Abstract
Background: The first-generation polymeric bioresorbable scaffolds resulted in higher than acceptable 3-year rates of device-related adverse outcomes.
Aims: We aimed to assess the intermediate-term safety and performance of a novel ultrathin-strut sirolimus-eluting iron bioresorbable scaffold (IBS) in non-complex coronary lesions.
Methods: The prospective, single-arm, open-label IBS first-in-human study enrolled 45 patients, each with a single de novo lesion. Enrolled patients were randomly assigned to 2 follow-up cohorts. Angiographic and imaging follow-up with intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography (OCT) were conducted at 6 and 24 months in cohort 1 (n=30) and at 12 and 36 months in cohort 2 (n=15). Clinical follow-up was conducted at 1, 6 and 12 months, and annually thereafter up to 5 years. The coprimary outcomes were target lesion failure (TLF) and angiographic late lumen loss (LLL) at 6 months.
Results: A total of 45 patients were enrolled between April 2018 and January 2019. The mean age was 53.2 years, 77.8% were male, and 26.7% had diabetes. The TLF rates were 2.2% at 6 months and 6.7% at 3 years, which in all cases were due to clinically indicated target lesion revascularisation. No deaths, myocardial infarctions or stent thromboses occurred during 3-year follow-up. In-scaffold LLL was 0.33±0.27 mm at 6 months and 0.37±0.57 mm at 3 years. By OCT, the proportion of covered struts was 99.8% at 6 months and 100% after 1 year. The 3-year strut absorption rate was 95.4%.
Conclusions: In this first-in-human experience, an ultrathin IBS was safe and effective for the treatment of de novo non-complex coronary lesions up to 3-year follow-up.
Introduction
Bioresorbable scaffolds (BRS) were introduced to address the long-term limitations of permanent metallic drug-eluting stents (DES), which include vascular inflammation, reactive dysmotility, neoatherosclerosis, and side branch jailing12. After providing temporary scaffolding and eluting an antiproliferative agent to inhibit excessive neointimal hyperplasia, the BRS is completely resorbed, “uncaging” the treated vessel to restore its capabilities for vascular adaptation and vasomotion3. However, large clinical trials of a first-generation thick-strut (~157 μm) polymer-based everolimus-eluting BRS (Absorb bioresorbable vascular scaffold [BVS]; Abbott) demonstrated increased rates of device thrombosis and myocardial infarction (MI) during the 3-year resorption window456. Suboptimal scaffold expansion − due to its thick struts, recoil and limited expansion capability – was largely responsible for the increase in early scaffold thrombosis, while in many cases, scaffold discontinuities and intraluminal scaffold dismantling, caused by uneven degradation during the bulk erosion process, contributed to late and very late scaffold thromboses27. Thus, a search ensued for alternate materials capable of reducing scaffold thickness while optimising the degradation process8. A bioabsorbable magnesium-based scaffold (AMS-1; first- and second-generation DREAMS; BIOTRONIK AG) was introduced and iterated, although safety and effectiveness concerns were raised given its thick struts (150 μm), premature absorption, loss of radial force, and post-resorption amorphous calcium phosphate residues391011.
Iron was suggested as an alternative bioresorptive metal in scaffolds. Iron is biocorrodible, has a strong radial force, acceptable malleability and plays a vital physiological role in human physiology. In animal studies, pure iron and nitride iron scaffolds have been shown to be safe and biocompatible1213141516. A novel sirolimus-eluting iron bioresorbable scaffold (IBS; Biotyx Medical, previously developed at Lifetech Scientific Company) has been developed, consisting of an ultrathin (70 μm) nitriding iron backbone with a zinc submicron layer, coated with poly-D,L-lactic acid (PDLLA) incorporating sirolimus1718. In porcine studies biocorrosion did not occur before 6 months, and strut coverage was more rapid than with the cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent (EES;XIENCE PRIME; Abbott), while other vascular responses were similar19. We, therefore, performed a first-in-human trial (IBS-FIM; ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03509142) using multimodality imaging, including quantitative coronary angiography (QCA), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT), to assess the feasibility, bioresorption, and potential safety and effectiveness of IBS for the treatment of patients with coronary artery disease.
Methods
Study design
IBS-FIM was a prospective, single-arm, open-label trial that enrolled 45 patients from Fuwai Hospital in Beijing, People’s Republic of China. To acquire serial intravascular imaging information at different intervals, the population was randomly divided in a 2:1 ratio into 2 cohorts. The 30 patients randomised to cohort 1 were assigned to undergo imaging follow-up at 6 months and 2 years, and the 15 patients randomised to cohort 2 were assigned to undergo follow-up imaging at 1 year and 3 years. Assessment using IVUS and OCT was performed post-procedure and at each of the angiographic follow-up time points. The protocol was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee at Fuwai Hospital.
Participants
Eligible subjects were between 18 and 75 years of age and had evidence of myocardial ischaemia indicating percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Angiographic inclusion criteria required the presence of a single target lesion that could be covered with a single study scaffold, with a target lesion length ≤18 mm, diameter stenosis (DS) ≥70% in a vessel with reference vessel diameter (RVD) between 3.0 and 3.5 mm by visual estimation and with Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) flow grade ≥1. Patients were excluded if they presented with acute myocardial infarction (MI), had undergone stent implantation in the target vessel within 1 year, had prior coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) or had contraindications for CABG, had severe heart failure, or had a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <40%. The complete list of inclusion and exclusion criteria appears in Supplementary Appendix 1. All subjects provided written informed consent.
Study device
The ultrathin-strut (70 μm) sirolimus-eluting IBS consists of an ultrathin (53 μm) nitriding iron (Fe-0.05%N) backbone, with a pure zinc submicron layer as a sacrifice anode to delay the onset of backbone degradation, and a PDLLA coating with sirolimus to deliver the drug and create a local low pH environment that accelerates the corrosion of the iron struts into soluble iron ions by polymer degradation once the zinc is exhausted1718. Two sets of gold radiopaque markers are located at both ends of the scaffold (Supplementary Figure 1). The drug loading density is 8 μg per mm of scaffold length, and the drug is completely eluted by 24 weeks. An asymmetric polymer matrix favours elution of the drug to the abluminal compartment.
