Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to develop a deep learning model for classifying frames with versus without optical coherence tomography (OCT)-derived thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA).
Methods and results: A total of 602 coronary lesions from 602 angina patients were randomised into training and test sets in a 4:1 ratio. A DenseNet model was developed to classify OCT frames with or without OCT-derived TCFA. Gradient-weighted class activation mapping was used to visualise the area of attention. In the training sample (35,678 frames of 480 lesions), the model with fivefold cross-validation had an overall accuracy of 91.6±1.7%, sensitivity of 88.7±3.4%, and specificity of 91.8±2.0% (averaged AUC=0.96±0.01) in predicting the presence of TCFA. In the test samples (9,722 frames of 122 lesions), the overall accuracy at the frame level was 92.8% within the lesion (AUC=0.96) and 91.3% in the entire OCT pullback. The correlation between the %TCFA burden per vessel predicted by the model compared with that identified by experts was significant (r=0.87, p<0.001). The region of attention was localised at the site of the thin cap in 93.4% of TCFA-containing frames. Total computational time per pullback was 2.1±0.3 seconds.
Conclusions: A deep learning algorithm can accurately detect an OCT-TCFA with high reproducibility. The time-saving computerised process may assist clinicians to recognise high-risk lesions easily and to make decisions in the catheterisation laboratory.
Introduction
Thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) is a precursor of plaque rupture with acute coronary thrombosis. It is characterised by an inflamed fibrous cap with a thickness <65 µm, a large necrotic core, and an infiltration of foamy macrophages1,2,3,4. Previous studies on the natural history of deferred coronary lesions demonstrated that the presence of TCFA is an independent predictor of future adverse cardiac outcomes5,6. Moreover, TCFA-containing lesions were associated with a high risk of distal embolisation and periprocedural myocardial infarction during percutaneous coronary intervention7,8. However, the majority of previous studies have conducted only qualitative assessments of TCFA (i.e., the presence or absence of TCFA within the target vessel), which represents poorly the status of the whole length of the vessel.
Currently, optical coherence tomography (OCT) is the only imaging modality with sufficient resolution (10-15 µm of spatial resolution) to measure fibrous cap thickness (FCT) and identify TCFA-containing lesions9,10,11. Although studies of FCT measurement ex vivo showed a good interobserver agreement relative to histology, its reproducibility in vivo remains poor12,13. Furthermore, the feature evaluated in the majority of these studies was not the extent of TCFA but rather the presence or absence of TCFA in any frame within a target vascular segment; this may not necessarily reflect the status of the entire vessel. Conversely, the quantification of TCFA by per-frame interpretation from a whole OCT pullback is time-consuming. Therefore, a standard interpretation algorithm is needed to reduce interobserver variation and the cost associated with OCT analysis.
Deep learning approaches have recently become dominant in various computer vision tasks such as classification, detection, and segmentation14,15,16. Convolutional neural networks, which is a type of deep learning, is designed to ascertain the spatial hierarchies of features via backpropagation automatically and adaptively. This data-driven approach can be applied to develop prediction models for medical imaging with excellent performance. Previous studies have developed deep learning algorithms for automatic OCT segmentation, tissue classification, and atheroma detection17,18. Although these studies highlighted the importance of the approaches for the accurate and rapid interpretation of OCT, their clinical implication was limited by the inclusion of only a small number of OCT cases, suboptimal accuracy, and the lack of an algorithm to identify a TCFA.
By using a larger OCT cohort (45,400 OCT frames in 602 coronary arteries), this current study was conducted to develop an end-to-end neural network model that can automatically classify frames with or without OCT-derived TCFA, as the prototype of vulnerable plaque.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION AND DATA COLLECTION
Between May 2010 and May 2016, 6,598 consecutive patients with stable and unstable angina underwent invasive coronary angiography at Asan Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea. Preprocedural OCT data were obtained in 798 patients at the discretion of the operators. All patients had at least one lesion with 30%-85% of angiographic stenosis. When multiple lesions were evaluated in one patient, the lesion with the highest degree of angiographic stenosis was selected. We excluded 171 stented lesions and 25 lesions because of poor imaging quality; 602 coronary lesions from 602 patients were studied in total. Patients were randomly assigned to training (n=480) or test (n=122) sets in a ratio of 4:1. Per-patient randomisation was conducted to avoid adjacent frames with similar characteristics from being enrolled into both the training and test sets. Furthermore, data from a non-overlapping population of 65 consecutive patients (with 65 unselected OCT pullback images acquired from the St. Jude Medical OCT system) who underwent preprocedural OCT between February 2016 and November 2017 were used for an additional validation study.
Clinical information was supported by the Asan Biomedical Research Environment system. All patients provided written informed consent. This study was approved by the institutional review board of Asan Medical Center.
