Abstract
Background: Few studies have evaluated intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) use in chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Aims: In CTO-PCI, we aimed to (1) evaluate the clinical benefits of performing post-stent IVUS in preventing adverse clinical events, and (2) identify IVUS parameters and cut-off values for prediction of target lesion revascularisation (TLR)/reocclusion.
Methods: A total of 1,077 patients with 1,077 CTO lesions treated with drug-eluting stents (DES) were included. Clinical outcomes during a median follow-up of 6.3 years were compared between subjects with and those without post-stent IVUS using the inverse probability weighting method.
Results: Of 1,077 patients, post-stent IVUS was performed in 838 (77.8%) cases while in the remaining 239 (22.2%) cases it was not. In the weighted population, the risk of TLR/reocclusion was significantly lower in subjects with post-stent IVUS (9.6% vs 18.9%, hazard ratio [HR] 0.54, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.34-0.86, p=0.01), compared with those without post-stent IVUS. Cox regression analysis showed that minimal stent area (MSA) measured by IVUS was the only parameter independently associated with TLR/reocclusion (HR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.64-0.95; p=0.01) and the optimal MSA cut-off value was 4.9 mm2 for prediction of TLR/reocclusion (area under the curve=0.632, p=0.001).
Conclusions: In CTO-PCI with DES, post-stent IVUS evaluation was associated with a lower risk of TLR/reocclusion. The final MSA was independently associated with TLR/reocclusion with a cut-off value of 4.9 mm2.
Introduction
Despite advances and the increasing success rates of chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), it remains associated with poorer clinical outcomes, especially higher rates of revascularisation compared with non-occlusive lesions1,2.
Recently, randomised trials and meta-analyses have repeatedly demonstrated that intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)-guided drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation significantly improved clinical outcomes, driven primarily by a lower risk of target lesion revascularisation (TLR), compared with angiography-only guidance3,4. IVUS is a useful tool to identify lesion severity, reference vessel size, lesion length, and extent of calcification in PCI planning5. In addition, according to the validated criteria for stent underexpansion and edge-related issues, post-stent IVUS has been used to optimise stent placement for the prevention of stent failure such as restenosis and early thrombosis5.
However, few studies have evaluated its role in stent deployment during CTO intervention and no data are available regarding the cut-off values for optimal stent expansion in CTO-PCI using DES6,7. Thus, this study aimed to (1) evaluate the benefit of performing post-stent IVUS in preventing adverse clinical events including TLR/reocclusion, (2) identify IVUS parameters for predicting TLR/reocclusion, and (3) assess the cut-off values of the IVUS parameters in CTO-PCI.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
The study population was obtained from the Asan Medical Center CTO registry, which contains prospectively collected data involving consecutive patients undergoing CTO-PCI since March 20038. This registry lists patients treated for one or more CTO lesions in major epicardial coronary arteries with a reference vessel diameter ≥2.5 mm. The current study analysed patients who underwent PCI between January 2007 and December 2016 entailing advanced CTO-PCI techniques such as the retrograde approach2. This study was approved by the institutional review board of Asan Medical Center and all participants provided written informed consent.
DEFINITIONS AND STUDY OUTCOMES
Procedures and stent implantation were performed according to standard protocols. Use of IVUS and specialised devices, techniques and the choice of stent type were all left to the operator’s discretion. Technical success was defined as a restoration of Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) grade 3 flow with a residual diameter stenosis (DS) of ≤30% within the treated segment, as determined by angiographic assessment9.
Revascularisation was defined as ischaemia-driven if there was angiographic DS ≥50%, as documented by a positive functional study, ischaemic changes on an electrocardiogram (ECG), or ischaemic symptoms. In addition, the lesions with angiographic DS ≥70% assessed by quantitative coronary analysis were considered to be “ischaemia-driven” even in the absence of documented ischaemia10. Death was considered to be of cardiac cause unless an unequivocal, non-cardiac origin was documented. Periprocedural myocardial infarction (MI) was defined as a peak elevation of the creatine kinase-myocardial band of more than tenfold above the upper reference limit within 48 hours after the procedure or a peak elevation of the creatine kinase-myocardial band of more than fivefold with new pathologic Q-waves in ≥2 contiguous leads or new persistent left bundle branch block (LBBB)11.
