Abstract
BACKGROUND: There are limited data about determinant factors of target lesion failure (TLF) in lesions after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using a drug-coated balloon (DCB) for de novo coronary artery lesions, including optical coherence tomography (OCT) findings.
AIMS: The present study aims to investigate the associated factors of TLF in de novo coronary artery lesions with DCB treatment.
METHODS: We retrospectively enrolled 328 de novo coronary artery lesions in 328 patients who had undergone PCI with a DCB. All lesions had been treated without a stent, and both pre- and post-PCI OCT had been carried out. Patients were divided into two groups, with or without TLF, which was defined as a composite of culprit lesion-related cardiac death, myocardial infarction, and target lesion revascularisation, and the associated factors of TLF were assessed.
RESULTS: At the median follow-up period of 460 days, TLF events occurred in 31 patients (9.5%) and were associated with patients requiring haemodialysis (HD; 29.0% vs 10.8%), with a severely calcified lesion (median maximum calcium arc 215° vs 104°), and with the absence of OCT medial dissection (16.1% vs 60.9%) as opposed to those without TLF events. In Cox multivariable logistic regression analysis, HD (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.26, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.00-5.11; p=0.049), maximum calcium arc (per 90°, HR: 1.34, 95% CI: 1.05-1.72; p=0.02), and the absence of post-PCI medial dissection on OCT (HR: 8.24, 95% CI: 3.15-21.6; p<0.001) were independently associated with TLF.
CONCLUSIONS: In de novo coronary artery lesions that received DCB treatment, factors associated with TLF were being on HD, the presence of a severely calcified lesion, and the absence of post-PCI medial dissection.
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using a drug-coated balloon (DCB) without a stent is one treatment option, especially in patients with high bleeding risk, a bifurcation lesion, or a small coronary artery lesion12. In previous reports, DCB implantation without a stent for de novo coronary artery disease was found to be non-inferior to drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation12. There have also been a few previous reports about the risk factors of clinical outcomes in de novo coronary artery lesions after DCB angioplasty without stents3. Previously, coronary artery dissections, after DCB treatment for de novo coronary artery lesions, were reported to have healed during the follow-up period4. Furthermore, post-PCI coronary artery dissection was positively associated with late lumen enlargement in intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging studies56. However, the predictors of clinical outcomes are still unclear.
OCT is a high-resolution imaging device which enables us to assess the intima, media and adventitia of normal coronary artery segments, as well as to carry out quantitative analysis of calcium (Ca) plaque, such as thickness, angle, and length, which are not analysable with other imaging devices789. We hypothesised that OCT findings could provide additive information to assess the predictors of clinical events in patients undergoing stentless PCI using a DCB. Therefore, the aim of the present study is to investigate the associated factors of clinical events in patients receiving DCB treatment for de novo coronary artery lesions, as assessed by OCT.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
This was a retrospective observational study at the Japanese Red Cross Musashino Hospital (Tokyo, Japan). From April 2018 to February 2023, there were 358 de novo culprit lesions that underwent PCI with a DCB and with OCT imaging. Lesions with anticipated difficulty in advancing the OCT catheter, such as lesions with severe narrowing, tortuosity or severe calcification, were excluded and not imaged by the operators. This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Japanese Red Cross Musashino Hospital (Date: 15 November, No. 5065).
CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY AND PROCEDURE ANALYSIS
The intervention was performed as reported in a previous study10. We used a paclitaxel-coated balloon (SeQuent Please; B. Braun) as the DCB device. Contemporary balloon angioplasty, including a semicompliant balloon, scoring balloon, or cutting balloon, before the DCB procedure was strongly recommended (the recommended balloon-to-vessel ratio was 0.8-1.0). In case of flow-limiting dissection after predilation or classification as National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) type D-F dissection, DES implantation was recommended, and these patients were thus excluded from our study11. The DCB was inflated for 30 to 45 seconds at nominal pressure, according to the morphological characteristics of the lesion (e.g., severity of calcification, length, tortuosity). Following DCB use, a final assessment was undertaken after at least 5 minutes, in order to check the early vessel recoil. In this event, bailout stent implantation was considered.
Quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) was performed using QCA-CMS (Medis Medical Imaging Systems). The minimum lumen diameter, reference diameter, % diameter stenosis, and lesion length were measured in diastolic frames from orthogonal projections. Angiographic calcification at the target lesion site was classified as none or mild, moderate, or severe7. Moderate calcification was defined as radio-opacities noted only during the cardiac cycle before contrast injection, whereas severe calcification was defined as radio-opacities seen without cardiac motion, usually affecting both sides of the arterial lumen. Coronary artery dissection was assessed by NHLBI classification11.
OCT IMAGE ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS
We used frequency-domain OCT (Dragonfly OPTIS or OpStar OCT imaging catheter [both Abbott]) or a high-frequency OCT system (Gentuity Vis-Rx Micro-Imaging Catheter [Nipro]), and all OCT images were analysed using proprietary software with previously validated criteria for OCT plaque characterisation1213.
We evaluated pre- and post-PCI OCT images quantitatively and qualitatively. At pre-PCI OCT, calcium was defined as a signal-poor or heterogeneous region with a sharply delineated border. The maximum arc of target lesion calcium was measured in degrees with a protractor centred on the lumen. The maximum calcium thickness was also measured14. A calcified nodule was defined as an accumulation of small calcium deposits underlying a calcified plaque, which included either a pathological eruptive calcified nodule or nodular calcification715. At post-PCI OCT, we assessed the final minimum lumen area and the presence or absence of coronary artery dissections16. The axial injury of the dissection was described as intimal dissection when only the intima was affected and the media was still intact, as medial dissection when the dissection extended into the media without disruption of the entire medial layer, and as adventitial dissection when the media was dissected throughout its thickness (Figure 1). In addition, the maximum dissection angle and longitudinal dissection length were assessed.

Figure 1. Representative images of medial and adventitial involvement of coronary artery dissection and injury. A1-3) Post-percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of medial involvement of the coronary artery dissection and injury. The double arrows indicate the media, while the arrowheads indicate medial involvement of the coronary artery dissection and injury. Medial dissection (grey), media (red), and adventitia (light green). A’) Post-PCI coronary angiogram corresponding to OCT images A1-3. B1-3) Post-PCI OCT images of adventitial involvement of the coronary artery dissection and injury. The arrowheads indicate the point of adventitial involvement of the coronary artery dissection and injury. The adventitia (light green) disappears at the dissection and injury segment (grey). B’) Post-PCI coronary angiogram corresponding to OCT images B1-3.
ENDPOINTS
The primary outcome comprised target lesion failure (TLF), defined as a composite of target lesion-related cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and target lesion revascularisation (TLR). Clinical follow-up data were obtained at outpatient clinical visits or via telephonic interviews. The diagnosis of MI was based on the universal definition of MI17. Any death of unknown cause was included as a cardiac death. TLR was defined as PCI for lesions in which the DCB was dilated due to recurrent stenosis. The clinical outcome was assessed by two investigators (M. Terui and D. Kachi) who were blinded to clinical and PCI information.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 22.0 (IBM). Categorical data are expressed as frequencies and were compared using the χ2 or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. Because most values were not normally distributed, continuous variables are expressed as median (interquartile range [IQR]) and were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test. Cox regression analyses for TLF were performed to identify predictors of TLF during the follow-up periods. Hazard ratios with corresponding 95% confidence intervals are reported. All variables associated with adverse events at the p<0.10 level in univariable analysis were then tested in a multivariable Cox regression analysis; p<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
Results
We excluded 30 lesions for the following reasons: 20 lesions lacked pre- or post-PCI OCT, 2 lesions had poor image quality, 5 lesions had undergone bailout stenting because of flow-limiting coronary artery dissection, and 3 lesions were in 3 patients who had experienced cardiogenic shock. Finally, we enrolled 328 patients (328 de novo coronary artery lesions) who had undergone DCB treatment as a finalised device with pre- and post-PCI OCT imaging. Among them, 75 patients presented with acute coronary syndromes (ACS; 18 with ST-elevation MI [STEMI], 47 with non-ST-elevation MI [NSTEMI], 10 with unstable angina), all of whom had undergone DCB PCI of the ACS culprit lesion. At the median follow-up of 460 days (IQR 286-770), TLF events occurred in 31 patients (9.5%). These TLF events included 4 cardiac deaths (1.2%), 12 non-fatal MI (3.7%), and 25 TLR (7.6%).
