
Abstract
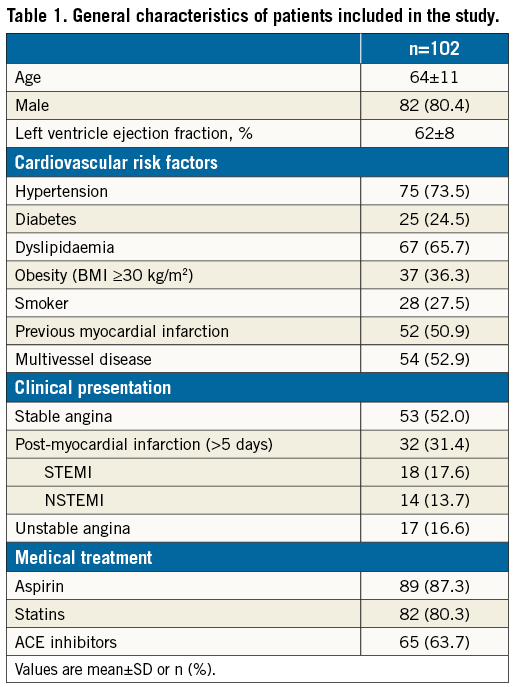
Aims: The index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR) is increasingly used to quantify microcirculatory function. However, in normal coronary arteries, resistance increases with the branching structure of the coronary tree, which suggests that IMR could be influenced by the amount of downstream myocardial mass (MM). We aimed to evaluate the influence of the amount of MM subtended to an intermediate stenosis on the IMR.
Methods and results: IMR, fractional flow reserve and coronary flow reserve (CFR) were measured in 123 coronary arteries (102 patients) with intermediate stenosis. Jeopardised MM was estimated with the Myocardial Jeopardy Index (MJI). MM was inversely associated with IMR (R2=0.16, p<0.001). Differently, CFR was MM-independent (R2=0.0). Vessels with IMR ≥30 U subtended lower amounts of MM than vessels with IMR <30 (MJI: 13.0% [Q1-3, 12.5-18.2%] vs. 20.4% [Q1-3, 15.1-25.5%], p<0.001) and, at multivariate analyses, MM, aortic pressure, minimum lumen diameter and age were independent IMR predictors (R2=0.24, p<0.001). Vessels with IMR ≥30 U and preserved CFR supplied the smallest MM amounts, suggesting an anatomically reduced but functionally preserved vascular bed.
Conclusions: The amount of myocardium subtending to a coronary stenosis is inversely associated with the IMR, while it is not associated with the CFR.
Abbreviations
CFR: coronary flow reserve
FFR: fractional flow reserve
ICC: intraclass correlation coefficient
IHD: ischaemic heart disease
IMR: index of microcirculatory resistance
LV: left ventricle
MJI: Myocardial Jeopardy Index
MM: myocardial mass
Pa: aortic pressure
Pd: distal pressure
Q: quartile
QCA: quantitative coronary angiography
Introduction
Myocardial flow impairment in ischaemic heart disease (IHD) can be due to obstructive or non-obstructive coronary involvement1. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a valuable tool to assess obstructive causes of IHD, but it does not inform whether concomitant non-obstructive involvement, generally caused by microcirculatory dysfunction, is present2. The index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR) allows the clinical assessment of microcirculatory resistance and, given its technical simplicity, is increasingly used as a tool to appraise microcirculatory function3. Yet, a theoretical concern that arises in relation to the widespread use of the IMR is that, in normal coronary arteries, resistance increases across the branching structure of the coronary tree, because coronary flow decreases while the driving pressure remains virtually unchanged4. This implies that IMR values could be influenced by the amount of myocardial mass (MM) subtended to the sensor or the epicardial stenosis, in a similar fashion to what has been proposed for FFR5. Whether this physiology basis also applies to clinical pathological settings where IMR is currently used, however, has not been addressed by previous research.