IVUS IMAGING, AND CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY AND ANALYSIS
Off-line IVUS analysis was performed using computerised planimetry (EchoPlaque 3.0; Indec Systems, Mountain View, CA, USA)10. At both the proximal and the distal reference segments (5 mm-long segment adjacent to the stent edge), the minimal lumen area (MLA) and external elastic membrane area were measured. The maximum plaque burden within the reference segment was calculated as plaque/external elastic membrane x100 (%)10. Quantitative angiographic analysis was carried out via standard techniques with automated edge-detection algorithms (CAAS 5; Pie Medical, Maastricht, the Netherlands). All baseline and procedural coronary angiograms were analysed independently by researchers in the angiographic core laboratory. Angiographic stenosis was defined as ≥50% DS. CTO lesion complexity was assessed by calculating the Japanese CTO (J-CTO) score for each case.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
To minimise confounding and residual selection bias in the comparison of observational treatments, the inverse probability weighting method based on the propensity scores was used to control imbalances in various baseline characteristics. To obtain estimates of the main effects, a pseudo data set was created by weighting each subject by inverse probability of treatment weight and analysed with conventional regression models. The sample size of the pseudo data sets can be different from the original data set because the number of observations is the sum of weights12. Propensity scores were estimated using a non-parsimonious multiple logistic regression model for treatment with IVUS guidance versus angiography guidance. The following variables were selected to calculate the propensity score: age, sex, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, current smoker, prior PCI, prior coronary artery bypass grafting, renal dysfunction, left ventricular ejection fraction, clinical presentation, target CTO lesions, in-stent restenosis, stent type generation, stent length per lesion, stent number per lesion, and average stent diameter. The model did not include procedural characteristics that might be affected by post-stent IVUS including adjunctive post-dilatation, final balloon size, and maximal inflation pressure. The balance of the pre-treatment covariates was assessed; significant improvement in baseline was achieved after weighting (Supplementary Table 1). In addition, we also performed a sensitivity analysis with the propensity score-matching method.
Cumulative incidence rates of adverse events were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were performed to identify the predictors of TLR/reocclusion. The various variables included in univariable analysis and the results are shown in Supplementary Table 2. Variables with a probability value ≤0.20 in univariable analyses were candidates for the multivariable Cox regression model. A backward elimination process was used to develop the final multivariable model, and the adjusted hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was calculated. To predict TLR/reocclusion or angiographic edge in-stent restenosis (ISR), a receiver-operating curve was used to identify the optimal cut-off values of IVUS parameters that minimised the distance between the curve and the upper corner.
P-values were two-sided, and p-values <0.05 were considered significant. We performed multiple imputations using Markov chain Monte Carlo methods in the SAS procedure due to missing data, albeit less than 3% were identified. Statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc (MedCalc Software, Mariakerke, Belgium), SAS software version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) and R software version 3.2.2 13 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria; www.r-project.org).
Results
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
From January 2007 to December 2016, 1,088 patients with 1,100 CTO lesions (including 12 patients with 2 CTO lesions) successfully underwent stent implantation. In 12 patients with 2 CTO lesions, only the first-treated CTO lesions were assessed, and 11 cases treated with bare metal stents were excluded. Finally, 1,077 patients with 1,077 lesions treated with DES were included in the present study. Among them, post-stent IVUS was performed in 838 (77.8%) cases, while the remaining 239 (22.2%) cases did not undergo post-stent IVUS (Figure 1). A total of 115 cases were excluded from the IVUS analysis for several reasons (Figure 1). Finally, 723 lesions were included in the analysis and clinical outcomes were assessed during a median follow-up period of 6.3 years (interquartile range: 3.5 to 9.0 years).
