Abstract
Background: Connecting the antegrade wire (AW) and the retrograde wire (RW) is a goal of chronic total occlusion (CTO) treatment, but angiographic guidewire location is sometimes misleading.
Aims: The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)-defined AW and RW position and procedural outcomes when treating CTO lesions using the retrograde approach.
Methods: Overall, 191 CTO lesions treated using an IVUS-guided retrograde approach at three centres in Japan, China, and the USA were included.
Results: When the AW and RW angiographically overlapped, four wire positions were seen on IVUS: (i) AW within the plaque (AW-intraplaque) and RW-intraplaque in 34%; (ii) AW-intraplaque and RW in the subintimal space (RW-subintima) in 28%; (iii) AW-subintima and RW-subintima in 22%; or (iv) AW-subintima and RW-intraplaque in 16%. The procedure succeeded without repositioning the wire in 89% of AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque, 61% of AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima and 57% of AW-subintima/RW-subintima, but only one (3%) AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque. Lesion and procedure complexity and failure/complications were greatest in AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque.
Conclusions: IVUS-identified vascular compartment concordance versus IVUS-identified vascular compartment mismatch leads to higher success rates irrespective of intraplaque or subintimal passage. AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque was associated with the most complex CTO morphology and procedure, and repositioning the wire was almost always necessary.
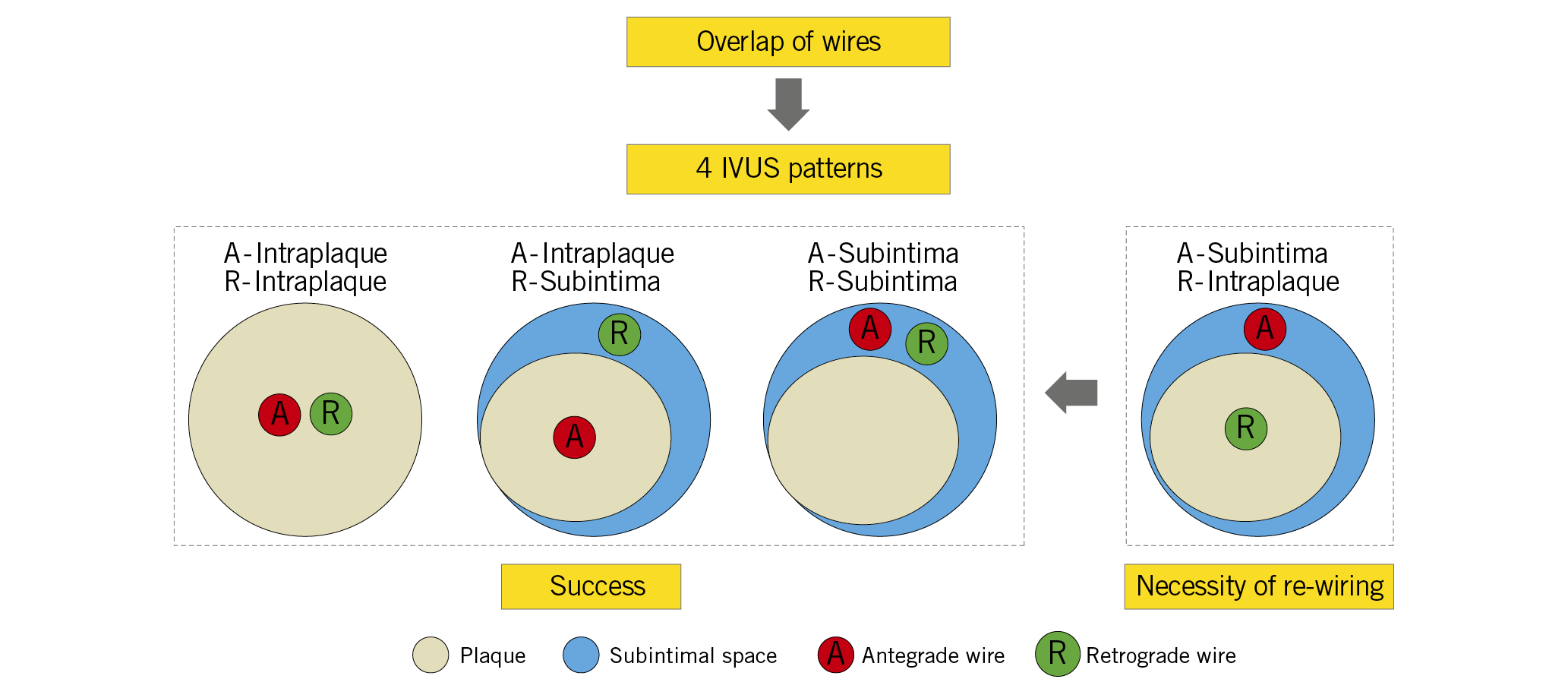
Visual summary. When the antegrade wire is in the subintimal space and the retrograde wire is in the intraplaque, re-wiring is almost always necessary.
Introduction
During the past two decades, there has been significant progress in CTO intervention equipment and techniques, especially the retrograde and reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde tracking and dissection (CART) techniques1,2,3. This has resulted in improved success rates4,5,6. For many interventionists, however, retrograde techniques remain unadopted due to the technical challenges of channel crossing and reverse CART that can lead to major complications.
