Abstract
Background: Compared with intravascular ultrasound guidance, there is limited evidence for optical coherence tomography (OCT) guidance during primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI) in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients.
Aims: We investigated the role of OCT in guiding a reperfusion strategy and improving the long-term prognosis of STEMI patients.
Methods: All patients who were diagnosed with STEMI and who underwent pPCI between January 2017 and December 2020 were enrolled and divided into OCT-guided versus angiography-guided cohorts. They had routine follow-up for up to 5 years or until the time of the last known contact. All-cause death and cardiovascular death were designated as the primary and secondary endpoints, respectively.
Results: A total of 3,897 patients were enrolled: 2,696 (69.2%) with OCT guidance and 1,201 (30.8%) with angiographic guidance. Patients in the OCT-guided cohort were less often treated with stenting during pPCI (62.6% vs 80.2%; p<0.001). The 5-year cumulative rates of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in the OCT-guided cohort were 10.4% and 8.0%, respectively, significantly lower than in the angiography-guided cohort (19.0% and 14.1%; both log-rank p<0.001). All 4 multivariate models showed that OCT guidance could significantly reduce 5-year all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR] in model 4: 0.689, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.551-0.862) and cardiovascular mortality (HR in model 4: 0.692, 95% CI: 0.536-0.895). After propensity score matching, the benefits of OCT guidance were consistent in terms of all-cause mortality (HR: 0.707, 95% CI: 0.548-0.913) and cardiovascular mortality (HR: 0.709, 95% CI: 0.526-0.955).
Conclusions: Compared with angiography alone, OCT guidance may change reperfusion strategies and lead to better long-term survival in STEMI patients undergoing pPCI. Findings in the current observational study should be further corroborated in randomised trials.
Previous studies have shown that compared with angiographic guidance alone, the application of optical coherence tomography (OCT) could impact decision-making, optimise percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), and improve outcomes12345. However, most studies have focused on patients with stable angina or non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and mainly on the process of stent implantation. Different from stable angina or non-ST-segment elevation ACS, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a result of transmural ischaemia and is mostly caused by ruptures or erosions and occlusive thrombosis, rather than a gradual narrowing of the coronary arteries6. Restoring myocardial perfusion as soon as possible by primary PCI (pPCI) is key in patients presenting with STEMI and, in current guidelines, has the highest level of recommendations in the management of these patients7. In the current study, we aimed to investigate whether OCT guidance could reduce long-term mortality compared with angiographic guidance alone in a large cohort of STEMI patients treated with pPCI.
Methods
Study population
All consecutive patients diagnosed with STEMI between January 2017 and December 2020 in the 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (Harbin, China) were retrospectively selected. The diagnosis of STEMI was based on clinical symptoms of continuous chest pain, ST-segment elevation>0.1 mV in at least 2 contiguous leads or new left bundle branch block on the electrocardiogram, and elevated cardiac markers, as described previously8. The main exclusion criteria were the following: (1) patients who did not undergo PCI but were treated with medical therapy; (2) patients with cardiogenic shock; (3) the presence of preinterventional thrombolysis; (4) elective PCI several days after admission; (5) use of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) or functional lesion assessment during pPCI; (6) culprit lesion located in the left main artery; (7) patients who refused further interventional treatments after index angiographic or OCT examinations; (8) patients recommended for coronary artery bypass grafting after index angiography; and (9) patients who were transferred to our hospital after pPCI in local hospitals.
Patients were divided into OCT-guided versus angiography-guided cohorts according to whether OCT or angiography was used to guide the pPCI procedure. Clinical and angiographic features, reperfusion strategies, and survival data were compared between cohorts.
This study was approved by the ethics board of our hospital, and all enrolled patients provided written informed consent. Reporting of this study complied with the STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement for cohort studies.
Percutaneous coronary intervention procedures
Due to the retrospective design, detailed PCI strategies and specific devices/medications were not prespecified and were at each operator’s discretion. For OCT guidance, there was a general, but not mandatory protocol in our centre according to contemporary expert documents and local clinical practice910. After index angiography, intracoronary nitroglycerine was administered before further intervention. Thrombus aspiration and/or gentle predilation with small balloons was commonly applied for lesions with total occlusion or severe stenosis to restore antegrade blood flow before the OCT examination. Further reperfusion strategies and the selection of devices were mainly based on a real-time comprehensive evaluation of the OCT and angiographic findings. Lesions without severe residual stenosis and diagnosed as plaque erosions, ruptures without dissection and/or haematoma, and those caused by spontaneous coronary artery dissections, spasm, or showing no obvious abnormalities in OCT images were potential candidates to avoid stent implantation811. For patients with a pre-PCI OCT examination and who required stent implantation, it was recommended to conduct lesion preparation, and choose an appropriate landing zone and stent size based on the OCT findings. Whenever possible, post-PCI OCT was routinely performed to optimise stent implantation. For patients who did not undergo pre-PCI OCT but had suboptimal post-PCI angiographic results (mainly including stent underexpansion, edge dissection, stent thrombosis, and other unexplained angiographic abnormalities), OCT was recommended to identify the underlying causes and guide further optimisations9.
