We present an 85-year-old female patient in New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Class III, with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, who experienced recurrent valvular heart failure hospitalisations and cardiac decompensation due to severe, torrential tricuspid regurgitation (TR) with a large coaptation defect (grade 5/5, 16 mm gap) (Figure 1A, Moving image 1). She also exhibited typical flow reversal in the liver veins, recurrent pleural effusion, and severe peripheral oedema. Due to her advanced age, clinical condition, complex anatomy, and comorbidities, which resulted in a calculated Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) short-term risk score of 13% and a TRI-SCORE of 5/12 with a predicted in-hospital mortality of 14%, she was deemed unfit for conventional tricuspid valve surgery and ineligible for established transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) or transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR) procedures by our institution's interdisciplinary Heart Team.
After careful consideration, the patient and her medical team decided to explore compassionate treatment options. Authorisation was obtained from the higher federal competent authority, the Bundesinstitut für Arzneimittel und Medizinprodukte (BfArM), for the implantation of the novel cross-caval prosthesis known as UNICA (Innoventric), under the compassionate use program, per the German Medicinal Product Act, in June 2023. UNICA is a single-stent, double-valve, heterotopic, cross-caval prosthesis designed to address the consequences of severe TR. Over the past decade, four different heterotopic devices have been clinically utilised: TricValve (OrbusNeich), SAPIEN valve (Edwards Lifesciences), TRICENTO (New Valve Technology), and Trillium (Innoventric). While TRICENTO and Trillium eliminate backflow at the right atrial (RA) level, UNICA addresses backflow at both the RA-inferior vena cava (IVC) and RA-superior vena cava (SVC) junctions.
The central part of the UNICA stent is bare metal with a large IVC sealing skirt, allowing for potential future transseptal puncture and valve-in-valve procedures if necessary. To comprehensively understand the patient's anatomy and the complexity of the case, a full-cycle heart computed tomography and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction were performed (Figure 1B). A personalised 3D print of the superior vena cava (SVC), inferior vena cava (IVC), and right atrium was created to aid in procedural planning and training (Figure 1C). Figure 1D illustrates the key features of the UNICA device.
With the patient's informed consent, the procedure was conducted under general anaesthesia and full heparinisation with an activated clotting time exceeding 250 seconds. Under sonographic guidance, a jugular vein puncture was performed, followed by the insertion of a 9 Fr sheath and the placement of pigtail catheters in the SVC, RA, right ventricle, and pulmonary artery to obtain pressure and invasive haemodynamic measurements. A second pigtail catheter was inserted via a 6 Fr sheath in the left common femoral vein and placed in the IVC. A 6 Fr sheath was placed over the right common femoral vein, and a multipurpose catheter was used to cross the heart and position an Amplatz Super Stiff guidewire (Boston Scientific) in the SVC. Subsequently, a 24 Fr Gore DrySeal sheath (W. L. Gore & Associates) was placed in the right femoral vein The deployment catheter carrying the crimped UNICA device (Figure 1E) was introduced into the Gore sheath over the Amplatz Super Stiff wire in a cross-caval position.
To guide the procedure, 20 ml of contrast agent was injected through the 9 Fr jugular sheath and 40 ml of contrast agent through the pigtail in the IVC, aligning with the pre-interventional plan and fluoroscopic angulation derived from the computed tomography scan (Figure 1B). The self-expanding UNICA device was deployed from the delivery catheter under fluoroscopic guidance based on the placement of radio-opaque markers (Figure 1F). Device deployment was strictly fluoroscopy-guided, with careful attention to the radio-opaque IVC skirt marker placement in the IVC-RA landing zone. Adequate device stability was confirmed through a push-pull test, leading to immediate implantation success, improved cardiac pressures, a reduction in peak central venous pressure from 29 to 12 mmHg, and a mild improvement in cardiac output. Right atrial angiography confirmed effective sealing at the cavo-atrial inflow (Moving image 2). Hepatic vein flow reversal was no longer detectable on echocardiography. Adequate UNICA valve function was observed in transoesophageal echocardiography (Moving image 3, Moving image 4).
Following the successful procedure, the delivery device was retracted, and the puncture site in the right femoral vein was closed with a Z-suture. The entire procedure, from puncture to suture, took 45 minutes, with a 7-minute skin-to-skin time for valve deployment. The patient was then transferred to the intermediate care unit for 24 hours of observation. Subsequently, she was moved to a regular care ward, where she quickly mobilised and reported an overall sense of well-being, except for slight intermittent right shoulder pain. The patient was discharged three days later. Post-intervention, she continued oral anticoagulation therapy for 6 months, as she was already on anticoagulation due to atrial fibrillation. After a 60-day follow-up, the patient had not been re-hospitalised, experienced an improvement in quality of life and functional capacity, progressed to NYHA Class II, and reported reduced peripheral oedema while on stable diuretic therapy.
