Abstract
Aims: The objective of this study was to evaluate the outcomes and identify the risk factors of in-hospital mortality among elderly patients undergoing PCI in Thailand.
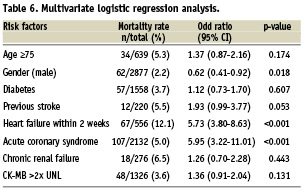
Methods and results: Included in this study were 4,156 consecutive patients (comprising 639 elderly [age ≥75 years] and 3,517 non-elderly [age <75 years]) undergoing PCI between May 2006 and October 2007. The success rate of PCI was less favourable among elderly compared to the non-elderly patients (91.2% vs. 87.5%; p=0.003). Elderly patients had higher rate of post PCI renal failure (3.9% vs. 1.8%; p=0.001), Q-wave myocardial infarction (3.0 vs. 1.4%, p=0.003), and unadjusted in-hospital mortality (5.3% vs. 2.4%, p≤0.001), compared with non-elderly patients. After adjustment for baseline variables, acute coronary syndrome and heart failure were the two variables most associated with increased mortality (OR=5.95, 95% CI=3.22-11.01), p<0.001 and OR=5.73,95% CI=3.80-8.63), p<0.001, respectively). According to the multivariate analysis, age was not significantly related with increased mortality (OR=1.37, 95% CI=0.87-2.16, p=0.174).
Conclusions: Our study highlights the safety and effectiveness of PCI in elderly patients since advanced age is not a predictor of in-hospital mortality.
Introduction
Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in elderly patients and represents a high cost to the healthcare system.1 The emergence of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for the treatment of coronary artery disease makes it the dominant revascularisation procedure in today’s cardiology practice. The data regarding the beneficial effect of PCI among the elderly, however, is limited because elderly patients are usually excluded from clinical trials.2,3 Previous studies showed that PCI among elderly patients was associated with more frequent procedural complications and less successful outcomes.4 Recently, however, PCI in the elderly has had more acceptable short-term outcomes.5 In order to guide today’s practice, evidence on the current effectiveness and safety of PCI among elderly patients is needed.
The Committee of the Thai Heart Association developed a percutaneous coronary intervention registry that includes all patients undergoing PCI in Thailand. This prospective registry provides an opportunity to evaluate the outcomes of PCI among unselected elderly patients. The objective of this study was to evaluate the safety and hospital outcomes of PCI among patients over 75 years of age and to compare the outcomes among younger patients.
Material and methods
The Thai Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Registry (TPCIR) is a clinical database, which includes all of the patients undergoing PCI between May 2006 and October 2007 at 27 cardiac centres in Thailand. Data collection was conducted by trained nurses and re-checked by the principle investigators at each site. Web-based, double data entry was used to prevent data entry error. Data were then sent to the data management centre at the Thai Heart Association Research Centre. Each electronic submission was re-examined by the researchers to ascertain completeness and accuracy.
The TPCIR includes information on: age, sex, clinical indications for PCI, the presence or absence of heart failure, coronary risk factors, kidney disease, cerebrovascular disease, coronary artery bypass surgery, coronary anatomy, type of stent, and in-hospital outcomes.
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient before performing the PCI procedure, and the research protocol was approved by each local institutional ethics committee.
Definitions
Death was defined as all causes of mortality during hospitalisation. Procedural success was defined as <50% residual stenosis with normal coronary flow. In-hospital adverse events included stroke (new neurological deficit occurring after the procedure and lasting >24 hours), renal failure (an increase in creatinine >2 mg/dL), myocardial infarction (CK-MB >2× upper normal limit), or access site complications e.g., haematoma, pseudoaneurysm.
Any bleeding complications were carefully assessed according to the standard of care. Major bleeding was defined as any bleeding associated with the need for blood transfusion, a drop in haemoglobin >3.0 g/dL, haematoma >10 cm for femoral access or >2 cm for radial access. Lesion characteristics were recorded by each operator according to the ACC/AHA classification.6 The patients were subdivided into elderly (>75 years of age) and non-elderly (<75 years of age).
Statistical analysis
The frequencies and percentages of the categorical data are presented. The continuous variables are reported as a mean ±standard deviation or median and 25th and 75th percentiles. Differences between the patient groups were examined using the chi-square or Fisher’s exact test or the Z-test for categorical variables. Differences in continuous variables between groups were assessed using the Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney U-test. Univariate analyses were used to examine the relationship between each variable and in-hospital death. Multivariate analyses was used to assess whether prognostic variables were statistically significant when adjusted for other variables significantly associated with in-hospital death in the univariate analysis. A p value of <0.05 was required for statistical significance. All of the analyses were done using STATA/SE 8 software package (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA).