In this study of patients with IHD, we sought to describe how subtended MM influences the IMR. For this purpose, stenosed coronary arteries undergoing FFR interrogation were further investigated with the IMR, and the amount of MM subtended to the index stenosis was estimated with well-validated angiographic indices. Additionally, coronary flow reserve (CFR) was also obtained, to achieve additional insights on the functionality of the downstream myocardial bed.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
Patients with a clinical indication for FFR interrogation of ≥1 intermediate coronary stenosis (40% to 70% diameter stenosis by quantitative coronary angiography [QCA]), investigated at Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain, were prospectively studied. Patients with myocardial infarction <5 days, contraindications to adenosine, left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction <30% or left main disease were excluded, as well as those with vessels supplying previously known infarcted territories (either by electrocardiographic findings or clinical history), with serial stenoses, marked diffuse narrowings or with surgical grafts. Approval from the institutional review board was obtained and all patients gave informed consent.
ANGIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS AND ESTIMATION OF SUBTENDED MYOCARDIAL MASS
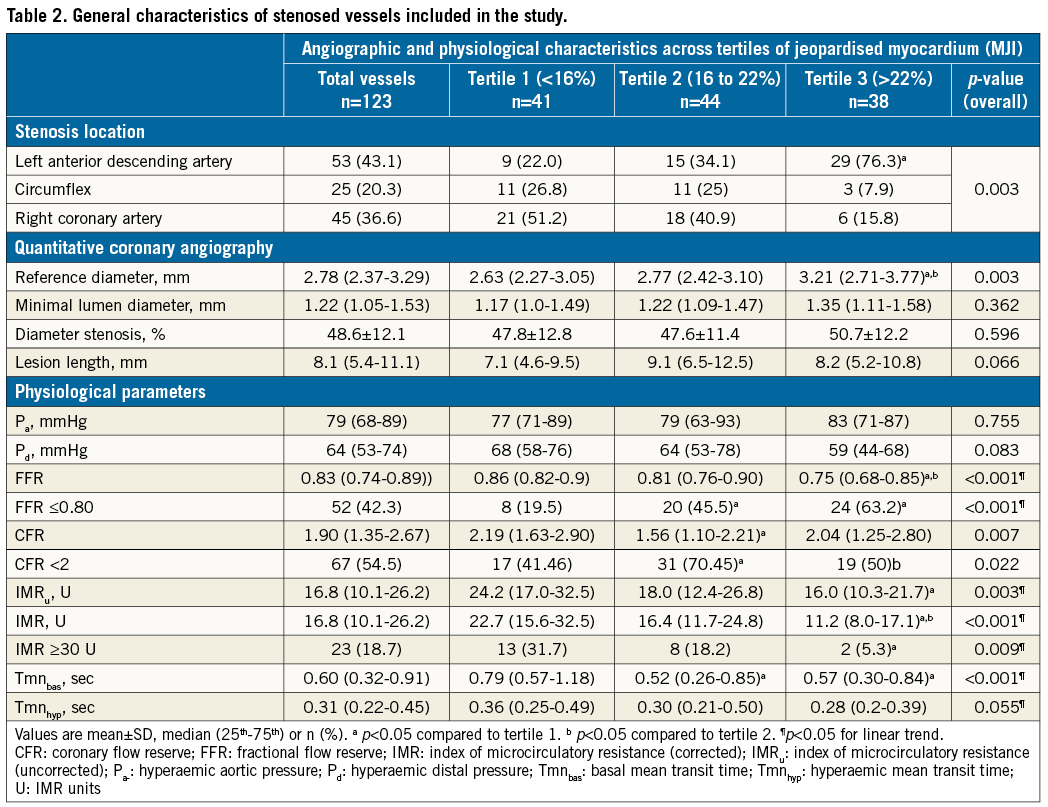
Optimal angiographic views were obtained following intracoronary nitrates (0.2 mg). Two experienced reviewers blinded to physiology data performed QCA (CASS II; Pie Medical Imaging, Maastricht, the Netherlands). Diameter stenosis, lesion length and reference and minimum lumen diameter were measured. One experienced reviewer blinded to physiology data calculated three well-validated angiographic indices of jeopardised myocardium, first from all angiograms and after three months in a random subsample of 30 patients. Specifically, to calculate MM in our study, we followed the methodology modified by Leone et al5. We used the Myocardial Jeopardy Index (MJI) as primary jeopardy score because it has been widely used as a method to calculate jeopardised myocardium6. The MJI incorporates the size, number and distribution of the coronary arteries, as well as coronary dominance. The three main coronaries and their terminal branches are graded based on vessel length and size. A score of 0 indicates a minor terminal artery, and a score of 3 represents a large vessel extending more than two thirds of the distance from base to apex. To calculate the amount of MM jeopardised by the investigated stenosis, all scores of branches distal to the lesion are summed and divided by the global score supplying the entire LV. This index expresses jeopardised MM as LV percentage.
