Abstract
Background: In-stent restenosis (ISR) is responsible for a rapid decline of vessel patency after stenting. To date, little is known about the role of in-stent neoatherosclerosis (NA) in stent failure in lower limb arteries.
Aims: This study aimed to determine the prevalence and patterns of in-stent NA in patients with symptomatic ISR of the lower extremity vasculature using intravascular optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging.
Methods: Patients underwent endovascular revascularisation for ISR including angiography and OCT imaging. NA was defined as the presence of at least 1 fibroatheroma or fibrocalcific plaque within the neointima of a stented segment.
Results: Using OCT, we imaged 24 symptomatic patients with lower extremity artery disease (LEAD), with a total of 30 ISR in the lower limbs, prior to their scheduled endovascular interventions. NA formation was observed in 23 (76.7%) lesions, while all stents with an implant duration >5 years (n=8) showed signs of NA. The time from stent implantation to OCT was significantly increased in lesions with NA (p=0.002). Lesions without NA had a significantly shorter duration from index procedure to OCT than those with ≥50 percent (n=9; p=0.003) or <50 percent (n=14; p=0.015) of frames exhibiting signs of NA. NA was predominantly characterised by fibroatheroma with thick fibrous caps with or without calcification.
Conclusions: In-stent NA is frequently identified by OCT imaging after endovascular therapy in lower limb arteries; this increased both in frequency and extent the longer the duration since implantation. Our findings indicate an active atherosclerotic process that may need tailored mitigation strategies.
Introduction
Lower extremity artery disease (LEAD) affects 12% to 20% of patients aged 60 years and older1. The global disease burden exceeds 200 million persons worldwide2. Currently, symptomatic LEAD is increasingly treated by endovascular approaches. Such procedures comprise a variety of techniques, including balloon dilatation (with or without drug elution), debulking and stent implantation. Treatment of superficial femoral artery (SFA) lesions is particularly challenging because of their length and mechanical vascular stress, often necessitating the implantation of self-expanding nitinol-based stents with (i.e., drug-eluting stent; DES) or without drug elution (i.e., bare metal stent; BMS). Favourable results after stenting were reported in shorter lesions (<150 mm) of the SFA or as a bail-out procedure in case of a flow-limiting dissection, early elastic recoil or significant residual stenosis after balloon angioplasty34.
However, late stent failure, defined as symptomatic in-stent restenosis (ISR) and/or stent thrombosis, still remains a major concern, with current generations of stents exhibiting restenosis rates of approximately 37% after 1 year56. One-quarter of patients suffering from restenosis 1 year after DES implantation present with chronic limb-threatening ischaemia (CLTI) indicating the clinical relevance of late stent failure in LEAD7. Stent thrombosis rates have recently been reported to range as high as 7.5% in the femoropopliteal vasculature8.
ISR often occurs soon after peripheral stent implantation, with a broad range of restenosis rates of 25-75% as early as 12 months after treatment depending on the type of intravascular procedure and patient subset910. To date, the failure modes responsible for this rapid decline of vessel patency are not fully understood.
Intravascular imaging techniques, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), allow the study of the nature of intimal changes after stent implantation in coronary arteries at a resolution surpassing all existing cardiovascular imaging modalities and offer important implications for interventional strategies1011. Since intravascular imaging is still novel in the treatment of the lower limb vasculature and, to date, the prevalence of atherosclerotic plaque formation after stent implantation, often referred to as neoatherosclerosis (NA), is not known, the aim of this study was to address this lack of knowledge by neointimal tissue analysis using OCT.
Methods
Study population
Consecutive patients >18 years of age presenting with symptomatic ISR, i.e., recurrent claudication and prior stent implantation in aorto-iliac and femoropopliteal segments, were prospectively enrolled into the study from June 2018 to February 2020, providing they consented to the study protocol. Haemodynamically relevant ISR was defined as a peak systolic velocity ratio of ≥2.4 using duplex ultrasound. Patients with occluded stents were excluded. Eligible patients were scheduled for angiography of the lower limb vasculature, which included OCT imaging. Clinical, procedural and imaging data were collected and entered into a central electronic database. The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained prior to the angiography, and the local ethics committee approved the study. Patients who presented with symptomatic ISR of the contralateral limb after their initial enrolment into this study were eligible for a second enrolment to assess ISR of the contralateral limb.
OCT image acquisition
Intravascular imaging was performed using angiography and a frequency-domain OCT system (OPTIS Imaging System; Abbott). A 6 Fr guiding catheter was placed proximal to the stenotic stent segment to provide sufficient flushing. An OCT catheter (Dragonfly Imaging Catheter; Abbott) was inserted distal to the stented vessel segment after the passage of a 0.014 inch guidewire. The entire length of the stenotic region within the stent was scanned using an automated OCT pullback at a speed of 20 mm/s. For image acquisition, flushing was obtained using iso-osmolar contrast media at a rate of 5-8 ml/s to allow for sufficient blood clearance. Intravascular imaging using OCT was performed in addition to the routine angioplasty procedures and did not affect decision-making for the treatment of the individual patient.