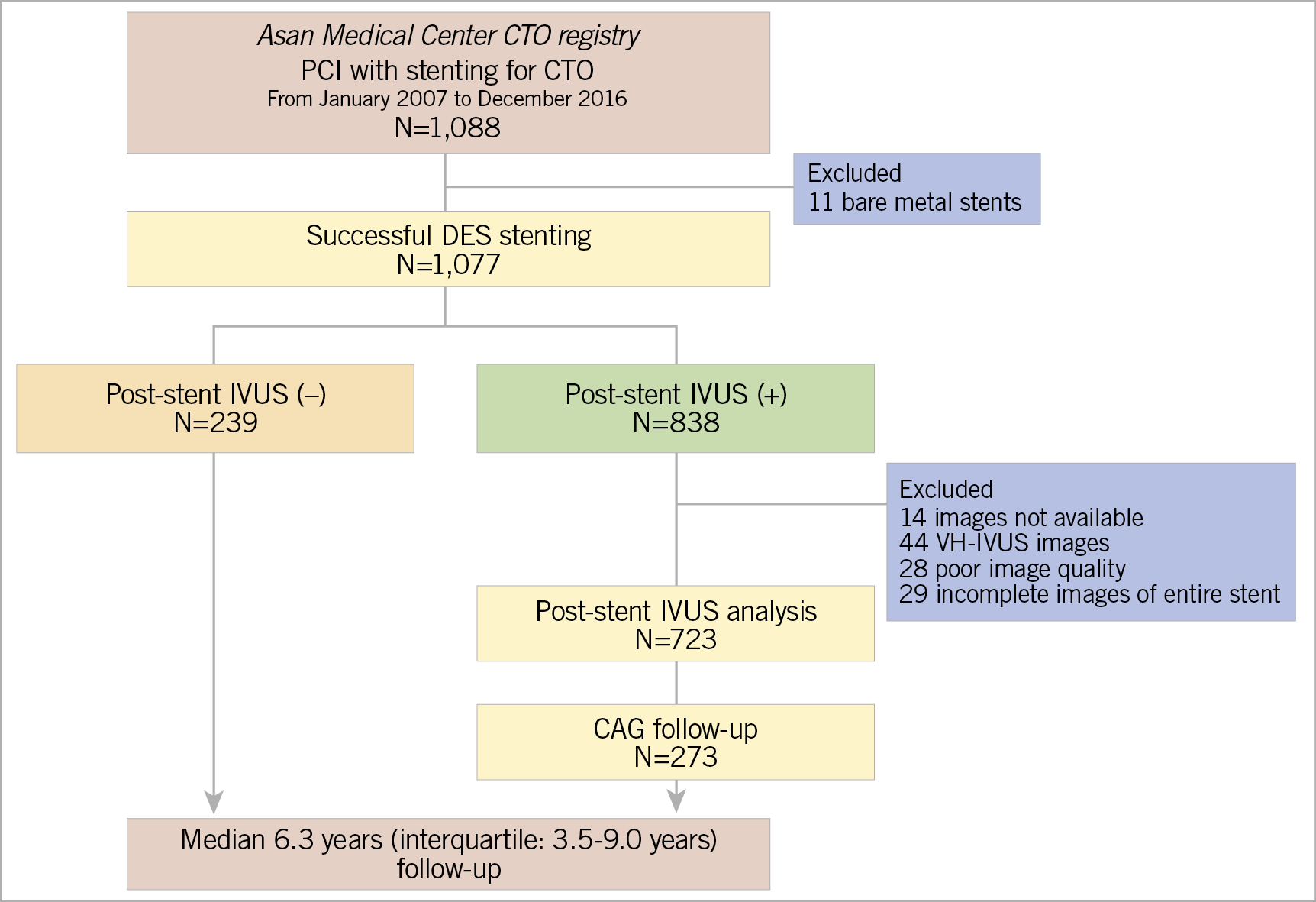
Figure 1. Study population. CAG: coronary angiography; CTO: chronic total occlusion; DES: drug-eluting stent; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; VH: virtual histology
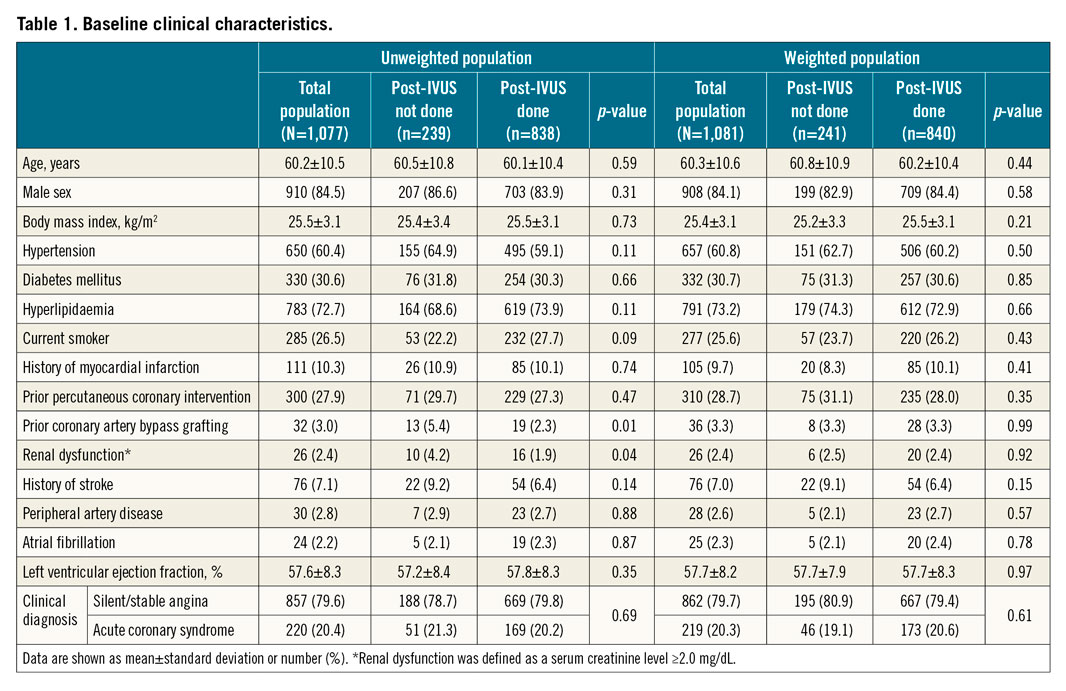
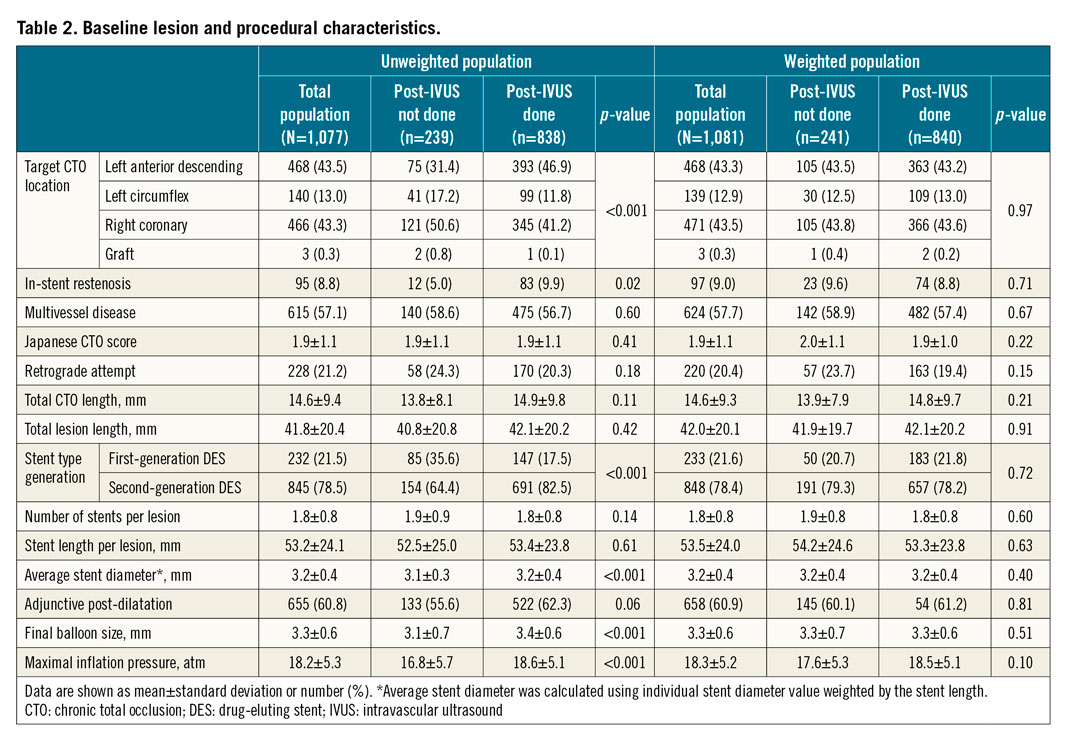
The baseline characteristics of the unweighted study patients are presented in Table 1 and Table 2. Patients undergoing post-stent IVUS had a greater prevalence of prior coronary artery bypass grafting, left anterior descending disease and ISR, and more frequently received second-generation DES with stents of a slightly larger diameter. Patients undergoing post-stent IVUS showed a significantly larger final balloon size (3.4±0.6 mm vs 3.1±0.7 mm; p<0.001) and higher maximal inflation pressure (18.6±5.1 atm vs 16.8±5.7 atm; p<0.001) compared with those without post-stent IVUS. In addition, there were no significant differences in in-hospital outcomes between the two groups according to whether post-stent IVUS was performed or not (Supplementary Table 3). After adjustment with the use of inverse probability weighting, all covariates were well balanced (Table 1, Table 2).
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
During the overall follow-up period, death occurred in 115 patients (16.6%), including 86 (13.4%) due to cardiac causes. Target vessel MI occurred in 37 patients (3.9%), and TLR/reocclusion occurred in 86 patients (11.6%).