Data collection
Patient characteristics, procedural details, and follow-up data were collected from the electronic medical record system and dedicated electronic follow-up system. Detailed definitions of cardiovascular risk factors are summarised in Supplementary Appendix 1512. Angiographic diameter stenosis data were collected from the intervention report and visually graded by the operators during PCI in at least 2 different angiographic projections. After discharge, all patients were routinely followed up at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months, and annually thereafter, through a combination of inpatient, outpatient, and telephone follow-ups. Unplanned follow-up visits in our hospital due to emergencies or other reasons were also recorded. Follow-up was censored at 5 years (1,825 days) or the last known contact time in this study. The primary endpoint was all-cause death, which is considered the most unbiased outcome in observational studies13. Cardiovascular death was reported as the secondary endpoint, which encompassed deaths due to cardiac reasons, vascular reasons, and undetermined reasons, according to the Academic Research Consortium-2 consensus document13. Detailed definitions are available in Supplementary Appendix 2.
Statistical analysis
SPSS Statistics, version 26.0 (IBM) was used for statistical analysis. A 2-sided p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Continuous variables are reported as mean±standard deviation (SD) or median (quartiles) and were compared using the Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test. Categorical variables are shown as absolute frequencies (relative percentages) and were compared using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Kaplan-Meier analysis and the log-rank test were performed for time-to-event endpoints. The reverse Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate the median follow-up time. Cox proportional hazards regression models were used to estimate treatment effects expressed as a hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI). Baseline clinical and angiographic characteristics, the year of admission, thrombus aspiration, and stent implantation at the culprit vessel were adjusted gradually in 4 multivariable models. Missing baseline data (4.4% of serum lipid-level data and 5.5% of left ventricular ejection fraction values) in the multivariate regression analysis were estimated by multiple imputation (5 times).
Propensity score matching (PSM) analysis was conducted without replacement using maximum execution performance to eliminate the effects of potential confounders on clinical outcomes. We adjusted all the clinical and angiographic characteristics in Table 1 as well as the year of admission between cohorts using propensity scores to match the patients 1:1, with a match tolerance of 0.02, yielding 1,050 patients in each matched cohort.
Table 1. Baseline clinical and angiographic characteristics.
| Overall (n=3,897) | Angiographic guidance (n=1,201) | OCT guidance (n=2,696) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 60.2±11.8 | 62.5±11.7 | 59.1±11.6 | <0.001 |
| Male | 2,794 (71.7) | 808 (67.3) | 1,986 (73.7) | <0.001 |
| Previous MI | 313 (8.0) | 116 (9.7) | 196 (7.3) | 0.013 |
| Previous PCI | 207 (5.3) | 61 (5.1) | 146 (5.4) | 0.666 |
| Dyslipidaemiaa | 2,505 (67.2) | 761 (66.8) | 1,744 (67.4) | 0.707 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1,242 (31.9) | 431 (35.9) | 811 (30.1) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 2,066 (53.0) | 698 (58.1) | 1,368 (50.7) | <0.001 |
| Smoking history | 2,604 (66.8) | 776 (64.6) | 1,828 (67.8) | 0.051 |
| CKD | 107 (2.7) | 64 (5.3) | 43 (1.6) | <0.001 |
| LVEFa, % | 56.5±7.7 | 54.7±8.9 | 57.3±7.0 | <0.001 |
| Culprit vessel | 0.001 | |||
| LAD | 1,822 (46.8) | 511 (42.5) | 1,311 (48.6) | |
| LCx | 441 (11.3) | 157 (13.1) | 284 (10.5) | |
| RCA | 1,634 (41.9) | 533 (44.4) | 1,101 (40.8) | |
| Preintervention of the culprit vessel | ||||
| DS, % | 97.3±7.5 | 97.8±6.1 | 97.0±8.0 | 0.001 |
| Total occlusion | 2,620 (67.2) | 815 (67.9) | 1,805 (67.0) | 0.577 |
| TIMI flow 0/1 | 2,986 (76.6) | 925 (77.0) | 2,061 (76.4) | 0.697 |
| Multivessel disease | 2,581 (66.2) | 900 (74.9) | 1,681 (62.4) | <0.001 |
| Values are mean±SD or n (%). aData for dyslipidaemia and LVEF were missing in 172 and 216 individuals, respectively. CKD: chronic kidney disease; DS: diameter stenosis; LAD: left anterior descending artery; LCx: left circumflex artery; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; MI: myocardial infarction; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; RCA: right coronary artery; SD: standard deviation; TIMI: Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction | ||||
Results
A total of 3,897 STEMI patients with pPCI were included in the final analysis: 1,201 (30.8%) cases in the angiography-guided cohort and 2,696 cases (69.2%) in the OCT-guided cohort. A detailed flowchart is shown in Figure 1. The proportion of OCT guidance varied significantly across the different years of admission (Supplementary Figure 1).
