
Abstract
Aims: We aimed to evaluate the relationship between CT-based annular perimeter oversizing and the incidence of paravalvular aortic regurgitation (PAR) and permanent pacemaker (PPM) implantation in patients treated with the new self-expanding CENTERA transcatheter heart valve (THV) for severe aortic stenosis.
Methods and results: One hundred and ninety-eight patients in the CENTERA-EU trial were stratified a priori into four groups based on the perimeter oversizing (2.5-10%, 10-15%, 15-20% and >20%). PAR at 30 days was moderate or higher in 0.6% of patients. The frequency of PPM implantation was 4.9%. The mean perimeter oversizing was 16.2±5.6%. For patients with a perimeter oversizing >10%, an inverse relationship between oversizing and ≥mild PAR was observed (43.3% for 10-15% oversizing; 37.7%, 15-20%; 33.3%, >20%). No association between oversizing and effective orifice area was observed. The optimal cut-off value of perimeter oversizing for the prediction of ≥mild PAR was 15.9% (AUC 0.718, 95% CI: 0.576, 0.860). No annular ruptures were observed.
Conclusions: The CENTERA THV appears to have a wide range of sizing tolerance. The degree of oversizing to mitigate PAR is relatively low compared to other self-expanding transcatheter devices. There appears to be no compromise between occurrence of PAR and PPM across this wide range of oversizing.
Abbreviations
AVA: aortic valve area
EOA: effective orifice area
MDCT: multidetector computed tomography
PAR: paravalvular aortic regurgitation
TAVR: transcatheter aortic valve replacement
THV: transcatheter heart valve
Introduction
Over the last decade, transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) has significantly changed the treatment of aortic stenosis in patients deemed prohibitive, high-risk and, recently, intermediate-risk for surgical valve replacement1-5. The clinical integration and success of TAVR has been facilitated by continuous innovation in transcatheter heart valve (THV) design, procedural technique and preprocedural planning. Amongst these technical refinements, the use of multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) for THV sizing has become routine and an essential part of TAVR planning, and CT-based sizing has been shown to reduce the risk of paravalvular aortic regurgitation (PAR) and associated adverse outcomes for both balloon-expandable and self-expanding TAVR systems6.
While the use of MDCT for THV sizing is now considered standard care, it is important to note that THVs differ in their structural design and thus require unique, device-specific sizing algorithms in order to optimise clinical outcomes. The CENTERA THV (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA, USA) is a novel self-expanding and repositionable valve system with a low-profile nitinol frame and minimal extension into the left ventricular outflow tract designed to minimise conduction disturbances. The first-in-human clinical experience with the CENTERA THV demonstrated its feasibility and good short-term and midterm clinical and haemodynamic outcomes at one year7. However, broader clinical use of the CENTERA THV will require the development of a comprehensive CT sizing algorithm. Thus, the aim of this analysis was to evaluate the relationship between CT-based annular oversizing and the incidence of PAR and permanent pacemaker implantation (PPM) in patients undergoing CENTERA THV implantation in the CENTERA-EU trial in an attempt to develop a device-specific CT sizing algorithm.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
The CENTERA-EU trial is a non-randomised, prospective, multicentre trial designed to evaluate the self-expanding CENTERA THV. Inclusion criteria included symptomatic (New York Heart Association functional Class II or greater) severe aortic stenosis as determined by echocardiography (severe symptomatic aortic stenosis requiring aortic valve replacement characterised by aortic valve area [AVA] <1 cm2 [or indexed AVA <0.6 cm2/m2] or mean gradient >40 mmHg [or peak aortic jet velocity >4.0 m/sec]) and a high-risk profile, as determined by logistic EuroSCORE and Society of Thoracic Surgeons score or a defensible high-risk profile as per Heart Team determination (comprising experienced cardiac surgeons, interventional cardiologists, and others). Complete details on inclusion and exclusion criteria are reported at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02458560. More details are provided in the Supplementary Appendix.
MDCT DATA ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS
CT data sets were provided to the CT core laboratory at St. Paul’s Hospital (Vancouver, BC, Canada). For image analysis, all data sets were transferred to a dedicated post-processing platform (Aquarius iNtuition, Version 4.4.2; TeraRecon, Foster City, CA, USA). All measurements were performed in accordance with the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT) Expert Consensus recommendation8. Further details are provided in the Supplementary Appendix.
