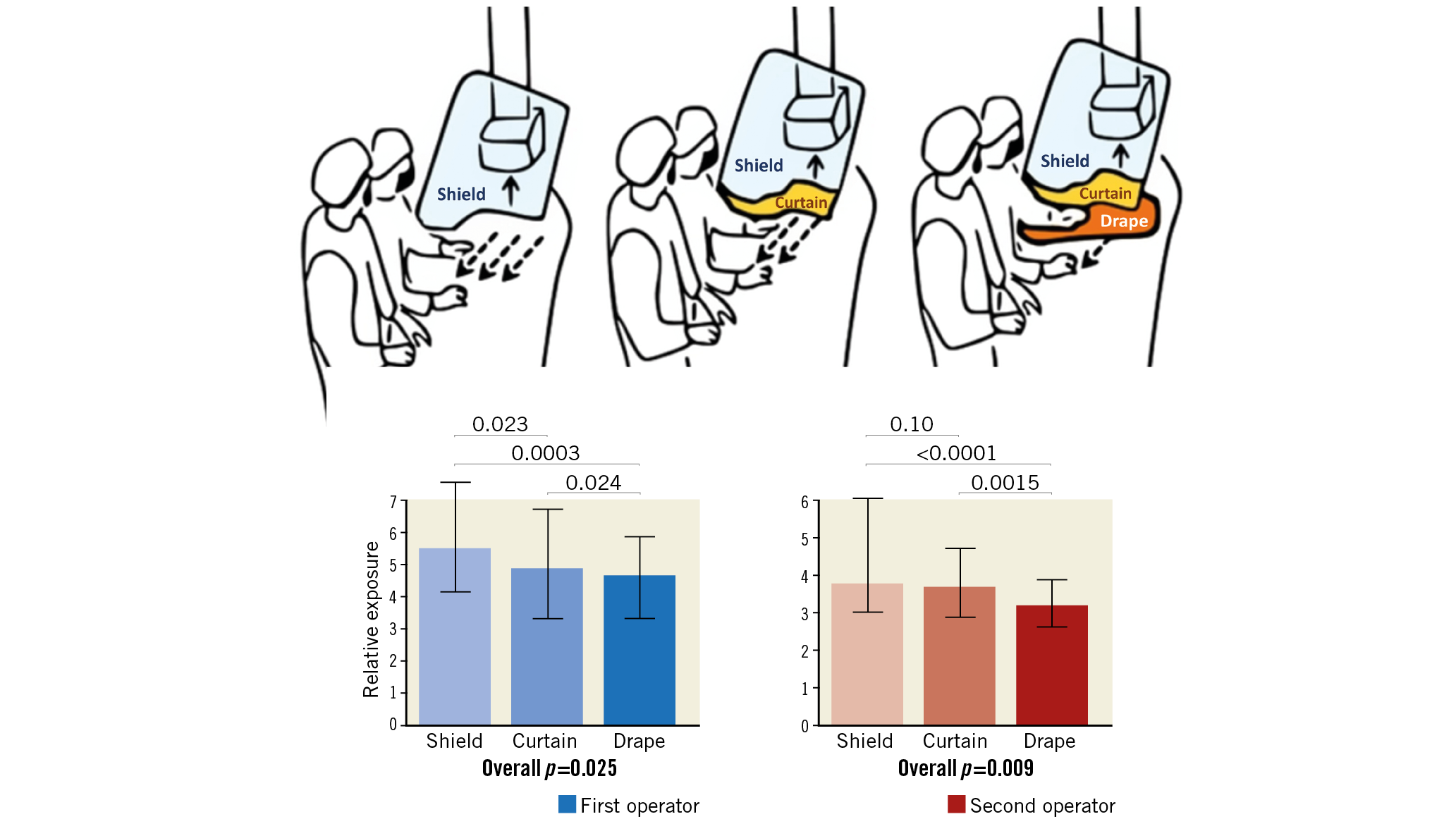
Visual summary. X-ray protection devices and their effects on radiation exposure.