The IBS is currently manufactured with diameters of 3.0 and 3.5 mm and lengths of 15, 18, and 23 mm. The integrity and scaffold force are maintained during the first 3 months18, after which it locally degrades into iron ions which diffuse into tissue and precipitate as particulates in the vessel wall (Supplementary Figure 2). The particulates are then transferred into haemosiderin by macrophages and are cleared by the lymphatic system for recycling151719. The iron content in a 3.0 mm diameter x 18 mm long IBS is 9 mg, which corresponds to the amount in approximately 20 ml of blood, or the weekly iron intake of an adult.
Procedure
Subjects received dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT; clopidogrel 75 mg/day and aspirin 100 mg/day), beginning at least 3 days preprocedure. Predilation of the target lesion with balloon angioplasty was required. After stenting, DAPT with clopidogrel (75 mg/day) or ticagrelor (90 mg twice daily) was prescribed for at least 12 months and aspirin (100 mg/day) was administered lifelong.
Follow-up
Clinical follow-up was conducted for all study participants at 1, 6 and 12 months, and yearly thereafter until 5 years. Subjects in cohort 1 underwent angiography, IVUS and OCT at 6-month and 2-year follow-up, while subjects in cohort 2 underwent the same assessments at 1-year and 3-year follow-up. In addition to standard assessments, OCT was used to semiquantitatively assess the in vivo degradation of the IBS as described below. At the present time clinical and imaging follow-up are completed up to 3 years.
Endpoints
The primary endpoints were target lesion failure (TLF: a composite of cardiac death, target vessel-related myocardial infarction [TV-MI] or clinically indicated target lesion revascularisation [CI-TLR]) and late lumen loss (LLL) by QCA at 6 months. Secondary endpoints included the rates of device, lesion, and clinical success immediately post-procedure; the patient-oriented clinical endpoint (PoCE), a composite of all-cause death, all MI, or any revascularisation; the components of TLF; and scaffold thrombosis. Other QCA endpoints included in-scaffold and in-segment acute recoil, RVD, minimum lumen diameter, percentage DS, binary restenosis, and vasomotion as assessed by QCA. IVUS endpoints included the vessel area, lumen area, scaffold area, neointimal area, percentage area obstruction, volumetric obstruction and late recoil area. OCT endpoints included strut coverage, area obstruction, late recoil and scaffold absorption. Detailed definitions of the endpoints are provided in Supplementary Appendix 2. All clinical endpoint events were adjudicated by a clinical events committee, independent from the investigators and sponsor.
Imaging assessments
QCA, IVUS and OCT analyses were performed at the core laboratory at Fuwai Hospital. QCA analysis was performed using CAAS Workstation 8.1 (Pie Medical Imaging) as previously described20. IVUS (OptiCross; Boston Scientific) was performed at an automated pullback speed of 0.5 mm/s and was analysed in 0.5 mm intervals by QIvus 3.0 (Medis Medical Imaging). Strut absorption on IVUS images was analysed at 1 mm intervals and categorised as obvious versus non-obvious according to the presence of a widening strut shadowing of >300 μm (Supplementary Figure 3). OCT image acquisitions were performed using the C7-XRTM frequency-domain system and Dragonfly imaging catheter (both Abbott). OCT images were acquired at 100 frames/s at a pull-back speed of 20 mm/s. Cross-sectional OCT images were analysed at 0.4 mm intervals by QIvus 3.0 as previously described2021. The absorption process of the IBS was semiquantitatively analysed by OCT, using a novel method22. Using postprocedural radial heights of the sharply delineated struts as reference, the struts at follow-up were categorised into 5 groups according to the height of the expanded bow area generated during the degradation process (Supplementary Figure 4). All images were analysed offline by an independent core laboratory (Interventional Cardiovascular Imaging Core Laboratory, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Beijing, People’s Republic of China) as previously described22. The full quantitative measurement and analysis methods are included in Supplementary Appendix 2.
Statistical analysis
The objective of this pilot study was to evaluate the feasibility and the preliminary safety and effectiveness outcomes of the IBS and to generate data to aid the design of subsequent large-scale, multicenter, randomised controlled clinical trials. The sample size of 45 patients was defined according to the requirements of the Center for Medical Device Evaluation, National Medical Products Administration in China, and was not powered for any specific endpoint. Categorical variables are presented as proportions and were compared using the Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests. Continuous data are presented as mean±standard deviation and were compared using paired t-tests. Missing data were not replaced. Significance was set at a 2-sided α=0.05. All analyses were performed with SAS software v9.4 (SAS Institute).
Results
Patients and procedures
Between April 2018 and January 2019, 45 patients (mean age 53.2 years, 77.8% male) with a single qualifying coronary artery lesion were enrolled and randomly assigned to imaging cohort 1 (n=30) or cohort 2 (n=15) after IBS implantation (Supplementary Figure 5). Because of scheduling issues, two patients in cohort 1 crossed over to the imaging follow-up timing of cohort 2. Thus, the imaging results are reported as 28 patients for cohort 1 and 17 patients for cohort 2.
Baseline characteristics are shown in Supplementary Table 1. By QCA the mean RVD and lesion length were 2.98±0.38 mm and 14.0±4.2 mm, respectively; 64.4% of lesions were in the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery. All lesions underwent predilatation, and 93.3% underwent post-dilatation. Device success occurred in 45 patients (100%). In one patient, a bailout IBS scaffold was required because of an edge dissection after the first IBS implant; the second scaffold was placed distally to overlap the first scaffold by several mm. There were no procedural complications, and lesion and procedural success were achieved in 100% of patients. Medications at discharge and during follow-up appear in Supplementary Table 2.