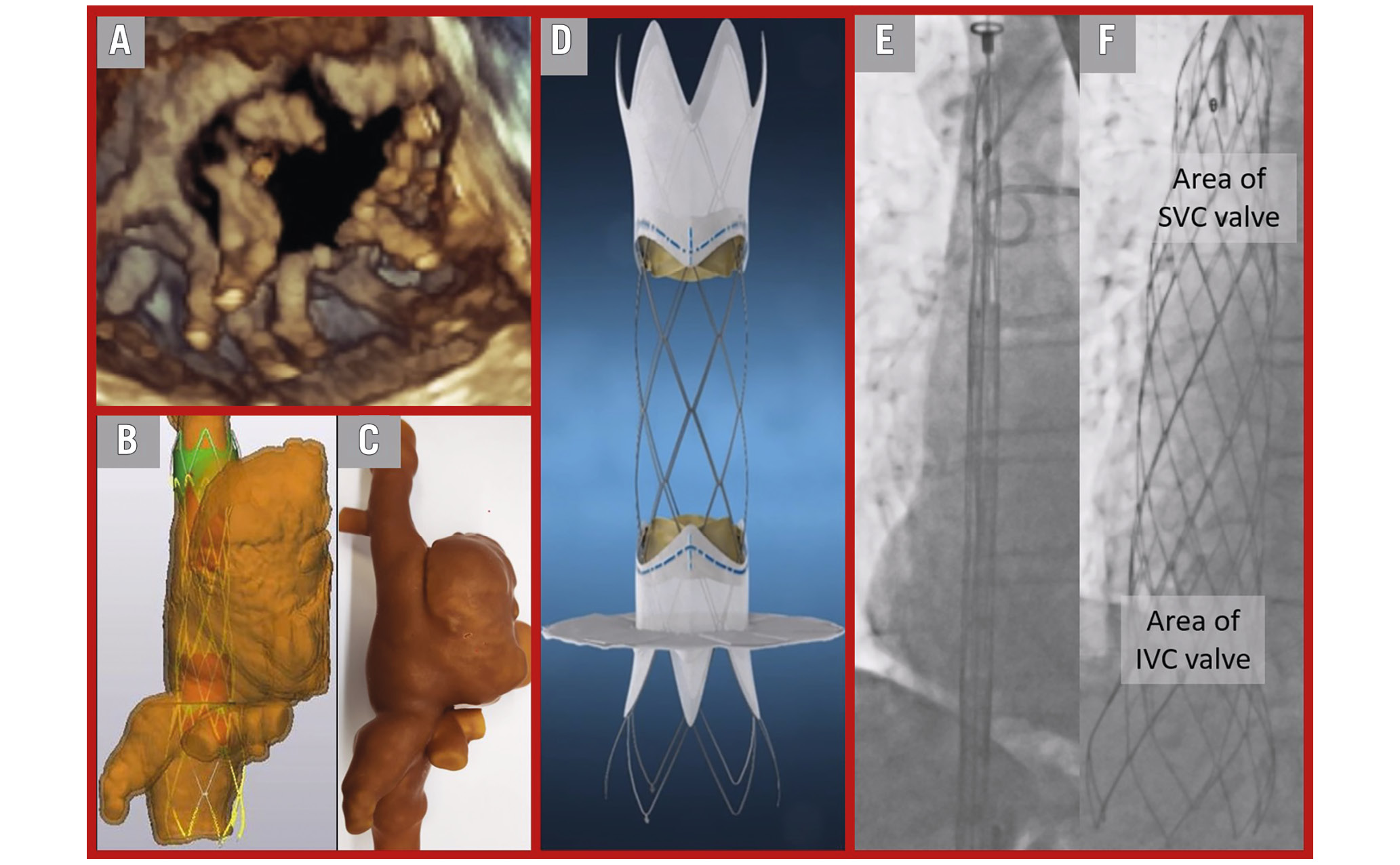
Figure 1. Stepwise approach to treatment of severe tricuspid insufficiency with the UNICA platform. A) 3D TOE reconstruction of a tricuspid valve showing a torrential defect. B) Computed tomography 3D reconstruction with a virtual UNICA device. C) Actual, personalised 3D print with the UNICA training device. D) Illustration of the UNICA device. E) Crimped UNICA device from IVC to SVC while generating the fluoroscopic roadmap angiography. F) Fully deployed UNICA device. 3D: three-dimensional; IVC: inferior vena cava; SVC: superior vena cava; TOE: transoesophageal echocardiography
Conflict of interest statement
M. Sherif reports being the principal investigator for Innoventric trials in valvular heart disease. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Preprocedural transoesophageal colour Doppler echocardiography of a tricuspid valve.
Moving image 2. Fluoroscopic result in right atrial angiography.
Moving image 3. Postprocedural transoesophageal echocardiography of the UNICA IVC valve.
Moving image 4. Postprocedural transoesophageal colour Doppler echocardiography of the UNICA IVC valve.