Introduction
Radiation exposure leads to deterministic damage, which appears only after high-dose exposure (e.g., cataract for the operator and skin lesions for the patient), but is also associated with a (less dose-dependent) stochastic risk for various malignancies1,2,3,4,5,6. Despite technological progress and improved X-ray technologies, the increasing complexity and number of interventions mean that radiation hazards remain an important issue, particularly in the cardiovascular field7,8.
The amount of backscattered radiation to which operators are exposed varies depending on operator experience, type of procedure performed, patient characteristics, type of X-ray apparatus and the use of protection devices9,10,11. The latter include disposable gloves and pads, shields, aprons as well as robotic systems12,13,14,15,16,17. Of note, the arterial access used for the angiography also affects radiation exposure and, since the effectiveness of the above-mentioned X-ray protection devices has been tested mainly in settings where the femoral access was used, their utility in the current routine of radial catheterisation remains to be tested. Due to their association with reduced bleeding risk and improved patient prognosis18,19, radial coronary procedures nowadays represent the standard of most interventional centres. While it remains unclear whether the radial access per se is associated with an increased radiation exposure for the operator, once the learning curve has been completed9,11, the effectiveness of radiation protection devices needs to be tested in this modified setting.
Material and methods
STUDY DESIGN
The study was designed as a prospective, single-centre, randomised, controlled, parallel group trial. Consecutive coronary procedures were randomised in a 1:1:1 ratio to one of three radiation protection interventions (described below) using block randomisation (each block 30 exams) without stratification. The randomisation list was generated with MedCalc (MedCalc Software Ltd, Mariakerke, Belgium) before the study began. The detailed protocol, which was approved by the local ethics committee (reference number 2018-13051-KliFo), was published elsewhere (Supplementary Appendix 1, Supplementary Figure 1),20. The sponsor of the study was the University Medical Center Mainz. Data were acquired between August 2018 and August 2019. The protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the local Landesärztekammer (2018-13051-KliFo).
HYPOTHESIS OF THE STUDY
We hypothesised that the use of a shield-mounted curtain and a radiation protection drape would be associated with a reduction in the operator’s radiation exposure in the setting of radial coronary diagnostic and interventional procedures.
MEASUREMENT OF SCATTERED RADIATION
Operators’ dosimetry was performed at chest height, outside the lead apron, with a personal dosimeter (Radex ONE; Quarta Rad, Wilmington, DE, USA) in the catheterisation laboratory during the coronary catheterisation. Both the first and second operators wore a dosimeter. Dosimetry data are entered in duplicate on paper and in an Excel database. Duplicate measurements were performed before initiation of enrolment and were performed at regular (two months) intervals to guarantee the quality of the measurements. Physicians were trained at the beginning of the study on how to use the dosimeters; their compliance with study procedures and the correct use of the dosimeters was controlled daily. Data entry was audited at weekly intervals. Patient dosimetry was not performed. All procedural decisions were left to the operators’ discretion; the study procedures did not interfere with clinical routine except for the radiation protection device used.
RADIATION PROTECTION
Procedures were randomised to one of three groups:
– a ceiling-mounted, 60×76 cm, 0.5 mm Pb, shield-only protection (MAVIG [MAVIG GmbH, Munich, Germany], shield group),
– shield and overhanging 0.5 mm Pb panel curtain (MAVIG, shield+curtain group) or
– shield, curtain and additional 75×40 cm, 0.5 mm Pb, custom-made reusable drape with a disposable sterile cover placed across the waist of the patient (shield+curtain+drape group). The operators were instructed on how to ensure that the drape be maintained in position (covering lower abdomen and groin area) during the procedure; compliance with correct use was monitored daily.
The interventions are shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1. The three interventions: shield group (left), shield+curtain group (middle) and shield+curtain+drape group (right).
Conventional radiation protection measures (lead aprons, lead collar) were used in all procedures, which were performed using the same X-ray equipment (Philips AlluraClarity FD10; Philips Medical Systems, Amsterdam, the Netherlands). A 20 cm field of view and a frame rate of 15 frames/s were used.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
PRIMARY OBJECTIVE
– The primary endpoint of the study was the difference in relative exposure of the primary operator among groups. Relative exposure was defined as the ratio between the operator’s exposure (E, in μSv) and patient exposure (dose area product, in cGy·cm²).