After the intracoronary administration of 0.2 mg nitroglycerine, OCT images were acquired using a non-occlusive technique with the C7XR™ system and Dragonfly™ catheters (LightLab Imaging/St. Jude Medical, St. Paul, MN, USA) at a pullback speed of 20 mm/s. A lesion was defined as the segment including frames with >0.5 mm maximal plaque thickness. When a vessel had multiple lesions, only one lesion containing the minimal lumen area site was selected and used for machine learning (ML). After the exclusion of OCT frames at the branching sites, a total of 45,400 OCT frames (training set: 35,678 frames in 480 patients, test set: 9,722 frames in 122 patients) were included in the final model.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Each OCT frame had a 0.4 mm interval and was labelled according to the presence or absence of TCFA. We defined OCT-derived TCFA as an OCT-delineated necrotic core with an angle ≥90° and an overlying FCT <65 μm at the thinnest part to be the histologically defined threshold for detection1,2,3,4. Supplementary Appendix 1 summarises the definitions of OCT findings and Supplementary Figure 1 provides the examples. All OCT images were analysed by two independent investigators who were blinded to the information on the patients. In the event of discordance between the readers, an assessment was obtained from a third independent investigator to determine a consensus. In the independent cohort including 65 OCT pullbacks, intraobserver and interobserver variability between two independent observers (P.H. Lee and S.W. Lee) was evaluated to separate the frames with versus without TCFA. The intraobserver and interobserver variability was assessed by kappa statistical analysis that corrected for the chance of simple agreement and accounted for systematic observer bias; a kappa >0.80 indicated good agreement, and a kappa between 0.61 and 0.80 indicated moderate agreement. S.J. Kang, a cardiologist, reviewed annotated images and supervised all the steps of data preparation.
Supplementary Appendix 2 describes the densely connected convolutional networks (DenseNet)19 and the hyperparameters used. A balanced number of images with versus without TCFA was randomly selected and used to train the model for each epoch. In the given number of TCFA-containing images, various augmentation techniques were utilised (Supplementary Appendix 2).
Because a guiding catheter tip in the ostium may lead to a false diagnosis of TCFA at the proximal end of an OCT image, we additionally conducted post-tuning of the model in 100 separate patients with 2,590 OCT frames showing a guiding catheter to discriminate a TCFA-mimicking catheter from the ground truth.
The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was based on the relative performance with consideration to the whole range of possible probability thresholds (from 0 to 1) and had an area ranging from “0.5” for classifiers without any prediction capability to “1” for perfectly classifying algorithms. Furthermore, a fivefold cross-validation was used in each training process to flag overfitting (Supplementary Appendix 3). The averaged performances were shown as mean±standard deviations. After the completion of cross-validation, the model was re-trained