
Introduction
The Roadsaver® carotid artery stent (Terumo Corp., Tokyo, Japan) has been introduced into clinical practice to increase plaque coverage during carotid artery stenting (CAS) thanks to its dual-layer design. Preliminary results have shown a good short-term clinical outcome1-3. However, longer-term clinical follow-up data are currently lacking. In addition, although some concern has been raised about the presence of a larger quantity of foreign material (double mesh) inside the carotid artery, no data are available about the Roadsaver stent restenosis rate.
Methods
Our study population comprised all consecutive patients who underwent CAS and received a Roadsaver stent between October 2014 and October 2015 in three high-volume Italian centres performing CAS.
Patients were scheduled to undergo clinical evaluations at baseline, at 24 hours from the procedure and at 30 days after CAS. Routine clinical follow-up was performed by telephone interviews and, whenever the physician felt it necessary, the patient was seen at an outpatient clinic. Doppler ultrasound was scheduled to be performed at six and at 12 months by the referral doctors. Data and documents were collected through regular phone calls by the assigned physicians. All patients received dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin+clopidogrel) for one month.
As to clinical endpoints, transient ischaemic attack (TIA) was defined as focal brain ischaemia with resolution of symptoms within 24 hours after onset. Stroke was defined as a new neurological deficit of sudden onset with focal symptoms and signs consistent with focal ischaemia lasting at least 24 hours in the absence of primary haemorrhage, which was not explained by other causes. Stroke was considered minor if the neurological deficit resolved completely within 30 days or did not lead to a functional impairment in daily activities.
Doppler evidence of restenosis was considered in the presence of peak systolic velocity (PSV) values above 250 cm/s. The decision about how to treat in-stent restenosis was left to the individual operators.
Results
The Roadsaver registry included 150 patients (age 74±8, 75% male) treated in the three institutions (Table 1). As previously reported, most treated patients were asymptomatic (n=107, 71%).
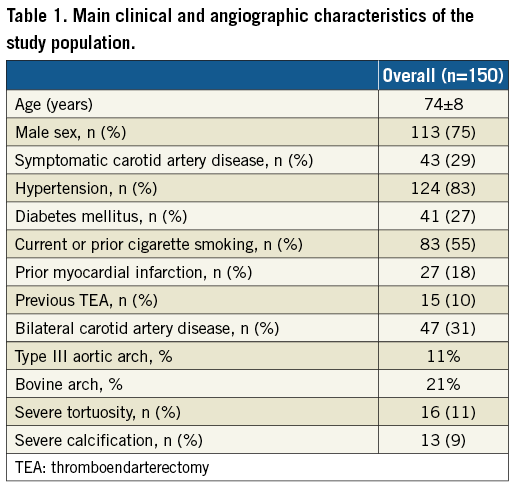
Data completeness at follow-up was 100%. In the whole population there were three deaths (2%) not related to the index procedure (Table 2). No major or minor cerebrovascular events were reported at 12-month follow-up.
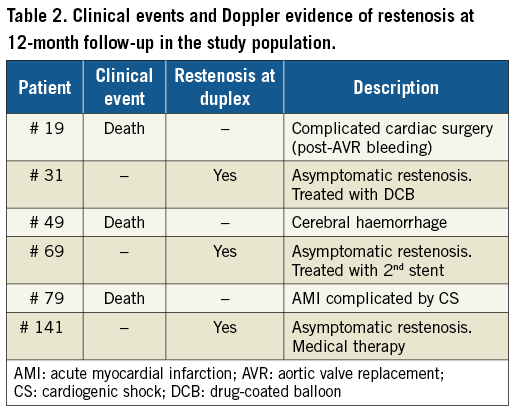
All patients underwent Doppler ultrasound follow-up after CAS. Of these, three patients showed significant increase of Doppler PSV values (i.e., >250 cm/sec). They underwent angiography confirming stent restenosis; two of them were treated with a second angioplasty procedure, and one with medical therapy (Table 2). Of note, in one case IVUS evaluation showed a significant plaque proliferation between the two layers of struts (Figure 1). The patient was treated with a drug-coated balloon angioplasty. His latest clinical and Doppler follow-up (24 months) confirmed a good result.