– The co-primary endpoint was the difference in relative exposure of the assistant operator among groups.
The analysis was performed on an intention-to-treat database, containing all randomised procedures.
SECONDARY OBJECTIVES
Secondary outcomes included:
– Difference in patient exposure among groups.
– Difference in operators’ absolute dose among groups.
– Difference in both primary outcomes in sub-analyses limited to:
– diagnostic versus interventional procedures in patients with body mass index (BMI) >30 vs ≤30;
– analysis of predictors of operator and assistant operator exposure in multivariable analysis
Data are presented as mean (SD), median (interquartile range) or n (%). Categorical data were analysed using the chi-square test and continuous variables were analysed using analysis of variance or the Kruskal-Wallis test as appropriate. The distribution of the data was tested by visual inspection of the Q-Q plots complemented by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. For comparison of the three treatment arms, an ordered test strategy was used: curtain and drape were first tested separately versus shield by a one-sided test for independent samples at a nominal level of 0.0125 to assure a multiple level of 0.025 by virtue of the Bonferroni correction method. The pre-specified analysis assumed that, if at least one of the two null hypotheses were rejected, the two interventional arms would be tested for difference by a two-sided t-test at a significance level of 0.05.
The primary analysis was based on an intention-to-treat analysis database, containing all procedures which were randomised.
The sample size calculation is based on the following assumptions: a two-tailed α-level=0.05 (confidence interval 95%), a β-level=0.10, a relative exposure of 6.0±5.0 µSv/cGy/cm² in the shield (control) group (based on historical data from our laboratory), an expected relative exposure of 5.0±5.0 µSv/cGy/cm² (effect size 1.0 µSv/cGy/cm²) in the shield+curtain and 4.0±5.0 µSv/cGy/cm² (effect size 2.0 µSv/cGy/cm²) in the shield+curtain+drape group. Given these assumptions, a sample size of 480 measurements would have been necessary; this set was however expanded to allow investigation of possible interactions beyond the primary analysis (secondary endpoints). Further details on the conduct of the study (data entry, auditing, dissemination etc.) have already been reported20. All analyses (including the randomisation list) were performed with MedCalc, v.15 (MedCalc Software Ltd).
Results
PATIENT AND PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS
The patient and procedural characteristics are presented in Table 1 and Table 2. Measurements were performed in a total of 614 procedures (193 in the shield group, 220 in the shield+curtain group, 201 in the shield+curtain+drape group). During the study period, 125 procedures (15 diagnostic) were performed on haemodynamically unstable patients in emergency settings. These procedures were not randomised and were not included in the study to avoid any delay in the treatment of the patients. All other procedures during the study period were randomised, and all randomised procedures were included in the analysis as randomised; there was no case of crossover. The data acquisition was completed as planned when the planned number of procedures was reached. There was a total of 322 (53%) coronary interventions (p=0.60 among groups); 260 (42%) procedures also involved a left ventricle angiography (p=0.794), 34 (6%) right heart catheterisations (p=0.063), and 16 (3%) left ventricle biopsies (p=0.842), without difference among randomisation groups. Patients’ characteristics potentially associated with X-ray exposure risk (sex, p=0.228, age, p=0.580, body surface area, p=0.158, history of bypass surgery, p=0.497, body mass index, p=0.388) were also not different among groups. Finally, in case of coronary interventions, parameters expressing procedural complexity (number of vessels treated, p=0.123, prevalence of chronic total occlusion procedures, p=0.588, use of additional imaging or haemodynamic tools, p=0.566 and 0.368) did not differ among groups. On average, 124±3 mL contrast medium were used per procedure, with a larger volume used in the shield+curtain versus shield versus shield+curtain+drape group (135±6 vs 122±5 vs 114±5 mL, p=0.020).