Clinical outcomes
All patients completed follow-up up to 3 years. Clinical outcomes are reported in Table 1. Four patients underwent TLR, three of which were clinically indicated. One patient experienced chest discomfort and palpitations at 6 months post-procedure. Angiography showed in-scaffold restenosis in the mid-LAD, and the patient underwent CI-TLR with a metallic DES. Two patients with recurrent angina had restenosis noted at the 12-month angiographic follow-up and underwent CI-TLR. Thus, the rates of TLF (and CI-TLR) were 2.2% at 6 months and 6.7% after 1 year. One additional patient underwent a non-TLR target vessel revascularisation (TVR). The detailed description of the cases of TLR and this TVR are included in Supplementary Appendix 3. There were no deaths, MIs or scaffold thromboses up to 3-year follow-up.
Table 1. Clinical outcomes at 3 years.
| 6 months n=45 | 1 year n=45 | 2 years n=45 | 3 years n=45 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target lesion failure | 1 (2.2) | 3 (6.7) | 3 (6.7) | 3 (6.7) |
| Patient-oriented composite endpoint | 2 (4.4) | 4 (8.9) | 4 (8.9) | 5 (11.1) |
| All-cause death | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac death | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Myocardial infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Target vessel myocardial infarction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Any revascularisation | 2 (4.4) | 4 (8.9) | 4 (8.9) | 5 (11.1) |
| Clinically indicated TVR | 2 (4.4) | 4 (8.9) | 4 (8.9) | 4 (8.9) |
| Clinically indicated TLR | 1 (2.2) | 3 (6.7) | 3 (6.7) | 3 (6.7) |
| Definite or probable device thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Data are number (%). TLR: target lesion revascularisation; TVR: target vessel revascularisation | ||||
QCA results
Baseline and post-procedure QCA results were similar between the 2 cohorts (Table 2, Supplementary Table 1). Acute recoil was 0.12±0.08 mm. Angiographic follow-up was completed in 100% of patients at 6 months and 12 months, in 75.0% of patients at 2 years, and in 47.1% of patients at 3 years (Supplementary Figure 5). As shown in Table 2 and Figure 1, in-scaffold LLL was 0.33±0.27 mm at 6 months, 0.39±0.50 mm at 12 months, 0.40±0.31 mm at 24 months, and 0.37±0.57 mm at 36 months. In paired analyses there was no significant increase in in-scaffold LLL from 6 months to 24 months (cohort 1: 0.31±0.26 mm and 0.40±0.31 mm, respectively; p=0.06) nor from 12 months to 36 months (cohort 2: 0.14±0.15 mm and 0.37±0.57 mm, respectively; p=0.26). Other paired QCA data in cohorts 1 and 2 are shown in Supplementary Table 3. Binary restenosis occurred in 3 patients (6.7%) up to 3 years. Vasomotion did not change from 6 months to 3 years.
Table 2. Quantitative coronary angiographic serial assessments.
| Post-procedure (all patients, n=45) | 6 months (cohort 1, n=28) | 1 year (cohort 2, n=17) | 2 years (cohort 1, n=21) | 3 years (cohort 2, n=8) | p-value post-procedure vs 6 months | p-value 6 months vs 1 year | p-value 1 year vs 2 years | p-value 2 years vs 3 years | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RVD, mm | In-scaffold | 3.08±0.39 | 3.00±0.33 | 2.93±0.38 | 3.04±0.36 | 3.00±0.35 | 0.33 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.78 |