The clinical outcomes are summarised in Supplementary Table 4. In the unweighted population, patients who underwent post-stent IVUS had a significantly lower cumulative TLR/reocclusion rate (9.7% vs 16.8%, HR 0.58, 95% CI: 0.36 to 0.93, p=0.02) compared with those without post-stent IVUS (Figure 2A). These results were consistent in the weighted population. Patients undergoing post-stent IVUS had a significantly lower cumulative TLR/reocclusion rate (9.6% vs 18.9%, HR 0.54, 95% CI: 0.34 to 0.86, p=0.01) compared with those without post-stent IVUS (Figure 2B). No significant difference existed between the two groups with respect to the risk of death, target vessel MI or stent thrombosis. Propensity score-matching analysis showed consistent results, demonstrating that the post-IVUS group was associated with a lower risk of TLR/reocclusion (Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Table 5).
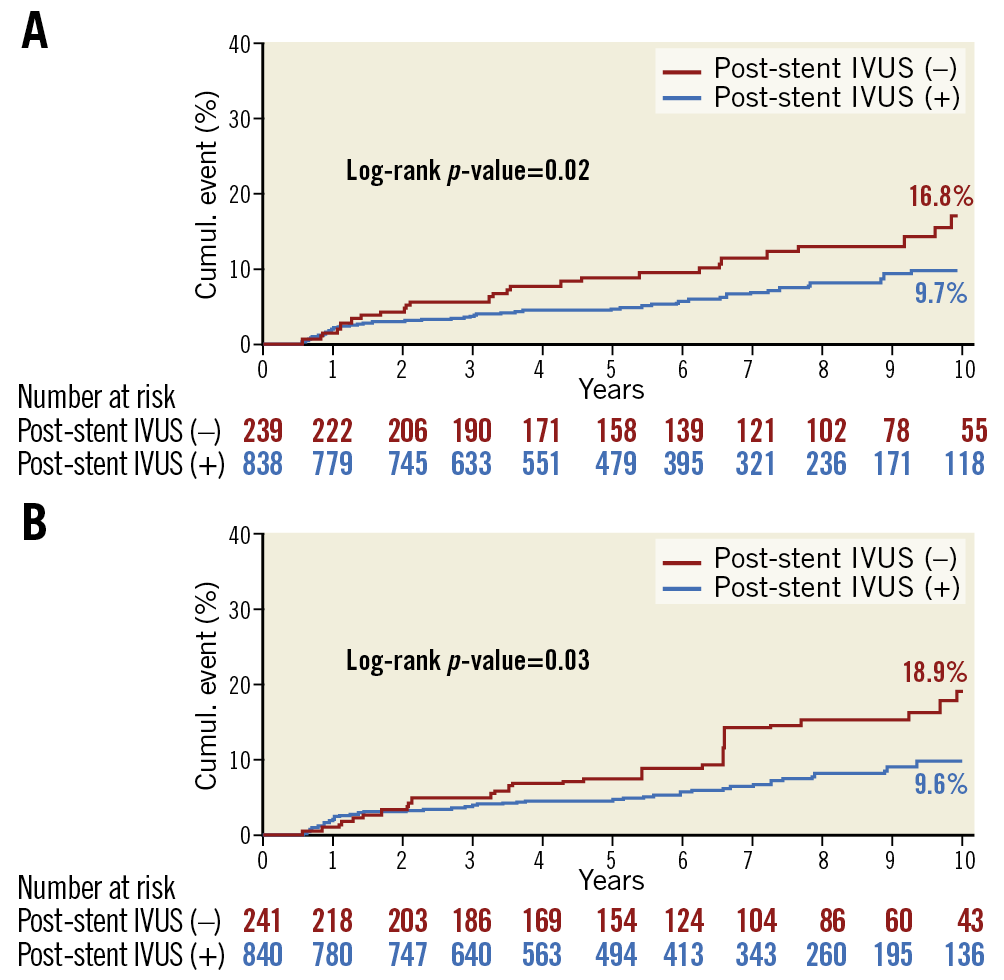
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier curves for target lesion revascularisation/reocclusion. A) Unweighted population. B) Weighted population. IVUS: intravascular ultrasound
IVUS ANALYSIS
Post-stenting IVUS findings are presented in Supplementary Table 6. In the post-stent IVUS analysis of 723 subjects, patients with TLR/reocclusion showed a significantly smaller MSA (4.6±1.2 mm2 vs 5.5±1.8 mm2; p=0.001).
Using multivariable Cox regression analysis, the absolute MSA measured by IVUS was identified as the only independent predictor of TLR/reocclusion (HR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.64 to 0.95; p=0.01) (Supplementary Table 7). The optimal MSA cut-off value in receiver-operating characteristic analysis was 4.9 mm2 for prediction of TLR/reocclusion with a sensitivity of 63.0% and a specificity of 58.3% (area under the curve=0.632, p=0.001) (Figure 3).