RADIATION EXPOSURE
Mean procedure time and fluoroscopy time were not different among groups (procedure time: 44±3 vs 46±2 vs 40±2 minutes in the shield, shield+curtain and shield+curtain+drape group, p=0.149; fluoroscopy time: 9±1 vs 9±1 vs 8±1 minutes, p=0.528). Mean dose area product was slightly higher in the shield+curtain group, although this difference did not reach significance (2,896±179 vs 3,352±192 vs 2,776±171 cGy·cm², p=0.056).
THE EFFECT OF PROTECTION DEVICES
Relative exposure data are presented in Figure 2. The relative exposure for both the first and the second operators showed a dose-response decrease in the three groups: as compared to the shield group, relative exposure decreased by 17.8% for the first and by 3% for the second operator in the shield+curtain group and by 19.7% and 39.3% for the first and second operators in the shield+curtain+drape group. For the primary endpoint (comparisons among groups), the use of a drape was associated with a significant reduction in relative exposure as compared to the shield group for both the first and the second operator (p=0.0003 and p<0.0001). In contrast, the comparison between the shield+curtain group and the shield group did not reach the pre-specified p-level of 0.0125 (p=0.023 for the first operator and p=0.10 for the second operator). The comparison between the shield+curtain+drape group and the shield+curtain group showed a lower relative exposure in the shield+curtain+drape group, which was particularly evident for the second operator (p=0.024 and p=0.0015). Accordingly, absolute exposure was lowest for both operators in the shield+curtain+drape group (Table 2). There was no difference in patient exposure, although a numerical trend towards higher exposure in the shield+curtain group was seen (Table 2).
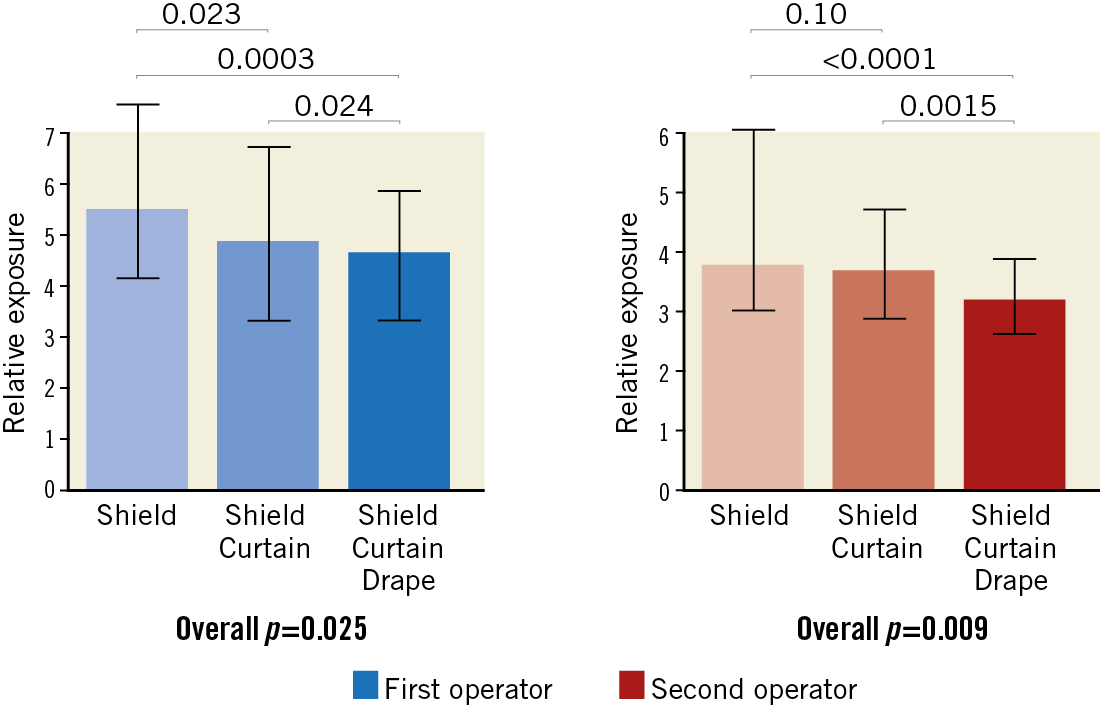
Figure 2. The impact of shield, shield+curtain and shield+curtain+drape on operators’ exposure. Blue bars: first operator (overall p=0.025). Red bars: second operator (overall p=0.009). All data are presented in relative exposure (E/DAP×10–3). There was a dose-dependent decrease in exposure for both operators. Bars express median and IQR. All analyses performed with the Kruskal-Wallis test.