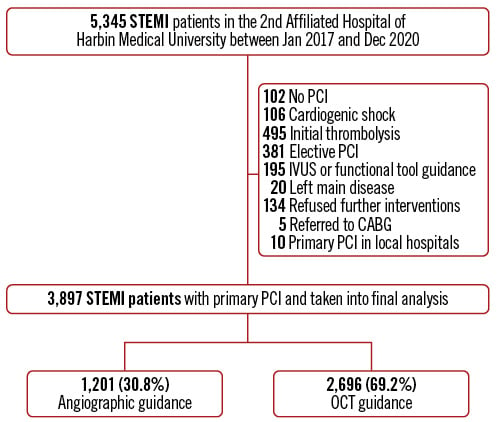
Figure 1. Study flowchart. CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Clinical characteristics
Baseline clinical and angiographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. The age of the overall population was 60.2±11.8 years, and 2,794 (71.7%) were male. Patients in the OCT-guided cohort were younger (59.1±11.6 years vs 62.5±11.7 years; p<0.001) and more likely to be male (1,986 [73.7%] vs 808 [67.3%]; p<0.001). Compared with the angiography-guided cohort, there was a lower prevalence of previous myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease in the OCT-guided cohort.
Angiographic and procedural features
As shown in Table 1, the distribution of culprit vessels was different between the 2 cohorts. OCT was more commonly used in patients with the left anterior descending artery as the culprit vessel. Preintervention angiographic diameter stenosis was more severe in the angiography-guided cohort than in the OCT-guided cohort, but there were a comparable proportion of totally occluded lesions and lesions with Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) flow 0/1.
Procedural characteristics during pPCI are shown in Table 2. In the OCT-guided cohort, the proportion of pre-PCI OCT evaluation was 97.0%. For those with OCT-guided stent implantation, the proportions of patients with both pre- and post-PCI, only pre-PCI and only post-PCI OCT evaluation were 87.9%, 7.3% and 4.8%, respectively. During pPCI, thrombus aspiration was used more commonly in patients treated with OCT guidance (2,317 [85.9%] vs 687 [57.2%]; p<0.001). Compared with the angiography-guided cohort, the rate of stent implantation at the culprit vessel was significantly lower in the OCT-guided cohort (1,688 [62.6%] vs 963 [80.2%]; p<0.001). All the stents implanted were drug-eluting stents. In patients treated with stent implantation at the culprit vessel, the total number of stents was smaller, the maximum stent diameter was larger (3.19±0.42 mm vs 3.10±0.42 mm; p<0.001), and there was a higher rate of post-dilation in the OCT-guided cohort than the angiography-guided cohort. The angiography-guided cohort had a higher rate of multivessel intervention during pPCI. Procedural details of the non-culprit vessels are shown in Supplementary Table 1.
Almost all patients received antiplatelet agent(s) and a statin at discharge. As for the choice of P2Y12 receptor inhibitor, ticagrelor was administered more frequently in the OCT-guided cohort when compared with the angiography-guided cohort (1,617 [60.3%] vs 621 [52.8%]; p<0.001). Usage of other medications at discharge appeared to be similar between the 2 cohorts (Supplementary Table 2).
Table 2. Procedural characteristics during primary PCI.
| Overall (n=3,897) | Angiographic guidance (n=1,201) | OCT guidance (n=2,696) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thrombus aspiration | 3,004 (77.1) | 687 (57.2) | 2,317 (85.9) | <0.001 |
| Stent implantation at the culprit vessel | 2,651 (68.0) | 963 (80.2) | 1,688 (62.6) | <0.001 |
| Total number of stentsa | 1.3±0.5 | 1.4±0.6 | 1.2±0.4 | <0.001 |
| Maximum stent diametera, mm | 3.16±0.42 | 3.10±0.42 | 3.19±0.42 | <0.001 |
| Post-dilationa | 2,070 (78.1) | 716 (74.4) | 1,354 (80.2) | <0.001 |
| Multivessel intervention | 151 (3.9) | 75 (6.2) | 76 (2.8) | <0.001 |
| Contrast-induced nephropathy | 311 (8.0) | 104 (8.7) | 207 (7.7) | 0.297 |
| Values are mean±SD or n (%). aFor patients with stent implantation at the culprit vessel. OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; SD: standard deviation | ||||
Long-term mortality
The median follow-up duration of the overall population was 3.5 years; it was 4.0 years in the OCT-guided cohort and 3.1 years in the angiography-guided cohort. The overall cumulative rates of all-cause mortality were 5.2% at 1 year, 8.9% at 3 years, and 12.9% at 5 years. Kaplan-Meier survival curves showed a lower cumulative rate of all-cause mortality in the OCT-guided cohort at 5-year follow-up (10.4% vs 19.0% in the angiography-guided cohort; log-rank p<0.001). Compared with angiographic guidance, patients treated with OCT guidance experienced a 52.9% risk reduction in all-cause mortality in the unadjusted Cox regression analysis (HR: 0.471, 95% CI: 0.386-0.573; p<0.001) (Figure 2).