Results
Patients and procedural characteristics
A total of 4,156 patients undergoing PCI were enrolled in the Thai Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Registry between May 2006 and October 2007. Of these patients, 3,517 were <75 years of age and 639 were ≥75 year of age. The baseline characteristics of both groups are shown in Table 1. The mean age was 79 in elderly group and 60 in the younger group. Elderly patients were more likely to have hypertension, heart failure, chronic renal failure, cerebrovascular disease and cardiogenic shock. Smoking and family history of coronary artery disease were more common in the non-elderly patients. Multivessel coronary artery disease and cardiogenic shock before PCI procedure were more common in the elderly group.
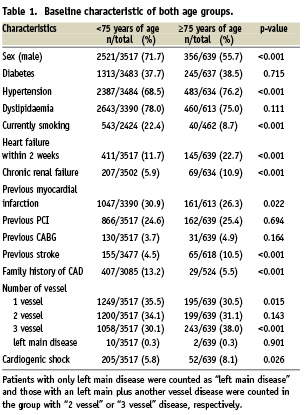
Indications for PCI and clinical presentation differed between the two groups (Table 2). The elderly patients were more likely to present with non ST elevation acute coronary syndrome (16.3% vs. 10.8%, p<0.001) but the proportion of ST elevation acute coronary syndrome within both groups was similar (13.8 % vs. 14.9%, p=0.482).
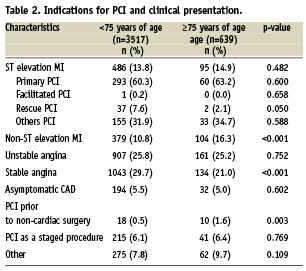
Table 3 shows the procedural characteristics of the patients. Overall, there were no significant differences between the elderly and non-elderly patients regarding the location and type of lesion. Drug eluting stents were used in about 50% of both groups and there was no difference in the type of stent used between the elderly and non-elderly groups.
In-hospital mortality and adverse effects
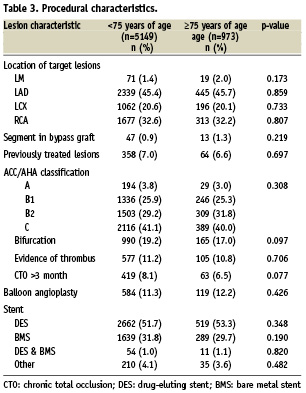
Overall in-hospital mortality rate was higher among elderly patients than non-elderly (2.4% vs. 5.3%; p<0.001) (Table 4); however, the subgroup analysis with respect to clinical presentation revealed a significantly increased mortality in only the elderly patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome compared to younger patients (8.3% vs. 4.3% ; p=0.002) (Figure 1). In patients with non acute coronary syndrome, in-hospital mortality was not significantly different between the elderly and non-elderly groups (1.4 % vs. 0.5%; p=0.071).
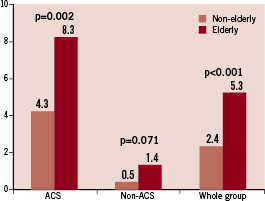
Figure 1. Comparison of in-hospital mortality rate between elderly and non-elderly patients. ACS: acute coronary syndrome
The success rate of PCI procedure was high in both groups, although the success rate of PCI was less favourable in the elderly patients (91.2% vs. 87.5 %; p=0.003). There was no significant difference between the elderly and non-elderly patients in their rate of stroke (0.5% vs. 0.2%; p=0.232) and urgent coronary artery bypass graft (0.8% vs. 0.5%; p=0.464).
The incidence of raising of the creatinine kinase MB level >2× upper normal limit after PCI was significantly higher in the elderly patients than the non-elderly patients (36.9% vs. 31.0; p=0.003). The elderly patients also had a greater incidence of post-PCI renal failure (3.9% vs. 1.8%; p=0.001). Access site complications – including bleeding, haematoma and thrombotic occlusion – were not significantly different between the two groups.