SUBGROUP ANALYSES
The difference among groups was maintained in several exploratory sub-analyses, including patients with BMI larger or smaller than 30, diagnostic and interventional procedures (all p<0.05) (Figure 3), as well as procedures requiring more than five minutes fluoroscopy (p=0.0098 for the first operator, p=0.0042 for the second operator). The difference among groups was attenuated in the case of the first operator performing diagnostic angiograms (p=0.29) (Figure 4).
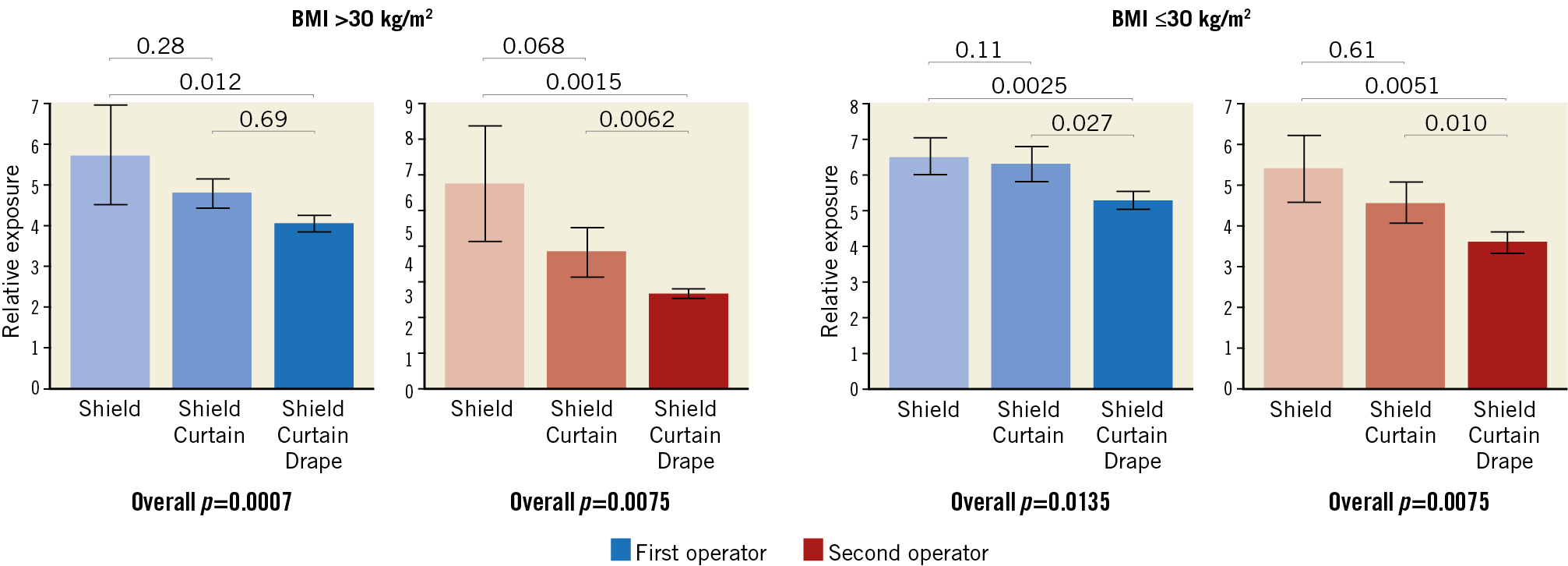
Figure 3. The impact of combinations of the three protection devices in subgroup analyses of procedures in patients with a BMI above or below/equal to 30 kg/m2. Blue bars: first operator. Red bars: second operator. All data are presented in E/DAP×10–3. All analyses performed with the Kruskal-Wallis test.