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) is important during reverse CART, especially for appropriate balloon sizing and understanding the cause of failure during each step1,7. Rathore et al1 first described IVUS-guided reverse CART; however, the four possible antegrade wire (AW) and retrograde wire (RW) locations within the CTO were not described in detail. We used IVUS to identify guidewire location after angiographic overlap of the AW and RW to categorise four possible patterns – (i) AW within the plaque (AW-intraplaque) and RW-intraplaque; (ii) AW-intraplaque and RW in the subintimal space (RW-subintima); (iii) AW-subintima and RW-subintima; and (iv) AW-subintima and RW-intraplaque– and clarified the association between various patterns and lesion characteristics, procedural success, and in-hospital outcomes.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
This was a retrospective observational study. Inclusion criteria were IVUS-guided CTO revascularisation requiring a retrograde approach in which the wire location was evaluated by IVUS when the AW and RW overlapped longitudinally on angiography. Exclusion criteria included lack of analysable IVUS images after RW crossing or in-stent CTO. CTO was defined according to previous criteria8; in patients without clinical evidence of occlusion duration, chronicity was based on angiographic anatomy suggesting long-standing occlusion. From January 2010 to December 2018, CTOs from three centres in Japan (Showa University Hospital, Showa), China (Xiangtan Central Hospital, Xiangtan), and the USA (NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA) were screened. The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the ethics committees of each centre.
CTO PROCEDURES
Procedures were performed by one of three experienced operators (M. Ochiai, H. Huang, or D. Karmpaliotis). Treatment strategy was at operator discretion based on the previously defined “hybrid” treatment algorithm2. When the AW and RW appeared overlapped longitudinally on angiography, IVUS was performed on the AW to confirm the location of the two wires. If the operator repositioned either of the wires, IVUS was repeated to confirm guidewire location. Repositioning the wire included either removing the guidewire from its initial position and redirecting it to a different tissue plane or using a new wire to penetrate the distal cap (retrograde) or proximal cap (antegrade). After successful RW crossing into the true lumen proximal to the CTO, IVUS was again performed to confirm wire location.
Guidewire penetration force was defined as low, intermediate, or high3. Total procedure or wire crossing time was from obtaining vascular access to removal of the last catheter or to externalising the RW into the antegrade guiding catheter. Wire crossing time after the first IVUS was the interval between the first IVUS and externalising the RW into the antegrade guiding catheter. Reverse CART involved using balloons over the AW to make a dissection within the CTO segment to create a connection between spaces containing the AW and RW with or without guide-catheter extension9. Successful recanalisation was restoration of antegrade Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) flow grade 3 with <30% treated segment residual diameter stenosis8.
IN-HOSPITAL OUTCOMES
In-hospital clinical safety endpoints included major adverse cardiac events and each component – all-cause death, myocardial infarction (MI), target lesion revascularisation, tamponade requiring either pericardiocentesis or surgery, or stroke10. Periprocedural MI was diagnosed using Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions criteria11. In addition, Academic Research Consortium-defined stent thrombosis10, any angiographic staining/extravasation, and clinically significant perforation (requiring treatment with pericardiocentesis, prolonged balloon inflation, beads, coils, thrombin, or surgery) were recorded. Individual events were confirmed by investigator consensus.
ANGIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS
Cine-angiograms were analysed with a computer-assisted, automated edge-detection algorithm (QAngio XA; Medis, Leiden, the Netherlands) by an experienced observer (Y. Fan)12. Occlusion length was measured with either antegrade or retrograde (simultaneous bilateral injection) filling of the distal vessel. Lesion complexity was summarised using the Multicenter CTO Registry in Japan (J-CTO) score13. Branch occlusion was final TIMI flow ≤1 in a previously patent side branch (diameter ≥1.5 mm).