on the whole training data set for a final prediction. The trained deep learning model provides a continuous number between zero and one for a referable classification of TCFA presence. The ROCs were plotted by varying the operating threshold, and the operating point with the largest area under the curve (AUC) value was selected. Figure 1 shows the overall flow chart for the development of the deep learning model. The diagnostic performances at the frame level were assessed within the lesion and in the entire frames of an OCT pullback. With a batch size of 256, total computational time for analysing an OCT pullback was calculated as the sum of data loading and inference time.
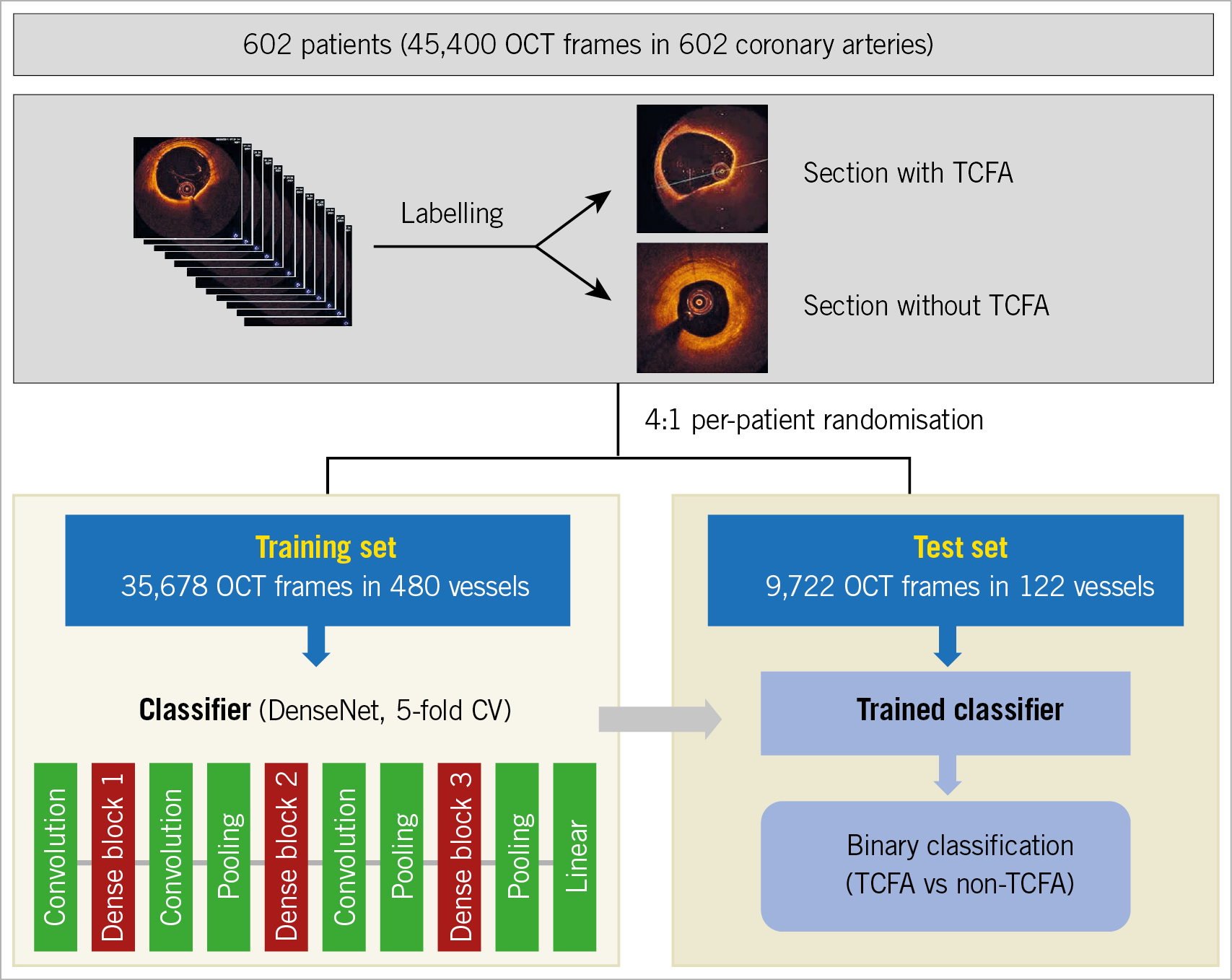
Figure 1. Flow chart of machine learning. TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma
To evaluate the performance at the vessel level, percent TCFA burden was calculated as the percentage of TCFA-containing frames in the total OCT frames within a vessel. Considering the potential clustering effect of multiple frames per vessel on the classification, the normalised diagnostic performances were calculated as the averages of the frame-level performances in each vessel (averaged sensitivity, averaged specificity and averaged overall accuracy). In addition, the performances in 122 randomly selected frames (including one frame per patient) in 122 test samples were calculated, and then the averaged performances of the 20 independent runs were shown as mean±standard deviations.
To assess how many were overlapping between the predicted versus the ground-truth TCFA frames in the test set, by using the definitions of true positive (TP), false positive (FP) and false negative (FN), the dice similarity coefficient (DSC) was calculated as 2TP/(2TP+FP+FN).
Gradient-weighted class activation mapping (Grad-CAM) was applied to the overall OCT frames that were classified as positive TCFA (Supplementary Appendix 4). Ultimately, this process helped to clarify whether the developed models utilised the histologically defined key features of TCFA (thin cap overlying necrotic core) as the main target for detection.
Results
CLINICAL AND LESION CHARACTERISTICS
Table 1 shows a summary of the clinical characteristics of patients and quantitative coronary angiographic data. The overall frequency of OCT-defined TCFA in our sample was 7.3%. In the training sample (including 480 lesions with 35,678 frames), TCFA was detected in 2,577 (7.2%) frames. In the test sample (including 122 lesions with 9,722 frames), 717 (7.4%) frames had a TCFA. For the diagnosis of TCFA, intraobserver and interobserver variability yielded moderate concordance (kappa=0.78 and kappa=0.74, respectively).
DEEP LEARNING PREDICTION OF TCFA
Table 2 summarises the frame-level performance in terms of classifying frames with versus without TCFA. The AUCs based on ROC analyses are shown in Figure 2. In the training samples, the deep learning model with fivefold cross-validation showed an overall accuracy of 91.6±1.7%, a sensitivity of 88.7±3.4%, and a specificity of 91.8±2.0% within the lesion (AUC 0.96±0.01). In the test samples, the overall accuracy was 92.8% (AUC 0.96) within the lesion and 91.3% (AUC 0.96) in the entire pullback images (Table 2).