| In-segment | 3.00±0.44 | 2.96±0.35 | 2.87±0.41 | 3.06±0.47 | 2.87±0.43 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 0.18 | 0.32 | |
| MLD, mm | In-scaffold | 2.78±0.36 | 2.46±0.44 | 2.37±0.58 | 2.39±0.44 | 2.51±0.46 | 0.001 | 0.56 | 0.90 | 0.54 |
| In-segment | 2.55±0.39 | 2.35±0.40 | 2.20±0.50 | 2.34±0.41 | 2.36±0.41 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 0.89 | |
| DS, % | In-scaffold | 9.3±6.5 | 17.5±12.6 | 18.1±18.6 | 21.2±10.8 | 16.0±15.1 | 0.003 | 0.91 | 0.55 | 0.30 |
| In-segment | 14.3±7.3 | 20.3±10.9 | 22.1±17.9 | 23.1±10.9 | 16.8±15.1 | 0.014 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.21 | |
| Binary restenosis | In-scaffold | - | 1 (3.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) | - | 0.55 | 0.57 | 1.00 |
| In-segment | - | 1 (3.6%) | 2 (11.8%) | 1 (4.5%) | 0 (0%) | - | 0.55 | 0.57 | 1.00 | |
| LLL, mm | In-scaffold | - | 0.33±0.27 | 0.39±0.50 | 0.40±0.31 | 0.37±0.57 | - | 0.63 | 0.95 | 0.86 |
| In-segment | - | 0.25±0.26 | 0.27±0.45 | 0.27±0.35 | 0.21±0.38 | - | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.67 | |
| Vasomotion, mm | - | 0.11±0.12 | 0.15±0.28 | 0.13±0.10 | 0.10±0.15 | - | 0.62 | 0.80 | 0.54 | |
| Quantitative flow ratio | 0.95±0.03 | 0.93±0.07 | 0.87±0.13 | 0.95±0.03 | 0.88±0.08 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.07 | |
| Data are mean±standard deviation or number (%). DS: diameter stenosis; LLL: late lumen loss; MLD: minimum lumen diameter; RVD: reference vessel diameter | ||||||||||
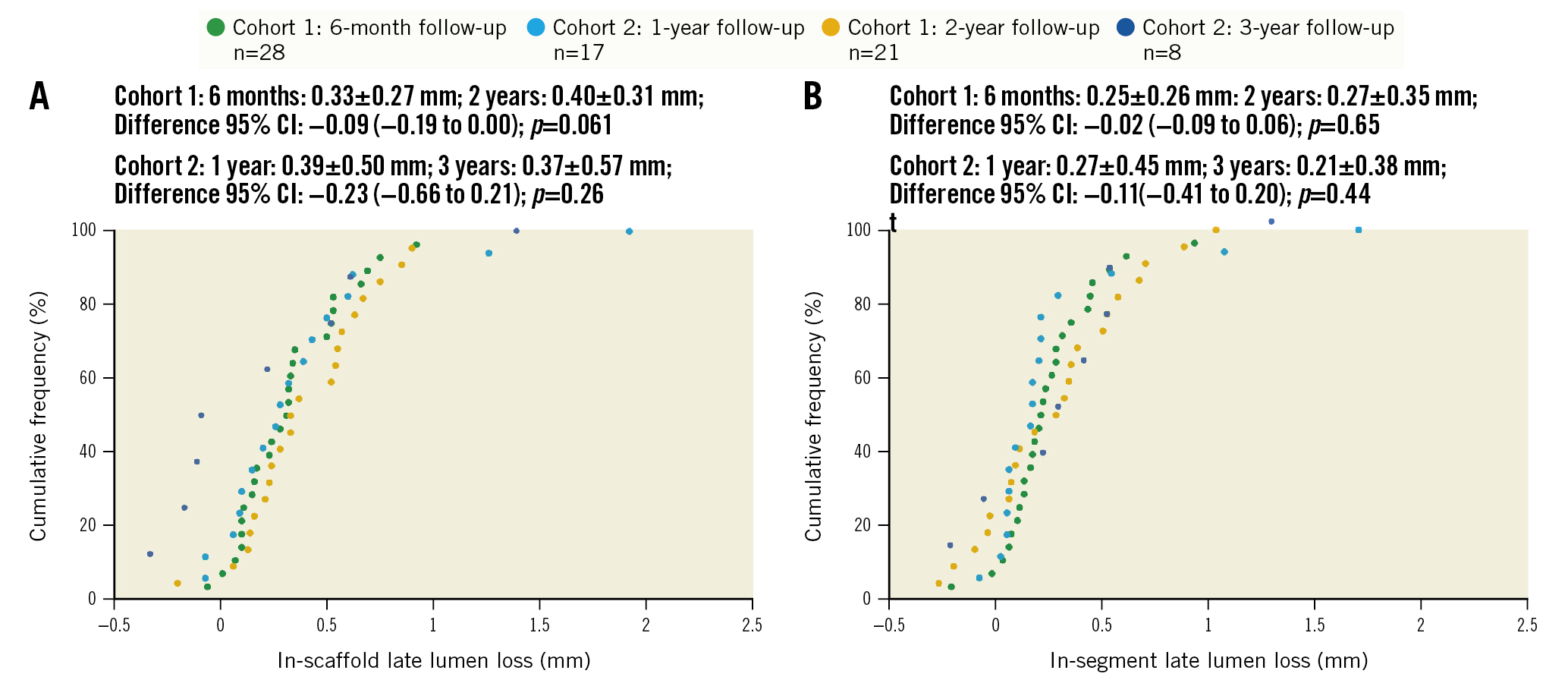
Figure 1. Cumulative frequency of in-scaffold and in-segment late lumen loss up to 3 years by quantitative coronary angiography. A) In-scaffold late lumen loss. B) In-segment late lumen loss. Paired difference calculated in 21 patients in cohort 1 and 8 patients in cohort 2. CI: confidence interval
IVUS results
IVUS measurements were available in 28 (100%) patients at 6 months, 17 (100%) patients at 1 year, 21 (75.0%) patients at 2 years, and 8 (47.1%) patients at 3 years. As shown in Table 3 and Supplementary Figure 6, the mean vessel, scaffold and lumen areas were stable between 6-month and 24-month follow-up but were larger at 36 months. The minimum lumen and scaffold areas progressively decreased up to 2 years but were larger at 3 years, while the degree of neointimal hyperplasia increased up to 3-year follow-up. The mean scaffold area recoil was 7% at 6 months, 3% at 1 year and 2 years, and −10.2% at 3 years (indicating expansion). Paired analyses showed that the minimum vessel area was significantly reduced from 6 months to 2 years in cohort 1, while plaque area was significantly increased from 1 year to 3 years in cohort 2 (Supplementary Table 4). The proportion of struts categorised as showing obvious absorption were 7.4%, 35.7%, 59.8% and 78.1% at 6 months, 1 year, 2 years and 3 years, respectively (Supplementary Figure 3).
Table 3. Intravascular ultrasound serial assessments.