IVUS ANALYSIS
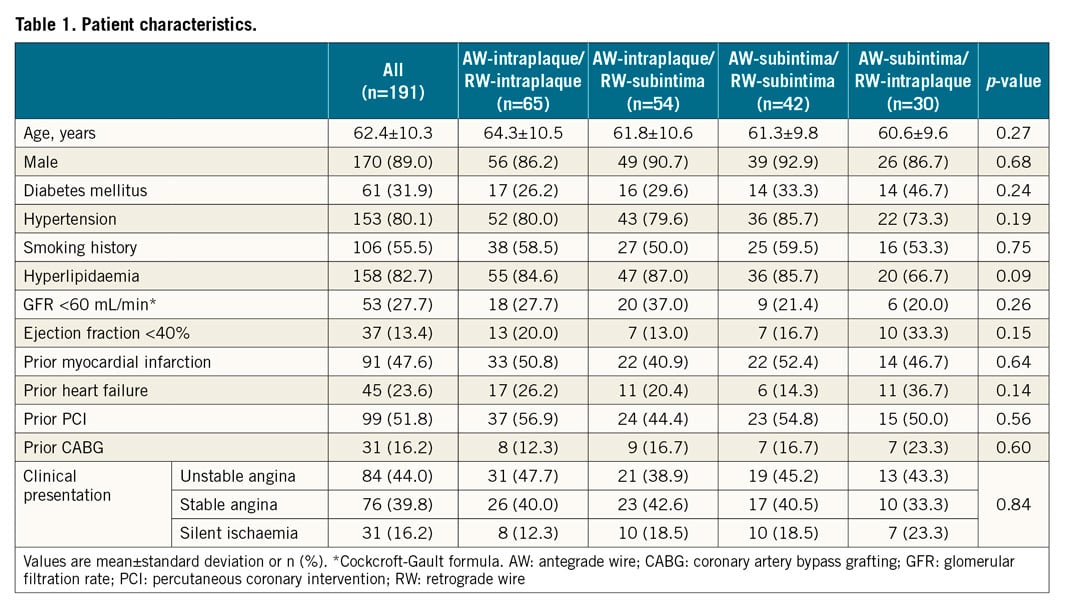
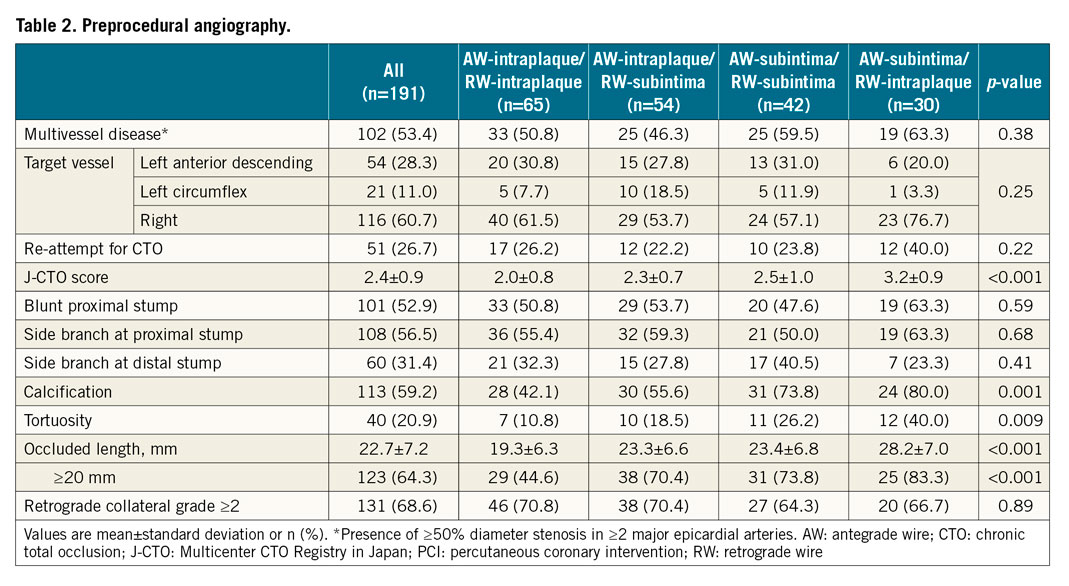
When the AW and RW overlapped angiographically, IVUS was performed after a 1.5-2.5 mm balloon predilation, if needed, using commercially available systems (Boston Scientific Corporation, Maple Grove, MN, USA; Philips, Rancho Cordova, CA, USA). Using planimetry software (echoPlaque; INDEC Medical Systems, Inc., Los Altos, CA, USA), IVUS analysis was performed as previously reported7. Intraplaque wire location was a wire located within the plaque, and subintimal wire location was a wire located in the subintimal space that was identified by the absence of arterial three-layer appearance (Figure 1). Four patterns were identified: (i) AW-intraplaque and RW-intraplaque; (ii) AW-intraplaque and RW-subintima; (iii) AW-subintima and RW-subintima; and (iv) AW-subintima and RW-intraplaque (Figure 2). The proximal and distal ends of the CTO were identified by matching IVUS images with the angiogram according to side branches. IVUS analyses were performed by experienced cardiologists (Y. Fan and A. Maehara).
