A 58-year-old man was admitted with an anterior myocardial infarction and cardiogenic shock. Severe lesions were found at the left anterior descending artery, the circumflex-marginal bifurcation, and the right coronary artery (chronically occluded) (Figure 1A-Figure 1C). Immediately after primary PCI, a second procedure was required due to stent thrombosis at the circumflex bifurcation previously treated. The overall duration of both procedures was 212 minutes (fluoroscopy: 71 minutes). Eighty-five cine runs were recorded, 47 in the right anterior oblique (RAO) view, 25-35º. The total skin dose was 5.2 gray, 2.5 of them in the same zone irradiated in RAO. After one month, the patient developed a skin lesion at the left scapular region. It progressed to a deep ulcer with bone exposure, needing plastic surgery two years later (Figure 1D-Figure 1I).
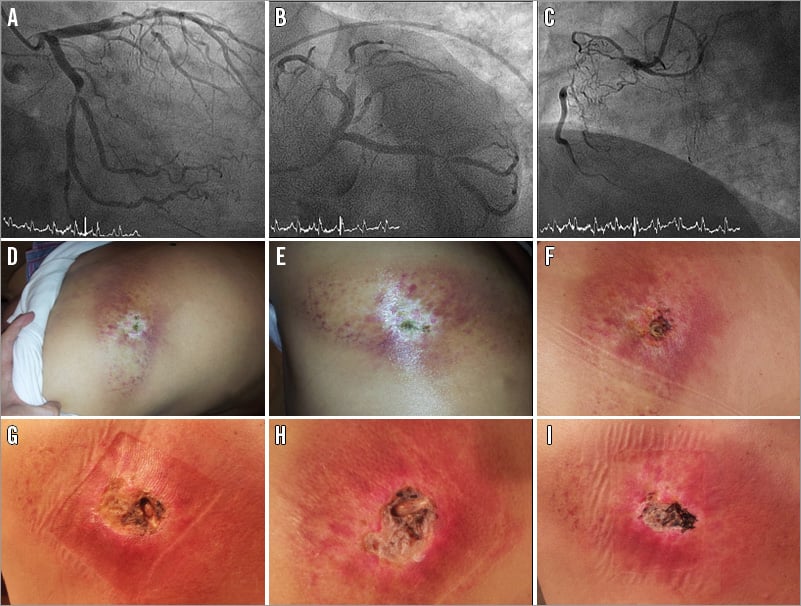
Figure 1. Coronary angiography and secondary skin lesions. A-C) Angiogram: three-vessel disease. D-I) Skin lesions: from slight erythema to a deep ulcer with bone exposure.
Cutaneous side effects are the main dose-dependent radiation consequences that are usually unrecognised, misdiagnosed, and under-reported. Their incidence is growing due to an increasing number of procedures and their complexity. For lengthy PCIs some measures should be implemented, namely: avoid high-intensity fluoroscopy mode, record more fluoroscopy images and fewer cine runs, minimise source-to-image distance, modify tube angle regularly and use fewer left anterior oblique angles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