| Post-procedure (all patients, n=45) | 6 months (cohort 1, n=28) | 1 year (cohort 2, n=17) | 2 years (cohort 1, n=21) | 3 years (cohort 2, n=8) | p-value post-procedure vs 6 months | p-value 6 months vs 1 year | p-value 1 year vs 2 years | p-value 2 years vs 3 years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean vessel area, mm2 | 17.4±3.5 | 17.3±3.5 | 17.5±3.6 | 17.4±3.6 | 20.4±4.0 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.07 |
| Min vessel area, mm2 | 14.3±3.3 | 14.0±2.8 | 13.6±3.1 | 13.5±2.7 | 15.6±3.4 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.87 | 0.08 |
| Mean lumen area, mm2 | 9.21±1.79 | 7.76±2.00 | 7.70±2.15 | 7.61±2.08 | 8.62±2.29 | 0.002 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.27 |
| Min lumen area, mm2 | 7.67±1.50 | 5.62±1.74 | 5.43±1.91 | 5.09±1.28 | 5.73±1.35 | <0.0001 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 0.24 |
| Mean plaque area, mm2 | 8.19±2.37 | 9.51±2.32 | 9.82±2.35 | 9.83±1.95 | 11.77±2.54 | 0.02 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.04 |
| Mean scaffold area, mm2 | 9.30±1.80 | 8.72±1.96 | 8.91±1.97 | 9.00±2.09 | 10.5±2.75 | 0.20 | 0.75 | 0.90 | 0.12 |
| Min scaffold area, mm2 | 7.77±1.51 | 6.93±1.54 | 6.75±1.42 | 6.39±1.38 | 7.82±2.20 | 0.02 | 0.71 | 0.43 | 0.04 |
| NHA, mm2 | - | 0.77±0.45 | 1.09±0.90 | 1.17±0.87 | 1.75±0.77 | - | 0.18 | 0.79 | 0.11 |
| Area obstruction, % | - | 11.8±5.7 | 14.7±10.3 | 15.9±9.1 | 18.3±5.21 | - | 0.31 | 0.70 | 0.48 |
| Volumetric obstruction*, % | - | 11.7±5.8 | 14.7±10.4 | 15.7±8.9 | 17.8±5.22 | - | 0.29 | 0.76 | 0.53 |
| Mean recoil area, mm2 | - | 0.67±0.90 | 0.23±1.08 | 0.46±1.91 | −0.88±2.63 | - | 0.15 | 0.64 | 0.14 |
| Recoil area, % | - | 7.0±10.0 | 2.7±13.0 | 3.3±20.7 | −10.2±27.0 | - | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.16 |
| Data are mean±standard deviation. *In-scaffold. Min: minimum; NHA: neointimal hyperplasia area | |||||||||
OCT results
OCT measurements were available in 28 (100%) patients at 6 months, 17 (100%) patients at 1 year, 21 (75.0%) patients at 2 years, and 8 (47.1%) patients at 3 years. As shown in Table 4 and Figure 2, the mean scaffold area did not change from post-procedure to 2 years but was larger at 3 years. The mean lumen area reached its nadir at 6 months, while the minimum scaffold and lumen areas decreased up to 2-year follow-up and then increased at 3 years. The neointimal area and percentage area obstruction peaked at 6 months and were unchanged up to 2 years; the neointimal area then increased at 3 years. Paired analyses showed similar results (Supplementary Table 5). In the patient who required bailout IBS treatment for an edge dissection, 6-month and 2-year follow-up angiography showed that the overlap region was well covered with tissue and that the lumen was patent without thrombosis (Supplementary Figure 7). The lumen and scaffold area evolution by OCT in the 4 patients who underwent TLR are shown in Supplementary Figure 8. Incomplete strut apposition was infrequent at all time periods, and late-acquired strut malapposition was not observed. The proportion of covered struts was 99.8% at 6 months and 100% at 1-year, 2-year and 3-year follow-up. The strut absorption rate was 34.3% at 6 months, 52.3% at 1 year, 82.3% at 2 years and 95.4% at 3 years (Supplementary Figure 9, Supplementary Figure 10).
Table 4. Optical coherence tomography serial assessments.
| Post-procedure | 6 months | 1 year | 2 years | 3 years | p-value post-procedure vs 6 months | p-value 6 months vs 1 year | p-value 1 year vs 2 years | p-value 2 years vs 3 years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strut level | n=20,917 | n=12,122 | n=7,072 | n=8,299 | n=3,231 | ||||
