Abstract
Background: Most studies dichotomise indices of coronary microvascular function to assess their prognostic values.
Aims: We aimed to investigate whether coronary flow reserve (CFR) and hyperaemic microvascular resistance (HMR) as continua predict major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), comprising all-cause death, myocardial infarction, revascularisation, and stroke in patients with ischaemia and non-obstructive coronary artery disease.
Methods: A total of 610 patients were included and followed up over a median of 8.0 years (199 individual MACE in 174 patients).
Results: Both CFR and HMR as continua predicted MACE with an odds ratio (OR) of 0.70 (per 1-unit increase, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.53, 0.92; p=0.01) and 1.63 (per 1 mmHg/cm/s, 95% CI: 1.20, 2.21; p=0.002), respectively. This relationship remained significant after adjustment for age and sex with an adjusted OR of 0.66 (per 1 unit increase, 95% CI: 0.49, 0.89; p=0.01) and 1.42 (per 1 mmHg/cm/s, 95% CI: 1.03, 1.94; p=0.03). HMR added prognostic value to CFR in predicting MACE (net reclassification index 0.17, 95% CI: 0.02, 0.31; p=0.03; integrated discrimination improvement 0.01, 95% CI: 0.0001, 0.02; p=0.046).
Conclusions: Both CFR and HMR as continuous variables predict future risk of MACE.
Introduction
Phenotypic identification of coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD) was aimed at characterising the underlying pathophysiology of patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD), which has been observed in 20-50% of patients referred for diagnostic coronary angiography1,2,3,4. Even though previous studies demonstrated the detrimental impact of CMD on quality of life and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE)3,5,6,7, physiological assessment of coronary microvascular function to diagnose CMD has not been standardised8.
Coronary flow augmentation in response to adenosine is a measure of endothelium-independent coronary microvascular function in the absence of epicardial CAD. Coronary flow reserve (CFR) <2.5 is used to diagnose endothelium-independent CMD and was associated with myocardial perfusion abnormality and a maladaptive physiological response during exercise9. The prognostic impact of endothelium-independent CMD on MACE has also been established10,11. However, similar to blood pressure, CFR, as a continuous variable, may be a predictor of MACE12,13.
Recently, hyperaemic microvascular resistance (HMR) was postulated to stratify patients with abnormal CFR into functional or structural CMD9,14. HMR >2.0 mmHg/cm/s was associated with attenuated improvement of myocardial perfusion post revascularisation15. However, it has not yet been determined whether higher residual microvascular resistance after adenosine infusion reflects structural microvascular disturbance or pharmacological resistance against adenosine. Higher HMR was associated with recurrent chest pain in patients with non-obstructive CAD16; however, there is a lack of evidence regarding the prognostic value of continuous or dichotomised HMR measurement on future adverse clinical outcomes.
This study aimed to investigate the individual prognostic values of both continuous and dichotomised HMR and CFR as measures of coronary microvascular function in predicting MACE. Also, we aimed to examine the incremental benefit of a combined HMR and CFR measurement strategy on the assessment of risk for MACE in patients with angina and/or ischaemia and non-obstructive CAD.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
In this observational cohort study, we enrolled patients who presented at the Mayo Clinic between 1992 and 2019 and who underwent comprehensive invasive coronary reactivity testing for evaluation of coronary microvascular function using CFR and HMR. Exclusion criteria are listed in Supplementary Appendix 1. This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the Mayo Clinic Institutional Review Board approved the study protocol. All patients provided written informed consent for participation in the current study.