Two other angiographic indices were also calculated as supportive analyses, the first of these being the APPROACH Jeopardy Score, which according to pathological data provides the percentage of LV supplied by a vessel or its branches7. The amount of MM jeopardised by the index lesion is calculated taking into account the downstream area and is expressed as LV percentage. If the lesion is located in the middle part of the vessel, the amount of jeopardised MM is reduced to two thirds of the region and to one third when the stenosis is located in the distal segment. The last of the three was the Duke Jeopardy Score, which divides the coronary tree into six segments: left anterior descending artery, diagonal, septal branches, circumflex, obtuse marginal branches and the posterior descending coronary artery8. Two points are assigned to each, and the sum expresses the amount of subtended myocardium that is jeopardised.
INTRACORONARY PHYSIOLOGY MEASUREMENTS
Pressure wires fitted with thermistors (PressureWire™ Certus™; St. Jude Medical, St. Paul, MN, USA) were used according to described methodologies9,10. Sensors were placed approximately three centimetres distal to the stenosis of interest to allow pressure recovery and, in proximal stenosis, an attempt was made to leave six centimetres between the guiding catheter and the sensor9. FFR was calculated as the ratio of distal coronary pressure (Pd) to aortic pressure (Pa) at stable hyperaemia during adenosine infusion (140 µg/kg/min) through a central vein. Persistence of calibration was checked. IMR was calculated as the product of hyperaemic Pd and hyperaemic mean transit time, and was corrected for collateral flow in arteries with FFR <0.75 using proposed methods10,11. Uncorrected IMR values are provided as well. CFR was calculated as the ratio of baseline to hyperaemic mean transit times9. FFR ≤0.80 and CFR <2 were used as cut-offs2 and, based on the reported variability of IMR in patients with and without IHD, values of IMR ≥30 U were considered abnormal12.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous variables are presented as mean±SD or median (quartile 1 and quartile 3 [Q1-3]) and categorical variables as counts and percentages. Normality and homogeneity of the variances were tested using Shapiro-Wilk and Levene tests. Data were analysed on a per-patient basis for clinical characteristics, and on a per-vessel basis for the other calculations. Independence was assumed for vessel-level analyses. Continuous variables were compared with Student’s t-tests or Mann-Whitney U tests, and categorical variables with χ2 or Fisher’s exact tests. Overall differences were compared with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Kruskal-Wallis, χ2 or Fisher’s exact tests, followed by post hoc t-tests, Mann-Whitney U or Fisher’s exact tests, with Bonferroni-adjusted significance level. Tests of linear trend across ordinal categories (polynomial contrasts for continuous and Mantel-Haenszel tests for categorical) were conducted. Correlation coefficients (Pearson’s r or Spearman’s ρ) were calculated and, for multiple comparisons, the significance level was adjusted with Bonferroni’s method. The intraobserver reproducibility of jeopardy scores was assessed with intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) in a random subsample of 30 patients. Linear and non-linear regressions with F-tests were used to obtain curves of best fit, following Box-Cox transformations to achieve approximate normality of residuals, when appropriate. Finally, linear mixed models were used to identify independent predictors of IMR, FFR and CFR, where clinically relevant variables5 (age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidaemia, body surface area, smoking, previous myocardial infarction, clinical presentation, QCA variables, Pa and MJI) were modelled using Mallows’ Cp as criterion for best fit. In order to account for the lack of vessel independence, mixed models were fitted adding the effect of patient as a random component. Results are presented as beta±robust standard errors, p-values and standardised beta (that represent standardised partial regression weights of each parameter) to facilitate comparisons. Differences were considered significant at p<0.05 (two-sided). The Stata 12.1 statistical software package (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) was used for calculations.