Four models were constructed: model 1 adjusted for all the baseline clinical and angiographic risk factors in Table 1 (including age, male sex, previous myocardial infarction, previous PCI, dyslipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, smoking history, chronic kidney disease, left ventricular ejection fraction, culprit vessel locations, preintervention diameter stenosis, preintervention TIMI 0/1, and multivessel disease); model 2 adjusted for the factors in model 1 plus the year of admission; model 3 adjusted for the factors in model 2 plus thrombus aspiration; and model 4 adjusted for the factors in model 3 plus stent implantation at the culprit vessel. Multivariate analysis in model 4 showed a 31.1% risk reduction in all-cause mortality in the OCT-guided cohort (adjusted HR: 0.689, 95% CI: 0.551-0.862; p=0.001) after adjustment for all clinical characteristics, angiographic risk features, thrombus aspiration, and culprit vessel stenting during pPCI. Similar results were shown in the other adjusted models (Figure 3). The detailed results of each model are shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure 2-Supplementary Figure 4. Thrombus aspiration and culprit vessel stent implantation during pPCI were not independently associated with long-term death in model 4.
When it came to cardiovascular mortality, the overall cumulative rates were 4.4%, 6.7%, and 9.9% at 1, 3 and 5 years, respectively. OCT guidance was protective as well (unadjusted HR: 0.470, 95% CI: 0.375-0.590; p<0.001), achieving a lower 5-year rate of cardiovascular mortality than angiographic guidance (8.0% vs 14.1%; log-rank p<0.001) (Figure 2). Multivariate analysis also showed a significant benefit in the OCT-guided cohort compared with the angiography-guided cohort in model 4 (adjusted HR: 0.692, 95% CI: 0.536-0.895; p=0.005) as well as in the other multivariate models (Figure 3, Table 3 and Supplementary Figure 2-Supplementary Figure 4).
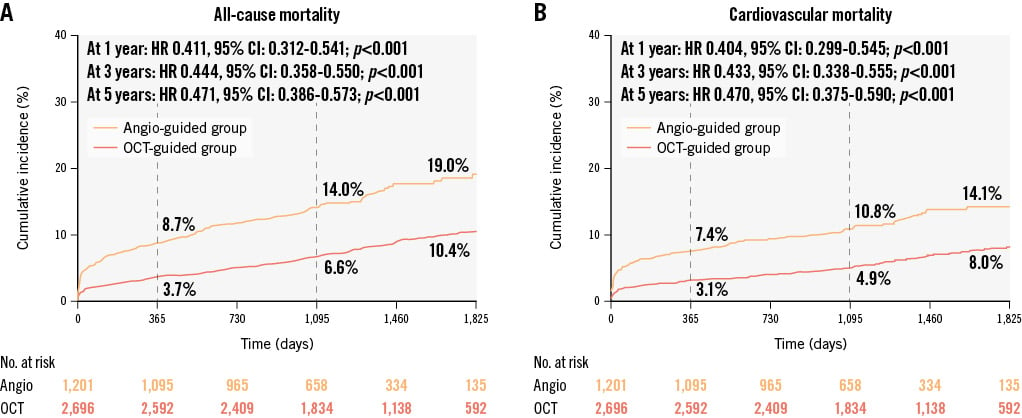
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence curves of long-term mortality in the overall population. Kaplan-Meier curves show the cumulative incidences of all-cause mortality (A) and cardiovascular mortality (B) in the 2 cohorts. There was significantly lower all-cause mortality in the OCT-guided cohort than the angiography-guided cohort at 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year follow-ups (all p-values<0.001). Similar results were shown in terms of cardiovascular mortality. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography
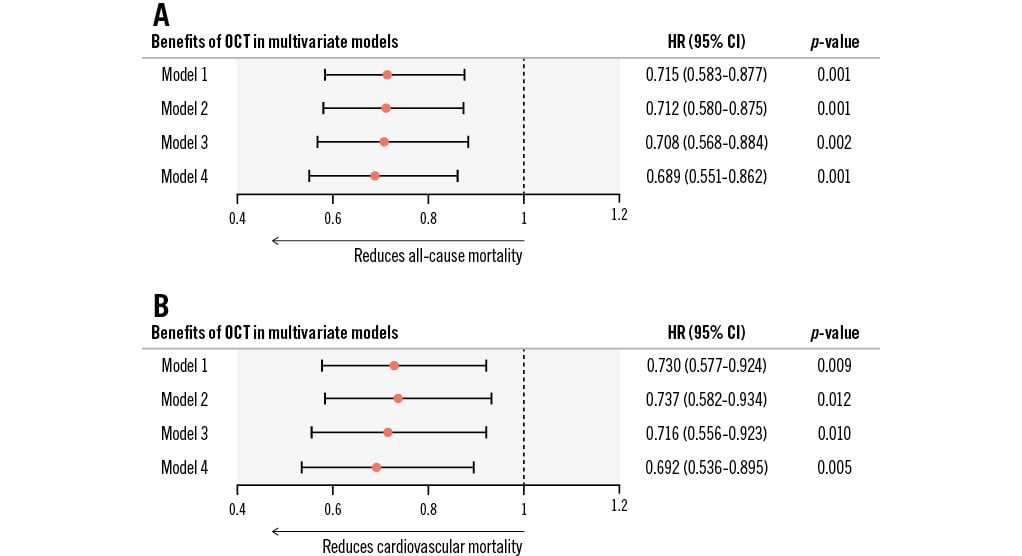
Figure 3. Benefits of OCT in reducing long-term mortality in multivariate models. For STEMI patients undergoing primary PCI, OCT guidance was able to consistently reduce 5-year all-cause mortality (A) and cardiovascular mortality (B) in multiple Cox regression models. Model 1 adjusted for baseline clinical and angiographic characteristics (including age, male sex, previous myocardial infarction, previous PCI, dyslipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, smoking history, chronic kidney disease, left ventricular ejection fraction, culprit vessel locations, preintervention diameter stenosis, preintervention Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction flow 0/1, and multivessel disease). Model 2 adjusted for all factors in model 1 plus the year of admission. Model 3 adjusted for all factors in model 2 plus thrombus aspiration. Model 4 adjusted for all factors in model 3 plus stent implantation at the culprit vessel. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Table 3. Predictors of 5-year mortality in multivariate model 4.