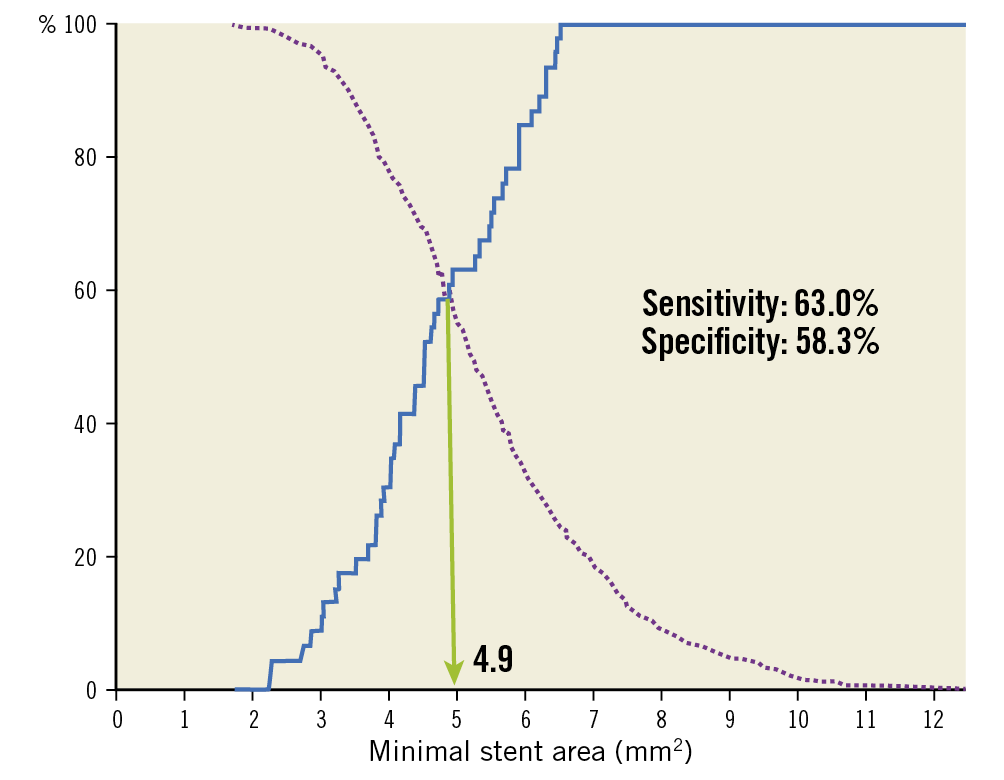
Figure 3. Optimal cut-off value of the final minimal stent area to predict target lesion revascularisation/reocclusion.
In 273 follow-up coronary angiographies in the post-stent IVUS group, 50 (9.2%) were identified as angiographic edge restenosis: 22 (8.1%) with proximal edge restenosis, 28 (10.3%) with distal edge restenosis, and 11 (4.0%) with both proximal and distal edge restenosis. For prediction of proximal edge restenosis, the cut-off for the reference plaque burden was 58.9% with a sensitivity of 70.0% and specificity of 74.1% (Figure 4A), while the cut-off for the reference plaque burden for the prediction of distal edge restenosis was 46.5% with a sensitivity of 79.2% and a specificity of 55.0% (Figure 4B).