Univariate and multivariate analysis
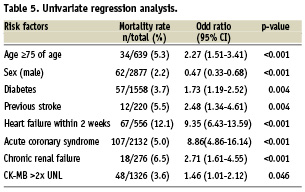
In the univariate analysis age ≥75 years, diabetes, previous history of cerebrovascular disease, congestive heart failure within two weeks prior to PCI, chronic kidney disease, CK-MB >2× upper normal limit after PCI and PCI in acute coronary syndrome were independently related with in-hospital mortality (Table 5). After adjustment for variables from Table 5, acute coronary syndrome and heart failure were the two variables most often associated with increased mortality (OR= 5.95, 95% CI=3.22-11.01, p<0.001 and OR=5.73, 95% CI=3.80-8.63, p<0.001, respectively). Age, however, was not significantly related to increased mortality (OR= 1.37, 95% CI=0.87-2.16, p=0.174) in the multivariate analysis (Table 6).
Discussion
We have demonstrated that acute coronary syndrome and heart failure are the two most important predictors of in-hospital mortality in patients undergoing PCI. Age itself was not a predictor of in-hospital mortality in this large PCI registry in Thailand.
Our study arose from daily routine practice providing evidence for the effectiveness of PCI in elderly patients. We clinically and angiographically characterised elderly patients with a relative large sample of subjects undergoing PCI. Elderly patients in our registry had more comorbidities, presented more often with heart failure, renal failure, and were more likely to present with more extensive coronary disease. Age-associated structural and functional changes of the coronary artery – including arterial wall thickening, increased vascular stiffness and endothelium dysfunction – might contribute to the lower success rate of the PCI procedure in elderly patients. Post PCI complications – such as renal failure and an increased CK-MB level – were more common in the elderly patients undergoing PCI. We did not observe a higher incidence of vascular access site complications in elderly patients compared to non-elderly patients.
Earlier studies thoroughly documented that age was a strong predictor of adverse outcomes after PCI;2,7-10 however, only small samples of elderly patients were included so the safety and efficacy regarding PCI in the elderly patients was limited. In one large, multicentre angioplasty registry5, age was a strong predictor of in-hospital mortality for emergency and elective PCI in elderly patients. By contrast, a recent study by Bagur et al11 showed that age was not a predictor of major cardiovascular outcome after PCI. Evidently, the continuous improvement of PCI techniques in the last decade – including the introduction of drug-eluting stents and highly efficacious pharmacological therapy – has made PCI a safe and effective coronary revascularisation procedure.
Predictive variations identified from multivariate analysis in our study are different from those of previous studies.12-16 In the Thai registry, congestive heart failure and acute coronary syndrome are strongly associated with in-hospital mortality (odds ratio=5.95 and 5.73, respectively). Feldman et al5, using the 2000/2001 New York State Angioplasty Registry, reported that age, congestive heart failure, renal failure, and peripheral vascular disease were predictive factors of in-hospital mortality in patients undergoing both elective and emergency PCI. In a systemic review and meta-analysis of 66 studies of coronary revascularisation in patients >80 years of age performed by Mc Kellar et al 17 the short- and long-term outcomes were acceptable. The pooled estimate for 30-day mortality in that review was 6.3%.
Our study demonstrates that PCI in elderly patients can be performed with a high rate of success (87%) and acceptable in-hospital outcomes. The procedural success rate continues to rise in other contemporary studies over against studies pre-dating the coronary stenting era18. Between 1990 and 2000, the success rate of PCI among elderly patients increased from 85% to 93%.4,13,19-21 Although a bleeding complication is one of the major concerns in elderly patients undergoing PCI, the risk of bleeding in the Thai PCI registry was not significantly different between the elderly and non-elderly patients.
In conclusion, the Thai PCI Registry which included more than 4,000 patients, provides strong evidence that PCI can be performed safely with acceptable outcomes in elderly patients, despite their having more frequent comorbidities and the risk of in-hospital mortality remaining high in patients with ACS and heart failure.
The limitation of this multicentre study registry is that post-interventional complications may be under reported. In addition, since the results of the procedure were reported by each investigator, without agreement from another investigator, there may be inconsistencies between investigators.
Acknowledgements
The Thai Acute Coronary Syndrome (TACSR) was supported by The Heart Association of Thailand under the Royal Patronage and the Clinical Research Collaboration Network (CRCN), the official research network of the Medical Research Foundation, Thailand. The authors thank the research nurses for their assistance and Mr. Bryan Roderick Hamman for assistance with the English-language presentation of the manuscript.