OCT image analysis
The target segment for OCT analysis of ISR was defined as the stented vessel segment exhibiting the minimal luminal diameter and the adjacent vascular segment ranging at least 20 mm proximally and distally. Raw data from OCT pullbacks were collected and analysed offline. Quantitative measurements were performed throughout the entire OCT pullback, using proprietary software (OPTIS Software equipped with AptiVue Software package E; Abbott Vascular). Each OCT sequence was assessed and analysed by independent investigators and evaluations were made by consensus. All cross-sectional images (frames) were screened for quality and excluded from the analysis if <270 degrees of the cross-sectional image were classified as visible and limited by residual blood or thrombus, or if a major side branch was present in the cross-section. Quantitative assessment included measurement of the target segment length and determination of luminal, stent and neointimal areas for each measured OCT frame. Struts were adjudicated as covered by neointimal tissue if they had a positive intimal thickness greater than the axial resolution of OCT (20 μm), as the significance of tissue coverage measuring less than the axial resolution of OCT remains questionable12. Struts were classified as malapposed if they were protruding into the lumen ≥200 μm, which represents the average strut thickness of the implanted stent types. According to previous reports, thrombus was defined as a mass attached to the luminal surface or floating within the lumen with either high backscattering, heterogeneous appearance and high attenuation (red blood cell-rich thrombus) or low backscattering, homogeneous appearance and low attenuation (white platelet-rich thrombus)12.
Definition of neoatherosclerosis
Neoatherosclerosis was defined as the presence of at least 1 fibroatheroma or fibrocalcific plaque within the neointima of a stented arterial segment. As previously defined, fibroatheromas were characterised by a signal-poor region within an atherosclerotic plaque showing high attenuation with diffuse borders and little or no backscattering13. A lateral plaque extension of at least 1 quadrant was required. Fibrocalcific plaques comprised a signal-poor or heterogeneous region with low attenuation and clearly visible demarcations of its borders. A fibroatheroma with a maximum cap thickness of 85 μm was defined as thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA). A ruptured plaque was defined as a plaque with a broken thin fibrous cap exhibiting a cavity, according to current criteria for plaque characterisation and adjunct thrombus formation12.
OCT plaque characterisation
We adjudicated the findings of the acquired OCT pullbacks based upon the definitions of NA and analysed all OCT segments on a frame level for the presence or absence of NA. In patients with NA, each plaque type was determined based on the definition of plaque types according to the current consensus standards for OCT analysis12. Discoveries of NA were summarised on frame and lesion levels. Binary classification was performed to differentiate between lesions with ≥50% or <50% of frames exhibiting signs of NA. The presence of NA was stratified according to the luminal diameter stenosis into 3 strata (25-49% stenosis; 50-74% stenosis; ≥75% stenosis).
Endpoints
The percentage of patients showing at least 1 NA plaque in ≥5 consecutive OCT frames were evaluated and compared on a lesion level. The type of angiogplasty used for the treatment of the lesions and the time frame from the index procedure to OCT imaging were also evaluated. These findings were adjudicated by 2 independent investigators. In case of divergent findings, a decision was made by consensus.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were summarised using frequencies and proportions and were compared using the chi-square test. Continuous data were summarised using mean±standard deviation or median (25th, 75th percentiles) and were compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Kruskal-Wallis test. The log-rank test was used to indicate differences among subgroups in time-to-event analyses which were illustrated using the Kaplan-Meier method. A Cox proportional hazards model was used to estimate hazard ratios between subgroups. All tests were 2-sided, and an alpha level of 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 28 (IBM).
Results
Patient characteristics
A total of 30 lesions in 24 patients presenting with symptomatic ISR and a history of prior stent implantation were included in this analysis. All patients presented with intermittent claudication (Rutherford stage 2/3; Fontaine class II). The median time from initial stent implantation to OCT imaging was 41 months (range: 5-125 months).
Patient characteristics are listed in Table 1. The average patient age was 70.5±9.4 years, and 63% of patients were male. Hypertension, a history or present status of smoking and hypercholesterolaemia were the most common cardiovascular risk factors, which were present in approximately 90% of patients. A total of 42% of patients were diabetic.