Results
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
Clinical, angiographic, and physiological characteristics of the study population (123 arteries in 102 patients) are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. The study comprised coronary stenoses of intermediate severity, both angiographically (diameter stenosis: 48.6±12.1%) and physiologically (median FFR=0.83 [Q1-3, 0.74-0.89]). Median IMR was 16.8 U (Q1-Q3, 10.1-26.2), and the median percentage of LV jeopardised by the investigated stenoses (MJI) was 19.2% (Q1-3, 13.6-25.0%). The intraobserver reproducibility of all jeopardy scores was satisfactory (ICC=0.99 [95% CI: 0.98 to 0.99], p<0.001 for MJI; ICC=0.99 [95% CI: 0.98 to 0.99], p<0.001 for the APPROACH Jeopardy Score; and ICC=0.93 [95% CI: 0.86 to 0.96], p<0.001 for the Duke Jeopardy Score).
JEOPARDISED MYOCARDIUM, CORONARY DIMENSIONS AND PHYSIOLOGICAL INDICES
Correlations between QCA parameters, physiological indices, and scores of jeopardised MM are provided in Table 2 and Table 3. Additional analyses of such variables across tertiles of MM are provided in Table 2. IMR correlated negatively with all jeopardy scores, with IMR decreasing with increasing MM (Figure 1). FFR was also inversely correlated with MM, with FFR decreasing with increasing MM. Notably, CFR was not correlated with any of the jeopardy scores (Figure 2, Table 3). Similar findings were observed after dichotomisation of physiology indices, where 23 (18.7%), 52 (42.3%) and 67 (54.5%) vessels had abnormal IMR (≥30 U), FFR (≤0.80) and CFR (<2), respectively. Indeed, vessels with IMR ≥30 U (n=23, 18.7%) subtended lower amounts of MM than vessels with IMR <30 U (MJI: 13.0% [Q1-3, 12.5-18.2%] vs. 20.4% [Q1-3, 15.1-25.5%], p<0.001); vessels with FFR ≤0.80 subtended larger MM than vessels with FFR >0.80 (MJI: 21.3% [Q1-3, 16.7-26.5%] vs. 16.7% [Q1-3, 13.0-21.7%], p<0.001) and, differently, vessels with CFR <2 subtended a statistically similar amount of MM to vessels with CFR ≥2 (MJI: 20.0% [Q1-3, 15.4-24.0%] vs. 17.0% [Q1-3, 13.0-26.1%], p=0.535) (Figure 3).
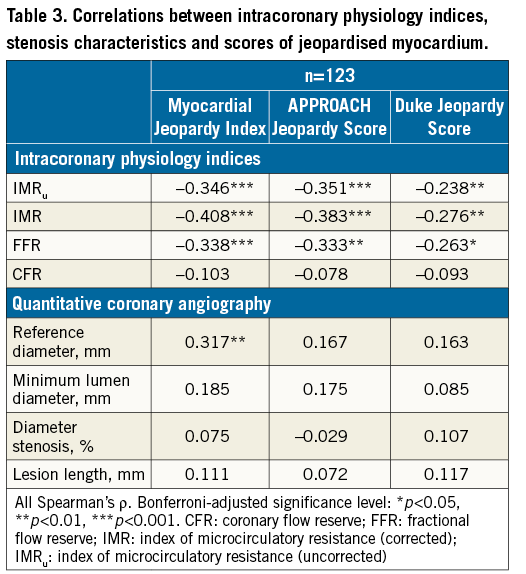
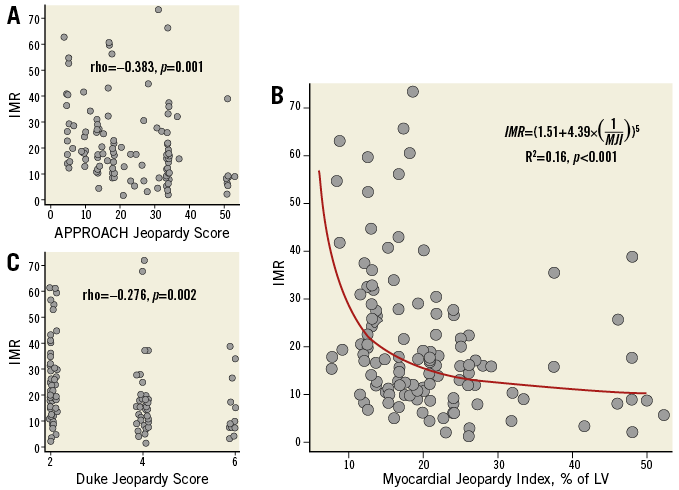
Figure 1. Relationship between IMR and indices of jeopardised myocardium. Equation denotes the best fit regression model and the R2 the model fit. In A and C “jitter“ was added to avoid overlapping of dots. Panel B depicts the significant inverse relationship between IMR and the amount of subtended myocardium estimated with the Myocardial Jeopardy Index.