| All-cause mortality | Cardiovascular mortality | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| OCT guidance | 0.689 | 0.551-0.862 | 0.001 | 0.692 | 0.536-0.895 | 0.005 |
| Age | 1.063 | 1.052-1.074 | <0.001 | 1.057 | 1.045-1.069 | <0.001 |
| Male | 0.831 | 0.666-1.037 | 0.101 | 0.792 | 0.614-1.022 | 0.073 |
| Previous MI | 1.315 | 0.891-1.941 | 0.168 | 0.986 | 0.607-1.601 | 0.953 |
| Previous PCI | 0.827 | 0.506-1.352 | 0.448 | 1.014 | 0.568-1.813 | 0.961 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.938 | 0.755-1.165 | 0.562 | 1.015 | 0.788-1.308 | 0.907 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.977 | 0.785-1.216 | 0.838 | 0.993 | 0.774-1.273 | 0.953 |
| Hypertension | 1.101 | 0.895-1.355 | 0.361 | 1.135 | 0.892-1.443 | 0.302 |
| Smoking history | 1.060 | 0.850-1.322 | 0.602 | 0.941 | 0.731-1.211 | 0.638 |
| CKD | 4.467 | 3.275-6.092 | <0.001 | 4.511 | 3.193-6.372 | <0.001 |
| LVEF | 0.951 | 0.941-0.961 | <0.001 | 0.944 | 0.932-0.955 | <0.001 |
| Culprit lesion in LAD | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | ||||
| Culprit lesion in LCx | 1.011 | 0.720-1.418 | 0.952 | 1.065 | 0.729-1.555 | 0.744 |
| Culprit lesion in RCA | 0.866 | 0.694-1.080 | 0.201 | 0.813 | 0.629-1.050 | 0.113 |
| Preintervention DS | 0.994 | 0.971-1.017 | 0.613 | 0.997 | 0.970-1.025 | 0.829 |
| Preintervention TIMI 0/1 | 1.528 | 1.062-2.197 | 0.022 | 1.399 | 0.919-2.129 | 0.117 |
| Multivessel disease | 1.123 | 0.884-1.426 | 0.342 | 1.219 | 0.922-1.611 | 0.164 |
| Admitted in 2017 | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) | ||||
| Admitted in 2018 | 0.896 | 0.681-1.179 | 0.434 | 0.983 | 0.712-1.358 | 0.917 |
| Admitted in 2019 | 0.818 | 0.618-1.083 | 0.160 | 0.880 | 0.631-1.227 | 0.450 |
| Admitted in 2020 | 1.016 | 0.732-1.412 | 0.923 | 1.253 | 0.863-1.818 | 0.236 |
| Thrombus aspiration | 0.992 | 0.760-1.296 | 0.956 | 1.071 | 0.784-1.462 | 0.667 |
| Stent implantation at the culprit vessel | 0.800 | 0.635-1.008 | 0.059 | 0.770 | 0.591-1.002 | 0.052 |
| CI: confidence interval; CKD: chronic kidney disease; DS: diameter stenosis; HR: hazard ratio; LAD: left anterior descending artery; LCx: left circumflex artery; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; MI: myocardial infarction; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; RCA: right coronary artery; TIMI: Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction | ||||||
Propensity score matching analysis
Baseline clinical and angiographic demographics and the year of admission showed satisfactory score matching comparability with a minimum p-value of 0.221, details of which are shown in Supplementary Table 3. In the PSM cohorts, there was still a higher rate of thrombus aspiration and a lower rate of stent implantation at the culprit vessel during pPCI. Detailed results of the procedural characteristics in the matched cohorts are shown in Supplementary Table 4 and Supplementary Table 5.
