An 82-year-old woman with a prior surgical aortic valve replacement in 2012 with a biological prosthesis (Trifecta 19 mm; Abbott Vascular) was admitted in March 2021 due to heart failure and unstable angina. Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) showed a degenerated biological aortic prosthesis with severe stenosis, and coronary angiography (CA) showed a severely calcified, critical stenosis in the right coronary artery (RCA) ostium. Multislice computed tomography (MSCT) (Moving image 1) confirmed severe RCA ostium calcification and showed a considerable risk of RCA obstruction with transcatheter aortic valve-in-valve implantation (ViV-TAVI) (Figure 1).
Simultaneous ViV-TAVI and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to the RCA using a chimney stenting technique was deemed appropriate by the Heart Team (Figure 1). After predilatation of the ostial RCA with a 4.0 mm non-compliant balloon, a 4.0x30 mm drug-eluting stent (DES) was parked in the mid-RCA, and a 23 mm Evolut PRO (Medtronic) transcatheter heart valve (THV) was deployed according to the manufacturer instructions for commissural alignment. Then, the DES was retracted to the ostial RCA and deployed alongside the THV frame. The angiographic result was considered satisfactory, and no intracoronary imaging was performed (Moving image 2). The patient was discharged uneventfully and remained asymptomatic until May 2022, when she was admitted with unstable angina. TTE showed normal THV function, and a new CA revealed severe in-stent restenosis (ISR) in the ostial RCA, so PCI was considered appropriate (Figure 1).
Via a 7 Fr right femoral access, a 6 Fr multipurpose guide catheter was successfully positioned through the THV cell above the RCA ostium (Figure 1, Moving image 3). Then, with the help of a Corsair (Asahi) microcatheter, after several attempts, a Fielder XT-A (Asahi) guidewire was advanced using a fishing technique through a side strut of the DES, as an end-on cannulation was considered unfeasible. Predilatation with 0.8 mm and 2 mm semi-compliant balloons and a 3.5 mm non-compliant balloon was performed. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) confirmed the guidewire position though a side strut of the DES and showed underexpansion of the DES at the RCA ostium (Moving image 4). Although the underlying mechanism of the stent underexpansion could have been a severely calcified and ostial lesion, a certain component of stent compression between the aortic wall and the THV frame could have also contributed. A 4.0x23 mm DES was then advanced with no resistance through the side strut of the previous stent and deployed into the ostial-proximal RCA, followed by proximal post-dilatation with a 4.5 mm non-compliant balloon. IVUS confirmed good expansion and apposition with a minimal luminal area of 9.6 mm2 (Moving image 5). Importantly, no guide catheter extension was needed throughout the procedure. The patient was discharged without complications and remained asymptomatic at 6-month clinical follow-up.
Chimney stenting is a bailout technique to treat coronary artery obstruction during transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI). Nonetheless, long-term data on the incidence of ISR and stent thrombosis are unclear. To date, only 1 case of ISR after chimney stenting has been reported, which also occurred in the RCA and required coronary artery bypass grafting1. To our knowledge, this is the first report of successful ISR PCI after chimney stenting.
Coronary access and PCI after chimney stenting remain challenging, especially in the setting of self-expanding THVs with tall frames and small cells. In this scenario, end-on cannulation of the coronary ostium might be unfeasible, and only a side-on cannulation of the protruding stent may be achieved, advancing the coronary guidewire through the struts of the stent2.
Finally, in patients at high risk for coronary artery obstruction during TAVI, IVUS facilitates assessment of coronary ostium patency and optimisation of chimney stenting and should therefore be considered in these cases345.