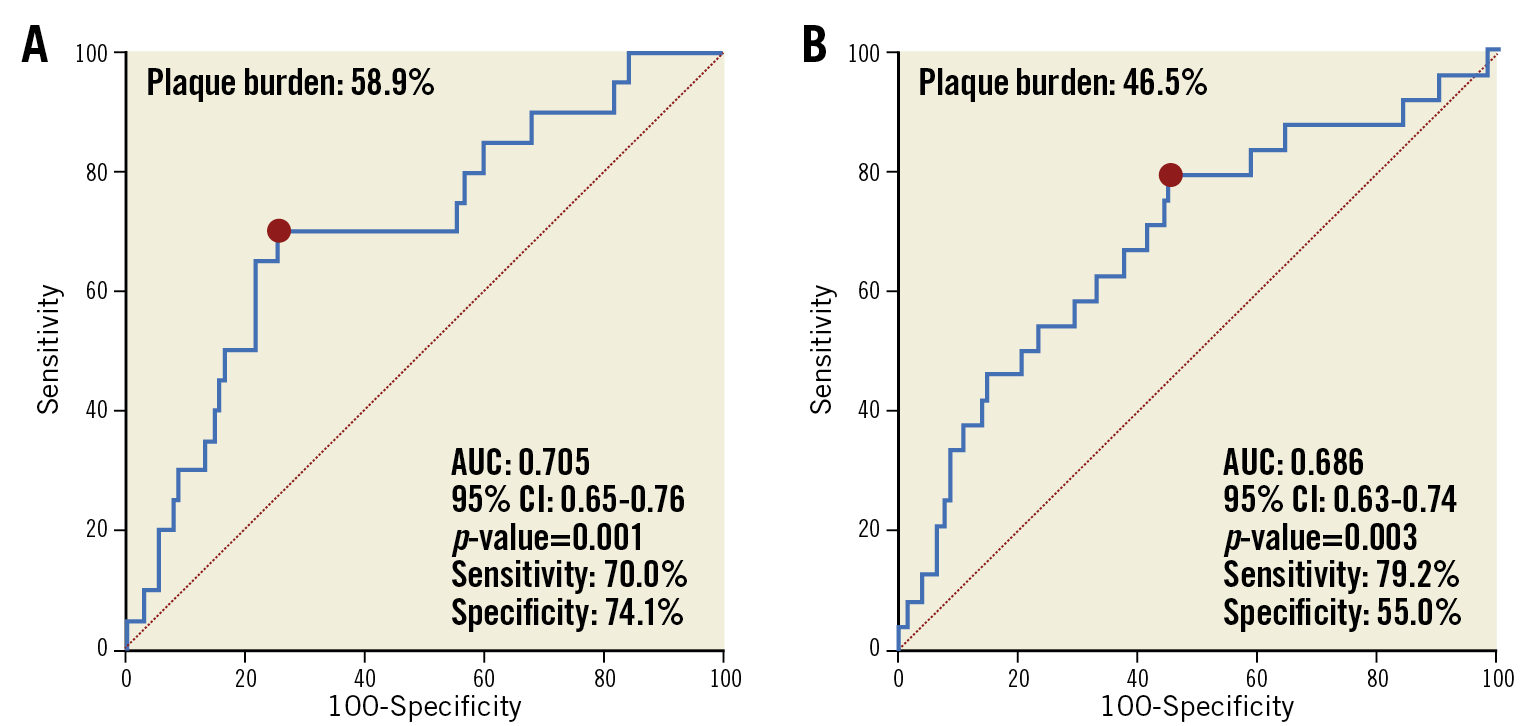
Figure 4. Receiver operating characteristic curves for intravascular ultrasound criteria of edge restenosis. A) Proximal reference segments. B) Distal reference segments. AUC: area under the curve
Discussion
The main findings of this study can be summarised by the following three points. 1) In CTO-PCI with DES, subjects with post-stent IVUS evaluation leading to larger final balloon size and higher maximal inflation pressure were associated with better clinical outcomes, driven primarily by a lower risk of TLR/reocclusion, compared with those without post-stent IVUS. 2) The MSA measured by IVUS was independently associated with TLR/reocclusion with a cut-off value of 4.9 mm2. 3) The reference plaque burden was associated with edge restenosis (DS ≥50%), with cut-offs of 58.9% for the proximal segment and 46.5% for the distal segment.
Until now, two randomised studies evaluating CTO-PCI showed that IVUS-guided DES implantation was associated with better clinical outcomes6,7; however, the observed benefits differed to some extent. In the AIR-CTO trial comprising 230 patients, IVUS guidance led to the improvement in in-stent late lumen loss. However, the benefits did not translate into a reduction of composite major adverse cardiac events, although the study was not powered for clinical events6. Notably, IVUS-guided stenting yielded a lower rate of definite/probable stent thrombosis at two years (0.9% vs 6.1%, p=0.043). Another randomised study involving 402 patients, however, demonstrated that major adverse cardiac event rates at 12 months were significantly lower in the IVUS-guided group than in the angiography-guided group (2.6% vs 7.1%; p=0.035)7. Occurrence of the composite of cardiac death or MI was significantly lower in the IVUS-guided group while the rates of TLR were not significantly different between the two groups.
At the present time when only small-sized studies with a short-term follow-up frame are available, our large-scale study including more than 1,000 CTO subjects with a long-term follow-up period (median 6.3 years) adds to the evidence supporting IVUS guidance for CTO-PCI with DES. To address the inherent limitation of observational studies, we used the propensity score method to reduce the impact of treatment selection bias or potential confounding variables. We found that performing IVUS following stenting was associated with a lower risk of TLR/reocclusion. These findings are consistent with those of recent randomised studies and meta-analysis revealing that IVUS-guided PCI is superior to angiography-guided PCI in reducing the risk of major adverse events, driven mainly by a reduction of ischaemia-driven TLR3,4. In the absence of a definitive survival benefit of CTO-PCI based on the current literature13, it might be reasonable not to anticipate improvement in mortality with IVUS use for CTO-PCI. However, taking into consideration a higher repeat revascularisation rate of CTO-PCI causing further cost and risk, a risk reduction of TLR by post-stent IVUS use could be of substantial clinical benefit.