The Kaplan-Meier curves for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality for the PSM cohorts are shown in Figure 4. Compared with angiographic guidance, OCT guidance was associated with a significantly lower rate of all-cause mortality (13.4% vs 17.0%; log-rank p=0.008) and cardiovascular mortality (10.0% vs 12.2%; log-rank p=0.023) over the 5-year follow-up period. The application of OCT during pPCI was a protective factor for all-cause mortality (PSM HR: 0.707, 95% CI: 0.548-0.913; p=0.008) and cardiovascular mortality (PSM HR: 0.709, 95% CI: 0.526-0.955; p=0.023) in the PSM cohorts.
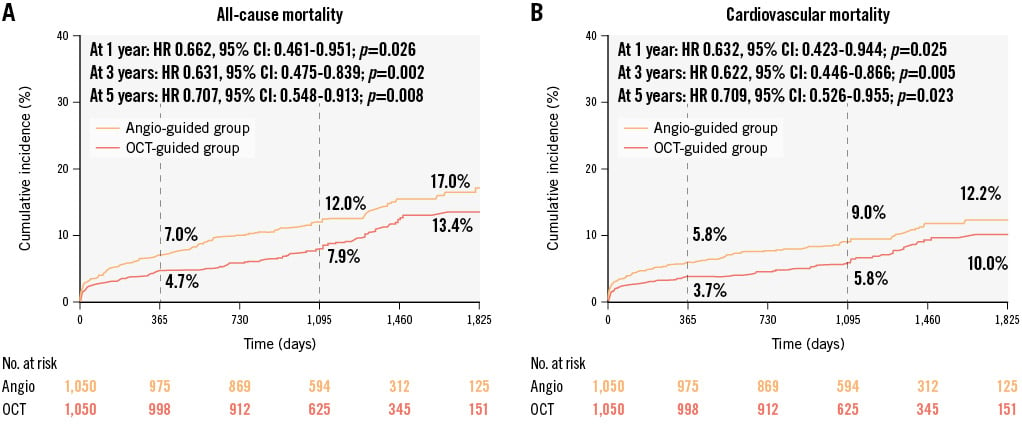
Figure 4. Cumulative incidence curves of long-term mortality in the matched cohorts. After propensity score matching, there remained significantly lower incidences of all-cause mortality (A) and cardiovascular mortality (B) in the OCT-guided cohort than the angiography-guided cohort at 1-year, 3-year and 5-year follow-ups. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the largest published study focusing on reperfusion strategies and long-term survival rates for OCT guidance versus angiographic guidance in STEMI patients undergoing pPCI. The main findings of this study are as follows: 1) Compared with angiography alone, OCT guidance during pPCI led to a reduction in culprit vessel stent implantation; 2) OCT guidance during pPCI in STEMI patients was associated with a significant risk reduction in all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality during a maximum follow-up of 5 years (Central illustration).
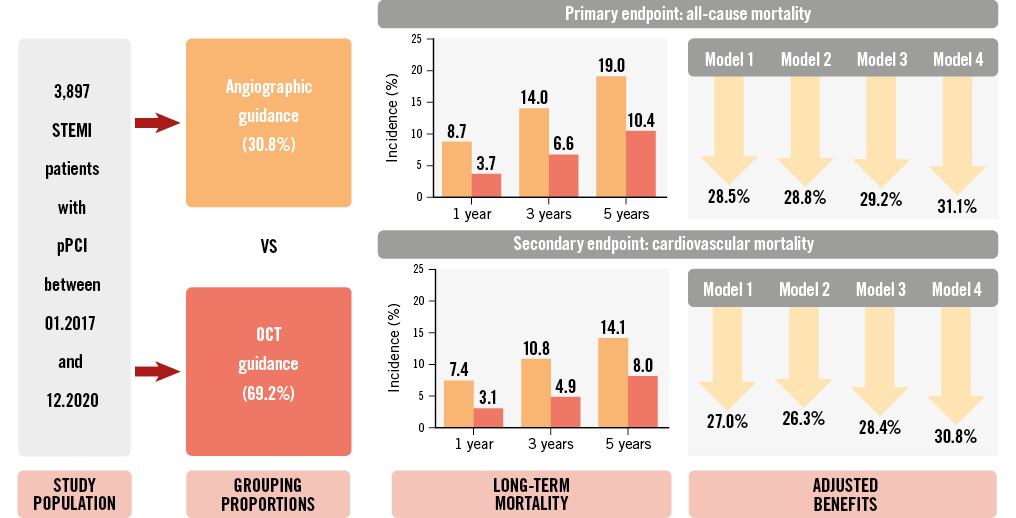
Central illustration. OCT guidance reduces long-term mortality in STEMI patients treated with pPCI. This cohort study included 3,897 ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients who underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI) and were followed for 5 years. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) guidance versus angiographic guidance robustly contributed to better long-term survival in multivariate series models.