CLINICAL, ANGIOGRAPHIC, AND PCI FINDINGS
The baseline characteristics are summarised in Table 1. The median patient age was 72 years (IQR 63-78), 81% were male, and 77% presented with stable angina. There was no significant difference in the frequency of coronary risk factors (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidaemia) nor in medications at the index PCI between the two groups (Supplementary Table 1). In patients with TLF, there was more renal insufficiency requiring HD than in those without TLF. In the angiographic and PCI procedural findings, more severe calcification was observed in patients with TLF than in those without, whereas there were no significant differences in terms of other findings, including post-PCI dissection severity per NHLBI classification, pre- and post-PCI QCA findings, and PCI procedural details (Table 2). True bifurcation lesions were found in 39 patients (11.9%), and there was no significant difference in the frequency of true bifurcation between the two groups (TLF: 19.4% vs non-TLF: 11.1%; p=0.24). In case of a true bifurcation lesion, sequential DCB treatment or balloon angioplasty of the side branch was undertaken at the operator’s discretion.
Table 1. Patient characteristics.
| Overall (n=328) | Patients with TLF (n=31) | Patients without TLF (n=297) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yrs | 72 (63-78) | 71 (65-77) | 72 (63-78) | 0.84 |
| Male | 264 (80.5) | 25 (80.6) | 239 (80.5) | 1.00 |
| Acute coronary syndrome | 75 (22.9) | 7 (22.6) | 68 (22.9) | 1.00 |
| Stable angina | 253 (77.1) | 24 (77.4) | 229 (77.1) | 1.00 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 125 (38.1) | 12 (38.7) | 113 (38.0) | 1.00 |
| Hypertension | 265 (80.8) | 27 (87.1) | 238 (80.1) | 0.47 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 233 (71.0) | 24 (77.4) | 209 (70.4) | 0.53 |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 85 (25.9) | 11 (35.5) | 74 (24.9) | 0.20 |
| Previous PCI | 146 (44.6) | 17 (54.8) | 129 (43.6) | 0.26 |
| CKD (eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 134 (40.9) | 16 (51.6) | 118 (39.7) | 0.28 |
| Renal insufficiency requiring HD | 21 (12.5) | 9 (29.0) | 32 (10.8) | 0.008 |
| Data are presented as median (interquartile range) or n (%). The p-value in bold indicates statistical significance. CKD: chronic kidney disease; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; HD: haemodialysis; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TLF: target lesion failure | ||||
Table 2. Angiographic and procedural results.
| Overall(n=328) | Patients with TLF(n=31) | Patients without TLF(n=297) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target vessel | 0.25 | |||
| LAD | 201 (61.3) | 21 (67.7) | 180 (60.6) | |
| LCx | 56 (17.1) | 2 (6.5) | 54 (18.2) | |
| RCA | 71 (21.6) | 8 (25.8) | 63 (21.2) | |
| Calcification | 0.04 | |||
| None or mild | 166 (50.6) | 11 (35.5) | 155 (52.2) | |
| Moderate | 40 (12.2) | 2 (6.5) | 38 (12.8) | |
| Severe | 121 (36.9) | 18 (58.1) | 103 (34.7) | |
| Post-PCI dissection (NHLBI classification) | 0.22 | |||
| Any dissection | 107 (32.8) | 12 (38.7) | 95 (32.0) | |
| Type A | 26 (7.9) | 1 (3.2) | 25 (8.4) | |