| Strut coverage thickness, μm | - | 194.1±140.1 | 185.6±139.3 | 183.0±107.1 | 279.7±148.5 | - | <0.0001 | 0.17 | <0.0001 |
| ISA | 224 (1.1) | 6 (0.05) | 1 (0.01) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | <0.0001 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.28 |
| Late-acquired ISA | - | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - | - | - | - |
| Cross-section level | n=2,239 | n=1,372 | n=851 | n=1,062 | n=416 | ||||
| Neointimal area, mm2 | - | 1.67±0.93 | 1.67±1.08 | 1.58±0.74 | 2.75±1.22 | - | 0.91 | 0.03 | <0.0001 |
| Covered struts | - | 1,369 (99.8) | 851 (100) | 1,062 (100) | 416 (100) | - | 0.29 | NA | 0.28 |
| Lesion level | n=44 | n=28 | n=17 | n=21 | n=8 | ||||
| Mean scaffold area, mm2 | 8.92±1.79 | 8.83±2.13 | 9.07±2.04 | 9.15±2.28 | 10.74±2.86 | 0.85 | 0.71 | 0.91 | 0.13 |
| Minimum scaffold area, mm2 | 7.37±1.55 | 7.04±1.80 | 7.12±1.65 | 5.99±1.41 | 7.51±2.13 | 0.41 | 0.88 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Mean scaffold diameter, mm | 3.35±0.34 | 3.32±0.42 | 3.37±0.38 | 3.37±0.42 | 3.66±0.48 | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.99 | 0.13 |
| Minimum scaffold diameter, mm | 3.13±0.34 | 3.11±0.40 | 3.13±0.38 | 3.10±0.38 | 3.39±0.43 | 0.83 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 0.09 |
| Mean luminal area, mm2 | 8.71±1.78 | 7.22±2.26 | 7.44±2.34 | 7.62±2.40 | 8.03±2.32 | 0.003 | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.68 |
| Minimum luminal area, mm2 | 7.11±1.53 | 4.81±2.21 | 5.22±2.16 | 4.43±1.53 | 4.55±1.59 | <0.0001 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 0.86 |
| Area obstruction, % | 18.2±6.3 | 19.9±8.9 | 19.5±11.9 | 18.1±7.9 | 25.4±6.46 | 0.38 | 0.88 | 0.67 | 0.03 |
| Healing score* | 197.8±5.7 | 0.1±0.4 | 0.01±0.1 | 0.0±0.0 | 0.0±0.0 | <0.0001 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.35 |
| Absolute late recoil, mm2 | - | 0.25±1.24 | −0.32±1.18 | −0.09±1.73 | −1.20±2.48 | - | 0.14 | 0.65 | 0.19 |
| Late recoil, % | - | 2.9±14.5 | −4.2±14.2 | −1.3±19.2 | −13.4±26.0 | - | 0.12 | 0.61 | 0.18 |
| Absorption, % | - | 34.3±11.1 | 52.3±11.9 | 82.3±10.0 | 95.4±3.8 | - | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Data are mean±standard deviation or number (%). *Healing score = (presence of intra-scaffold structure × 4) + (presence of both malapposed and uncovered struts × 3) + (presence of uncovered struts alone × 2) + (presence of malapposition alone × 1). ISA: incomplete strut apposition | |||||||||
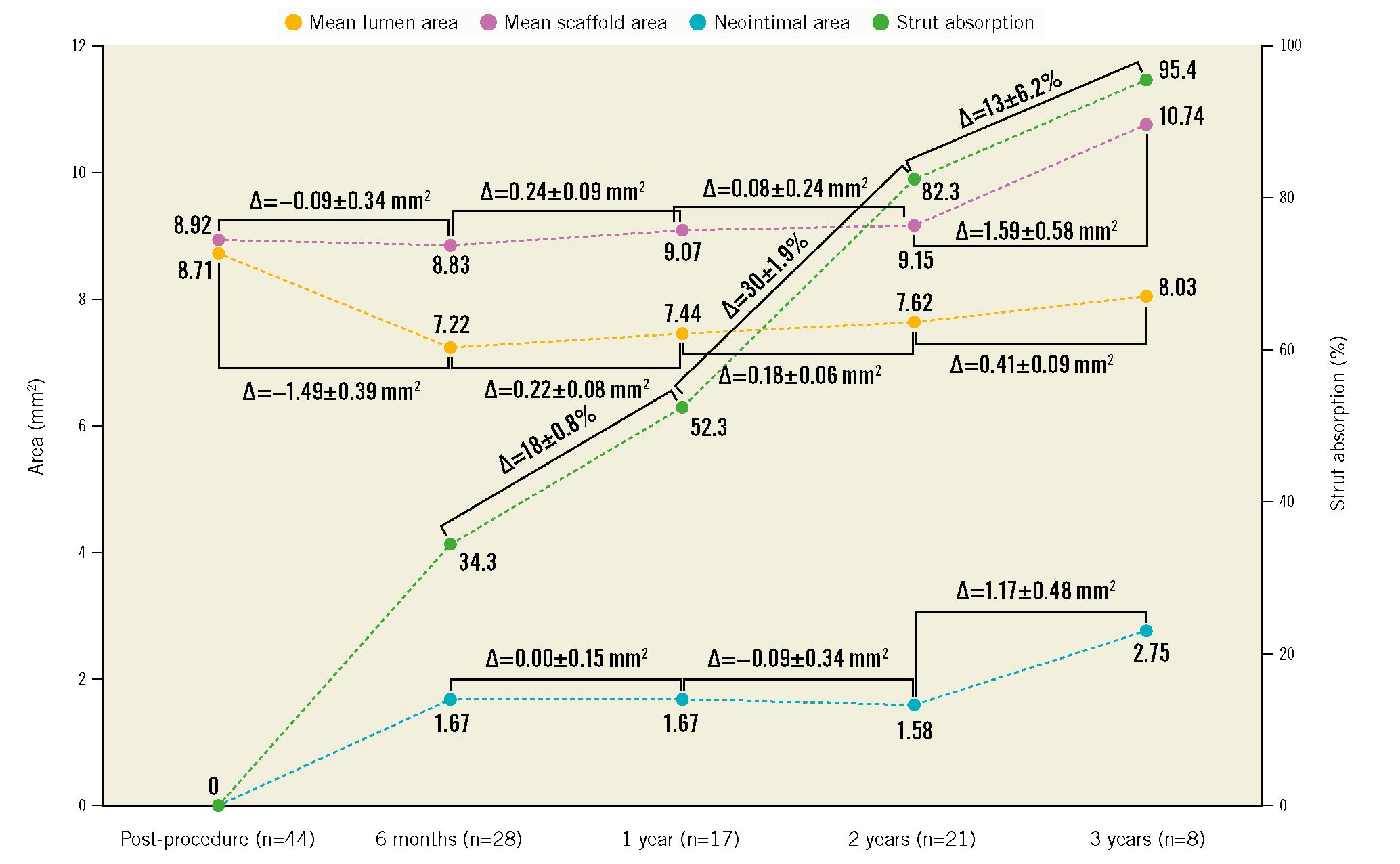
Figure 2. Serial OCT assessments up to 3-year follow-up. The orange line illustrates mean lumen area changes; the purple line illustrates mean scaffold area changes; the blue line illustrates neointimal area changes; the green line illustrates percentage of strut absorption changes.
Discussion
The major findings from this first-in-human study, in which the outcomes of a novel ultrathin-strut sirolimus-eluting IBS were evaluated up to 3 years with clinical and multimodality imaging, are as follows: 1) coronary implantation of the IBS was feasible in non-complex lesions, with 100% device, lesion and procedural success; 2) long-term safety and effectiveness in these non-complex lesions were demonstrated, with a 6.7% 3-year TLF rate, all due to CI-TLR, with no deaths, MIs or scaffold thromboses; 3) the QCA in-scaffold LLL up to 3 years was acceptable (mean 0.37 mm), with only 3 cases (6.7%) of in-segment binary restenosis; 4) strut coverage was rapid, and no strut fractures or late-acquired malapposition were observed; and 5) the rate of strut resorption steadily increased from 34.3% at 6 months to 95.4% at 3 years, without malapposition during the bioresorption process (Central illustration).