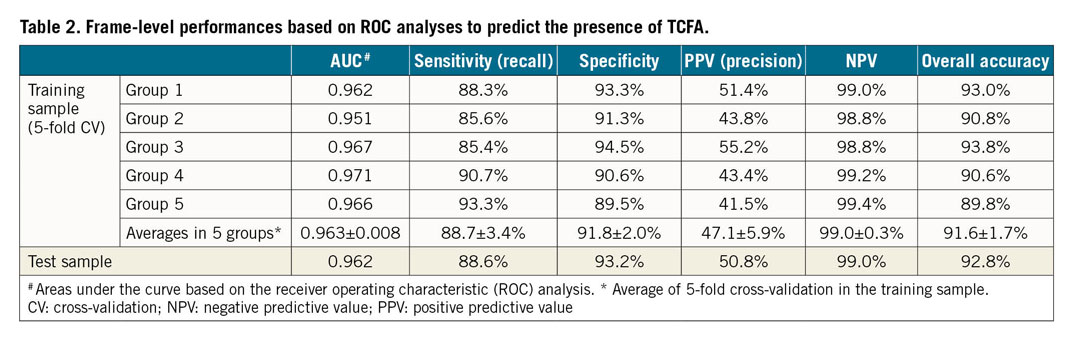
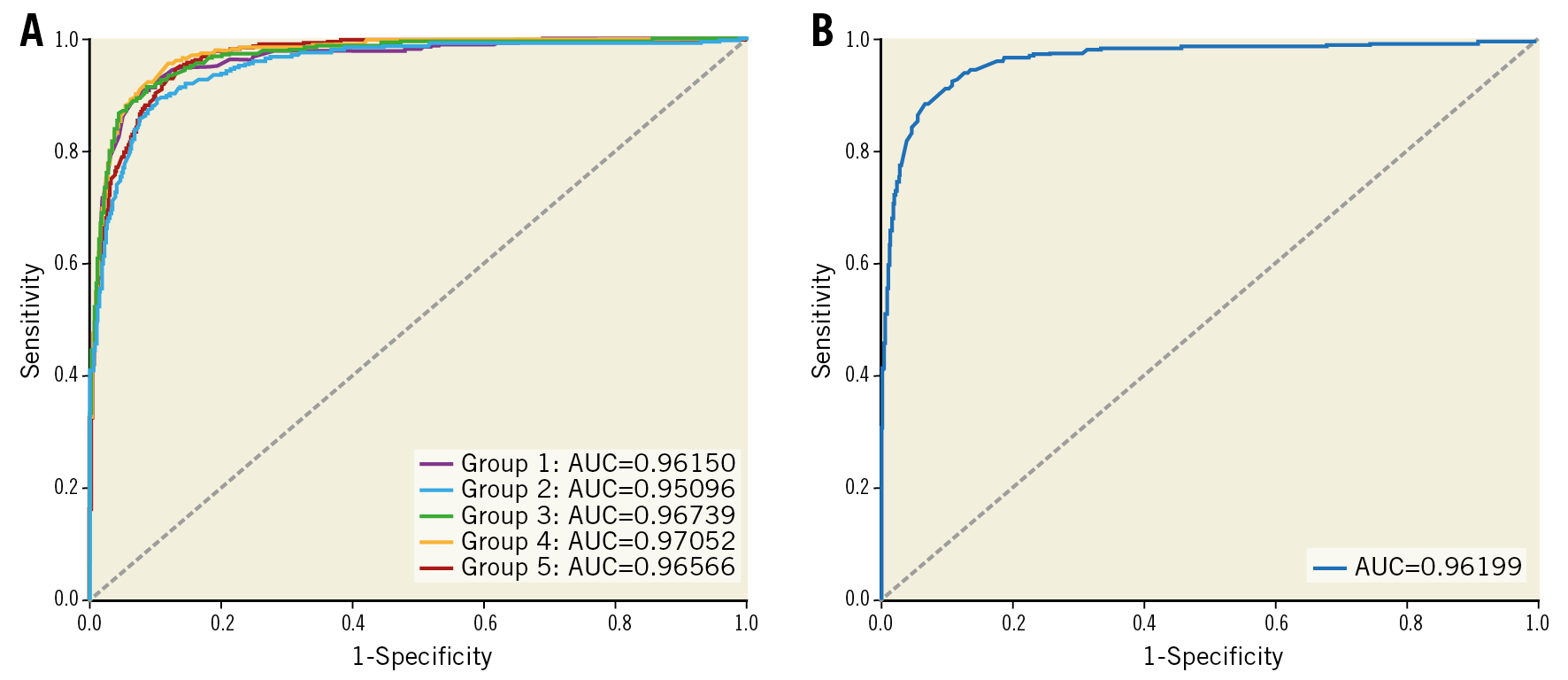
Figure 2. ROC analysis. A) Areas under the curve in the training set with fivefold cross-validation. B) Area under the curve in the test set.
When the normalised diagnostic performances in a vessel unit were assessed by averaging the frame-level performances for each vessel, the averaged sensitivity was 94.5±14.6%, the averaged specificity was 92.8±9.2%, and the averaged overall accuracy was 92.9±7.9%. In addition, the 20 independent runs by random sampling of one frame per patient in the 122 test samples showed an averaged sensitivity of 88.4±12.9%, an averaged specificity of 93.7±1.9%, and an averaged accuracy of 93.3±1.9%.
Supplementary Table 1 shows a summary of frame-level performances based on the precision-recall curves of the training and test sets. In the test set, DSC between the predicted and the ground-truth TCFA frames was 0.73.
Among 112 TCFA lesions with at least two consecutive TCFA-containing frames, 103 (92.0%) were truly classified as “positive” by the model. The length of the TCFA lesions classified as “positive” (vs “negative”) was significantly greater (6.8±6.7 frames vs 2.0±0.7 frames, p<0.001).
Figure 3 shows the vessel-level performances in the test set. The number of TCFA-containing frames within a vessel predicted by the model correlated significantly with the expert estimation (r=0.88, p<0.001). Furthermore, there was a significant correlation between percent TCFA burden per vessel as predicted by the model versus by experts (r=0.87, p<0.001).