Table 1. Patient characteristics.
| No. of patients | 24 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean±SD | 70.5±9.4 | ||
| Sex | Male | 15/24 (63) | |
| Female | 9/24 (37) | ||
| Risk factors | |||
| Hypertension | 22/24 (92) | ||
| Hypercholesterolaemia | 20/24 (84) | ||
| Total cholesterol (mg/dl), mean±SD | 154.3±33.1 | ||
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dl), mean±SD | 59.2±18.4 | ||
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dl), mean±SD | 87.3±33.4 | ||
| Triglycerides (mg/dl), mean±SD | 141.6±108.9 | ||
| Patients on statin therapy | 22/24 (92) | ||
| Diabetes | 10/24 (42) | ||
| HbA1c (%), mean±SD | 6.6±0.9 | ||
| (Ex-)smoker | 21/24 (88) | ||
| Family history | 5/24 (21) | ||
| Comorbidities | CAD | 9/24 (38) | |
| Previous MI | 7/24 (29) | ||
| Carotid artery stenosis | 5/24 (21) | ||
| Symptoms | Intermittent claudication (Rutherford 2/3, Fontaine II) | 24/24 (100) | |
| Renal function | Estimated GFR (ml/min/1.73m2) mean±SD | 72.9±17.0 | |
| CKD stage | G1 | 3/24 (13) | |
| G2 | 16/24 (67) | ||
| G3 | 4/24 (17) | ||
| G4 | 1/24 (4) | ||
| Data are presented as n/N (%) unless otherwise stated. CAD: coronary artery disease; CKD: chronic kidney disease; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; MI: myocardial infarction; SD: standard deviation | |||
Lesion characteristics
Table 2 summarises the features of all ISR. The medial and distal SFA accounted for 90% of lesions evaluated in this study. Left and right lower extremities were equally affected. At the initial procedure, all but 1 lesion were treated using a self-expanding BMS, predominantly a Smart vascular stent system (Cordis; 73%) and an Everflex peripheral stent (Medtronic; 20%). In 1 lesion a single Supera vascular mimetic implant (Abbott) was implanted, and a single below-the-knee lesion was treated using a balloon-expandable DES (XIENCE; Abbott Vascular). The mean stent diameter was 6.0±0.7 mm and the mean stent length was 95.6±44.9 mm. Duplex ultrasound before OCT imaging showed a mean peak systolic velocity of 300.1±128.5 cm/s. The average ankle-brachial index (ABI) prior to the procedure was 0.67±0.21. Upon implementation of the Tosaka classification system14, 12 lesions (40%) were classified as class I (i.e., focal ISR) and 18 lesions (60%) as class II (i.e., diffuse ISR). After successful OCT acquisition, endovascular treatment was carried out in all lesions. Twenty-five lesions were treated by balloon angioplasty involving a paclitaxel-eluting balloon. Four lesions were treated with an endovascular procedure using a paclitaxel-eluting balloon and a self-expanding BMS. A single lesion was treated using plain balloon angioplasty and a self-expanding BMS.
Table 2. Lesion characteristics.
| No. of lesions | 30 | |
|---|---|---|
| Target lesion artery | External iliac artery | 1/30 (3) |
| Superficial femoral artery | 27/30 (90) | |
| Medial | 13/30 (43) | |
| Distal | 14/30 (47) | |
| Popliteal artery | 2/30 (7) | |
| Side | Left | 15/30 (50) |
| Right | 15/30 (50) | |
| Stent types | S.M.A.R.T. | 22/30 (73) |
| EverFlex | 6/30 (20) | |
| Supera | 1/30 (3) | |
| XIENCE | 1/30 (3) | |
| Stent diameter (mm), mean±SD | 6.0±0.7 | |
| Stent length (mm), mean±SD | 95.6±44.9 | |
| Ultrasound findings | Peak systolic velocity (cm/s), mean±SD | 300.1±128.5 |
| ABI before intervention, mean±SD | 0.67±0.21 | |
| ABI after intervention, mean±SD | 0.86±0.18 | |
| Tosaka classification | Class I | 12/30 (40) |
| Class II | 18/30 (60) | |
| Data are presented as n/N (%) unless otherwise stated. ABI: ankle-brachial index; SD: standard deviation | ||
Optical coherence tomography analysis
The findings of the OCT analysis are summarised in Table 3. The visibility of the vessel’s intimal layer by OCT near-infrared light intensity provided sufficient image quality for neointimal tissue analysis in our study, without the use of the distal occlusion technique. Light reflection and sunflower artefacts caused by stent struts were conducive to the differentiation of neointimal changes from the underlying plaque and could be detected in all lesions, as shown in the Central illustration. The mean luminal stenosis at the site of NA was 67.2±18.3%.
Neoatherosclerosis, defined as the presence of at least 1 fibroatheroma or fibrocalcific plaque identified in ≥5 consecutive frames within the neointima of a target segment, was observed in 23 (77%) of 30 lesions. A total of 2,527 of 7,907 analysed frames (27.2% [4.8-51.8]) showed the presence of NA. NA was identified at the site of the minimal luminal diameter (≥75% stenosis) in 15 (65%) of 23 lesions, while NA was located at sites with 50-74% luminal stenosis in 5 (22%) lesions and sites with 25-49% luminal stenosis in 3 (13%) lesions within the target segment.