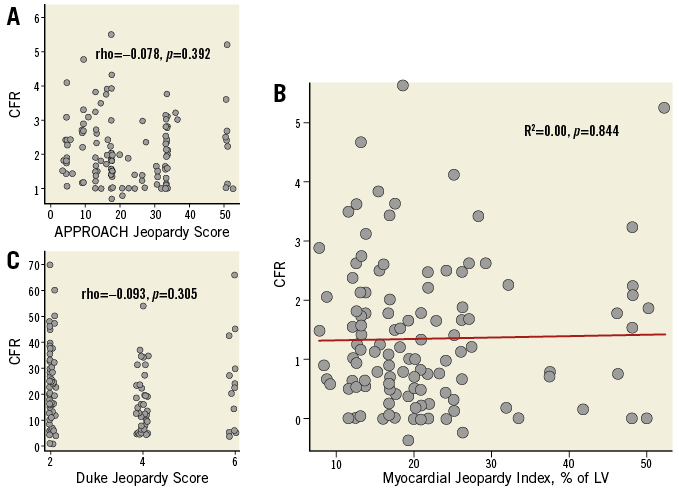
Figure 2. Relationship between CFR and indices of jeopardised myocardium. In A and C “jitter” was added to avoid overlapping of dots. Panel B depicts the lack of a statistically significant relationship between CFR and the amount of subtended myocardium estimated with the Myocardial Jeopardy Index.
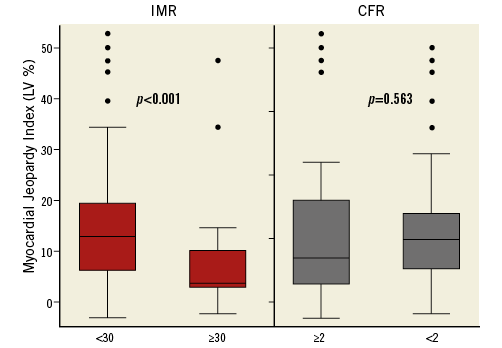
Figure 3. Box plots of the amount of myocardial mass (MJI) subtended to the coronary stenosis according to categorised values of IMR and CFR.
Finally, MM was a strong independent predictor for both IMR and FFR (Table 4). CFR, however, could not be satisfactorily modelled, as the best attempt (age, previous remote myocardial infarction and reference diameter, R2=0.04) did not reach statistical significance (p=0.156).