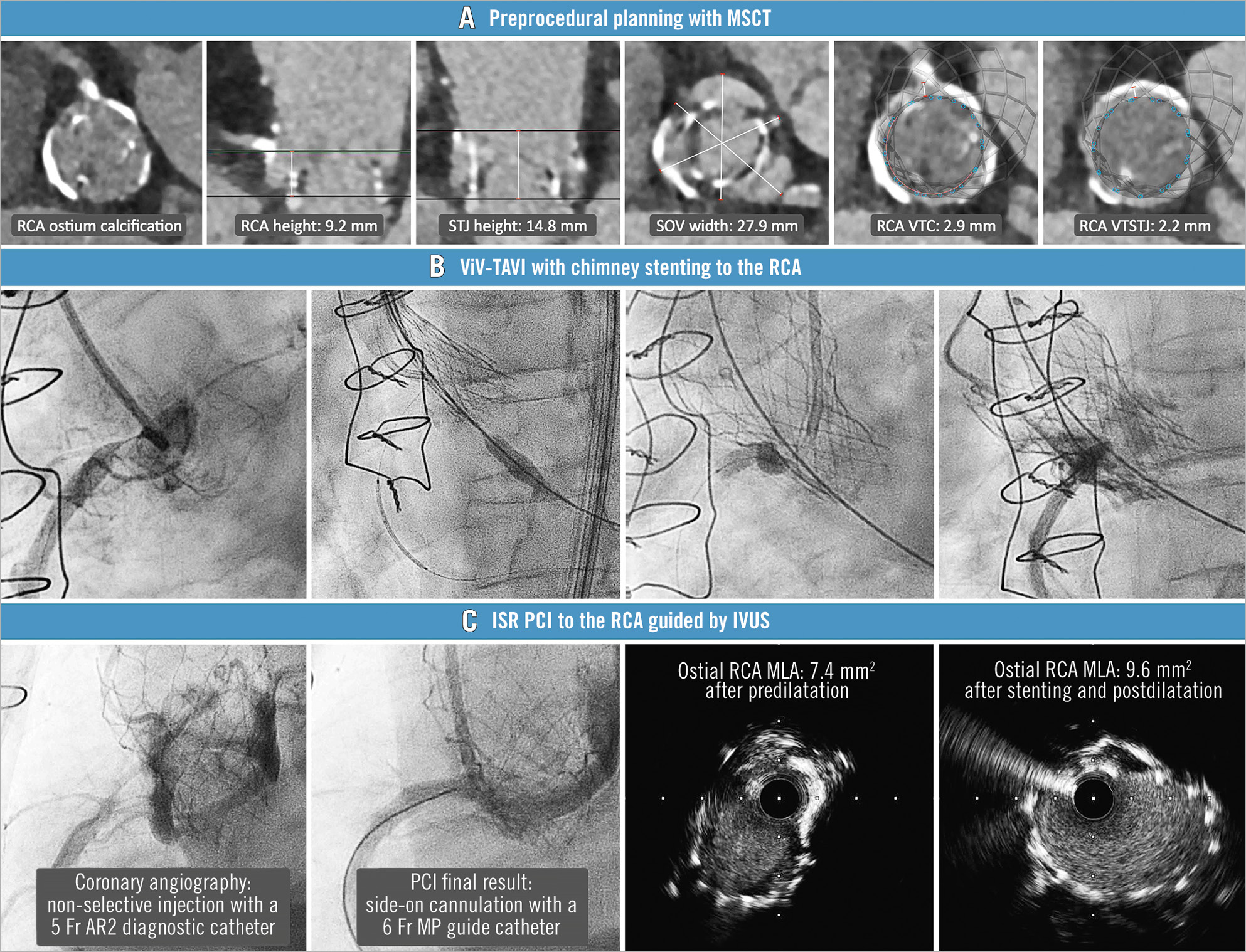
Figure 1. ISR PCI after chimney stenting during ViV-TAVI. A) Preprocedural planning with MSCT showing severe calcification in the RCA ostium and considerable risk of RCA obstruction with ViV-TAVI. B) ViV-TAVI with chimney stenting to the RCA. C) ISR PCI to the RCA guided by IVUS. AR2: Amplatz right 2; Fr: French; ISR: in-stent restenosis; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MLA: minimal lumen area; MP: multipurpose; MSCT: multislice computed tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; RCA: right coronary artery; SOV: sinus of Valsalva; STJ: sinotubular junction; ViV-TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve-in-valve implantation; VTC: virtual transcatheter heart valve to coronary artery ostium distance; VTSTJ: virtual transcatheter heart valve to sinotubular junction distance
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Preprocedural MSCT for ViV-TAVI planning.
Moving image 2. ViV-TAVI and chimney stenting to RCA procedure.
Moving image 3. PCI to ISR of ostial RCA.
Moving image 4. IVUS after predilatation.
Moving image 5. IVUS after stent deployment.