The most frequently observed finding were fibroatheromas with thick fibrous caps, which were present in all lesions with NA (n=23). OCT revealed TCFA in 3 lesions, and 2 lesions showed signs of thrombus attached to the luminal surface of the plaque. Fibrocalcific plaques were present in 6 lesions. One lesion showed eruptive calcification gently protruding into the lumen with adjunct thrombus. Nine lesions revealed signal-rich regions with high backscattering, likely representing neointimal macrophage infiltration. In about half of the segments (48%), the lipid arc of the main NA plaque extended to 3 or even 4 quadrants (180-360 degrees). Representative OCT images are shown in the Central illustration. Intraobserver and interobserver variability for neointimal tissue characterisation was assessed in 50 randomly selected frames and showed high concordance (κ=0.92 and κ=0.85).
Table 3. Results of optical coherence tomography analysis.
| No. of lesions | 30 | |
|---|---|---|
| Target segment length (mm), mean±SD | 42.4±10.5 | |
| Stent area (mm2), mean±SD | 26.9±7.2 | |
| Minimal luminal area (mm2), mean±SD | 5.6±4.6 | |
| Neointimal area (mm2), mean±SD | 12.6±5.3 | |
| Coverage | Lesions with ≥1 frame with uncovered struts | 14/30 (47) |
| Frames with uncovered struts (%), median (IQR) | 0.0 (0.0-11.5) | |
| Apposition | Lesions with ≥1 frame with malapposed struts | 17/30 (57) |
| Frames with malapposed struts (%), median (IQR) | 12.4 (0.0-24.6) | |
| NA (lesions with ≥1 plaque) | 23/30 (77) | |
| Frames with NA (%), median (IQR) 27.2 (4.8-51.8) | ||
| Fibroatheroma | Thick-cap fibroatheroma | 23/30 (77) |
| Thin-cap fibroatheroma | 3/30 (10) | |
| Plaque rupture | 1/30 (3) | |
| Fibrocalcific plaque | 6/30 (20) | |
| Calcified nodule | 1/30 (3) | |
| Lipid arc in culprit plaque | <90° | 4/23 (17) |
| 90-179° | 8/23 (35) | |
| 180-269° | 6/23 (26) | |
| 270-360° | 5/23 (22) | |