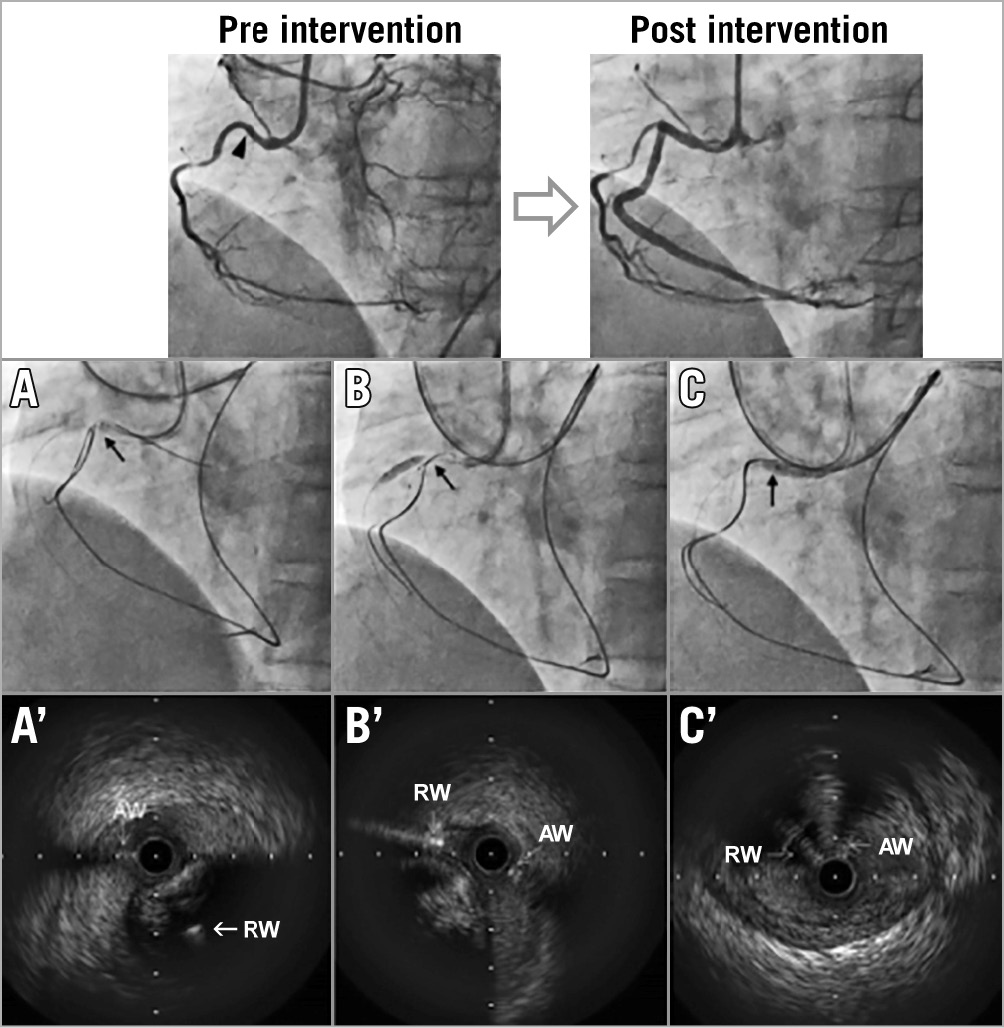
Figure 1. Chronic total occlusion treated with intravascular ultrasound-guided retrograde approach. The top panels show pre-intervention and final angiography. Black arrowhead indicates the proximal cap of the CTO. Lower panels show angiography (A-C) and corresponding IVUS (A′-C′) at each step. Black arrow indicates IVUS location. When the AW and RW overlapped longitudinally (A), IVUS (A′) showed a subintimal AW and an intraplaque RW. After repositioning the RW (B), IVUS (B′) showed that both the AW and the RW were subintimal. Subsequently, the RW crossed into the true lumen proximal to the CTO (C, C′). AW: antegrade wire; CTO: chronic total occlusion; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; RW: retrograde wire
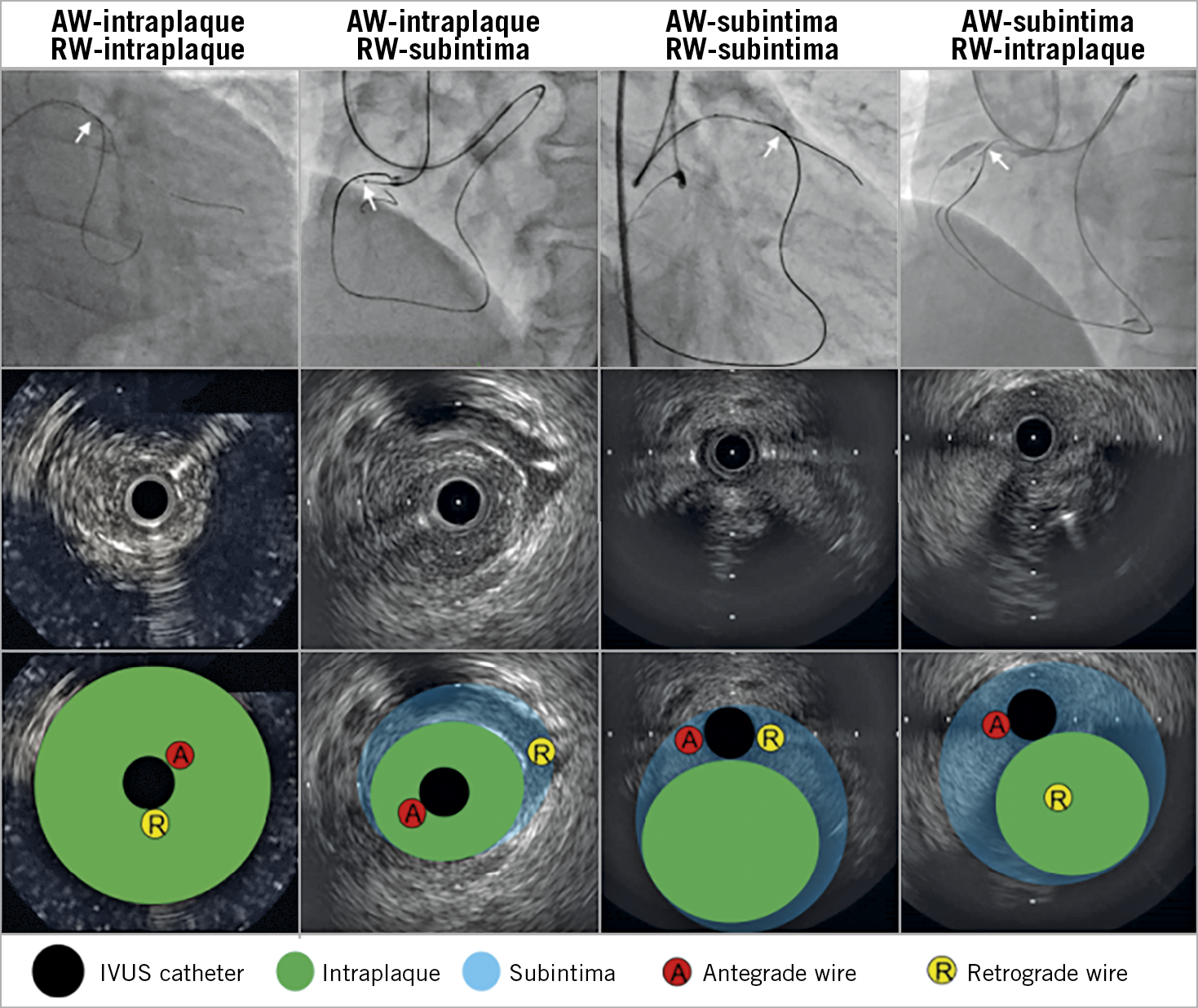
Figure 2. Four patterns of antegrade and retrograde wire positions. In the top panels, angiography shows overlapped AW and RW. White arrows indicate IVUS location. Middle panels show corresponding IVUS images; bottom panels show the same IVUS images with annotation. AW: antegrade wire; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; RW: retrograde wire
STATISTICAL ANALYSES
All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS, Version 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Categorical variables are shown as percentages and were compared using the χ2 test and continu-ous variables are shown as mean±standard deviation and were compared using ANOVA or Kruskal-Wallis tests, as appropriate. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