ECHOCARDIOGRAM DATA ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) was performed by the sites at baseline, discharge, and 30 days after the procedure in accordance with the study protocol. Anonymised data sets were provided to and evaluated by a dedicated core laboratory (Medstar Health Research Institute, Washington DC, USA). Echocardiographic measurements included standardised assessment of the derived valve area, valve area and effective orifice area (EOA). PAR was graded in accordance with the Valve Academic Research Consortium criteria9.
DEGREE OF PERIMETER OVERSIZING
As provided by the manufacturer, the 23, 26, and 29 mm CENTERA THVs have nominal perimeters of 72.2, 81.6, and 91.1 mm, respectively (Figure 1). The THV was considered oversized when the THV nominal perimeter was greater than the CT-derived annular perimeter. Relative percent perimeter oversizing was calculated as follows, using the nominal THV values provided by the manufacturer: (CENTERA THV nominal perimeter/annular perimeter–1)×100. Patients were a priori categorised into four groups depending on the degree of relative perimeter oversizing, based on bench testing recommendations and oversizing thresholds used for other self-expanding devices, as follows: 2.5~10%, 10~15%, 15~20% and >20%.
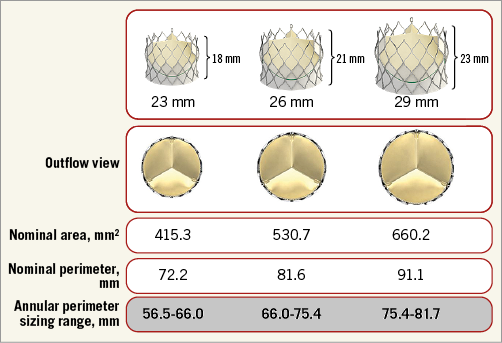
Figure 1. Nominal value of the CENTERA transcatheter heart valve.
STUDY ENDPOINTS AND FOLLOW-UP
Study endpoints were:
– The incidence of PAR determined by TTE at 30 days after the index procedure.
– The frequency of PPM implantation due to a conduction disturbance according to the valve size and degree of its perimeter oversizing by 30 days after the index procedure.
– Maintenance of aortic valve EOA at 30 days determined by echocardiography.
– The incidence and severity of PAR, EOA and PPM implantations according to the extent of the oversizing across multiple variables (area, perimeter, eccentricity, and mean diameter).
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Categorical variables were summarised as percentages whereas continuous variables were reported as mean±SD or median (first and third quartile). The chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was used to test for differences among categorical variables. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used to test for differences among continuous variables. For regurgitation, the four levels of none/trace, mild, moderate, and severe were coded 0, 1, 2, and 3. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed to determine the predictive ability of several measures (percent oversizing by area, percent oversizing by perimeter, measured annulus perimeter, annulus area, and eccentricity). Eccentricity was calculated as (long axis–short axis)/short axis) on incidence of new PPM and ≥mild paravalvular regurgitation. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. CT analyses were performed using R version 3.2.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Clinical results analyses were performed using SAS software version 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Further statistical methods are provided in the Supplementary Appendix.
Results
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS AND PROCEDURAL OUTCOMES
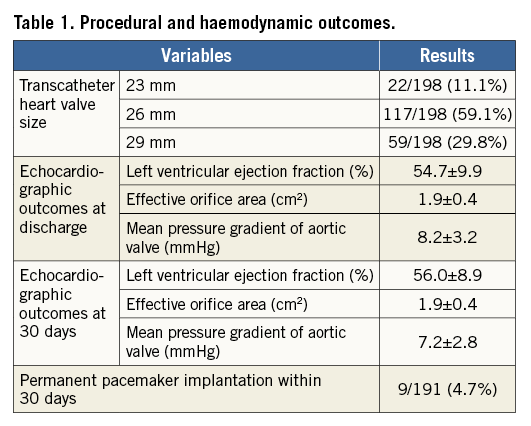
The baseline patient characteristics are presented in Supplementary Table 1. Mean age was 83±5 years with 31.3% of patients being male. The mean EuroSCORE II and STS scores were 5.1±3.96 and 6.2±4.22, respectively (Supplementary Table 1). Permanent pacemaker, within 30 days of THV implantation, occurred in 4.9% (9/184) of patients (Table 1) with seven of these reported as conduction abnormalities with atrioventricular block grade III. Additional procedural and haemodynamic outcomes are given in Table 1.