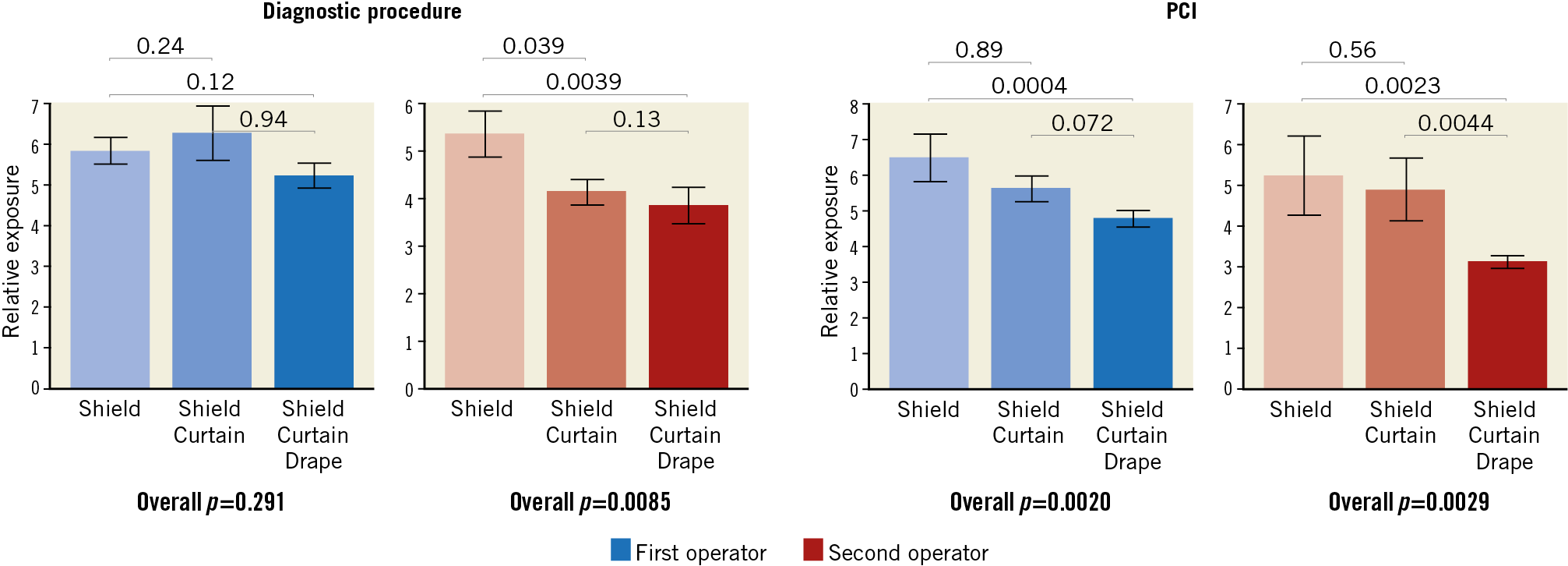
Figure 4. The impact of combinations of the three protection devices in subgroup analyses of diagnostic-only procedures versus coronary interventions (PCI). Blue bars: first operator. Red bars: second operator. All data are presented in E/DAP×10–3. All analyses performed with the Kruskal-Wallis test.
Discussion
In a large-scale, all-comer, controlled, randomised study we tested the effect of two radiation protection devices and compared their effectiveness against the current standard (shield only). We found that the use of these additional devices attenuated the relative operators’ radiation exposure by approximately 20-40%, with a significant effect for both the first and the second operators. This effect was preserved in sub-analyses in diagnostic and interventional procedures, in procedures conducted in patients with BMI larger or smaller than 30, and it was more evident in more complex procedures requiring prolonged fluoroscopy time.
Mean dose area product was slightly higher in the shield+curtain group, although this difference did not reach significance.