CORONARY REACTIVITY TESTING
Coronary reactivity testing was performed to evaluate coronary microvascular function, as previously described17,18,19 (Supplementary Figure 1). In brief, patients without significant epicardial coronary artery stenosis (≤40% angiographic stenosis in major vessels) further proceeded with coronary reactivity testing. A Doppler guidewire (FloWire®; Volcano Therapeutics Inc, Rancho Cordova, CA, USA) was advanced within a coronary infusion catheter and positioned in the mid-left anterior descending artery (LAD). Incremental doses (18-72 μg) of adenosine were administered until maximal hyperaemia was achieved. Haemodynamic measurements were recorded at baseline resting and hyperaemic conditions. CFR was calculated as the ratio of hyperaemic flow velocity to baseline resting flow velocity. Lower CFR was defined as CFR <2.514,20. Adenosine non-responders were defined as those who had CFR during the first dose of adenosine equal to or higher than CFR during the higher dose of adenosine, indicating an abnormal dose-response relationship between the intracoronary dose of adenosine and the coronary flow velocity obtained21. Given that the difference between distal coronary pressure and aortic pressure was negligible under the condition that we only included patients with non-obstructive CAD, we calculated the ratio of the mean aortic pressure during hyperaemia and the hyperaemic flow velocity as the valid approximation of HMR (distal coronary pressure/hyperaemic flow velocity). Higher HMR was defined as HMR >2.0 mmHg/cm/s15,22 (or >2.5 mmHg/cm/s14,23). CMD was defined by the presence of lower CFR and/or higher HMR.
CLINICAL ASSESSMENT AND FOLLOW-UP
Clinical history, laboratory data, and current medications were collected from a detailed chart review by investigators (A. Ahmad and F. Sebaali) who were blinded to the results of coronary reactivity testing. Patients were followed up for MACE, including all-cause mortality, myocardial infarction, revascularisation for stable angina (percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting), and stroke, via a standardised questionnaire sent out at one time. Self-reported MACE on the questionnaire were independently adjudicated and confirmed in patients whose medical charts were available.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Detailed statistical methods are described in Supplementary Appendix 2.