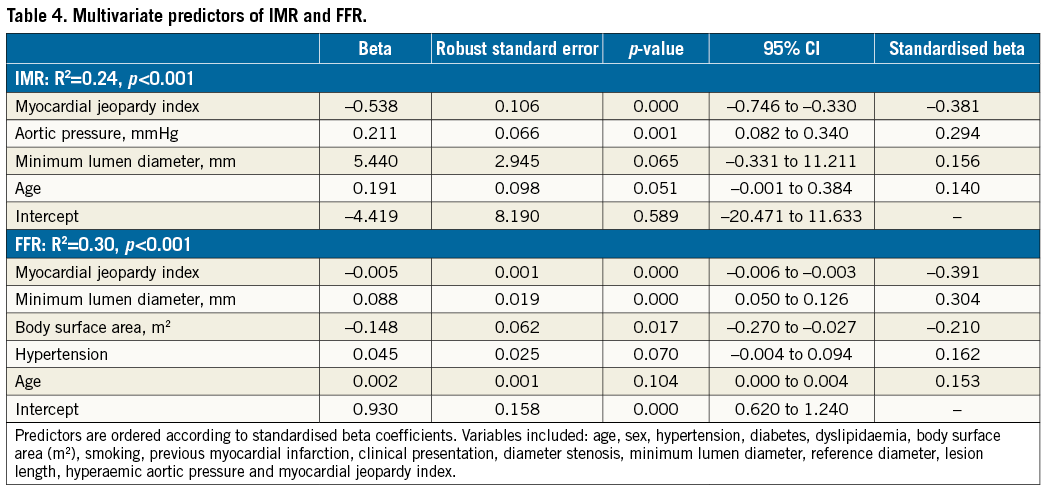
INFLUENCE OF JEOPARDISED MYOCARDIUM ON THE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN IMR AND MEAN TRANSIT TIMES
As theoretically expected in normal coronary arteries, increasing amounts of MM were associated with increasing magnitudes of baseline and hyperaemic flow, as demonstrated by a negative association of MM with baseline (ρ=–0.284, [95% CI: 0.112 to 0.439], p=0.001) and hyperaemic (ρ=–0.271, [95% CI: 0.098 to 0.427], p=0.002) mean transit times. IMR exhibited a comparable but inverse behaviour (Figure 4), since it increased with increasing baseline (ρ=–0.579, [95% CI: –0.686 to –0.448], p<0.001) and hyperaemic mean transit times (ρ=–0.636, [95% CI: –0.730 to –0.517], p<0.001). Therefore, as MM decreased, baseline and hyperaemic mean transit times increased, and IMR increased. Figure 4 provides detailed analyses of these relationships from the perspective of the IMR. High IMR values were distributed towards higher values of baseline and hyperaemic mean transit times (i.e., lower magnitudes of absolute flow) and lower values of MM.
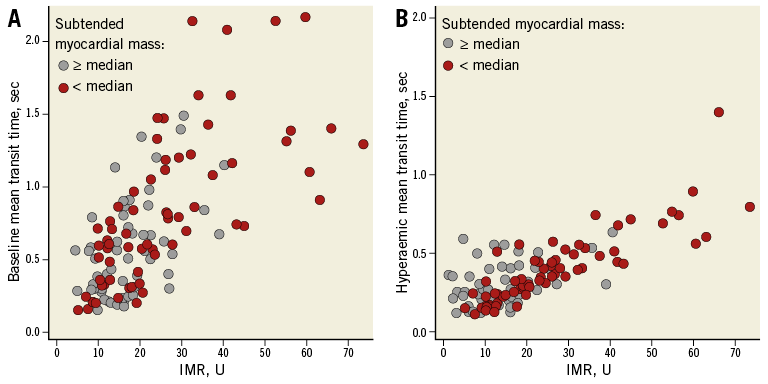
Figure 4. Relationship of the IMR with baseline and hyperaemic mean transit times. High IMR values were distributed towards higher values of mean baseline and hyperaemic transit times (i.e., lower magnitudes of baseline flow and hyperaemic flow, respectively). Furthermore, vessels subtending smaller amounts of myocardial mass (below the median value of MJI) were distributed towards lower values of baseline flow, lower values of hyperaemic flow, and higher values of the IMR.
INFLUENCE OF JEOPARDISED MYOCARDIUM ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IMR AND CFR
The relationship between IMR and CFR is provided in Figure 5. MM was significantly different across the quadrants of the IMR and CFR relationship (overall p=0.010). Vessels supplying perfusion to the largest amounts of MM (highest tertiles of MJI) were distributed towards lower values of IMR, irrespective of CFR. Interestingly, vessels with high IMR and normal CFR supplied perfusion to the smallest amounts of MM.