ANNULAR DIMENSIONS AND PERIMETER OVERSIZING
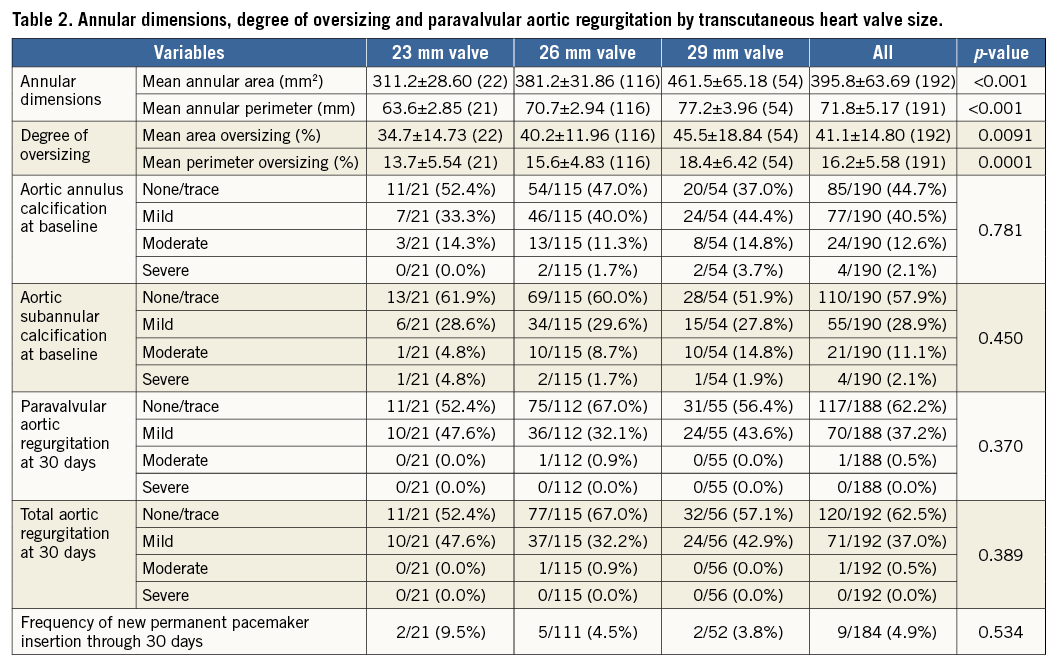
For the entire cohort, mean annular perimeter was 71.8±5.2 mm, with a mean perimeter oversizing of 16.2%. Patients with 23, 26, and 29 mm CENTERA THVs had mean annular perimeters of 63.6±2.9 mm, 70.7±2.9 mm and 77.2±4.0 mm, respectively. This resulted in mean perimeter oversizing of 13.7%, 15.6% and 18.4%, respectively (Table 2). There were no significant differences in the incidence and severity of annular and subannular calcifications among cohorts stratified by valve size (p=0.78 in annular and p=0.45 in subannular calcification) (Table 2).
PAR INCIDENCE AND SEVERITY STRATIFIED BY PERIMETER OVERSIZING
The frequency of PAR stratified by a priori defined cohorts of perimeter oversizing is presented in Table 3. At 30 days after procedure, trace/no PAR was observed in 62.1% of patients, while 37.4% of patients exhibited mild PAR. Moderate PAR was observed in 0.5% of patients. No subjects experienced severe PAR. No relationship between the incidence of ≥mild PAR and the range of perimeter oversizing was observed across the predefined groups (30.0% incidence for 2.5-10% oversizing, 43.3% incidence for 10-15%, 37.7% incidence for 15-20% and 33.3% incidence for ≥20%). Changes in total aortic regurgitation and PAR at discharge and 30 days after valve implantation are shown in Figure 2. Oversizing by all other tested parameters showed no significant relationship with PAR (Supplementary Table 2, Supplementary Table 3).