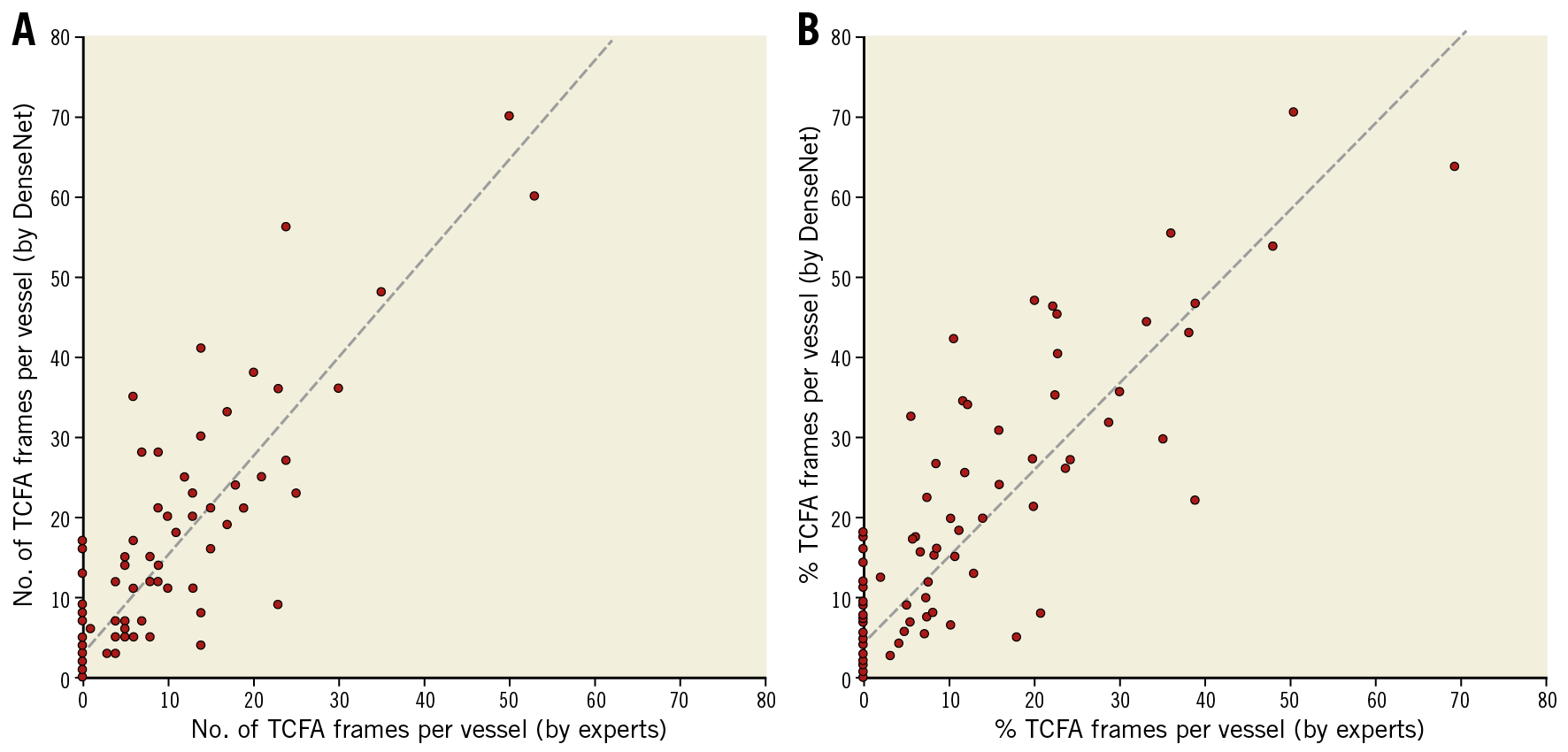
Figure 3. Vessel-level performances. A) The number of TCFA-containing frames per vessel as predicted by the model was related significantly to the expert-measured values. B) There was a significant correlation between the model-predicted %TCFA burden versus the expert-measured %TCFA burden.
In the non-overlapping cohort including 65 OCT pullback images, the frame-level performances were tested in the entire pullback images. To classify frames with versus without TCFA, the sensitivity, specificity and overall accuracy were 93.9%, 89.7% and 89.9%, respectively (AUC 0.97) (Supplementary Table 2). In addition, the total computational time per OCT pullback (including 344.1±76.2 frames) was 2.1±0.3 seconds, which was much shorter compared to the expert’s interpretation (288.9±269.9 seconds, p<0.001).
REGIONS OF ATTENTION
In the test set, localisation maps were generated by Grad-CAM to demonstrate the regions of attention for predicting a TCFA (Figure 4). In the region of attention, the red-coded area (>0.8) was localised at the site of the thin cap in 593 (93.4%) of the 635 frames that were assessed as truly positive for TCFA by the model.