From January 2010 to December 2018, 1,902 CTO lesions were treated with IVUS guidance at three centres; 1,244 were antegrade only, and 467 retrograde did not have IVUS at the time of wire overlap. Thus, 191 CTO lesions undergoing IVUS-guided retrograde CTO were included in the current study (Supplementary Figure 1).
INITIAL IVUS EVALUATION AND CTO MORPHOLOGY
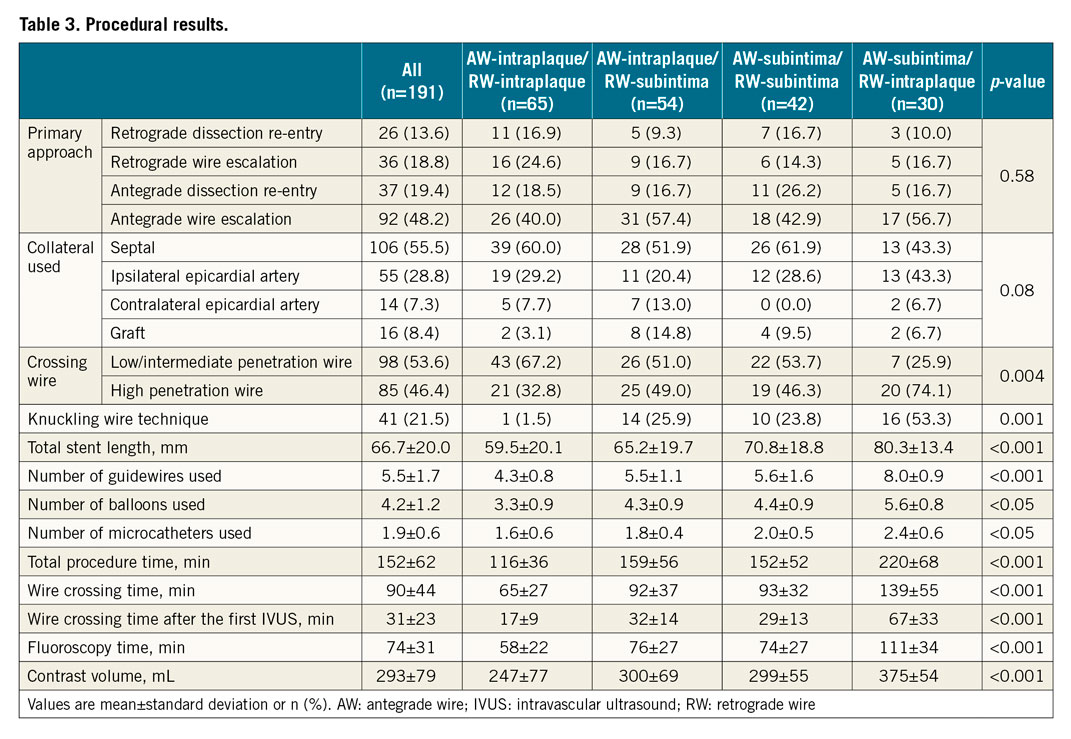
When the AW and RW overlapped on angiography, IVUS showed the following guidewire location patterns: AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque in 34% (n=65), AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima in 28% (n=54), AW-subintima/RW-subintima in 22% (n=42), and AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque in 16% (n=30) (Figure 3). AW/RW overlap was within the CTO in 46.6%, proximal to the proximal cap in 34.6%, and distal to the distal cap in 18.8%. There were no differences in patient characteristics among the four patterns (Table 1). The J-CTO score was highest in AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque and lowest in AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque (3.2±0.9 versus 2.0±0.8, p<0.001) (Table 2). Moderate or severe calcification, tortuosity, and longer CTO length were most common in the AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque group.