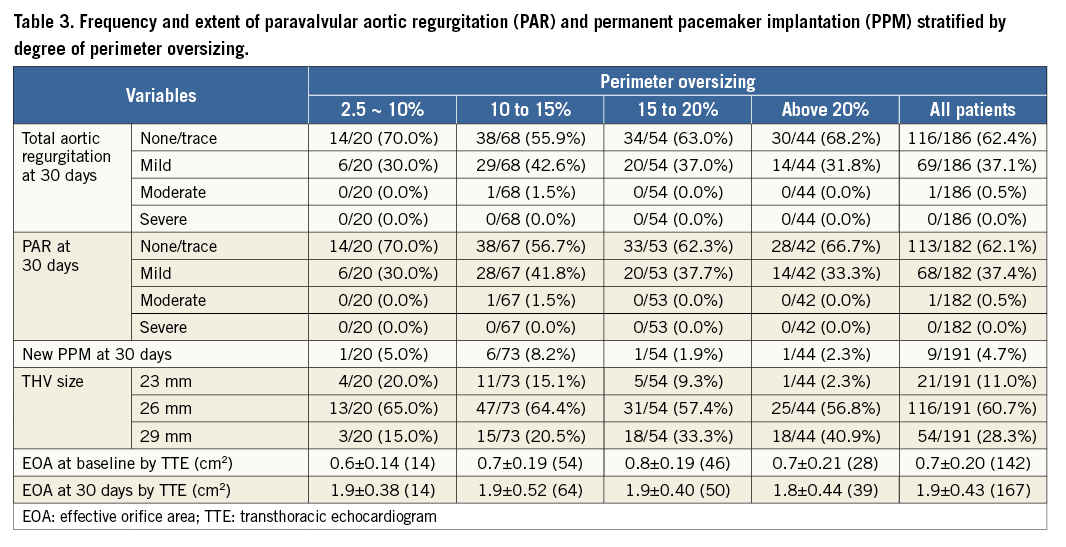
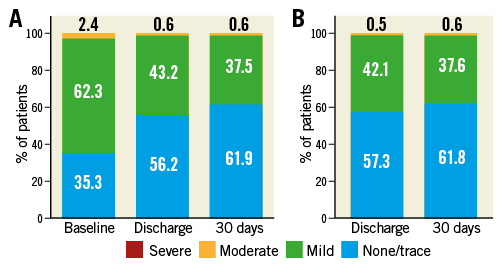
Figure 2. Total aortic regurgitation and paravalvular aortic regurgitation at discharge and 30 days after valve implantation. A) Aortic regurgitation at baseline, discharge and 30 days after valve implantation. B) Paravalvular aortic regurgitation at discharge and 30 days after valve implantation.
HAEMODYNAMIC PERFORMANCE AND PERMANENT PACEMAKER
EOA and mean pressure gradient on discharge TTE significantly improved compared to baseline (0.7±0.2 cm2 and 40.5±13.2 mmHg at baseline vs. 1.9±0.48 cm2 and 8.2±3.23 mmHg at discharge, p<0.001) (Table 2, Figure 3). No significant changes in EOA or mean pressure gradient of the aortic valve were observed between discharge and 30-day follow-up. There was no association between percentage of perimeter oversizing and EOA (Table 3, Figure 3). Variables of oversizing and annulus size were not predictive of PPM with AUCs not statistically different from 0.5 (Supplementary Table 4).