The present study is the first report of a novel IBS coronary artery implanted in a human. The iron content in a 3.0x18 mm IBS is 9 mg, which is equivalent to that in approximately 20 ml of blood or the weekly iron intake of an adult. Thus, IBS scaffold implantation should not induce iron overload. Compared with most bioabsorbable polymeric scaffolds, the strut thickness of the IBS is substantially less and the resorption rate is faster23. The thin iron struts may result in better tissue embedding and more rapid endothelialisation, which may prevent acute and acquired malapposition and late scaffold intraluminal dismantling23. Indeed, by OCT 99.8% and 100% of all struts were covered by 6 months and 12 months, respectively, and no cases of late malapposition of scaffold discontinuities were observed. It is possible that this rapid endothelialsation rate would enable shortening DAPT to 6 months, a hypothesis that requires testing in future studies. The scaffold also provided acceptable acute radial strength, and recoil up to 3 years was minimal. Angiographic vasoreactivity was evidenced as soon as 6 months after implantation and was stable over time.
As measured by QCA, the mean 0.33 mm in-scaffold LLL of the IBS at 6 months is higher than that of contemporary permanent metallic DES, such as EES (0.17 mm)24 and some polymeric BRS23, such as the Absorb BVS (0.16 mm)25 and DESolve (Elixir Medical; 0.20 mm)21, but lower than the third-generation magnesium BRS Magmaris (BIOTRONIK; 0.44 mm)11. However, the in-scaffold LLL of permanent DES and most polymeric and magnesium-based BRS continue to increase up to 3 years (ranging from 0.27 to 0.54 mm)11242526, similar to that of the IBS. Moreover, there was no significant increase in the IBS in-segment LLL up to 3 years, consistent with the constancy of the mean thickness of strut coverage and in-scaffold volumetric obstruction measured by OCT and IVUS during this period.
In the present study, we utilised a novel OCT-based semiquantitative method to analyse the IBS absorption process, based on experimental observations15. The zinc buffer layer on the scaffold backbone was specifically designed to prevent the IBS from degradation within 3 months after implantation. Thus, assuming minimal bioresorption within the first 3 months, it may be estimated that the absorption rate during follow-up was approximately 11.4% per month from 3 to 6 months, 3% per month from 6 months to 1 year, 2.5% per month from 1 to 2 years, and 1.1% per month from 2 to 3 years. Despite the ongoing absorption process up to 3 years, the mean lumen area, scaffold area and extent of neointimal hyperplasia were stable during this period. The mean scaffold area measured by OCT and IVUS showed no significant reduction from post-procedure to 3 years, indicating sufficient radial force of the scaffold to maintain its geometrical shape during the bioresorption process. The mean luminal area decreases from post-procedure to 6 months were mainly due to neointimal proliferation, while compensatory expansive remodelling was observed from 2 years to 3 years as observed in previous BRS studies12728. However, in selected cases the strut bioresorption rate may be too fast, resulting in early scaffold collapse, as seen in the second TLR case. To prevent such early strut biocorrosion, the IBS processing may be further improved by tightening control of the minimum thickness of the zinc layer and the maximum thickness of the polymer coating.
Compared to the other currently available bioabsorbable metal scaffold, the magnesium-based Magmaris, the IBS is thinner (70 μm vs 150 μm), and the Magmaris completely resorbs within 12 months, as compared with >3 years with the IBS, as demonstrated in the present study1729. The mean 6-month QCA in-scaffold LLL of the IBS from the present study (0.33 mm) was slightly less than that with the Magmaris (0.44 mm)11. In the BIOSOLVE-IV study, the 12-month TLF rate with the second-generation Magmaris (the DREAMS 2G) scaffold in 1,075 patients was low (4.3%, including 0.2% cardiac death, 1.1% TV-MI, and 3.9% TLR), with 0.5% definite or probable device thrombosis, and all events occurred between 6 and 95 days after PCI29. While the absence of any deaths, MIs or scaffold thromboses up to 3 years with the IBS is promising, the sample size is too small to draw meaningful comparisons. Moreover, a new third-generation Magmaris (DREAMS 3G) has reported even lower 6-month in-scaffold LLL (0.21 mm) and TLF rate at 6 months (0.9%) (Haude M. Safety and Clinical Performance of the Sirolimus Eluting Resorb-able Coronary Magnesium Scaffold System [DREAMS 3G] in the Treatment of Subjects With De Novo Lesions in Native Coronary Arteries - BIOMAG-I First-In-Human Trial. TCT 2022, Boston, MA, USA); longer-term follow-up results are warranted with this device to enable comparison with the IBS in comparable patients.