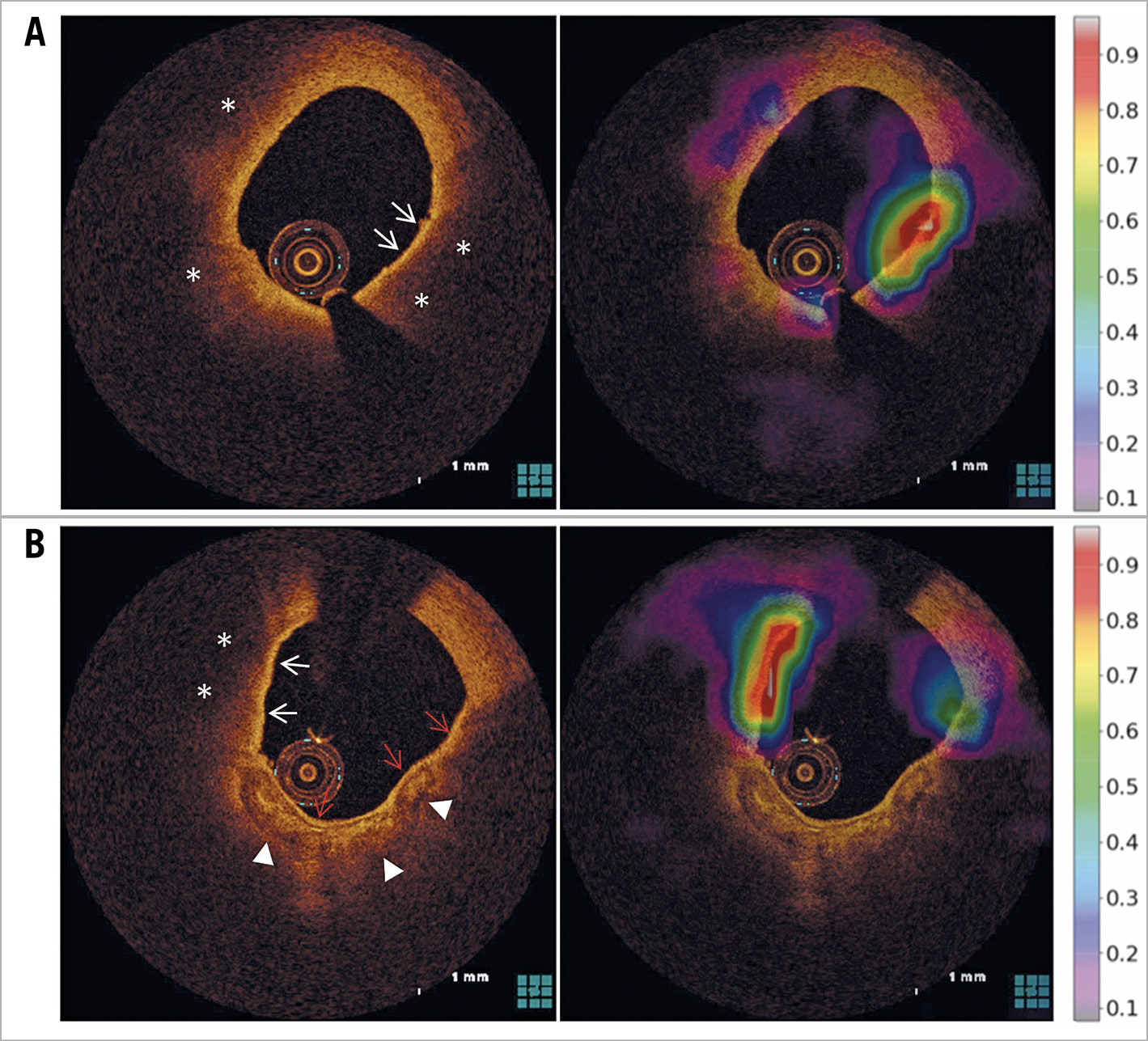
Figure 4. Activation maps using the Grad-CAM technique. Two examples of TCFA-containing frames that were truly classified as a “TCFA” by the model. A) The red-coded area was localised at the site of the thin cap (white arrows) overlying the necrotic core (*). B) In the direction of 10 o’clock, the red-coded area was localised at the region of the thin cap (white arrows) overlying the necrotic core (*). Conversely, in the direction of 3-7 o’clock, a red-coded area was not seen. Although the red arrows indicate a signal-rich band that mimicked a thin cap, it overlies calcification and not a necrotic core. The white arrowheads show the abluminal border of calcification.
FALSE POSITIVE DIAGNOSIS
In the test set, 616 frames were misclassified as a TCFA (FP) and were subsequently reviewed by experts to identify the reasons. In 93.4% of those misclassified frames, the red-coded area was localised at a region mimicking a thin cap but was not determined as a TCFA for the following reasons (Figure 5): 1) the presence of fibrous tissue overlying calcification with an invisible abluminal border in 152 (24.6%) frames, 2) superficial infiltration of macrophages or microcalcification with backscattering in 108 (17.6%) frames, 3) a relatively thin fibrous cap that was not thin enough to meet the histological threshold of 65 µm in 106 (17.1%) frames, 4) an arc of signal-poor necrotic core less than 90° in 92 (14.9%) frames, 5) tangential signal loss caused by an eccentric catheter position or side branch opening in 71 (11.6%) frames, 6) a thin intimal layer facing the media of a normal vascular segment in 42 (6.8%) frames, 7) structures mimicking a TCFA caused by various artefacts including non-uniform rotational distortion and guidewire artefact in 41 (6.7%) frames, and 8) a signal-rich luminal border of red thrombus in 4 (0.7%) frames.