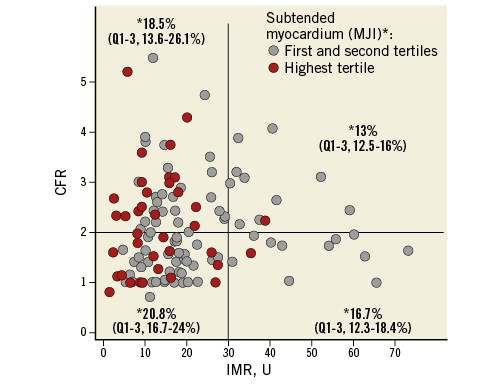
Figure 5. Scatter plot showing the relationship of IMR with CFR. The horizontal line is placed at the CFR cut-off value of 2, and the vertical line at the IMR cut-off value of 30 U. MJI was significantly different across such quadrants (overall p=0.010). Vessels supplying perfusion to the highest amounts of MM are highlighted in red (highest tertile of MJI). Please note how these vessels are distributed towards lower range of IMR values, irrespective of the CFR. Finally, vessels with normal CFR (>2) and high IMR (>30 U) subtended the smallest amounts of MM.
Discussion
This study addressed a theoretical concern for the clinical use of resistance indices to assess microcirculatory function, namely the physiologically expected increase in estimated coronary resistance across the branching structure of the coronary tree4. This is important at a time when, in addition to obstructive involvement, microcirculatory dysfunction is increasingly acknowledged as a determinant of clinical outcomes1, and when the IMR appears to many as its soundest diagnostic invasive clinical test3. Our findings suggest an influence of the amount of MM subtended to a coronary stenosis on the IMR; however, this influence seems to be rather modest. Furthermore, this study suggests that CFR is not significantly affected by MM, which, as explained below, could refine the interpretation of high IMR values in selected cases. In the following paragraphs, these aspects and their possible clinical implications are discussed in detail.
CLINICAL VALUE OF THE IMR
Coronary resistance indices have been demonstrated to correlate better with histologically demonstrated anomalies of the coronary microcirculation than relative indices such as CFR13. The IMR is a technically simple method that combines a thermodilution-derived index of coronary flow with intracoronary pressure to interrogate the minimum achievable microcirculatory resistance of a specific vascular bed10. IMR is reproducible, and mounting evidence supports its value as a meaningful diagnostic tool in both acute and chronic IHD settings3,14. High IMR values have been associated with larger myocardial infarctions, worse myocardial recovery, larger periprocedural myonecrosis and, most importantly, with worse survival at long term3,14. However, it has to be kept in mind that, as with any new diagnostic tool, IMR should be the subject of scrutiny. Although initial experimental studies demonstrated a moderate correlation of the IMR with true microcirculatory resistance10, the possible influence of subtended MM on the IMR has not previously been explored. This is important because, in normal coronary arteries, theoretical coronary resistance should increase in every bifurcation, because coronary flow decreases while the driving pressure remains almost unchanged4. Our study substantiates this physiological background in human pathological settings, because IMR values increased as the amount of subtended MM to the stenosis decreased, and such influence persisted as independent after multivariate adjustments. Moreover, high IMR values were distributed towards higher values of mean transit times (i.e., lower magnitudes of baseline and hyperaemic flow), a phenomenon expected in dysfunctional myocardium, but also in anatomically reduced normal vascular beds. Hence, our study suggests that IMR might reflect not only the functionality of the microcirculatory bed under interrogation, but also to some degree its extent. Nevertheless, and of importance for the applicability of the IMR as a tool to appraise the coronary microcirculation, we observed that the physiological influence of MM on the IMR was only modest, as it only explained a small percentage (16%) of IMR variability. We believe that this substantiates the clinical use of a single IMR cut-off for pragmatic clinical assessment of microcirculatory function, which is further supported now by two studies in normal coronary arteries that have reported the highest limit for “IMR normality” –<27.2 U15 and <30 U12– within a very narrow range.