| Data are presented as n/N (%) unless otherwise stated. IQR: interquartile range; NA: neoatherosclerosis; SD: standard deviation | ||
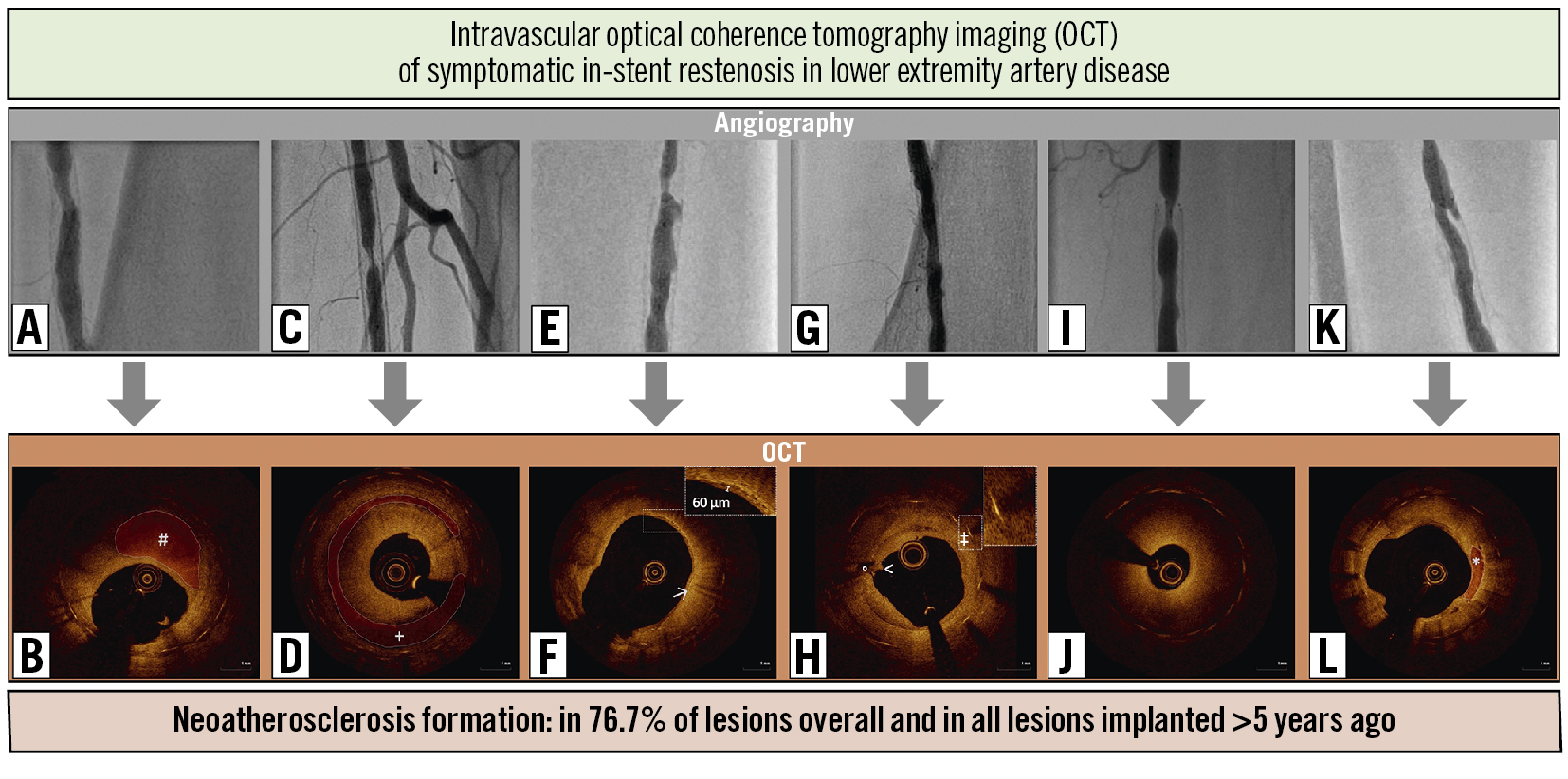
Central illustration. Combined assessment of symptomatic in-stent restenosis using angiography and intravascular optical coherence tomography imaging (OCT). A, C, E, G, I and K) Top row, angiography showing in-stent restenoses of the superficial femoral artery in 6 representative cases. B, D, F, H, J and L) Lower row, OCT revealing the corresponding neointimal changes. B) Homogeneous signal intensity adjacent to the luminal (#) surface with a signal-poor region in the deeper neointimal layer and a lateral extension of 2 quadrants, representing focal fibroatheroma with a thick fibrous cap. D) Circular fibroatheroma (+) extending to all 4 quadrants of the neointima. F) Fibroatheroma with a thin fibrous cap (thickness <85 µm) infiltrated by macrophages (highlighting high signal intensity with backscatter). H) Thrombus attached to the luminal (<) surface of a fibrocalcific plaque adjacent to an eruptive calcified nodule (°). Sunflower artefact (‡) caused by stent struts. J) Heterogenous tissue representing neointimal hyperplasia. L) Sharply delineated areas of reduced signal intensity with clear borders representing fibrocalcific plaque (*).
Time dependence of neoatherosclerosis
NA was present in all lesions (n=8) analysed >5 years after the index procedure. The results were stratified according to the presence (n=23) or absence (n=7) of at least 1 neoatherosclerotic plaque in the stented segment, and the time from the index procedure to OCT was significantly increased in lesions with NA (p=0.002) (Figure 1A). Lesions without NA (n=7) had a significantly shorter duration from the index procedure to OCT acquisition than both those with ≥50 percent (n=9; hazard ratio [HR] 0.20, 95% confidence interval [95% CI]: 0.07-0.58; p=0.003) or <50 percent (n=14; HR 0.29, 95% CI: 0.11-0.78; p=0.015) of frames exhibiting signs of NA (Figure 1B).