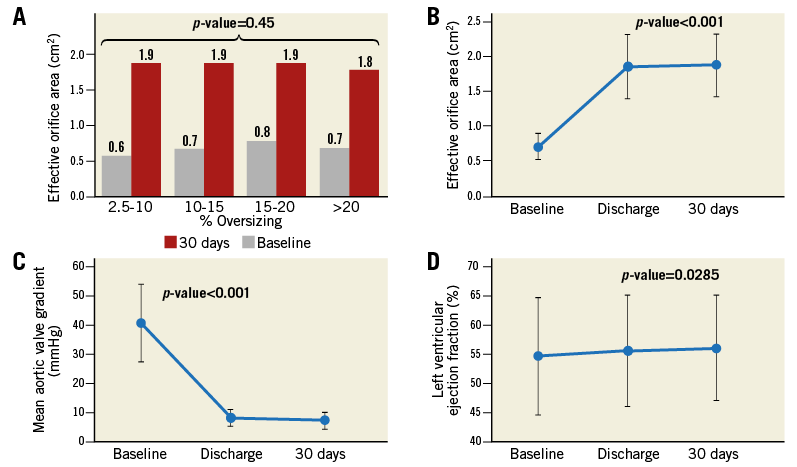
Figure 3. Echocardiographic measurements at baseline, discharge and 30 days after the implantation of a CENTERA THV. A) Effective orifice area (EOA) according to perimeter oversizing at baseline and 30 days. B) Haemodynamic changes of the EOA at baseline, discharge and 30 days. C) Mean pressure gradient of aortic valve at baseline, discharge and 30 days. D) Left ventricular ejection fraction at baseline, discharge and 30 days. EOA and mean pressure gradient of aortic valve were well maintained at 30 days after discharge.
LANDING ZONE CALCIFICATION
ROC curve analysis for the prediction of PAR by the aortic annulus and subannular calcifications was performed. There was poor relationship between ≥mild PAR and the presence of aortic annular calcification (sensitivity 67.2%, specificity 51.8%, AUC 0.596) and aortic subannular calcification (sensitivity 52.2%, specificity 64.3 and AUC 0.578) (Supplementary Table 5).
Discussion
In our analysis of the initial international experience with the CENTERA THV, we sought to define a CT-based optimal sizing strategy. Interestingly, unlike other THV devices, the CENTERA THV exhibited comparable clinical and echocardiographic outcomes across a wide range of oversizing thresholds, suggesting wide sizing tolerance. Further, we noted no meaningful relationship between landing zone calcification and the incidence or severity of PAR. These findings provide a framework for the establishment of a scientifically supported sizing algorithm for the new-generation CENTERA THV to be integrated and validated in clinical practice. Importantly, there was also no increase in new-onset conduction disturbances or need for PPM implantation with higher thresholds of oversizing across multiple measures.
INCIDENCE AND EXTENT OF PAR AND CONDUCTION DISTURBANCES AND OVERSIZING
The development of ≥moderate PAR after TAVR is closely related to adverse outcomes, especially long-term mortality10,11. A meta-analysis revealed that post-procedural, ≥moderate PAR ranges from 12% to 39% for self-expanding valves and 3% to 23% for balloon-expandable valves12,13. The only randomised study to compare self-expanding versus balloon-expandable THVs demonstrated a significantly higher rate of residual ≥moderate AR for the self-expanding versus balloon-expandable groups (18% vs. 4%, respectively)14. In our study, PAR at 30 days was moderate or higher in 0.6% of patients and an inverse relationship between oversizing and ≥mild PAR was observed (43.3% for 10-15% oversizing; 37.7%, 15-20%; 33.3%, >20%). Further analysis evaluating the relationship of oversizing across all traditional annular measures found none of them to be good predictors of PAR or need for PPM.
CENTERA SIZE SELECTION ACCORDING TO PERIMETER OVERSIZING
It is important that valve sizing and selection be carried out in a device-specific fashion to optimise clinical outcomes from TAVR using new THVs. It is well known that THV undersizing is a potential cause of PAR and device embolisation, while aggressive oversizing might contribute to annular rupture, coronary obstruction, atrioventricular block, peri-aortic haematoma, ventricular septal rupture, or anterior mitral leaflet injury15. Thus, appropriate oversizing using the 3-dimensional MDCT annular measurement is essential to minimise the risk of complications and to optimise clinical outcomes following TAVR. Given the historical reliance on perimeter annular measurements for self-expanding devices, we have developed a perimeter sizing algorithm for the CENTERA THV, the first such algorithm for an Edwards Lifesciences THV16,17.