Results
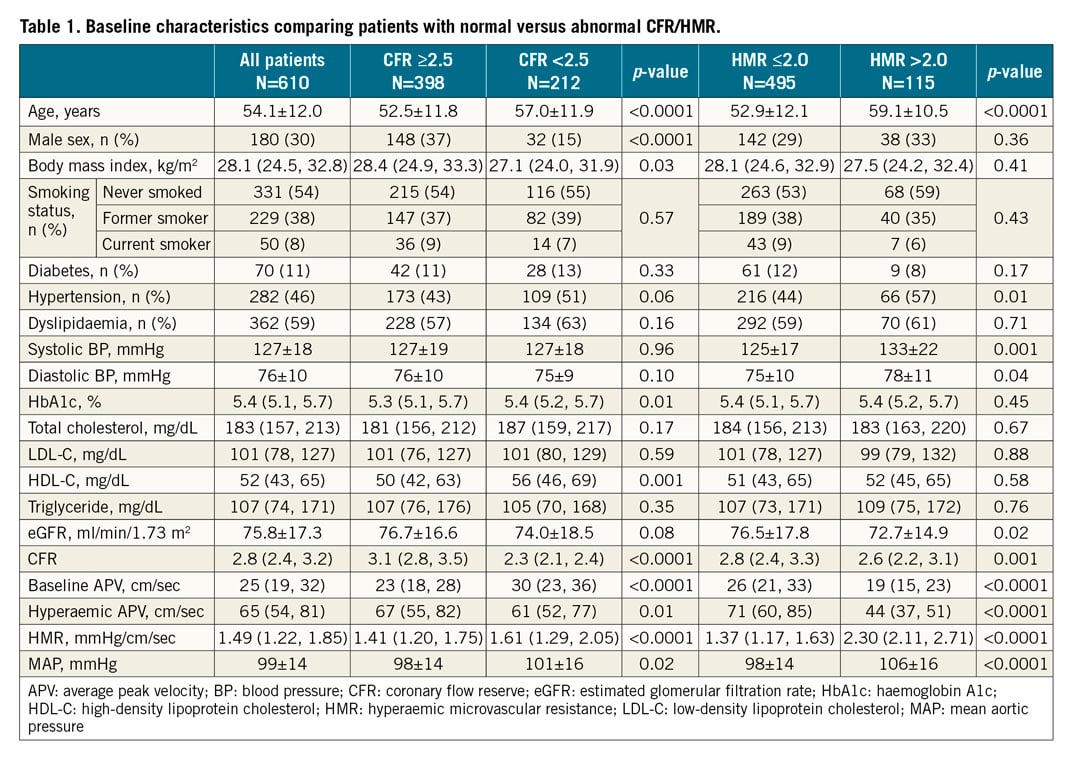
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
We enrolled 806 patients with available outcome data by questionnaire and excluded 196 patients because of the lack of CFR or HMR measurements, leaving a total of 610 patients in the analyses (Supplementary Figure 2). Distribution of CFR and HMR and the correlation between them are shown in Supplementary Figure 3. Baseline characteristics are summarised in Table 1 using CFR of 2.5 and HMR of 2.0 mmHg/cm/s as cut-offs. Of 610 patients (mean age 54.1±12.0 years, 30% male), 212 patients (35%) had lower CFR, 115 patients (19%) had higher HMR, and 57 patients (9%) had both lower CFR and higher HMR. Patients with lower CFR were older and more likely to be female. Patients with higher HMR were also older; however, the sex proportion was similar to patients with lower HMR. Furthermore, patients with higher HMR were more likely to have hypertension and impaired renal function. Comparison of baseline characteristics between patients with and without CMD (defined by the presence of CFR <2.5 and/or HMR >2.0) is summarised in Supplementary Table 1. Patients with CMD (N=270, 44%) were older and more likely to be female. Patients with CMD were more likely to have hypertension, higher HbA1c and total cholesterol levels, and decreased renal function.
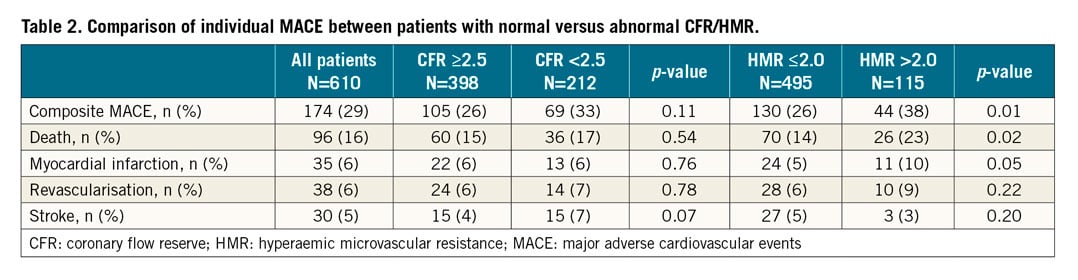
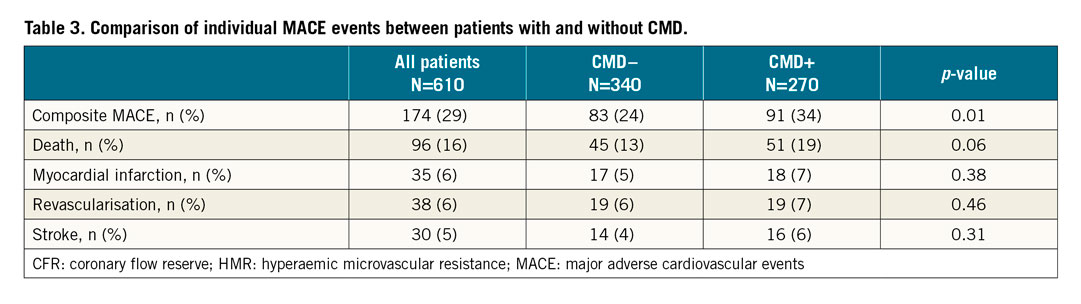
COMPOSITE MACE
The median duration from coronary reactivity testing to questionnaires filled or death was 8.0 (interquartile range, 4.7-13.4) years. Of 610 patients, 199 individual MACE events (96 all-cause death, 35 myocardial infarction, 38 revascularisations, and 30 strokes) were reported in 174 patients. We could adjudicate and confirm individual events in 160 patients (92%). The incidence of composite MACE was significantly higher in patients with higher HMR than in those with lower HMR (Table 2). Patients with CMD had a significantly higher incidence of composite MACE than those without (91 [34%] vs 83 [24%], p=0.01) (Table 3).