Impact of OCT on primary percutaneous coronary intervention strategies
In the current study, OCT examination was usually performed after implementing thrombus aspiration or gentle predilation with a small balloon to achieve TIMI flow 2/3. Intravascular imaging such as IVUS and OCT can compensate for the limitations of coronary angiography while simultaneously providing valuable cross-sectional insights into luminal stenosis, plaque morphology, and vulnerability. The EROSION series of studies proved that, for STEMI patients with a residual angiographic diameter stenosis ≤70%, OCT guidance enabled the majority of erosions, certain ruptures without dissection and/or haematoma, and calcified nodules without obstructive stenosis to avoid stent implantation, with no excess in long-term clinical outcomes1415. Besides, OCT was also able to help identify uncommon causes of STEMI such as spontaneous coronary artery dissection, spasm, and non-atherosclerotic thromboembolism, some of which had no obstructive luminal stenosis, and stent implantation was therefore also avoided1116. In the EROSION III study, 56.2% of STEMI patients (86.2% with culprit erosions and 40.5% with culprit ruptures) were treated without stenting after OCT assessment, resulting in a 15% reduction in stent implantation compared with the angiography-guided group11. In the present study, we extended the study population to 3,897 STEMI patients who were treated with pPCI and followed for up to 5 years, finding a 17.6% reduction of stenting in the OCT-guided cohort compared with the angiography-guided cohort. Our results confirmed the role of OCT in altering reperfusion strategies and improving long-term survival outcomes. This benefit might be attributed to the superiority of OCT in simultaneously assessing morphological severity and underlying STEMI mechanisms in order to choose appropriate reperfusion strategies for each lesion and to achieve optimal post-PCI results1115.
During pPCI of STEMI patients, approaches for restoring blood flow mainly include balloon predilation, thrombus aspiration, and/or direct stent implantation. The negative results of TOTAL, TASTE, and other studies in improving clinical outcomes reduced the recommendation level of routine thrombus aspiration in STEMI in the contemporary guidelines7. However, several studies have also indicated that STEMI patients with a high thrombus burden might benefit from thrombus aspiration17. In the current study, although thrombus aspiration was more commonly used in the OCT-guided cohort, it was not independently related with all-cause or cardiovascular mortality in multivariate analysis. Thrombus aspiration made it possible to evaluate residual thrombus burden and assess culprit lesion morphology using OCT, after which precise interventional treatment (stenting or not and also the size of devices) was conducted according to the OCT findings. This might have contributed to the improved survival in the OCT-guided cohort. Besides, several studies have focused on STEMI patients with a large thrombus burden and on identifying the effective methods to remove thrombus1819. The COCTAIL II trial revealed that intralesional abciximab enabled better myocardial reperfusion than intracoronary abciximab18. Another prospective non-randomised study found that for selected ACS with a large thrombus burden, these might be treated safely with aspiration thrombectomy and no stent or deferred stents under the facilitation of OCT19.
Compared with the angiography-guided cohort, OCT-guided patients more often received ticagrelor at discharge, which has stronger antithrombotic functions than clopidogrel and has been proven to be safe and effective in the novel OCT-guided non-stenting strategy for ACS caused by plaque erosion in the EROSION study8.
Long-term mortality of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Recently, an analysis of the NORIN-STEMI registry in India reported 11% mortality at 1-year follow-up, slightly higher than the angiography-guided cohort in our study20. Another study conducted by Jamal et al reported 11.1% 3-year mortality for STEMI patients who received pPCI, slightly lower compared to the angiography-guided cohort (14.0%) and significantly higher than the OCT-guided cohort (6.6%) in our study21. Two large-scale registries in France and Denmark reported the 5-year rate of all-cause death for STEMI with pPCI to be 16% and 23.3%, respectively, which were comparable with the angiography-guided cohort and higher than the OCT-guided cohort in our study2223. These discrepancies were reasonable and may be attributed to variations in study design, patient characteristics and the high rate of OCT utilisation (69.2%) in our centre.
