
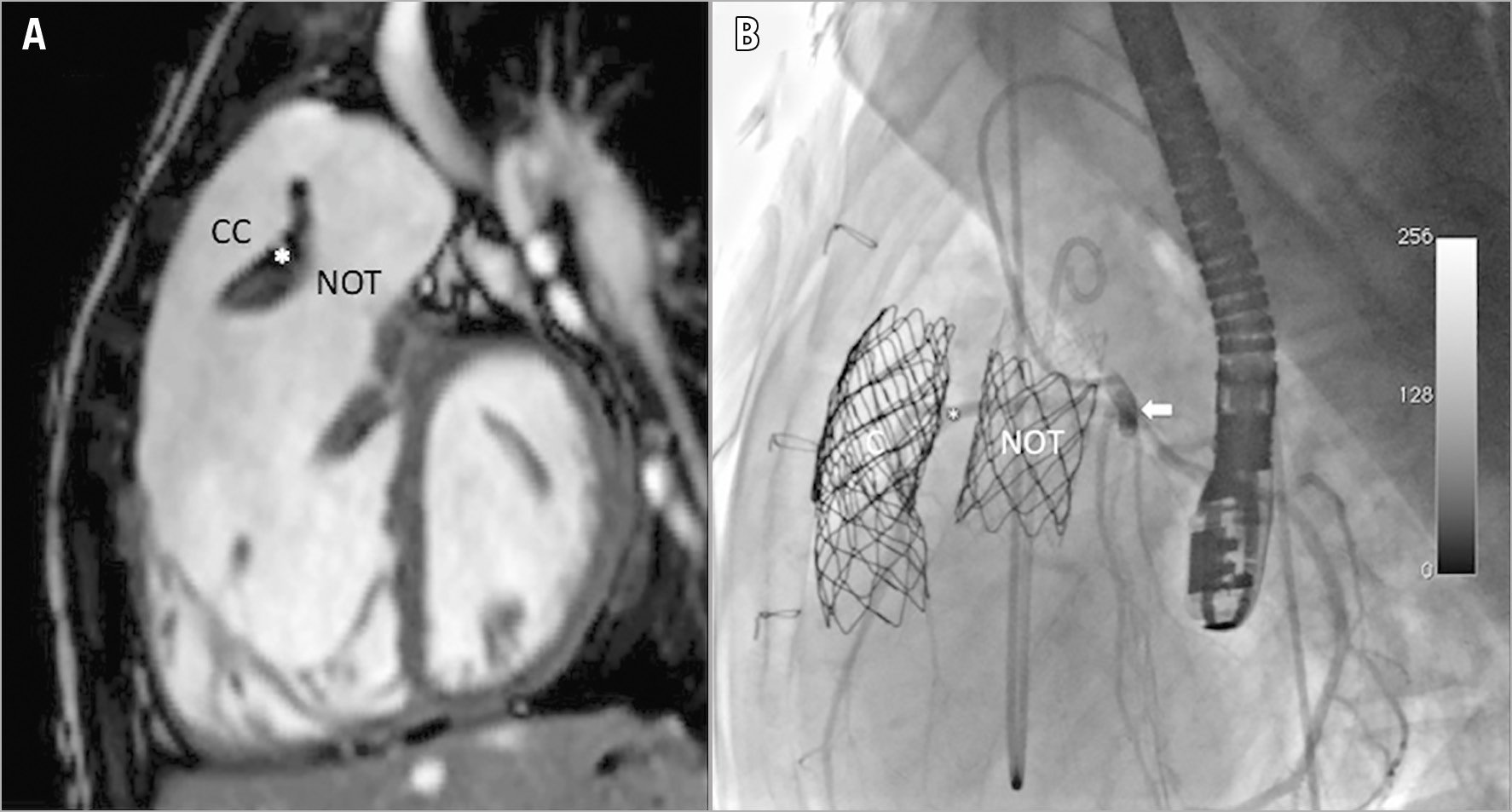
Figure 1. Tetralogy of Fallot with acquired double right ventricular outflow tract. Initial MRI (A) and final angiography in the native RVOT (B). CP stent implanted in Contegra conduit (CC) and AndraStent 43XL stent implanted in the native outflow tract (NOT). Selective coronary angiography (arrow) shows normal coronary flow in the anomalous coronary artery (*) between the Melody valves. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
Tetralogy of Fallot (ToF) is the most common cyanotic congenital heart defect (≈4.5%)1. Approximately 5% have an anomalous coronary artery crossing the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT)2.
A 14-year-old girl presented with ToF and an anomalous coronary artery crossing the RVOT and left atrial isomerism, also called polysplenia (which is associated with paired left-sidedness viscera – left atrial appendages, bilobed lungs, long hyparterial bronchi, multiple small spleens and interruption of the inferior vena cava [IVC] with azygos continuation). After corrective surgery, the immediate postoperative period was complicated by severe stenosis in the RVOT. A 14 mm Contegra® valved conduit (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) was implanted between the anterior wall of the RV and the pulmonary artery trunk in a non-anatomical position, avoiding the anomalous coronary artery and native RVOT. Ten years after surgery, the patient was referred to our hospital, presenting severe stenosis and regurgitation in both the native RVOT and the Contegra conduit, resulting in severe RV dilation (right ventricular end-diastolic volume index [RVEDVi] by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging [CMR]: 209 ml/m2) (Figure 1A).
The initial procedure to treat conduit dysfunction was performed through right internal jugular vein access (due to interruption of the IVC). A MAXI™ LD 20 mm diameter balloon (Cordis, Cardinal Health, Milpitas, CA, USA) was used for conduit sizing and coronary compression test. The landing zone for the Melody™ valve (Medtronic) was created by implanting two overlapping CP Stents™ (NuMED Inc., Hopkinton, NY, USA), mounted on a MAXI LD balloon, with resolution of both conduit stenoses at the proximal and distal surgical anastomosis. The first 20 mm Melody valve was implanted with good angiographic results, and no regurgitation or residual stenosis. In a second elective procedure, the native RVOT was treated; a selective coronary compression test with a MAXI LD 20 mm diameter balloon demonstrated no dynamic coronary flow compromise, with the right coronary artery passing between both outflow tracts. In this case, an AndraStent® 43XL (Andramed, Reutlingen, Germany), mounted on a MAXI LD balloon first, and a second 20 mm Melody valve were implanted with good angiographic and haemodynamic results (Figure 1B).
At seven-year follow-up, the patient showed marked clinical improvement as well as improved functional capacity, asymptomatic from a cardiovascular point of view with aspirin therapy.
Patients with an anomalous coronary anatomy have a significantly increased operative morbidity and mortality and have an increased risk of coronary compression during percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation (PPVI).
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on two percutaneous Melody valves implanted in a double RVOT with good angiographic and clinical results during a seven-year follow-up.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L. Zunzunegui is a physician proctor for the Melody valve. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