LOGISTIC REGRESSION ANALYSIS TO PREDICT COMPOSITE MACE
Logistic regression analysis was performed to estimate the prognostic value of individual CFR and HMR as both dichotomised and continuous variables and CMD for the risk of composite MACE. Higher HMR was significantly associated with increased risk of composite MACE as dichotomised and continuous variables, with odds ratios (OR) of 1.73 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.14, 2.66; p=0.01) and 1.63 (per 1 mmHg/cm/s, 95% CI: 1.20, 2.21; p=0.002), respectively (Figure 1A). Higher CFR was significantly associated with lower risk of composite MACE as a continuous variable, with an OR of 0.70 (per 1-unit increase, 95% CI: 0.53, 0.92; p=0.01) (Figure 1A). After adjustment for other covariates, higher HMR and CFR remained significantly associated with composite MACE as continuous variables (Figure 1B, Figure 1C). The discriminatory accuracy improved after adding HMR to CFR in predicting MACE (Supplementary Appendix 3, Supplementary Table 2). CMD was significantly associated with an increased risk of composite MACE (OR 1.57, 95% CI: 1.11, 2.24; p=0.01) and remained significant after adjustment for other covariates (Figure 1A-Figure 1C). When we divided patients into two groups by HMR of 2.5 mmHg/cm/s, HMR >2.5 (N=34) was significantly associated with an increased risk of composite MACE (OR 3.44, 95% CI: 1.71, 6.94; p=0.001; age- and sex-adjusted OR 3.08, 95% CI: 1.51, 6.28; p=0.002). Logistic regression analysis was also performed by dividing patients into four groups (Supplementary Appendix 4, Supplementary Figure 4A-Supplementary Figure 4D).