Benefits of OCT in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
As the earliest and most widely used intravascular imaging modality, the benefits of IVUS in improving clinical outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) have been widely proven2425262728. Two large-scale registries in Korea (the COREA-AMI registry and the KAMIR-NIH registry) demonstrated that the utilisation of IVUS during PCI was associated with improved long-term cardiovascular prognosis when compared with angiographic guidance2425. Two nationwide studies in the USA enrolling hundreds of thousands of patients found that the utilisation of IVUS during PCI was able to reduce the rates of in-hospital death and readmission for patients with AMI and STEMI2627. Results from the J-MINUET registry in Japan showed better in-hospital survival in AMI patients with IVUS/OCT guidance during urgent PCI compared with standard angiographic guidance28.
Advantages of IVUS include the detection of plaque burden and vascular remodelling. However, the diagnosis of thrombus by IVUS is presumptive. OCT is the best way to detect thrombus and the only technique to positively diagnose plaque erosion in vivo, although it cannot see through red blood cell-rich thrombus. These advantages maintain OCT as a promising tool in the management of STEMI. The recent published OCTIVUS trial demonstrated a non-inferior clinical outcome in OCT-guided PCI versus IVUS-guided PCI, yet patients diagnosed as STEMI were excluded in the trial design29. No significant difference in 2-year mortality was observed in ILUMIEN IV, which compared the clinical outcomes of OCT-guided PCI with angiography-guided PCI in high-risk patients or lesions, 57% of which were ACS. There are many potential reasons for the inconsistent findings between ILUMIEN IV and the current study (such as different populations, study designs and interventional approaches), among which the most important points might be the exclusion of STEMI ≤24 hours from the onset of ischaemic symptoms and the requirement of stent implantation for all patients in ILUMIEN IV4.
So far, few large-scale studies have focused on the role of OCT in improving the long-term prognosis of STEMI patients. A retrospective study with 270 ACS patients in each matched cohort showed a reduced number of stents and a numerically, but not statistically, lower incidence of 2-year major adverse cardiovascular events in the OCT-guided cohort than in the angiography-guided cohort30. Another meta-analysis with 2,612 cases revealed that OCT-guided PCI was associated with better prognosis compared to angiography-guided PCI in ACS patients31. Kim et al reported a risk reduction in 1-year patient- and device-oriented endpoints in 209 OCT-guided patients compared with 5,679 angiography-guided cases in a PSM subset analysis of the KAMIR-NIH registry and found these benefits were mainly driven by reduced all-cause mortality and cardiac mortality, respectively32. The protective value of OCT in reducing in-hospital death was not observed in the J-MINUET registry, which might be attributed to the limited number of patients in the OCT-guided cohort (only 152 patients, 5.5% of the overall population)28.
Compared with IVUS, the use of OCT in AMI patients was low: only 2.4% in the Republic of Korea, 5.5% in Japan, and less than 1% in the USA272832. The main reasons include high cost, insufficient clinical training, and a lack of high-quality evidence. In the current study, approximately two-thirds of STEMI patients treated with pPCI received OCT guidance, which significantly changed reperfusion choices and resulted in robust benefits in long-term survival. Instead of employing a one-size-fits-all approach for stent implantation in STEMI, it might be a better paradigm to perform OCT after restoring antegrade blood flow, then making further reperfusion decisions, optimisations, and tailored medications according to the comprehensive findings from angiography and OCT.
Limitations
First of all, this was a retrospective and non-randomised cohort study, which introduced unknown biases that cannot be controlled for. The lower clinical and angiographic complexities in the OCT-guided group than the angiography-guided group was an important selection bias. Multivariate regression analysis and PSM analysis were conducted to reduce the impact of potential confounders. Besides, all patients between 2017 and 2020 were enrolled to minimise subjective selection bias, and follow-up was collected routinely in a real-time manner, which ensured the quality of data. Second, this study specifically focused on all-cause death and cardiovascular death, without analysing other events such as revascularisation. The Academic Research Consortium-2 consensus document highlighted death as the most convincing and accurate clinical endpoint, as it was least affected by the methods of follow-up and other uncertainties13. Third, the type of available devices varied according to the year of enrolment. Fourth, due to the effect of COVID-19, characteristics and interventional strategies for patients in 2020 might have been different from the previous years. The year of admission was included in the multivariate analysis and PSM cohorts to mitigate potential effects. Fifth, the current study concentrated on the utilisation of OCT or not during pPCI, thus detailed results of angiographic and OCT data measured by the core lab were not reported.
Conclusions
In this large-scale observational study, the utilisation of OCT guidance during pPCI in STEMI patients was associated with a reduction in long-term mortality when compared with angiographic guidance alone. Further studies with prospective randomised designs are warranted to confirm these findings.
Impact on daily practice
The current large-scale cohort study proved for the first time that, for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients who undergo primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI), optical coherence tomography (OCT) guidance is associated with a shift in the decision-making process and a significant reduction in long-term mortality compared with angiographic guidance alone. These findings provide strong evidence for the application of OCT as an optimising tool in the pPCI process for STEMI patients and should be considered as a paradigm for future studies and clinical practice.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the patients who participated in this study, as well as all investigators, operators and coordinators.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81827806 to B.Y.).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