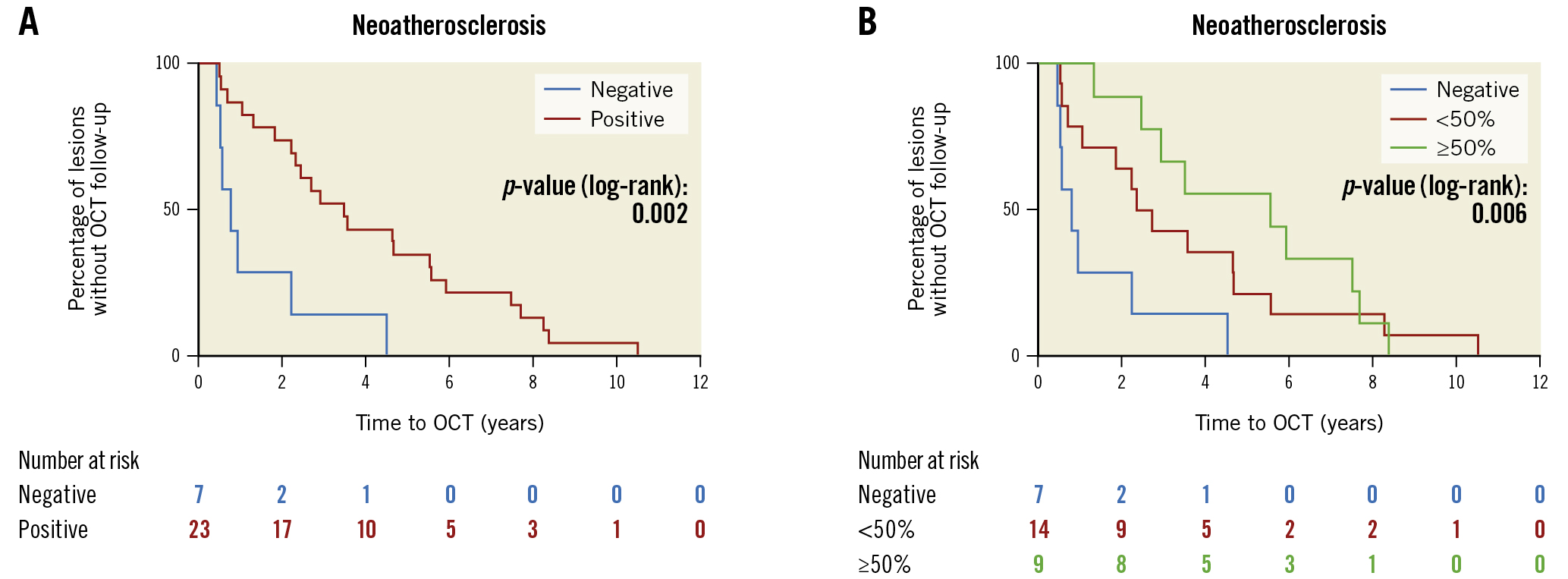
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimators representing the percentage of lesions without OCT follow-up. A) Time from index procedure to OCT was significantly increased in lesions with NA (p=0.002). B) Lesions without NA (n=7) had both a significantly shorter duration from index procedure to OCT acquisition than those with ≥50 percent (n=9; p=0.003) or <50 percent (n=14; p=0.015) of frames exhibiting signs of NA. NA: neoatherosclerosis; OCT: optical coherence tomography
Neoatherosclerosis following DEB treatment
A total of 18 (60%) lesions were treated with a drug-eluting balloon (DEB) between stent implantation and OCT imaging. No relationship was found between the presence of NA and the previous use of DEB (DEB vs no DEB: 83.3% vs 66.7%; p=0.290) (Figure 2A). NA was identified in all lesions that had been treated at least twice with a DEB (n=6). In lesions undergoing DEB treatment, there was neither a significant difference in the percentage of lesions with NA when stratified into lesions with a history of one versus more than one angioplasty involving a DEB within the target stent segment (75.0% vs 100.0%; p=0.180), nor after one or multiple DEB, compared to lesions without a history of DEB treatment (75.0% vs 66.7%; p=0.653; 100.0% vs 66.7%; p=0.109) (Figure 2B).
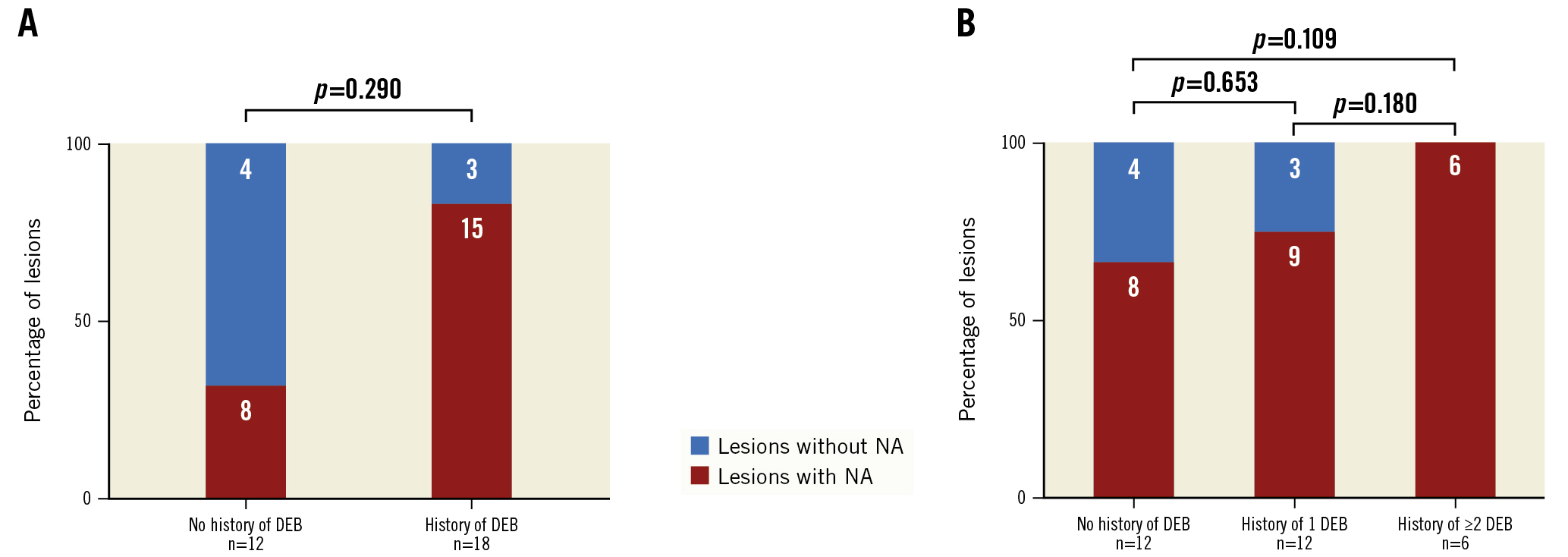
Figure 2. Neoatherosclerosis following DEB treatment A) Percentage of segments with at least 1 NA plaque in patients with (n=18) or without (n=12) history of peripheral intervention involving a DEB (history of DEB). B) Percentage of segments with at least 1 NA plaque further stratified into patients with history of one (n=12) or more than one (n=6) peripheral intervention involving a DEB (history of DEB). DEB: drug-eluting balloon; NA: neoatherosclerosis
Discussion
The major findings of this OCT study in patients with femoropopliteal LEAD with ISR are as follows:
- (i) Neoatherosclerosis is evident and commonly distinct within the lower limb vasculature after stent implantation, accounting for more than three-quarters of all lesions.
- (ii) The formation of NA is associated with the length of time since stent implantation. Different plaques can be simultaneously characterised within the same lesion while fibroatheromas with thick caps are the predominant type of ISR within the femoropopliteal vasculature.
- (iii) Signal-rich regions, likely implicating neointimal macrophage/foam cell infiltration, were detected as an important bystander of NA.
The pathology of neoatherosclerosis in the lower limb vasculature