POSSIBLE ADJUVANT ROLE OF CFR FOR THE INTERPRETATION OF HIGH IMR VALUES
Finally, an interesting finding from our study is the absence of an association between CFR and subtended MM. This also fits the theoretical basis since, by normalising hyperaemic flow to baseline flow, CFR should intrinsically correct for the magnitude of flow within the myocardial bed under investigation16. Therefore, CFR should be comparable in arteries of different length and diameter, and should not be affected by downstream MM. Consequently, it is reasonable to speculate that, under particular conditions, CFR could help to refine IMR interpretation. Specifically, functionally normal but anatomically reduced vascular territories should theoretically exhibit preserved CFR and concomitant high IMR values. Nonetheless, and because our study was performed in vessels with intermediate stenosis, this possible adjuvant role of CFR should be considered cautiously and only in cases where CFR is preserved, because an exhausted CFR could mean either epicardial or microcirculatory disease9.
How can these considerations be reconciled with the evidence gathered in support of the clinical value of IMR3,14? Simply stated, high IMR values could be general reflections of “low-flow states”, which in most cases can be attributable to microcirculatory dysfunction, or lesser residual viable myocardium. In some other cases, however, lower magnitudes of flow might be normal, if the vascular bed under interrogation is anatomically reduced but functionally preserved, as suggested by a normal CFR. This proposal requires further validation in dedicated studies.
Limitations
Firstly, MM was not measured directly. An ideal study would require metabolic demonstration of the MM functionality and viability (either by cardiac magnetic resonance or positron emission tomography) as well as the documentation of differential microvasculopathy within the same heart. However, the angiographic scores used have been clinically used to assess the influence of MM on other indices of coronary physiology such as FFR5, and have been thoroughly validated against either pathological data or cardiac magnetic resonance7,17. Also, we included patients with a history of remote myocardial infarctions. Whilst some have suggested an influence of myocardial infarction on distant microcirculatory function18, others have found that IMR does not change significantly after a few days or weeks following an acute infarction in non-culprit territories19. Furthermore, the mean period of time between the infarctions and the physiological interrogation in our small population with stabilised acute coronary syndromes was long (8.2±3.8 days [min 5, max 20 days] in the STEMI and 7.2±1.8 days [min 5, max 11 days] in the non-STEMI populations), and all patients were stabilised and asymptomatic several days before the index procedure. In this regard, we find it reassuring that the mean IMR values observed in our study were similar to those reported by other investigators who have assessed IMR only in populations of stable patients12,20. Next, IMR is also influenced by the haemodynamics of the LV and the coronary wedge pressure, which were not measured. Because of this, we decided to correct IMR values for possible collateral flow contribution when FFR was <0.75, using proposed methods11. A separate analysis (not shown) using uncorrected IMR values led to the same conclusions reported in this manuscript. Also, our conclusions are limited by a relatively small sample size and, being a single-centre experience, the external reproducibility of our findings has to be challenged. Finally, the translation of our findings to resistance indices derived from Doppler flow velocity is unknown. Theoretically and although technically more demanding, resistance indices derived from Doppler flow velocity should be less influenced by MM, because the decrease in flow velocity from proximal to distal segments is smaller than the decrease in volumetric flow16. Nonetheless, and in spite of these limitations, we believe that the observations gathered contribute to improving the interpretation of the available invasive methods to assess IHD.
Conclusions
In this study, we observed that the amount of MM subtended to an epicardial stenosis was inversely associated with the IMR whilst CFR was MM-independent.
| Impact on daily practice Our study suggests that IMR might reflect not only the functionality of the microcirculatory bed under interrogation, but also to some degree its extent. Nevertheless, the physiological influence of MM on the IMR was only modest, which we believe substantiates the clinical use of a single IMR cut-off for pragmatic clinical assessment of microcirculatory function. |
Acknowledgements
M. Echavarría-Pinto acknowledges the Fundación Interhospitalaria Investigacion Cardiovascular, Spain, for a clinical scholarship.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Echavarría-Pinto, T. van de Hoef, J. Piek and J. Escaned have served as speakers in educational events organised by St. Jude Medical and Volcano Corporation. J. Davies is a consultant for Volcano Corporation. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

