Introduction
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has become a mainstay in treatment for severe symptomatic aortic stenosis (AS) patients1. Over the past decades, various transcatheter devices have been invented and tested for safety and efficacy2. This manuscript aims to report a novel device and initial experience with the SinoCrown system (Lepu Medical Technology Co., Ltd).
SinoCrown has numerous unique design features that distinguish it from other self-expanding valves. It is made up of a self-expanding nitinol stent and three valve leaflets which are made of bovine pericardial tissue (Figure 1). It was designed with a short stent that could reduce the risk of coronary obstruction. The pre-bend designed for the delivery system increases flexibility and controllability during propulsion. For transfemoral delivery, flexible delivery catheters are available in three sizes (18, 19 and 21 Fr). For transapical delivery, a 27 Fr flexible delivery catheter is included. A new version of the catheter is being developed for release which will have a smaller delivery system. The delivery system has a stable and reliable locking/unlocking structure that ensures the unlocking of the artificial valve. The entire hanging connection design ensures that the device is 100% retrievable and repositionable. It is suitable for both transfemoral and transapical pathways. The SinoCrown bioprosthetic valve has an inner and an outer skirt design, which reduces perivalvular leakage. It has three positioning markers at the bottom of the valve stent that are convenient for marking the position during valve implantation.
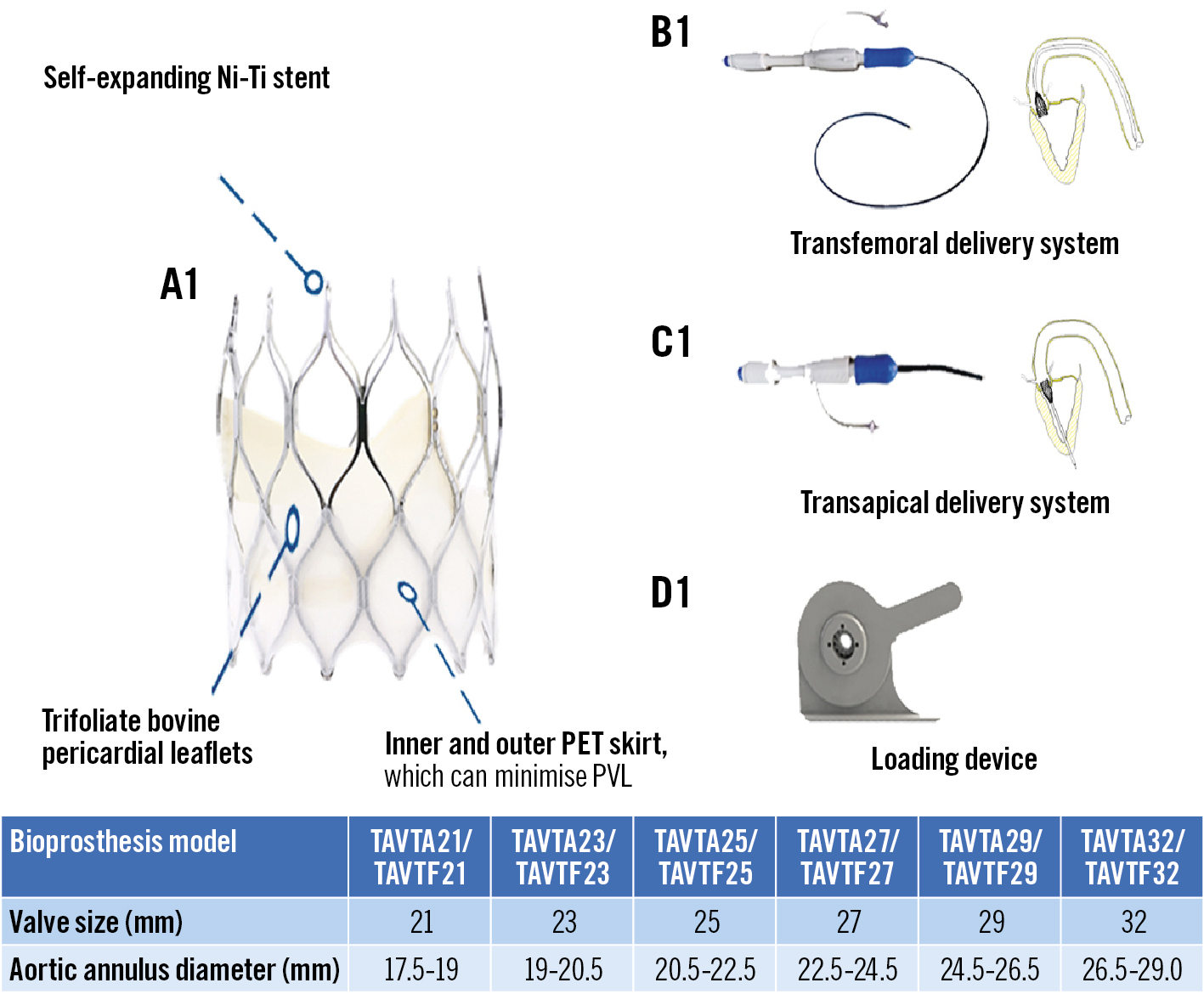
Figure 1. SinoCrown valve and its delivery system with 2 implantation pathways. The SinoCrown valve was designed with a short stent that could better expose coronary artery ostia, and reduce the risk of coronary obstruction. A short stent implantation has less influence on the cardiac conduction system, thus reducing the incidence of pacemaker implantation. Ni-Ti: nickel-titanium ; PET: polyethylene terephthalate; PVL: paravalvular leak
Methods
This was the first trial of SinoCrown in the People's Republic of China. Ethics committee approvals were obtained. The trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov with the identifier NCT05202977. A total of 10 patients with severe symptomatic AS were scanned by transthoracic echocardiography and multislice computed tomography (MSCT). Clinical endpoints were based on the Valvular Academic Research Consortium-2 (VARC-2) criteria3. The primary endpoint was the immediate postoperative device success rate. The patient inclusion criteria included (1) age ≥65 years old, (2) severe native AS confirmed by echocardiography (orifice area <0.8 cm2, peak velocity ≥4.0 m/s, pressure gradient ≥40 mmHg), (3) prohibitive risk for surgical aortic valve implantation assessed by a cardiac surgeon and a cardiologist and then discussed by the Heart Team, and (4) signed informed consent. Exclusion criteria included not being suitable (coronary artery height <10 mm, sinus size <30 mm, valve cusp length>coronary artery height) or refusal for TAVI treatment. Clinical follow-up occurred from the time of discharge from the hospital up to 30 days. All events, such as mortality, cardiovascular mortality and other complications, were noted during hospitalisation and follow-up.