In the DES era, a threshold of stent expansion (5.0–5.5 mm2) measured by IVUS has been proposed to predict the occurrence of late clinical events14,15. Accordingly, several current studies using DES have adopted MLA in the stented segment >5.0 mm2 as one of the IVUS optimisation criteria7,16. Similarly, in the present analysis, the MSA was solely identified as a predictor of TLR/reocclusion, and our results showing an MSA cut-off of 4.9 mm2 for CTO lesions are in line with previous reports of various stenotic lesions14,15. It is believed that, based upon IVUS findings, a larger post-procedural MLA followed by more frequent adjunct post-dilation with a large-sized balloon may be a major contributing factor for prevention of restenosis after DES implantation4. Our findings that the post-stent IVUS group showed a higher proportion of adjunctive post-dilatation and larger final balloon size with higher maximal inflation pressure also support the proposed explanation. However, further investigations are warranted to elucidate the precise mechanisms underlying the clinical benefits of post-stent IVUS.
Despite the importance of full lesion coverage for better clinical outcomes, the use of longer stents has also been implicated as a risk factor for adverse clinical events. Thus, an acceptable residual plaque at the stent deployment site has been investigated to avoid unnecessarily long stents. Recently, in a study with second-generation DES, a reference segment with a maximum plaque burden >55% predicted edge restenosis with similarity of proximal and distal plaque burden10. The cut-off value of residual plaque burden for the proximal edge ISR was comparable to that reported in previous studies, whereas that of the distal edge ISR was relatively small in the present study. CTOs represent the most advanced form of atherosclerotic disease and are frequently associated with diffuse long lesions, which may inevitably lead to stenting in smaller calibre vessels accompanying considerable plaque burden. In this regard, our results might indicate a prudent distal landing of stents for CTO lesions, targeting areas with a lesser plaque burden area to prevent distal edge ISR. Given the higher restenosis rate in longer stented lesions17, and negative correlation between total stent length and MSA18, meticulous technique to obtain an optimal final MSA and select the shortest stent possible at the acceptable landing zone using IVUS guidance is needed.
Limitations
This study had several limitations. First, the retrospective nature and observational design of the analyses are associated with an inherent selection bias. Although we used propensity analysis to enable an even more rigorous adjustment for differences in baseline characteristics, the estimates of relative treatment effects might have incompletely corrected the imbalance. Second, the decisions as to whether or not to perform post-stent IVUS and the mode of application of IVUS images during procedures were left to the discretion of each operator, with no specific guidelines for stent optimisation. Third, a total of 115 cases were excluded from IVUS analysis, and follow-up angiography was available in only 273 (32.6%) patients among 838 patients with post-stent IVUS. Therefore, the possibility of selection bias cannot be excluded. Fourth, low rates of false lumen involvement assessed by post-stent IVUS were revealed in the study, but this finding might be unreliable. Because the false lumen created during the procedure is generally obliterated by stenting, post-stent IVUS is limited in evaluating false lumen status. The clinical impact of pre-stent IVUS findings including false lumen involvement should be investigated in future studies.
Conclusions
In CTO-PCI with DES, subjects with post-stent IVUS evaluation were associated with a significantly decreased risk of TLR/reocclusion compared with those without post-stent IVUS assessment. The MSA may be the most important IVUS predictor for TLR/reocclusion with a cut-off value of 4.9 mm2 for CTO lesions.
Impact on daily practice
In CTO-PCI with DES, post-stent IVUS evaluation was associated with improved clinical outcomes, driven primarily by a lower risk of target lesion revascularisation (TLR)/reocclusion, compared with procedures without post-stent IVUS. The minimal stent area measured by IVUS was independently associated with TLR/reocclusion with a cut-off value of 4.9 mm2. In order to reduce the subsequent risk for adverse cardiac events after CTO-PCI, operators could consider performing post-stent IVUS and assessing adequate stent expansion.
Conflict of interest statement
E.S. Brilakis has received consulting/speaker honoraria from Abbott Vascular, American Heart Association (associate editor Circulation), Amgen, Asahi Intecc, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Cardiovascular Innovations Foundation (Board of Directors), ControlRad, CSI, Elsevier, GE Healthcare, Infraredx, Medtronic, Siemens, and Teleflex, and research support from Regeneron. He is the owner of Hippocrates LLC, and shareholder of MHI Ventures and Cleerly Health. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