THE IMPACT OF RADIATION EXPOSURE AND DEVICES TO LIMIT IT
Patient and operator exposure from procedures in the catheterisation laboratory is historically associated with a potential health burden particularly in the cardiovascular field, which contributes 40% of total medical radiation exposure2,21. The incidence of radiation-induced pathologies is proportional to the duration of the professional career and the complexity of the catheterisation procedures22,23,24. Even though much has been done to increase awareness and safety standards25, radiation protection remains a priority for staff and policy makers. A recent survey documented that the exposure to radiation remains the major factor restraining women from a career in interventional cardiology26. Finally, despite the increased awareness and technical developments in radiation protection, the treatment of increasingly complex patients and lesions that would previously have required surgical revascularisation or medical therapy alone has led to increased operator exposure. In a recent report, a 54% increase in the average fluoroscopy time was reported when procedures performed in the year 2016 were compared to those performed in 200625.
An additional significant change that has been introduced in coronary procedures, and is now included as class I recommendation in the revascularisation guidelines27, is the systematic use of the radial approach. Despite its advantages, the radial approach has been associated with increased levels of radiation exposure28,29,30. Even though this effect appears to be attenuated at the end of the learning curve31,32, the switch to a transradial approach implies that the use of devices previously developed for the transfemoral access needs to be re-evaluated. In this context, studies have shown that the use of adjunctive radiation protection drapes leads to a reduction in operator dose during transradial percutaneous coronary procedures14,33,34,35,36,37. The limitation of most of these investigations is however their small sample size. In the largest of these trials, 766 procedures were randomised to a conventional setting, use of a disposable pad, or use of a sham pad16. The study showed that the use of the pad led to a 20% reduction in operator exposure compared to the conventional setting, and up to a 44% reduction compared to the use of the sham device, i.e., analogous to what we observed in the present trial with a reusable drape in a study of similar size. In daily clinical practice, the use of disposable pads is limited by the high costs, which are currently not reimbursed. Further, some of the previous studies used larger drapes which are less practical to use and do not allow easy access to alternative puncture sites in case of emergency. The findings of the present study show that a reusable alternative might lead to equivalent results.
Limitations
We observed a large variability in radiation exposure and in fluoroscopy use among groups which, despite the large sample size, does not allow testing the effectiveness of the protection devices in small subgroups. This variability reflects day-to-day clinical practice for interventional cardiologists. The fact that the interventions led to a significant reduction in radiation exposure in several sub-analyses is a strength of the study. Radiation exposure was measured at chest level (outside the lead apron), while eye or hand exposure was not assessed. Current guidelines use chest dosimetry. The same method (one measurement at chest level) was used in the recent paper by Vlastra et al16. As in the study by Vlastra, dosimetry at patient level was also measured, but there is no rationale to believe that interventions aimed at reducing backscattering will also reduce direct patient radiation. Total administered radiation was used as a surrogate of patient dosimetry and to standardise relative exposure among groups. A number of other variables might influence radiation exposure, for instance the access side (right versus left). However, despite the size of the database, the low prevalence of these variables does not allow drawing conclusions on their impact (e.g., only 26 patients underwent left cannulation of the left radial artery). There was a numerical trend towards higher dose-area values in the shield+curtain group. Although this is counterintuitive given the randomised design and the absence of a difference in overall radiation time, it might be that the presence of the curtain could have led the operators to pay less attention to limiting radiation use.
Finally, this was a single-centre study and there was no control group without a shield, since this would have exposed the staff to avoidable increased radiation and would therefore have been ethically and practically unacceptable.
Conclusions
We demonstrate that the use of a reusable drape, with lower costs as compared to single-use devices, reduces the relative operators’ radiation exposure by approximately 20-40%. This effect appeared to be more evident in coronary interventions as compared to diagnostic exams, and in patients with BMI >30 as compared to those with BMI <30. Although not specifically tested here, this might be a particularly useful approach for complex procedures, e.g., in the setting of chronic total occlusions and complex bifurcation interventions.
|
Impact on daily practice Despite significant technological advances, exposure to scattered radiation remains a deterrent for many (particularly women) interested in interventional cardiology. The use of additional radiation protection devices reduces this health hazard significantly. In this randomised study, we show that the use of a small reusable drape placed across the patient’s waist may reduce operator exposure. This might be a viable and cost-effective measure, particularly for complex procedures. |
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