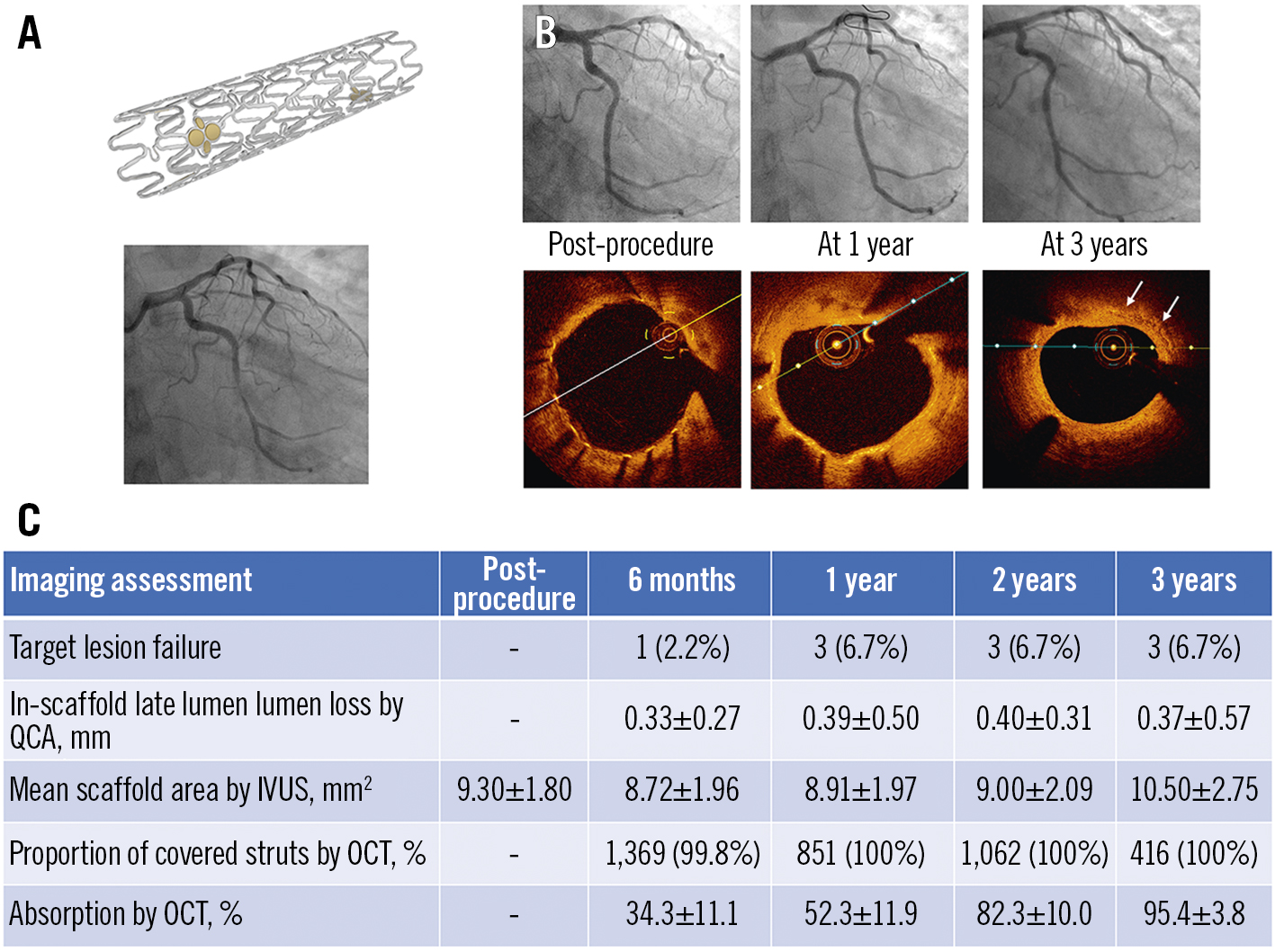
Central illustration. Clinical performance of the novel ultrathin sirolimus-eluting iron bioresorbable scaffold. The iron bioresorbable scaffold (A), a representative case with angiographic and OCT follow-up at 1 and 3 years (B), and selected study results from the first-in-human experience in its implant in 45 patients with a single non-complex coronary artery lesion (C). IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; OCT: optical coherence tomography; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography
Limitations
There are limitations to the present study. First, this was a small, single-arm, first-in-human study, with the results reflecting the performance of the IBS in a highly selected, non-complex patient and lesion population, which may have contributed to the low rate of observed TLR. Second, the absence of a concurrent control arm limits the interpretation of our results. Third, additional OCT analyses are needed to assess the properties of this novel device. In particular, the OCT semiquantitative method proposed in the present study to evaluate the rate of bioabsorption warrants further evaluation. Finally, the results are complete up to 3-year follow-up; longer-term clinical and imaging follow-up is warranted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of this new device.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the 3-year clinical outcomes and serial multimodality imaging assessments of the novel IBS have demonstrated the feasibility and potential safety and effectiveness of this device for the treatment of patients with non-complex coronary artery lesions.
Impact on daily practice
Three-year clinical follow-up results and serial multimodality imaging assessments of the novel IBS − an ultrathin (70 μm) sirolimus-eluting iron bioresorbable coronary scaffold consisting of a 53 μm nitriding iron backbone with a pure zinc submicron layer − in the treatment of patients with non-complex coronary lesions documented its feasibility and preliminary safety and efficacy. Late lumen loss was acceptable (mean 0.33 mm at 6 months and 0.37 mm at 3 years), and by 3 years the scaffold was 95.4% absorbed. A randomised trial with adequate statistical power is warranted to assess the clinical performance of IBS compared with contemporary metallic drug-eluting stents in patients with coronary artery disease.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the participating patients for their contributions to the trial. We also thank all the physicians and nurses who cared for these patients and all the clinical and research staff who assisted in the study.
Funding
The IBS-FIM trial was funded by Biotyx Medical, Shenzhen, People’s Republic of China. Biotyx Medical was involved in the study design, monitoring and data collection. The corresponding author directed the study, had full access to all the data and final responsibility for the data interpretation and decision to submit for publication. The funder had the right to anon-binding review of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
R. Gao has received institutional research grants from Biotyx Medical. G.W. Stone has received speaker honoraria from Medtronic, Pulnovo, Infraredx, and Abiomed; has served as a consultant to Valfix, TherOx, Robocath, HeartFlow, Ablative Solutions, Vectorious, Miracor Medical, Neovasc, Ancora, Elucid Bio, Occlutech, CorFlow, Apollo Therapeutics, Impulse Dynamics, CardioMech, Gore, Amgen, Adona Medical, and Millennia Biopharma; and has equity/options in Ancora, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, BioStar family of funds, SpectraWAVE, Orchestra BioMed, Aria, Cardiac Success, Valfix, and Xenter. G.W. Stone’s daughter is an employee at IQVIA. G.W. Stone’s employer, Mount Sinai Hospital, receives research support from Abbott, Abiomed, Bioventrix, Cardiovascular Systems, Inc., Philips, Biosense Webster, Inc., Shockwave Medical, Vascular Dynamics, Pulnovo Medical, and V-Wave Ltd. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