| Type B | 74 (22.6) | 11 (35.5) | 63 (21.2) | |
| Type C | 7 (2.1) | 0 (0) | 7 (2.4) | |
| Pre-PCI QCA | ||||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 0.83 (0.60-1.14) | 0.80 (0.51-1.14) | 0.83 (0.62-1.14) | 0.56 |
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 2.49 (2.13-3.06) | 2.44 (2.13-2.86) | 2.49 (2.12-3.10) | 0.75 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 64.5 (53.6-75.4) | 64.8 (54.9-75.9) | 64.5 (53.6-75.3) | 0.71 |
| Lesion length, mm | 13.5 (9.9-20.6) | 13.5 (10.2-22.2) | 13.4 (9.9-20.6) | 0.45 |
| Post-PCI QCA | ||||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.79 (1.49-2.12) | 1.92 (1.55-2.30) | 1.77 (1.49-2.10) | 0.18 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 27.6 (21.1-34.9) | 29.2 (23.5-36.0) | 27.4 (20.7-34.8) | 0.42 |
| PCI procedure | ||||
| Scoring balloon | 204 (62.2) | 17 (54.8) | 187 (63.0) | 0.49 |
| Cutting balloon | 102 (31.1) | 12 (38.7) | 90 (30.3) | 0.45 |
| Maximum balloon size, mm | 2.5 (2.5-3.0) | 2.5 (2.5-3.0) | 2.5 (2.5-3.0) | 0.74 |
| Maximum inflation pressure, atm | 12 (10-16) | 14 (11-18) | 12 (10-16) | 0.09 |
| Guide extension catheter | 67 (20.4) | 9 (29.0) | 58 (19.5) | 0.24 |
| Rotational atherectomy | 26 (7.9) | 3 (9.7) | 23 (7.7) | 0.72 |
| Directional atherectomy | 16 (4.9) | 2 (6.5) | 14 (4.7) | 0.66 |
| Orbital atherectomy | 111 (33.8) | 13 (41.9) | 98 (33.0) | 0.32 |
| Excimer laser | 59 (18.0) | 6 (19.4) | 53 (17.8) | 0.81 |
| DCB diameter, mm | 3.00 (2.50-3.50) | 3.00 (2.50-3.25) | 3.00 (2.50-3.50) | 0.59 |
| Total DCB length, mm | 27.6 (21.1-34.9) | 25.0 (20.0-30.0) | 25.0 (20.0-40.0) | 0.81 |
| Data are presented as n (%) or median (interquartile range). The p-value in bold indicates statistical significance. DCB: drug-coated balloon; LAD: left anterior descending artery; LCx: left circumflex artery; NHLBI: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; RCA: right coronary artery; TLF: target lesion failure | ||||
OCT FINDINGS
Table 3 shows the OCT findings of patients with versus without TLF. On pre-PCI OCT, more severely calcified plaque (median maximum calcium angle: 215° [IQR 109-349] vs 104° [IQR 0-253]; p=0.007) and calcified nodules (23% vs 10%; p=0.07) were more commonly found in patients with versus without TLF, whereas the reference lumen area, lipidic plaque angle, and minimum fibrous cap thickness did not differ significantly between patients with versus without TLF. On post-PCI OCT, coronary artery dissection with medial involvement was less common in patients with TLF than in those without (16% vs 61%), whereas dissection with no or intimal involvement (48% vs 21%) or adventitial involvement (36% vs 18%) was more commonly observed among patients with versus without TLF. A coronary artery dissection angle >60° and dissection length >2 mm were found in 97.3% and 82.9% of patients, respectively, and there was no significant difference between patients with and without TLF (maximum dissection angle >60°: TLF 71.0% vs no TLF 84.2%; p=0.08; dissection length >2 mm: 96.8% vs 97.3%; p=0.60). The post-PCI minimum lumen area (MLA) was similar between the two groups.
Table 3. Optical coherence tomography findings.
