
Balloon pulmonary angioplasty (BPA) is a developing method for the treatment of patients with inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH); however, the optimal technique of the procedure is still the subject of debate1.
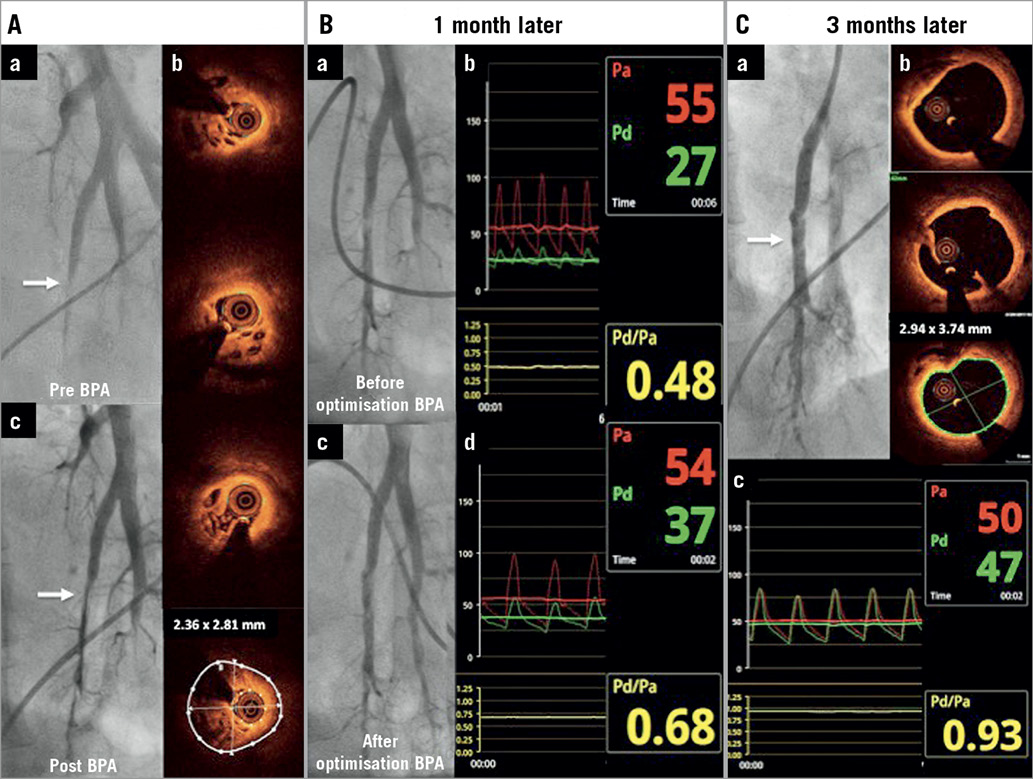
A 50-year-old female with non-operable peripheral type CTEPH (San Diego classification type 3) (Moving image 1, Moving image 2) with World Health Organization (WHO) class III dyspnoea and with a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) of 58 mmHg underwent a BPA session. The left A10 segmental artery was subtotally occluded (Panel Aa). Optical coherence tomography (OCT) (DragonFly™; St. Jude Medical, St. Paul, MN, USA) revealed intravascular colander-like structures (Panel Ab). Considering the very high mPAP, resulting in a high risk of post-reperfusion injury, a 2.0×20 mm angioplasty balloon was inflated (Panel Ac). One month later, remarkable dilation of the treated vessel was visible (Panel Ba). However, a significant pressure gradient through the treated lesion was revealed (Panel Bb). Hence, optimisation with a 3.5×20 mm balloon was performed and the peripheral pressure reached 37 mmHg (Panel Bc, Panel Bd). Three months later, the artery was significantly dilated, although no additional treatment was performed at the lesion (Panel Ca). OCT revealed positive remodelling of the artery, healed dissection and compressed mural lesions (Panel Cb, Moving image 3). Moreover, the pressure gradient across the lesion was eliminated (Panel Cc). After the next three BPA sessions, mPAP was reduced to 34 mmHg and no complications were observed.
A stepwise increase of perfusion pressure in the pulmonary artery distal to the occlusion site with partial detachment of the organised thrombi may be due to dilation of the pulmonary artery over time and positive remodelling of the vessel2. Thus, the immediate elimination of the pressure gradient may not be necessary for the long-term success of BPA, especially in patients with very high pulmonary pressure. Although imaging and physiological measures are generally known to be of value, this report shows how to incorporate them clinically for individual patient care. A multimodality approach to the treated lesions might be helpful in the proper planning and optimising of the procedure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
Moving image 1. Left pulmonary artery angiography.
Moving image 2. Right pulmonary artery angiography.
Moving image 3. Optical coherence tomography co-registration three months after balloon pulmonary angioplasty.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Left pulmonary artery angiography.
Moving image 2. Right pulmonary artery angiography.
Moving image 3. Optical coherence tomography co-registration three months after balloon pulmonary angioplasty.

