A 60-year-old man underwent sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) implantation (Figure 1A and Figure 1B). At two months (Figure 1C), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) images showed homogenous echolucent appearance within the stent, recognised as a “black-hole” phenomenon (Figure 1E)1. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the corresponding segment demonstrated a layered structure composed of thin inner layers with high-intensity signals and outer layers with low-intensity signals (Figure 1G). At eight months (Figure 1D), on the IVUS images, previous echolucent intraluminal tissue changed into isoechoic tissue (Figure 1F). OCT images demonstrated that inner layers increased in thickness and signal intensity, and that the intensity of the outer layers increased as well (Figure 1H).
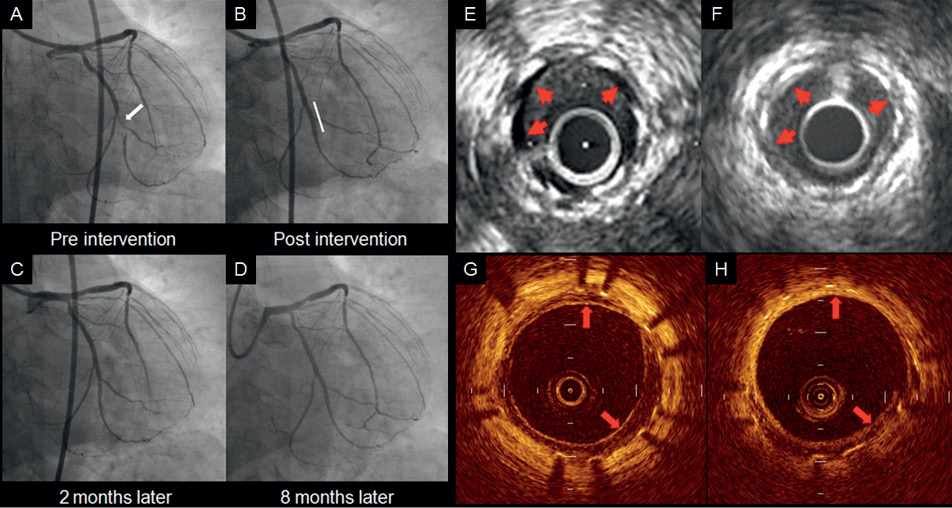
Figure 1. A) Coronary angiogram showed lesion of the left circumflex coronary artery (LCX). B) Post-intervention coronary angiogram (CAG) with implantation of sirolimus-eluting stent (SES) showed a good result. C) Two-month follow-up: CAG revealed no in-stent restenosis. D) Eight-month follow-up: CAG revealed no in-stent restenosis. E) Two-month follow-up: cross-sectional intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) image showed echolucent intraluminal tissue called “black hole” phenomenon. (red arrows). F) Eight-month follow-up: IVUS image demonstrated that echolucent intraluminal tissue changed into the isoechogenic neointimal formation. (red arrows). G) Two-month follow-up: cross-sectional OCT image showed a layered structure composed of thin inner layers with high-intensity signal and outer layers with low-intensity signal, corresponding to the “black hole” phenomenon by IVUS images. (red arrows). H) Eight-month follow-up: cross-sectional OCT image demonstrated that thin inner layers with high-intensity signals, seen at two-months follow-up, increased in thickness and signal intensity, and outer layers with low-intensity signals also increased in signal intensity. (red arrows).
The IVUS “black-hole” phenomenon is defined as a homogeneous black-appearing image inside of a stent typically after brachytherapy or DES implantation1. In this case, the IVUS black hole was visualised by OCT as a layered structure with inner high-intensity and outer low-intensity layers. Histologic assessment revealed a hypocellular matrix of proteoglycans or immature smooth muscle cells in the IVUS “black-hole” and in the OCT layered appearance following SES implantation1,2. Serial IVUS findings demonstrated that the “black-hole” phenomenon disappeared during follow-up, and that the serial OCT findings also revealed alteration of the layered appearance. These changes suggest that the hypocellular matrix was replaced by other neointimal components such as matured smooth muscle cells or collagen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Online data supplement
Moving image 1A. Two-month follow-up: IVUS image showed echolucent intraluminal tissue called the “black hole” phenomenon.
Moving image 1B. Eight-month follow-up: IVUS image demonstrated that echolucent intraluminal tissue changed into the isoechogenic neointimal formation.
Moving image 2A. Two-month follow-up: OCT image showed a layered structure composed of thin inner layers with high-intensity signals and outer layers with low-intensity signals, corresponding to the “black hole” phenomenon by IVUS images.
Moving image 2B. Eight-month follow-up: OCT image demonstrated that the thin inner layers with high-intensity signal, seen at two-month follow-up, increased in thickness and signal intensity, and the outer layers with low-intensity signal also increased in signal intensity.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1A. Two-month follow-up: IVUS image showed echolucent intraluminal tissue called the black hole phenomenon.video1A
Moving image 1B. Eight-month follow-up: IVUS image demonstrated that echolucent intraluminal tissue changed into the isoechogenic neointimal formation.
Moving image 2A. Two-month follow-up: OCT image showed a layered structure composed of thin inner layers with high-intensity signals and outer layers with low-intensity signals, corresponding to the black hole phenomenon by IVUS images.
Moving image 2B. Eight-month follow-up: OCT image demonstrated that the thin inner layers with high-intensity signal, seen at two-month follow-up, increased in thickness and signal intensity, and the outer layers with low-intensity signal also increased in signal intensity