We have read with interest the manuscript entitled “Clinical performance of drug-eluting stents with biodegradable polymeric coating: a meta-analysis and systematic review” by Ahmed et al1, recently published in “EuroIntervention”. Unfortunately, from our point of view, their meta-analysis presents several important methodological drawbacks.
First of all, Ahmed et al included in their meta-analysis the COSTAR II trial2; this study was set up to test a novel stent designed specifically for drug delivery via individual wells filled with a drug and an absorbable polymer in a structure of cobalt-chromium alloy. This structure is profoundly different in comparison to the other bioabsorbable polymer drug-eluting stents (BP-DES) studied in the six other randomised controlled trials (RCT) included in their review, where the entire stent surface is coated by a bioabsorbable polymer. Actually, the results of COSTAR II show a different trend in comparison to the other studies included in the review of Ahmed et al. The importance of avoiding “pooling apples and oranges” is a matter of fact when dealing with meta-analyses, in which the investigation of the sources of heterogeneity can be extremely difficult.
A second issue of concern is that at least six studies should be included in a meta-analysis to guarantee adequate reliability, according to the recommendations of the Cochrane Collaboration Group3 and the MOOSE Group4. However, only four studies with definite stent thrombosis (DST) data were included by Ahmed et al.
Finally, publication bias was not formally excluded by Ahmed et al1. An investigation of this bias can be performed using a graphical test, such as the “funnel plot”, created by plotting the estimated treatment effect against the study size5. Alternatively, the Egger test can quantitatively rule out the risk of such a bias6. In the meta-analysis by Ahmed et al no funnel plot or Egger test results were provided, even if these data could be easily calculated. In relation to target lesion revascularisation (TLR), the Egger test and the analysis of funnel plot strongly suggest publication bias. In relation to definite stent thrombosis (DST), the Egger test and the funnel plot cannot even be calculated due to the insufficient number of studies included.
As the COSTAR II trial population represents a consistent portion (31%) of the population meta-analysis of Ahmed et al1, we decided to recalculate the odds ratios relative to the target lesion revascularisation (TLR) and the DST endpoints after excluding the COSTAR II study. We observed similar rates of TLR and DST for BP-DES and permanent polymer DES (PP-DES), as already pointed out by Ahmed et al. However, we observed a high level of heterogeneity that prevented us from drawing any definite conclusions (Figure 1, Panel A and Figure 1, Panel B), especially in the case of the DST endpoint, with only three studies included and an I² (heterogeneity) of 42.8% (Figure 1, Panel B).
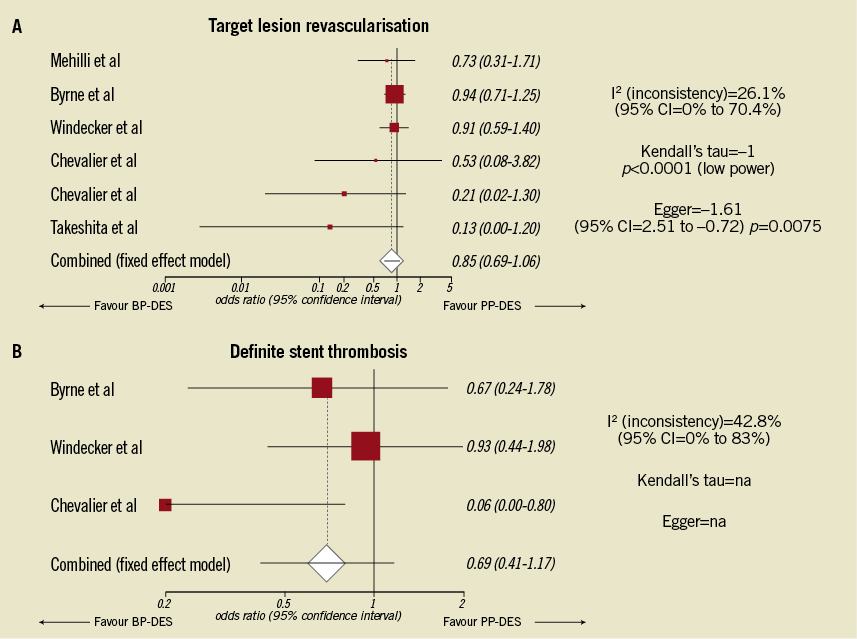
Figure 1. Meta-analysis forest plot showing odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals for the target vessel revascularisation (panel A) and definite stent thrombosis (panel B) endpoints after the exclusion of the COSTAR II study data. BP-DES: bio-absorbable polymer DES, PP-DES: permanent polymer DES
We think that, before performing a meta-analysis, the researchers should clearly have in mind the questions they are going to answer. If the question is whether BP-DES and PP-DES are different in terms of TLR, then the large and well-conducted LEADERS study7 is sufficient to meet this demand by itself. If the question whether BP-DES and PP-DES are different in terms of DST, unfortunately the meta-analysis of Ahmed et al does not produce sufficient evidences for a proper application.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest and did not receive grants or financial support from industry or from any other source to prepare this manuscript.