Our study represents the first report on employing intravascular OCT imaging to assess NA in a dedicated patient cohort with symptomatic ISR of the lower limb vasculature. Histologic correlation studies in stented coronary arteries have shown a reliable correlation of neointimal OCT patterns with specific histologic intimal features in restenotic lesions after stenting, which allow the differential diagnosis of neointimal changes15. However, reports about NA in patients with LEAD are still sparse16. Reduced neointimal proliferation was reported by Kozuki et al using frequency-domain OCT imaging 8 months after paclitaxel-coated nitinol stent implantation into the SFA. Conversely, delayed arterial healing consisting of peri-strut low-intensity areas and macrophage accumulation was greater when compared with BMS17.
Tekieli et al reported on the in-stent neoatherosclerotic progression of a thin-cap fibroatheroma using intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) virtual histology imaging in a first-generation (single-layer) carotid stent, which was treated with the use of a MicroNet-covered stent (CGuard, InspireMD)18. Imaging by OCT provided better visualisation of plaque, calcification and stent struts in LEAD, when compared with IVUS, in a study reported by Pavillard et al19, while Eberhardt et al described underestimated plaque area measurements using OCT imaging, when compared to IVUS, owing to a limited penetration depth of first-generation time-domain OCT devices20.
To overcome the limitations of qualitative visual interpretation of plaque morphology related to the 10x lower resolution of IVUS images, several post-processing methods for computer-assisted tissue characterisation have been developed. In a seminal study, Kawasaki et al compared the diagnostic accuracy of OCT, integrated backscatter IVUS, and conventional IVUS for tissue characterisation of coronary plaques in grossly diseased coronary arterial sites. They compared OCT and IVUS images with histology of 42 coronary arteries from 17 cadavers. In this analysis, OCT showed the best potential for tissue characterisation of coronary plaques, while integrated backscatter IVUS better identified fibrous lesions and lipid pools when compared with conventional IVUS21.
We detected atherosclerotic changes within the neointima of ISR in 77% of all lesions. When compared to ISR in other vascular beds, the rate of NA in our study was higher than that which was reported from coronary ISR, ranging between 38-65% depending on stent types, as reported by Song et al22. The reasons for an overall higher rate of NA observed in our study, as compared to previous reports from coronary ISR, are yet unknown. Atherosclerotic processes are difficult to compare among different vascular beds as the use of different types of stent implants and variances in haemodynamics impair direct comparison. However, we observed comparably larger chronic plaques and a low rate of unstable inflammatory plaques, such as TCFA or ruptured plaques, in the lower limb vasculature.