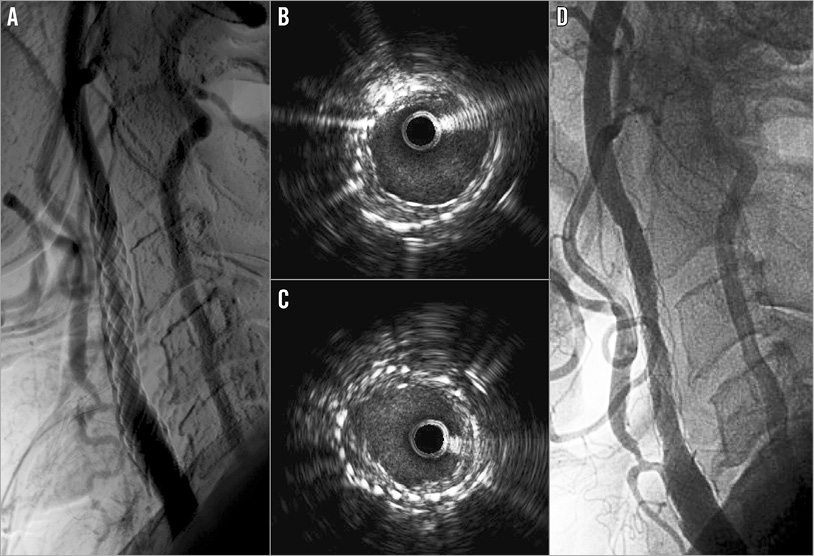
Figure 1. Follow-up of a patient previously treated with a Roadsaver carotid artery stent. Angiographic evidence of right internal carotid restenosis (A). IVUS evaluation depicted plaque neoproliferation between the two layers of struts (B, C). Finally, it was decided to treat the patient with a drug-coated balloon angioplasty after positioning a distal filter; the final result was good (D).
External carotid artery (ECA) patency was reported in all patients.
Discussion
Double-mesh carotid stents have somewhat revolutionised CAS. Since their introduction into clinical practice, clinical results in the short term have been good2,3, with a low incidence of delayed embolic events and new ipsilateral magnetic resonance imaging ischaemic brain lesions4. The greatest part of its anti-embolic effect has been related to a higher capability of plaque containment, as confirmed by optical coherence tomography studies showing a relatively low rate of plaque prolapse3,5. Despite being used more and more in clinical practice, Roadsaver long-term results are still unknown.
In our multicentre and multidisciplinary case series of patients, we showed favourable long-term clinical outcomes: we reported no cerebrovascular events. All deaths were convincingly not related to the stenting procedures, thus reflecting the global higher cardiovascular risk of our study population. In addition, Doppler results showed a restenosis rate which does not seem different from other stents6, although no definite answer can be provided by our non-randomised observational study. Of interest, all restenosis cases were asymptomatic. The possible explanations for this are merely speculative. However, it is worth mentioning that in one case of restenosis we performed intravascular imaging, showing plaque growth between the two layers of struts. As is known, in-stent restenosis has been classically attributed to neointimal hyperplasia and vascular remodelling7. The use of a Roadsaver double-mesh stent could be associated with a novel pattern of restenosis, with plaque growth happening in the not negligible space between the two layers, but still trapped by the inner line of struts, which could be associated with a lower embolic risk. Future studies will have to assess this novel pattern better and clarify its relation with clinical outcome.
Limitations
Many limitations of the present report should be acknowledged. First, it is an observational study reporting clinical practice and leaving the standard practice of single institutions (and operators) unchanged. Second, the lack of an external adjudication committee might be responsible for the lack of accuracy in detecting clinical events. However, the low number of patients and events could be related to the prevalence of asymptomatic disease in the original study population.
Conclusions
The use of the Roadsaver stent in high-risk clinical or anatomical conditions is associated with good short and midterm results. Of note, this stent does not seem to be associated with a higher rate of in-stent restenosis at 12-month follow-up. However, prospective studies with an external adjudication committee aimed at comparing its performance with traditional carotid stents are warranted in order to confirm this result.
| Impact on daily practice The Roadsaver double-mesh carotid stent has shown good procedural and short-term results. Our data confirm the efficacy of this stent at 12-month follow-up and they do not suggest any concern about a higher risk of restenosis up to one year from the revascularisation procedure. |
Conflict of interest statement
F. Castriota, A. Micari and A. Cremonesi have previously received consultancy fees from Terumo but not in relation to the present article. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