From our results, the CENTERA device appears to have a very broad sizing range without a traditional “optimal” oversizing threshold. In addition, the outcomes with modest nominal oversizing are extremely strong, which suggests that much lower thresholds of oversizing may be acceptable than with other self-expanding devices previously evaluated and available in current clinical practice. Also, in our study, EOA and mean transprosthetic pressure gradient were 1.9 cm2 and 7.2 mmHg with moderate PAR in 0.6% of patients. These results suggest favourable outcomes compared with outcomes using other self-expanding THV with reported mean transprosthetic gradients between 7.7 and 11.5 mmHg with rates of moderate or higher PVR between 1.0% and 13.1%5,18-21.
The presence of heavy calcification in the landing zone of the aortic annulus and subannular space has been known to be an independent cause of PAR22. Interestingly, in our analysis, it was observed that the landing zone calcification did not affect the incidence or severity of PAR. The reasons for this are not entirely clear and continued evaluation with growing clinical experience is warranted.
Study limitations
There were several study limitations. First, the number of patients enrolled in the CENTERA-EU study was small compared to the total population undergoing TAVR. However, this represents nearly all those who have had a CENTERA THV worldwide to date and provides important first-in-human experience to inform the development of a sizing algorithm. In addition, given that this was a non-randomised clinical observational trial, we cannot exclude the potential of a selection bias. Overall, the burden of PAR was low. Given the modest number of patients treated with perimeter oversizing of 2.5% to 10%, conclusions cannot be drawn, and these findings need further downstream assessment. Also of note, oversizing thresholds were defined by the stated nominal size of the valve at the waist deployed at the annular level, not above or below where the CENTERA valve flares. Finally, we lack information on implantation depth which is known to be an important predictor of post-TAVR conduction disturbances.
Conclusions
In this clinical trial, the CENTERA THV exhibited similar echocardiographic outcomes across a wide range of annular oversizing with even modest oversizing yielding low rates of PAR and PPM implantation. Our analysis suggests that the CT sizing for the CENTERA device may be broad, allowing a wide range of annular oversizing. Prospective validation of these sizing recommendations in larger clinical cohorts is an important next step in the use of the CENTERA THV.
| Impact on daily practice Based on the study findings, it would appear that the CENTERA THV exhibits a uniquely wide range of oversizing tolerance with even modest perimeter oversizing yielding low rates and burden of PAR, and a higher degree of oversizing yielding no increased rates of PPM implantation. |
Conflict of interest statement
J. Leipsic is a consultant to Edwards Lifesciences, Circle Cardiovascular Imaging, and HeartFlow, and has institutional core laboratory contracts with Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. P. Blanke is a consultant for Circle CVI, Edwards Lifesciences and Abbott. H. Reichenspurner receives speaker support and travel honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences and is a consultant to HeartWare/Medtronic. U. Schäfer receives travel compensation from Symetis and Abbott Vascular as well as research funding, travel support, and speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences for whom he is a proctor. D. Tchétché is a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences. A. Linke has stock options with Claret Medical, has received grant support from Medtronic, Edwards Lifesciences, and Boston Scientific, and is a consultant to Abbott Vascular. M. Spence receives research funding, travel support, and speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences and is a proctor for Edwards Lifesciences, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. L. Søndergaard is a proctor for and has received institutional grants from Edwards Lifesciences. G. Schymik is a proctor for and has received speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences. M. Abdel-Wahab is a proctor for Boston Scientific and has received speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. D. Walters is a proctor for and has performed clinical research for Edwards Lifesciences. A. Kasel is a proctor for Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. S. Windecker has received research grants to the institution from Bracco Pharmaceutical, Boston Scientific, St. Jude Medical, and Terumo. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
Supplementary Appendix. Methods, procedure and image analysis.
Supplementary Table 1. Baseline characteristics.
Supplementary Table 2. ROC analysis for prediction of PAR % perimeter oversizing valve implant population (N=198).
Supplementary Table 3. Frequency and extent of regurgitation perimeter oversizing valve implant population (N=198).
Supplementary Table 4. ROC analysis for predication of new permanent pacemaker implantation valve implant population (N=198).
Supplementary Table 5. ROC analysis for prediction of PAR % by aortic annulus calcification valve implant population (N=198).
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