During TAVI, valve size was selected based on the MSCT, taking into consideration the annulus diameter and annulus perimeter measurements. For example, a 21 mm valve fits within an annulus diameter of 17.5-19.0 mm and an annulus perimeter of 55-60 mm (a 23 mm valve fits an annulus diameter of 19.0-20.5 mm, a 25 mm valve fits an annulus diameter of 20.5-22.5 mm; the same rules follow for 27, 29, and 32 mm valves).
Results
The median age (age range) of the patients (N=10, 5 men and 5 women) was 77.5ï¼69.0-83.0ï¼years. Calcification volume based on MSCT in this study was 1,066.5 (43.0-2,484.0) mm3.
The procedural success rate was 100%, and the device success rate was 90%. The transfemoral pathway was used in 80% of patients and the transapical pathway in 20%. All patients underwent SinoCrown valve implantation under general anaesthesia. Coronary obstruction, access-related vascular complications, moderate or severe paravalvular leak (PVL) and aortic root injury/rupture were all absent during the procedure.
At 30 days, there were no deaths, disabling strokes, myocardial infarctions, conversions to surgery, or major procedure-related complications. New pacemaker implantation was required in one patient (10%) for a third-degree atrioventricular transmission and complete left bundle branch block. SinoCrown implantation succeeded in reducing the mean valve gradient from 60.5 (40.0-98.0) to 8.0 (2.0-17.0) mmHg (p<0.001) and increased the effective orifice area from 0.6 (0.3-1.0) to 2.0 (1.3-2.6) cm2 (p<0.001) at 30 days. PVL was absent in 8 patients (80%), and 2 patients (20%) had trace levels. All patients were in NYHA Class I–II at a mean follow-up of 1 month. There were no other adverse events at 30 days.
Discussion
TAVI has become a mainstay in treatment for patients with severe AS, and for both high- and low-risk surgical patients45. Device success was achieved in all patients, and all bioprostheses were implanted accurately.
The SinoCrown valve gradually unhooks from the delivery system via the rotary knob, so the valve is completely released and implanted separately. One of its advantages is that it is 100% retrievable; prior to rotating the unlocking knob, the entire valve can be retrieved.
According to the pathological conditions of the patient’s peripheral vascular disease, the SinoCrown can be delivered through a transfemoral or a transapical delivery system, both of which are suitable for the majority of AS patients.
One benefit of the design of an ultra-short stent frame is that AS patients with coronary heart disease may be likely to be accepted for percutaneous coronary intervention after TAVI.
Limitations
This is the first use of SinoCrown. The main limitations are the small number of patients studied and the lack of comparison with other TAVI devices.
Conclusions
Prior experience shows that the new transcatheter aortic bioprosthesis was safely implanted in AS patients. However, more cases and long-term follow-ups are needed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of SinoCrown.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2020YFC2008100), the Beijing Science and Technology Plan (Z181100001918029), and the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS; 2017-I2M-3-002).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