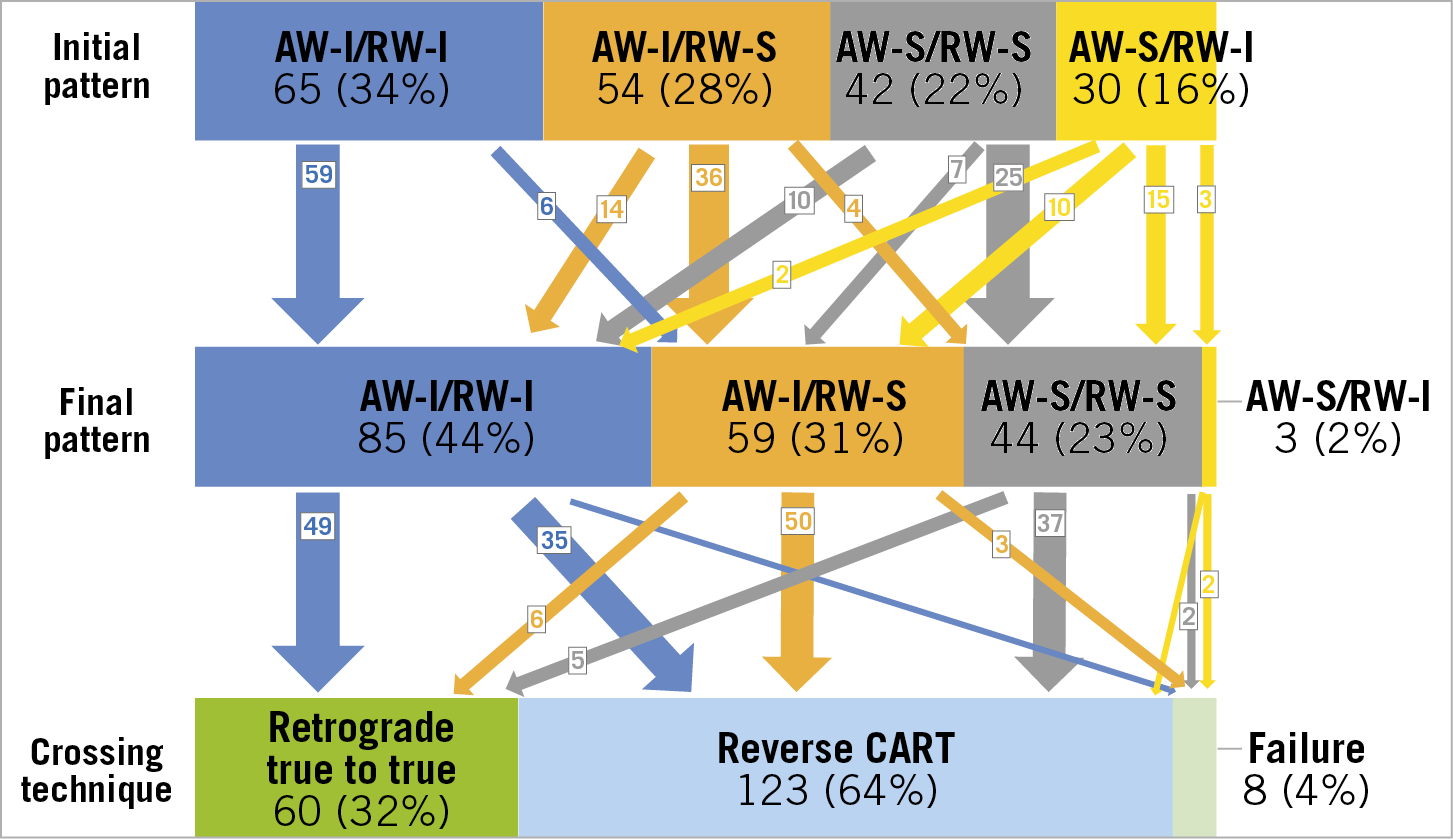
Figure 3. Intravascular ultrasound patterns before and after wire repositioning, if necessary, and final crossing techniques. Initial pattern was defined by IVUS after AW and RW overlapped longitudinally on angiography. The final pattern indicates IVUS patterns after repositioning the wire (if necessary) and before crossing. AW: antegrade wire; I: intraplaque; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; RW: retrograde wire; S: subintima
IVUS-GUIDED WIRE REPOSITIONING
After the first IVUS evaluation, the operator could advance the RW into the true lumen proximal to the CTO without repositioning the wire in 89% (58/65) of AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque, 61% (33/54) of AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima, and 57% (24/42) of AW-subintima/RW-subintima, but only 3% (1/30) of AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque (Figure 3).