The predominant plaque types identified in our study were fibroatheromas with thick fibrous caps exhibiting a necrotic core. Fibroatheromas frequently showed spotty or sheath-like calcifications mainly localised in the peri-strut regions, as reported from neointimal plaques in histologic studies in first- or second-generation DES and bare metal stents in the coronary arteries23. The development of a necrotic core is attributed to apoptotic cell death of foamy macrophages24. Unlike native disease, necrotic core formation in NA is thought to occur from macrophage apoptosis in the absence of a lipid pool, as the necrotic core is typically found within clusters of macrophage foam cells in the peri-strut regions or near the luminal surface25.
Time dependence and differential diagnosis of neoatherosclerosis
Lesions exhibiting NA, as compared to those without NA, were characterised by a longer duration from stent implantation, emphasising a time-dependent nature of in-stent NA in LEAD of the lower limb. Similar to previous reports about NA in coronary artery disease (CAD), we observed the presence of plaque formation within months to years after stent placement26.
A differential diagnosis between NA and thrombus formation may sometimes be challenging and may also have affected the rate of NA detected in our study. Homogeneous OCT patterns correlated not only with smooth muscle cells in a proteoglycan/collagen matrix but also, although less often, with organised thrombus in 9% of cases in a coronary histologic correlation study by Lutter et al15. Thus, we rated well-classified patterns, like tissue coverage with an irregular surface or an intraluminal protruding mass, as indicative of thrombus formation in our analysis, but cannot discard the possibility of underestimation of thrombus formation since we did not have histologic evidence12.
Signal-rich regions with high light attenuation and backscattering within the neointimal tissue were mainly localised in the peri-strut region or adjacent to the luminal surface, as shown in the Central illustration. We characterised those regions as indicative of neointimal foam cell infiltration, as previously reported from early stages of NA in coronary arteries, and rated those findings as an important bystander of NA26. Conversely, Phipps et al reported that bright spots on OCT correlated with a variety of plaque components that caused sharp changes in the refraction index from a histologic correlation study and were not specific to macrophage infiltration27. However, those signal-rich regions were neither evaluated in neointimal tissue nor in peripheral vessels.
Association with drug elution
Selected DES that are available for femoropopliteal artery disease have demonstrated better long-term patency when compared with BMS and plain balloon angioplasty2829. Different from DES, the usage of DEB represents a stent-free drug-eluting technology that has shown to effectively reduce neointimal proliferation30.
In our study, we included only 1 patient with an everolimus-eluting stent (in a below-the-knee lesion), while prior paclitaxel-eluting balloon treatment accounted for 57% of all lesions (n=17), and 40% (n=12) had not been previously treated using a drug-eluting device. In the latter, the rate of NA was numerically lower as compared to lesions previously treated with DEB. However, our data showed no relationship between NA and the use of DEB.
While intravascular imaging proved helpful to better characterise different patterns of in-stent restenosis in our study, further understanding of its prognostic and therapeutic consequences in LEAD is warranted.
Since the perception of NA in LEAD is still novel, a few studies have already been dedicated to the therapeutic implications of NA in coronary restenosis. Recent reports have proposed differential interventional strategies for the treatment of NA in CAD employing rotational atherectomy and intravascular lithotripsy31. Others have reported a correlation between in-stent restenosis and the absence of previous treatment with statins, implicating an impact of improved LDL lowering32.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. Firstly, this study was a single-centre study with a limited sample size. Secondly, we did not evaluate the clinical outcomes of patients after treatment for ISR. Therefore, we were not able to correlate our imaging findings to clinical limb-specific events in the longer-term follow-up. Thirdly, despite its high axial resolution, OCT has some inherent limitations in plaque visualisation and is not able to show all aspects of plaque pathology, as confirmed by human autopsy studies. Its application in LEAD is still novel and requires further validation including histologic correlation.
Conclusions
In-stent NA was frequently observed in ISR of the lower limb and increased both in frequency and extent with longer-term implantation, as identified using OCT. Fibroatheromas with or without calcification were the predominant plaque type. The identification of OCT patterns indicating NA in the aftermath of lower limb stent implantation might contribute to the development of tailored mitigation strategies. Therefore, future studies with larger cohorts and histologic correlation are warranted.
Impact on daily practice
In-stent restenosis (ISR) is responsible for a rapid decline in vessel patency after stenting, and little is known about the role of in-stent neoatherosclerosis (NA) for stent failure in patients with lower extremity artery disease. In our study, intravascular imaging using optical coherence tomography (OCT) proved to be a helpful tool in shedding light onto the nature of ISR with NA formation and predominantly thick-cap fibroatheroma in 23 (76.7%) lesions, especially for ISR occurring late after implantation. Further studies with larger cohorts and histologic correlation of OCT-findings are needed, possibly implementing tailored mitigation strategies of in-stent NA in LEAD.
Funding
The study was supported by a research grant from Abbott Medical, Germany.
Conflict of interest statement
T. Koppara received research grants and speaker honoraria from Abbott Medical, Germany. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.