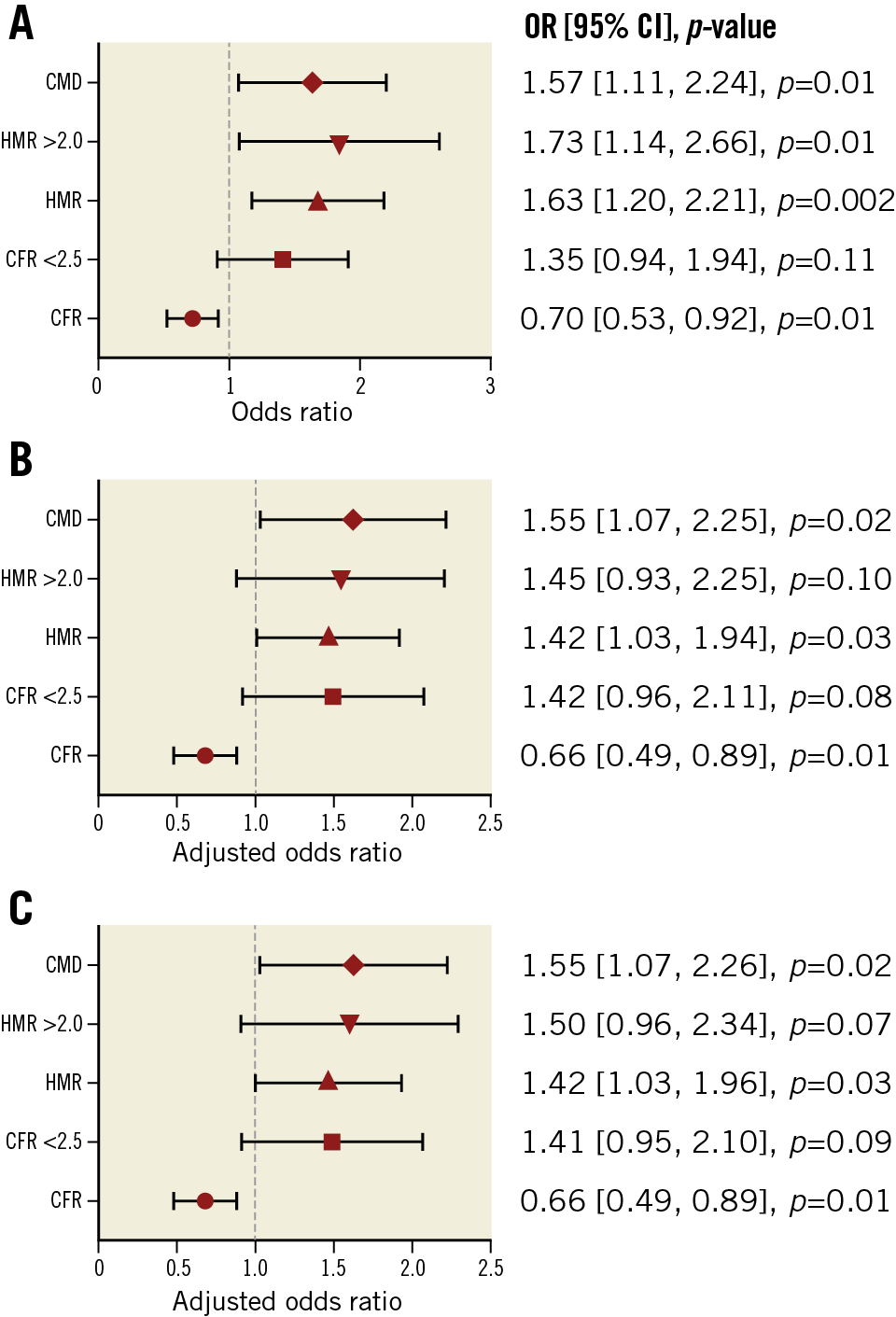
Figure 1. Association between CFR, HMR, and composite MACE. Forest plots showing the association between coronary physiologic parameters (CFR and HMR), CMD, and future risk of MACE. A) Univariate. B) Multivariate (model 1: age and sex). C) Multivariate (model 2: age, sex, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, body mass index, and estimated glomerular filtration rate). CFR: coronary flow reserve; CI: confidence interval; CMD: coronary microvascular dysfunction; HMR: hyperaemic microvascular resistance; MACE: major adverse cardiovascular events; OR: odds ratio
THE PREVALENCE OF ADENOSINE NON-RESPONDERS
The administered doses of adenosine by which maximum CFR was achieved were not different between patients with higher versus lower CFR or lower versus higher HMR (CFR 44±15 μg vs 46±15 μg, p=0.33; HMR 45±15 μg vs 44±16 μg, p=0.75). However, the prevalence of adenosine non-responders was significantly higher in patients with lower CFR than in those with higher CFR (49% vs 37%, p=0.02), whereas no significant difference was observed between patients with higher versus lower HMR (49% vs 41%, p=0.18) (Figure 2). Adenosine responders tended to have higher average peak velocity compared to adenosine non-responders at given doses of intracoronary adenosine (Supplementary Figure 5).