In 17/42 CTOs with an AW-subintima/RW-subintima in which the wire was repositioned, there was a shorter subintimal length (8.4±2.5 mm versus 12.5±4.7 mm, p=0.048), smaller haematoma arc (110±46° versus 179±58°, p=0.03), and smaller calcium arc (89±65° versus 152±11°, p=0.03) compared to CTOs in which the wire was not repositioned. A similar trend was observed in the AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima. After wire repositioning, 26% (14/54) of AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima and 24% (10/42) of AW-subintima/RW-subintima were changed to the AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque. Among 30 AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque, wire repositioning was necessary in all except one case.
TECHNIQUES TO CONNECT THE AW AND RW
After wire repositioning (if necessary), the final IVUS patterns were AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque in 44% (n=85), AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima in 31% (n=59), AW-subintima/RW-subintima in 23% (n=44), and AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque in 2% (n=3) (Figure 3).
Overall, 183 cases (96%) were successful. In the AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque, RW escalation penetrated from the distal true lumen to the proximal true lumen (true-to-true RW crossing) in 58% (49/85); the rest were successful using the reverse CART technique. Reverse CART was successful in 85% (50/59) of AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima and 84% (37/44) of AW-subintima/RW-subintima. There was only one case with an AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque that succeeded using reverse CART.
Overall, there were eight failures in which the AW and RW could not be connected. Three had an initial IVUS AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque. The final IVUS patterns were one AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque, three AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima, two AW-subintima/RW-subintima, and two AW-subintima/RW-intra-plaque.
Among 183 successful cases, the final crossing point of the RW into the AW space moved from the original overlap segment to another location in 28.4% (33/116) in which the wire was not repositioned and in 55.2% (37/67) after wire repositioning.
FINAL RESULTS AND IN-HOSPITAL COMPLICATIONS
When an initial IVUS AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque was found, a high penetration wire and a knuckling wire were often necessary; this was associated with longer stents, more equipment, and longer wire crossing and procedure times versus other patterns (Table 3). The AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque showed a longer subintimal length versus other patterns (Supplementary Table 1). However, the final minimal stent area was similar among all four patterns in the 183 successful cases.
There was no death, in-hospital repeat revascularisation, or probable/definite stent thrombosis. There were three clinically significant perforations: two cases were treated by covered stent and one by prolonged balloon inflation (Table 4). Clinically significant perforation and tamponade were numerically higher in AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque (6.7%), and branch occlusion was the most common in the AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque (23.3%).

Discussion
Major findings were as follows. (i) When performing a retrograde CTO, IVUS showed four AW/RW patterns – AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque, AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima, AW-subintima/RW-subintima, and AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque. These patterns were associated with lesion complexity and with difficulties and techniques needed to achieve procedural success. (ii) The AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque had the most complex CTO morphology and procedures. (iii) In AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque, almost all CTOs required wire repositioning, in the AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima or AW-subintima/RW-subintima approximately half of the CTOs required repositioning of the wire, and wire repositioning was not necessary when both guidewires were intraplaque. Ultimately, IVUS-identified vascular compartment concordance leads to higher success rates irrespective of intraplaque or subintimal passage versus IVUS-identified vascular compartment mismatch.
Connecting the AW and RW is the most difficult part of the retrograde approach and typically requires various CART techniques; however, guidewire location is not always predictable angiographically7. The current report supports using IVUS to determine AW/RW location and select the CTO strategy. Practically, operators should adopt IVUS when they cannot make the connection quickly or wire position is uncertain angiographically.
The most difficult situation was a subintimal AW, but an intraplaque RW; this was seen in the most complex CTOs and took the longest to resolve. Balloon dilation on the AW simply enlarged the subintimal space without disrupting the plaque necessary to connect the AW and RW. When this pattern was found, repositioning the RW and puncture and disruption of the plaque using a high penetration force guidewire accompanied by balloon dilation was necessary to connect the true lumen where the RW was located within the subintimal space where the AW was located. When this failed, knuckling the retrograde wire could be considered. Recognition of this pattern was the most useful to change the strategy and promote safer and more effective procedures. A subintimal AW/intraplaque RW may often occur during antegrade dissection as the primary procedure in the most complex lesions. Primary antegrade dissection trended towards being more frequent among US operators than among Asian operators (28.6% versus 17.3%) and being more frequent recently (22.1% after 2015 versus 12.7% before 2014) (Supplementary Table 2, Supplementary Table 3).
Favourable patterns were when both the AW and RW were subintimal or when the AW was intraplaque, but the RW was subintimal. When the AW was intraplaque, but the RW was subintimal, the next step should be to crack the plaque to make a connection. Thus, the largest balloon sized by IVUS should be used to complete reverse CART.