| Overall (n=328) | Patients with TLF (n=31) | Patients without TLF (n=297) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCT calcified nodule | 38 (11.6) | 7 (22.6) | 31 (10.4) | 0.07 |
| Pre-PCI MLA, mm2 | 1.22 (0.86-1.86) | 1.30 (0.95-1.98) | 1.20 (0.86-1.82) | 0.57 |
| Maximum lipid arc, ° | 141 (0-212) | 0 (0-193) | 142 (0-214) | 0.17 |
| Minimum fibrous cap thickness | 137 (87-200) | 160 (120-190) | 130 (90-200) | 0.50 |
| Pre-PCI maximum calcium angle, ° | 114 (0-262) | 215 (109-349) | 104 (0-253) | 0.007 |
| Pre-PCI maximum calcium thickness, µm | 745 (0-1,098) | 1,120 (755-1,262) | 650 (0-1,050) | <0.001 |
| Pre-PCI calcium length, mm | 4.0 (0.0-16.2) | 17.0 (4.0-30.0) | 4 (0.0-15.0) | <0.001 |
| Proximal reference lumen area, mm2 | 5.86 (4.49-7.33) | 5.59 (5.07-6.92) | 5.89 (4.47-7.37) | 0.79 |
| Distal reference lumen area, mm2 | 5.05 (3.52-7.21) | 5.01 (3.90-7.35) | 5.06 (3.48-7.20) | 0.77 |
| Mean reference lumen area, mm2 | 5.50 (4.18-7.28) | 5.35 (4.27-6.92) | 5.54 (4.17-7.30) | 0.97 |
| Post-PCI MLA, mm2 | 3.25 (2.50-4.48) | 3.07 (2.43-4.66) | 3.26 (2.51-4.42) | 0.93 |
| Post-PCI dissection | <0.001 | |||
| None or intimal involvement | 77 (23.5) | 15 (48.4) | 62 (20.9) | |
| Medial involvement | 186 (56.7) | 5 (16.1) | 181 (60.9) | |
| Adventitial involvement | 65 (19.8) | 11 (35.5) | 54 (18.2) | |
| Maximum dissection angle, ° | 116 (73-161) | 88 (53-164) | 118 (76-161) | 0.12 |
| Longitudinal dissection length, mm | 9.8 (6.1-14.4) | 9.8 (7.7-13.8) | 9.8 (6.0-14.6) | 0.78 |
| Data are presented as n (%) or median (interquartile range). p-values in bold indicate statistical significance. MLA: minimum lumen area; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TLF: target lesion failure | ||||
PREDICTORS OF TARGET LESION-RELATED CLINICAL EVENTS
Table 4 shows univariable and multivariable Cox regression analyses to predict TLF. In the multivariable Cox regression analysis, the presence of HD, a larger maximum calcium angle, and the absence of medial dissection remained independent predictors of TLF. When we divided patients into 4 groups, with the presence or absence of post-PCI medial dissection and a maximum calcium arc >180° or ≤180°, TLF event probability was highest in patients with both an absence of medial dissection and a maximum calcium arc >180° (medial dissection [-], Ca >180°); whereas it was lowest in those with both a presence of medial dissection and a maximum calcium arc ≤180° (medial dissection [+], Ca ≤180°) in the Kaplan-Meier analysis (p<0.001) (Central illustration).
Table 4. Predictors of target lesion failure.