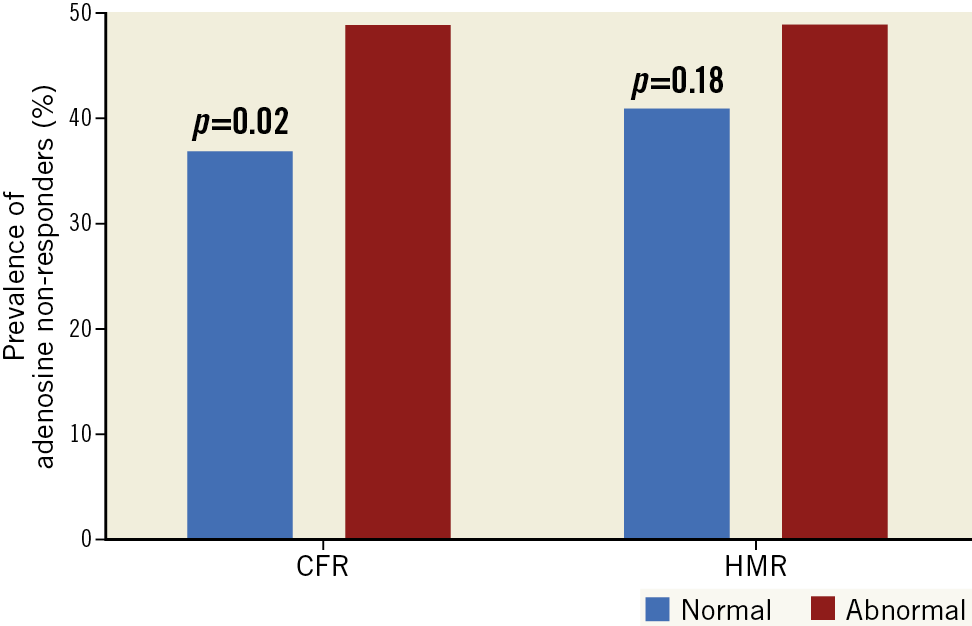
Figure 2. Adenosine responders versus non-responders. A) Bar graphs showing the prevalence of adenosine non-responders (%). B) Dose-response relationship between intracoronary adenosine and APV. APV: average peak velocity; CFR: coronary flow reserve; HMR: hyperaemic microvascular resistance
Discussion
This study demonstrated that both continuous CFR and HMR, measures of coronary microvascular function, are predictors of long-term MACE, even after adjustment for age and sex. Dichotomised CFR <2.5 and HMR >2.0 mmHg/cm/s were not significantly associated with an increased risk of MACE individually after adjustment for age and sex; however, CMD, defined as having abnormal CFR and/or abnormal HMR, remained significantly associated with an increased risk of MACE even after adjustment. Thus, the current study underscores the importance of a comprehensive assessment of coronary microvascular physiology in the cardiac catheterisation laboratory, including coronary vasomotor response and residual microvascular resistance in response to adenosine, to stratify long-term risk in patients presenting with angina and non-obstructive CAD.
CFR AND MACE
The myocardium maintains a high oxygen extraction rate at rest, and thus depends mainly on coronary blood flow to meet its oxygen demand24,25,26. Coronary blood flow is controlled by a complex interplay between epicardial and microvascular coronary arteries27. In the absence of obstructive epicardial artery disease, CFR mainly reflects the endothelium-independent microvascular vasomotor response to pharmacologically induced increased demand, usually by adenosine infusions20. CFR can be measured using different modalities, including the gold standard invasive assessment by intracoronary Doppler flow wire or using non-invasive assessment using positron emission tomography or transthoracic echocardiography. Decreased CFR is consistently associated with an increased risk of MACE28. However, most of the previous studies dichotomised CFR to assess its prognostic value. One observational study reported that invasively measured CFR <3.0 was associated with a sixfold increased risk of all-cause death compared to CFR ≥3.0 over a mean follow-up of 8.5 years29. Another study employing invasively measured CFR also reported that patients with CFR ≤2.0 had a threefold increased risk of MACE compared to those with CFR >2.0 over five years30. In this study, dichotomised invasively measured CFR <2.5 showed a borderline significant association with an increased risk of MACE after adjustment for age and sex, whereas continuous CFR predicted the risk of MACE even after adjustment for other covariates, consistent with the previous observation showing the significant association between continuous CFR measured by positron emission tomography and MACE13. These results highlight the prognostic value of CFR as a continuous variable in predicting MACE.