When both the AW and RW were subintimal, 88% were successful by reverse CART, although it was necessary to move the reverse CART site to a more favourable location with less calcium. US and Asian operators took different approaches when both wires were subintimal. The US approach was to create a connection in the subintimal space and complete the CTO procedure; this was successful in 13 (100%). Japanese and Chinese operators repositioned the wire after confirming limited injury and non-calcified CTO morphology to achieve both AW and RW intraplaque wiring; converting an AW-subintima/RW-subintima to an AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque was successful in 14 (93.3%). A similar trend was observed when the AW was intraplaque, but the RW was subintimal. We have reported that CTOs with subintimal stenting (54% of lesions) had more target vessel revascularisation versus those with intraplaque stenting at one year, although subintimal tracking no longer correlated with outcome after adjusting for patient and procedural factors14. Thus, intraplaque stenting requiring repositioning of the guidewire may not be necessary and can be reserved for lesions with limited calcium and vessel injury having a high possibility of intraplaque re-wiring.
Finally, the most favourable, ideal scenario was when both the AW and RW were intraplaque: a connection could be achieved by antegrade balloon dilation in the CTO body. This pattern did not require repositioning of the wire in most cases, and successful wire crossing was often performed using a low or intermediate penetration force guidewire.
Although the retrograde approach has been considered more complex than the antegrade approach, in our study the overall successful recanalisation rate of the IVUS-guided CTO procedure was 95.8%. The prevalence of in-hospital events was 4.2%, similar to previous series that included only retrograde CTO procedures4,6,15.
Limitations
This was a retrospective, observational study. The number of patients included was relatively small. Long-term follow-up was not available. The procedure was performed over a long period (2010-2018) during which there were major device improvements. Finally, procedures were performed by experienced CTO operators in dedicated, high-volume centres, limiting extrapolation to less experienced operators/centres.
Conclusions
IVUS-identified vascular compartment concordance leads to higher success rates irrespective of intraplaque or subintimal passage than IVUS-identified vascular compartment mismatch. An AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque pattern was associated with the most complex CTO morphology and procedure, and repositioning of the wire was almost always necessary.
|
Impact on daily practice When performing a retrograde CTO, IVUS was useful to determine four possible locations of the AW and RW – AW-intraplaque/RW-intraplaque, AW-intraplaque/RW-subintima, AW-subintima/RW-subintima, and AW-subintima/RW-intraplaque. Lesion complexity and success of wire crossing varied among patterns. When the AW was subintima and the RW was intraplaque, wire repositioning was almost always necessary for success; approximately half of the CTOs required repositioning of the wire when the AW was intraplaque and the RW was subintima or when the AW and the RW were both subintima. Repositioning was not necessary when both wires were intraplaque. |
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dominic P. Francese, MPH, for assistance in preparing the manuscript.
Appendix. Study collaborators
Juan J. Russo, MD, Megha Prasad, MD, Yousif Ahmad, MD; NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA. Fotis Gkargkoulas, MD, Martin B. Leon, MD; Clinical Trials Center, Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY, and NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA. Gregg W. Stone, MD; Clinical Trials Center, Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY, and The Zena and Michael A. Wiener Cardiovascular Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Maehara reports grant support from and being a consultant for Abbott Vascular and Boston Scientific. M. Matsumura reports being a consultant for Terumo. Z.A. Ali reports institutional research grants to Columbia University from Abbott, and Cardiovascular Systems Inc., being a consultant to Amgen, AstraZeneca, and -Boston Scientific, and having equity in Shockwave. A. Kirtane reports institutional funding to Columbia University and/or Cardiovascular Research Foundation from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Abiomed, CSI, CathWorks, Siemens, Philips, and ReCor Medical. In addition to research grants, institutional funding includes fees paid to Columbia University and/or Cardiovascular Research Foundation for speaking engagements and/or consulting. A. Kirtane also reports personal fees for consulting for Neurotronic, and travel expenses/meals from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Abiomed, CSI, CathWorks, Siemens, Philips, ReCor Medical, Chiesi, Opsens, Zoll, and Regeneron. M. Leon reports institutional research grants and being a non-paid advisor for Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, being a non-paid advisor for Sinomed, and equity in Medinol. G.W. Stone declares speaker and other honoraria from Cook, Terumo, Orchestra Biomed, and Qool Therapeutics, being a consultant to TherOx, Reva, Vascular Dynamics, Robocath, HeartFlow, Gore, Ablative Solutions, Matrizyme, Miracor, -Neovasc, V-Wave, Abiomed, Shockwave, MAIA Pharmaceuticals, Cardiomech, SpectraWAVE, Valfix, Ancora, and Vectorious, and having equity/options from Applied Therapeutics, Biostar family of funds, MedFocus family of funds, Aria, Cardiac Success, Cagent, SpectraWAVE, Valfix, Ancora, Orchestra Biomed, and Qool Therapeutics. G.S. Mintz reports honoraria from Boston Scientific, Philips, Medtronic, and Abiomed. M. Ochiai reports honoraria from Abbott Vascular, Asahi Intecc, Boston Scientific, and Terumo. D. Karmpaliotis reports honoraria from Abiomed, Boston Scientific, and Abbott Vascular, and equity in Saranas, SoundBite, and Traverse Vascular. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