| Univariable logistic regression | Multivariable logistic regression | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | |
| HD | 2.49 | 1.05-5.91 | 0.04 | 2.26 | 1.004-5.11 | 0.049 |
| OCT calcified nodule | 0.81 | 0.30-2.15 | 0.66 | |||
| Maximum calcium angle (per 90°) | 1.40 | 1.07-1.83 | 0.01 | 1.34 | 1.05-1.72 | 0.02 |
| Absence of medial dissection | 10.63 | 3.77-29.9 | <0.001 | 8.24 | 3.15-21.6 | <0.001 |
| Adventitial dissection | 0.62 | 0.28-1.39 | 0.24 | |||
| p-values in bold indicate statistical significance. CI: confidence interval; HD: haemodialysis; HR: hazard ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography | ||||||
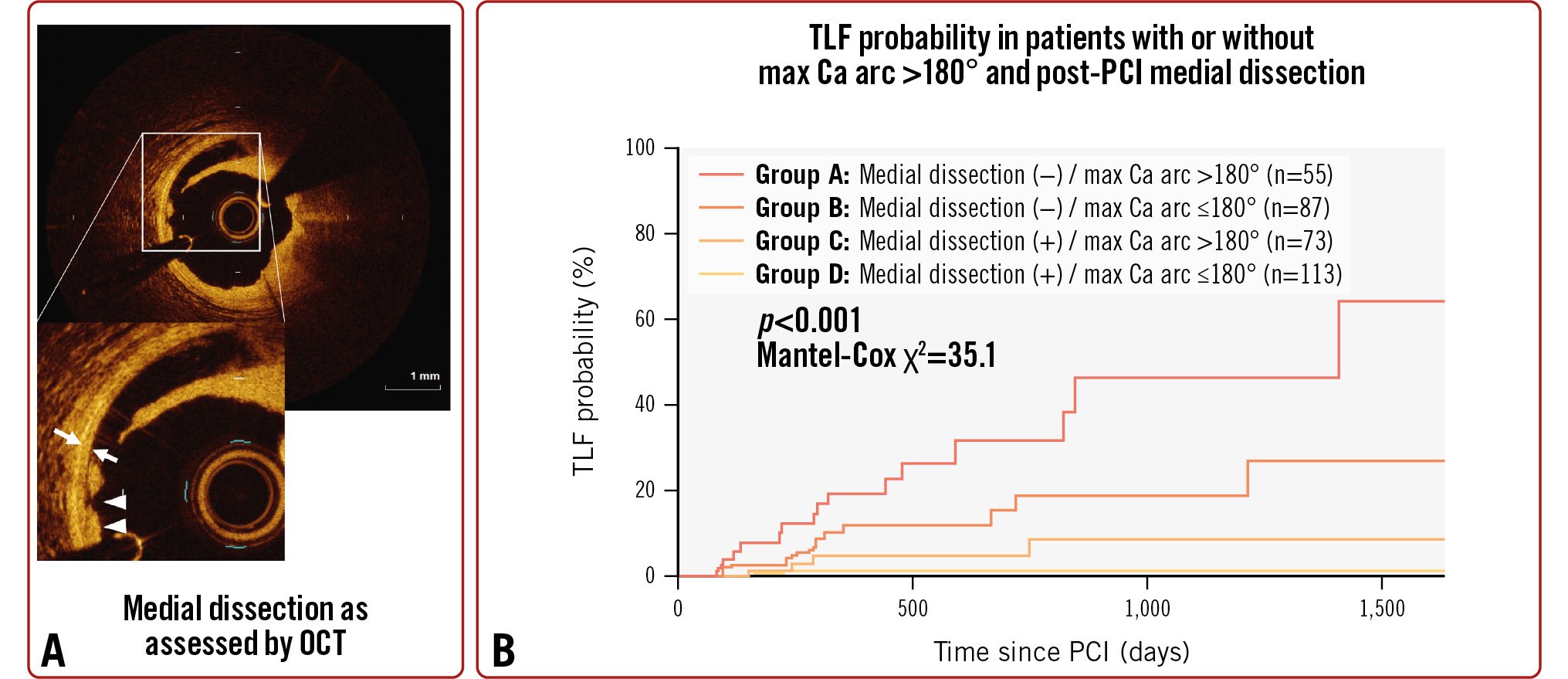
Central illustration. Predictors of target lesion failure in de novo coronary lesions treated with a drug-coated balloon. A) OCT imaging, with double arrows indicating the media and arrowheads indicating medial dissection of the coronary artery. B) Kaplan-Meier curve showing TLF event probability in patients with versus without medial dissection and a maximum calcium arc >180° or ≤180°. TLF events were highest in those patients who had a maximum calcium arc >180° but lacked medial dissection, whereas the fewest TLF events occurred in those who had a maximum calcium arc of ≤180°and also had medial dissection (p<0.001). Ca: calcium; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TLF: target lesion failure
Discussion
In this study, TLF was found in 31 patients (9.5%) and was associated with the presence of HD, more severely calcified plaque, as well as the absence of post-PCI medial dissection on OCT. Furthermore, patients with an absence of post-PCI medial dissection and with severely calcified plaque on OCT were associated with a worse prognosis.
In the present study, HD was found to be associated with TLF, though the frequency of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) values were similar between patients with and without TLF. As reported in past studies, patients with renal insufficiency requiring HD had a worse prognosis than those without despite the use of second-generation DES1819. Furthermore, Ito et al reported that patients requiring HD showed a poorer prognosis than those not requiring HD after DCB treatment for de novo coronary lesions, as the present study has also demonstrated20. Although it remains unclear whether there was an additive impact of HD on TLF of severely calcified lesions, one previous study of patients with angiographic calcium reported that the clinical 5-year event rates were higher in patients with versus without HD21.