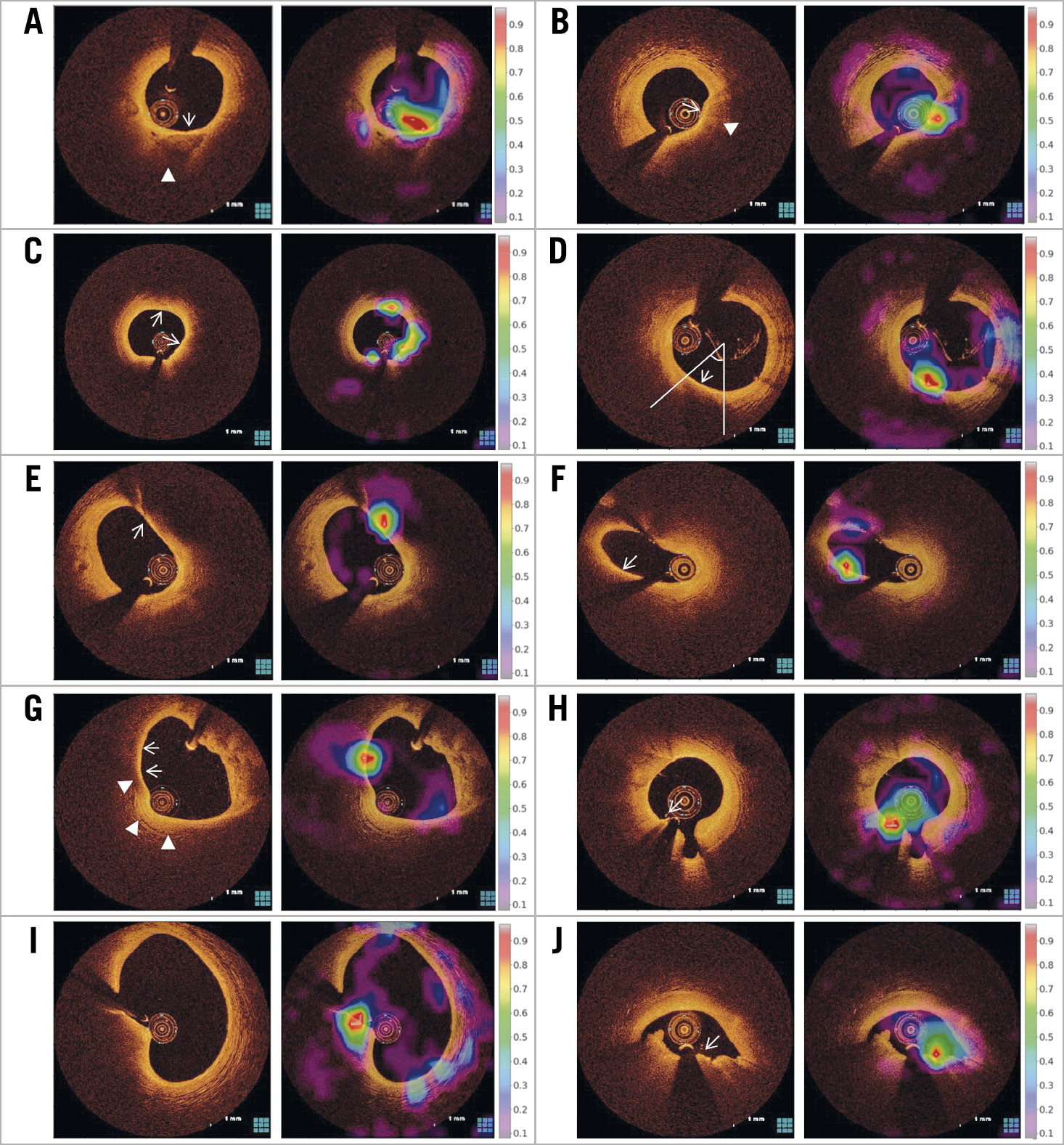
Figure 5. Reasons for false-positive diagnosis. A) The red-coded area was localised to the fibrous tissue (arrow) overlying calcification with an invisible abluminal border (arrowhead). The presence of calcium was confirmed by experts reviewing the adjacent frames with a clear abluminal border. B) Superficial infiltration of macrophages (arrow) mimicked a thin cap but was associated with backscattering (arrowhead). C) The thickness of the fibrous cap (arrows) was relatively thin but was less than 65 µm. D) Although the FCT (arrow) was 60 µm, the arc of the signal-poor necrotic core was less than 90°. E) & F) The red-coded area was localised at the site of the tangential signal loss (arrows) caused by eccentric catheter position (E) and side branch opening (F). G) A thin intimal layer (arrows) facing the media (arrowheads) of a normal vascular segment mimicked a thin cap. H) The red-coded area was seen on the signal-rich surface of the guidewire (arrow). I) This near-normal segment was misclassified as TCFA by non-uniform rotational distortion as an imaging artefact. J) The red-coded area was localised on the signal-rich luminal surface of red thrombus (arrow).
In Figure 3, 38 of 69 (55%) vessels without TCFA were misclassified as TCFA-containing vessels by the model. Among those with an FP diagnosis, 15 (40%) vessels did not have TCFAs that were detected at two or more consecutive frames. The number of TCFA-containing frames within a vessel predicted by the model correlated significantly with the expert estimation (r=0.88, p<0.001) (Figure 3). Furthermore, there was a significant correlation between percent TCFA burden per vessel as predicted by the model versus by experts (r=0.87, p<0.001).
FALSE NEGATIVE DIAGNOSIS
In the test set, 82 frames were misclassified as non-TCFA (FN) and were also reviewed by experts. Among the misclassified frames, 64 (78%) frames were located adjacent to a TCFA-containing frame, thus suggesting that the FN diagnosis frequently occurred at the transition zone between the frames with and without a TCFA.