HMR AND MACE
In this study, we demonstrated that HMR as a continuous variable was associated with future risk of MACE. Further, HMR might have an additional prognostic value in predicting MACE over CFR. Patients with HMR ≥2.0 mmHg/cm/s are reported to have a higher plaque burden and more diffuse CAD than those with HMR <2.0 mmHg/cm/s22. Our patients with higher HMR were more likely to have poorly controlled hypertension, which is consistent with a previous report showing that patients with HMR ≥2.0 mmHg/cm/s had more established cardiovascular risk factors (uncontrolled hypertension and diabetes mellitus), indicating the existence of structural remodelling in the microvasculature4,14. In addition to the structural remodelling, patients with higher HMR were reported to have impaired endothelium-dependent systemic vasodilation with a resultant increase in systolic blood pressure during exercise, reflecting the systemic nature of microvascular disease and indicating that an exercise-induced increase in adenosine or shear stress does not translate into vasodilation14,31. Endogenous adenosine has been shown to contribute to exercise hyperaemia based on the linear correlation between interstitial adenosine and femoral artery blood flow during lower limb exercise, which reduces 20% by theophylline, an adenosine receptor antagonist32,33. In this study, we showed that adenosine non-responders were significantly more prevalent in patients with lower CFR than in those with higher CFR, indicating that an impaired adenosine signalling pathway might be involved in the reduction in vasomotor response to adenosine. Intact endothelium is not necessary for the response to adenosine in vitro; however, there are conflicting results demonstrating that the vasodilatory effect of adenosine is inhibited by a nitric oxide inhibitor in vivo in humans34. Given that impaired shear stress-induced vasodilation is related to higher microvascular resistance at hyperaemia, our previous observation showing that coronary microvascular endothelial dysfunction was associated with low shear stress, a higher plaque burden and unstable plaque features, may partly explain why these patients with higher HMR had a higher plaque burden35,36. Increased microvascular resistance is an independent predictor of plaque instability, which in turn is related to lower fractional flow reserve, reaffirming the presence of cross-talk between the coronary microvasculature and the epicardial vessels37. Though further studies are warranted to identify the link between microvascular resistance, its relationship with epicardial vessels, and worsening clinical outcomes38, our current data show that HMR as a continuous variable independently predicts future risk of MACE and mortality with the largest data set so far.
Limitations
Limitations of this study are discussed in detail in Supplementary Appendix 5. First, because of its retrospective observational cohort design, causal associations cannot be derived from the current study. Second, clinical outcomes were collected by questionnaires. Therefore, recall bias might have affected the results. Since coronary reactivity testing was part of clinical assessment to guide therapy, patients and attending physicians were not blinded to the measurements, potentially affecting medical therapies with resultant change in outcomes. Our lack of data regarding the specific causes of death limits our ability to assess the association between CMD and the specific cause of death meaningfully. Interestingly, reduction of CFR is reported to be independently associated with cardiovascular as well as cancer mortality39, which is consistent with our previous observation showing that abnormal peripheral microvascular vasomotor response is associated with increased risk of incident cardiovascular events and cancer40,41,42. Third, we used aortic pressure during hyperaemia for the approximation of coronary pressure to calculate HMR. Given that only patients with non-obstructive CAD were included in the study, the difference between aortic pressure and coronary pressure is negligible and calculation of HMR using mean aortic pressure is valid.
Conclusions
Lower CFR and higher HMR are associated with an increased risk of MACE as continuous variables. These findings highlight the concept that functional coronary vasomotor response to adenosine and residual hyperaemic microvascular resistance both affect long-term clinical outcomes. Future studies are required to validate these findings in different populations.
|
Impact on daily practice Dichotomising physiological parameters is useful to stratify patients by cut-offs; however, optimal cut-off values may differ depending on the population and the clinical outcomes being predicted. Both CFR and HMR as continuous variables predict MACE in patients with chest pain and non-obstructive CAD and can be used to evaluate the future risk of MACE in this population. |
Funding
This study was partly supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH grant numbers DK120292 and DK122734) and the Mayo Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Lerman reports consulting for Philips. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