In the present study, calcium severity of the target lesion was found to be associated with clinical outcomes. As reported previously, intervening in severely calcified coronary lesions remains challenging2223. Although Mitsui et al reported that the use of DCB is non-inferior to DES in patients with severely calcified plaques requiring orbital atherectomy24, calcium represents a barrier to optimal drug absorption25. Thus, adequate lesion preparation including rotational atherectomy or orbital atherectomy, which can reduce the calcium burden, might be effective when use of DCB for de novo lesions with severe calcification is considered, as has been reported by past non-randomised observational studies2426.
The present study demonstrates that angiography-defined coronary artery dissection has a similar incidence in patients with and without TLF, while medial dissection by OCT imaging is a predictor of TLF. These findings can be explained by the difference in resolution between OCT imaging and angiograms. In a past OCT study27, coronary artery medial dissection after stenting was found in 14-25% of patients, though dissection of at least type B by angiography was found in only 1%. OCT is a high-resolution imaging device which enables us to detect more dissection than on an angiogram. Thus, the ability of OCT to detect dissections not visible by angiography might be useful to treat de novo coronary artery lesions with DCB.
In this study, medial dissection was a powerful predictor of a better outcome. According to previous studies, the clinical outcomes of patients with post-PCI coronary dissection were not inferior to those not treated with post-PCI coronary dissection when treated with DCB for de novo coronary lesions428. In a previous animal model study, tubulin, as a paclitaxel-binding specific protein, exhibited predominantly subintimal and adventitial localisation. Therefore, intimal disruption was considered potentially more detrimental to current paclitaxel-based DCB; those findings were in line with those of the present study29. On the other hand, a previous IVUS study by Yamamoto et al reported that late lumen enlargement after DCB treatment was observed in lesions with non-flow-limiting coronary dissection. Similar findings were reported by an OCT study5. Intravascular imaging, especially OCT, enables the detection of the presence or absence of medial dissection – both pre- and post-PCI − and provides additional information about risk stratification in terms of pre-PCI plaque morphology (e.g., calcium arc, calcium thickness). Therefore, when a stentless strategy with DCB for treating a de novo coronary artery lesion is considered, both patient characteristics and OCT findings such as pre-PCI calcium severity and the presence or absence of post-PCI coronary dissection are useful for predicting future events.
Our study demonstrated no significant difference in the frequency of coronary risk factors nor in medications at the index PCI between the two groups. In the registry data of DCB treatment from the Republic of Korea, there were no significant differences of event-free survival in patients with de novo coronary lesions in terms of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, or CKD3. Similarly, Funatsu et al reported no independent predictors of coronary risk factors, other than current smoking and HD30. While aforementioned reports were observational studies with relatively small numbers of events, it remains unclear whether there are modifiable coronary risk factors after PCI with DCB in de novo coronary lesions. Thus, further large-scale clinical studies are warranted.
Limitations
The present study had several limitations. First, in this retrospective observational study, PCI procedural details, including DCB size and length, were left to the operator’s discretion. Therefore, selection bias was inevitable. Second, the study population was small. Third, we excluded lesions for which advancing the OCT catheter was anticipated to be difficult, such as those with severe narrowing, tortuosity, or calcification. Fourth, the present study included only Japanese patients. The mean vessel size and the frequency of use of PCI devices, including imaging catheters and debulking devices, in the present study was different than in Western countries. Therefore, the generalisability is limited. Fifth, left main lesions were excluded in the present study because of the difficulty of overall OCT imaging in the left main trunk. Finally, the multivariable model for TLF was possibly overfitted because of the small number of TLF events.
Conclusions
In de novo coronary artery lesions treated with DCB, patients with HD, a severely calcified lesion, and with an absence of post-PCI medial dissection were associated with TLF.
Impact on daily practice
Patients on haemodialysis (HD), with severe calcium on pre-percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) optical coherence tomography (OCT), and without post-PCI medial dissection as assessed by OCT were associated with target lesion failure (TLF) in a stentless PCI strategy with a drug-coated balloon (DCB) for de novo coronary artery lesions. Therefore, when a stentless strategy with DCB for a de novo coronary artery lesion is considered, not only patient characteristics, but also OCT findings, such as pre-PCI calcium severity and the presence or absence of post-PCI coronary dissection, are useful to predict future TLF events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