Discussion
We aimed to determine whether a deep learning model could accurately predict the presence of a TCFA in OCT images. The main findings of the current study are as follows. 1) In the test samples, the overall accuracy for predicting a TCFA was 92.8% within the lesion and 91.3% in the entire pullback. 2) In the frames that were classified as TCFA, the activated map was localised at the site of the thin fibrous cap overlying the necrotic core in the majority.
Near-infrared light-based OCT has been the gold standard for the in vivo detection of TCFA because of the high spatial resolution and strong contrast between the lumen and vessel wall9,10,11. An ex vivo study reported a high level of interobserver agreement between OCT-measured and histologically measured FCT. Conversely, the intraclass correlation coefficient for the in vivo measurement of FCT by OCT ranges from 0.48 to 0.5612,13,14, mainly because of the uncertainty in defining the necrotic core facing the border of the fibrous cap and macrophage infiltration, as well as imaging artefacts and other OCT features that may mimic a TCFA. Moreover, the quantification of TCFA by per-frame interpretation from a whole OCT pullback is time-consuming. In this current study, interobserver variability yielded moderate concordance (kappa=0.74), while the ML model consistently separated a TCFA from a non-TCFA within only a few seconds per whole pullback. Therefore, the development of an automatic algorithm based on standardised interpretation protocols is needed to reduce interobserver variation and the cost associated with OCT analysis.
Convolutional neural network is a category of deep neural networks in which the connectivity pattern between neurons resembles the organisation of the human visual cortex for recognising patterns. By hierarchical processing with convolutional layers, the various activations of one neuronal layer are passed to the next layer, which allows the neural network to assemble more complex, higher-level features. Several studies have proposed automatic algorithms for OCT segmentation and plaque characterisation. Rico-Jimenez et al developed a computational method for automated atherosclerotic plaque characterisation in 57 OCT cases20. To classify the OCT B-scans as the plaques with versus without lipid, the overall accuracy was 85%. More recently, Abdolmanafi et al developed a convolutional neural network that includes 26 OCT pullbacks to classify the intima versus medial layer of the coronary artery automatically with an accuracy of 96%17. Gessert et al also showed that convolutional neural networks trained on 49 patients identified atherosclerotic plaques with an accuracy of 91.7%18. However, the previous studies (including only a small number of OCT cases) did not predict the presence of TCFA, a prototype of vulnerable plaques.
Our deep learning model using 602 OCT cases quickly identified TCFA-containing frames in the entire pullback images, with a frame-level accuracy of 91.3%. Although deep learning is considered a “black box”, the gradient-based Grad-CAM analysis provided a class-discriminative visualisation map that highlighted a target region for prediction. The red-coded activation maps were localised to the thin cap overlying lipid core in the majority, thus indicating that this model could identify TCFA-containing lesions with good performance and with reasonable explanation.
The current model showed a negative predictive value of 99.0% for predicting a TCFA-containing frame but the positive predictive value (PPV) was only 50.8%. The FP cases were frequently associated with a signal-rich collagen band overlying a calcification with a poorly delineated abluminal border or a superficial radial shadowing caused by scattering macrophages or microcalcification. Considering that these findings mimicked a thin fibrous cap, it is sometimes a challenge even for clinicians to discriminate these features from a TCFA. In the setting of an eccentric catheter position or side branch opening, tangential signal dropout (as an imaging artefact that occurs when the light beam strikes the tissue under a glancing angle and travels almost parallel to the vessel wall) led to a misclassification of a stable plaque as a TCFA13. Therefore, to improve the PPV, the model needs to be further trained on pre-specified subgroups of a larger cohort with the known OCT characteristics of calcification, macrophage infiltration, tangential signal drop, various extents of necrotic core, red thrombus, and imaging artefacts. Moreover, given that the expert’s decision was affected by the contextual findings of the adjacent frames and the corresponding frame, training the deep learning model by using additional features obtained from adjacent frames may further improve the diagnostic performance.
Limitations
Given the low incidence of TCFA, the class imbalance may have affected the high rate of FP diagnosis. Although the algorithm replicated the expert classification, the optimal threshold of OCT-measured cap thickness and the angular extent of TCFA still remain ambiguous. With a lack of external validation, the model requires studies of histological and clinical validation. Because the possibility of overfitting cannot be completely excluded, the model performances should be validated in a large prospective cohort. Although the normalised diagnostic performance and the averaged accuracy of 20 runs with one frame per patient were shown to be consistently good, there may be a potential clustering effect of multiple frames per vessel.
Conclusions
A deep learning algorithm can accurately detect an OCT-TCFA with high reproducibility. The time-saving computerised process may assist clinicians to recognise high-risk lesions easily and to make decisions in the catheterisation laboratory.
|
Impact on daily practice Deep learning algorithms can accurately identify the presence of a TCFA by detecting a thin cap. With excellent per-frame and per-vessel performances, the model classified the lesions with and without TCFA in the entire pullback within a few seconds. This data-driven approach may assist clinicians to recognise high-risk coronary lesions quickly. |
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health & Welfare Affairs, Republic of Korea (HI17C1080), and the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1A2B4005886).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.