Abstract
Background: Clinical and angiographic outcomes following recanalisation of coronary chronic total occlusions (CTO) through contemporary dissection and re-entry techniques (DART) as opposed to intraplaque techniques remain controversial.
Aims: The aim of this study was to compare clinical and angiographic outcomes following subintimal and intraplaque CTO recanalisation.
Methods: A total of 454 consecutive patients undergoing successful CTO recanalisation (473 vessels) were included. Intraplaque techniques were used in 403 (85.2%) and DART in 70 (14.8%) vessels. Surveillance angiography was scheduled at 6-9 months and clinical follow-up was performed up to 12 months.
Results: There were no significant differences in terms of the cumulative incidence of MACE (p=0.908) or binary restenosis (p=0.320) between the two groups. There was no independent correlation between recanalisation technique and MACE occurrence or in-segment binary restenosis. Target lesion revascularisation (TLR) was performed in 60 (17.5%) and 12 (18.1%) (p=0.719) lesions, respectively. The occurrence of occlusive restenosis was low (7 [2.3%] vs 1 [1.6%]; p=0.824) and comparable between groups.
Conclusions: Contemporary DART are associated with similar midterm clinical and angiographic outcomes compared to intraplaque recanalisation. The rate of occlusive restenosis was low and comparable in both groups. Regardless of recanalisation technique, the overall incidences of binary restenosis and TLR following CTO recanalisation remain higher than those reported for non-CTO PCI.
Introduction
Chronic total occlusions (CTO) are found in a significant proportion of patients displaying obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD). Historically, CTO percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been associated with lower procedural success and higher major periprocedural complication rates compared to non-CTO PCI1. However, recent advances in recanalisation techniques, the introduction of dedicated equipment and the elaboration of systematic algorithmic approaches have significantly improved procedural success and reduced the occurrence of major complications2,3.
In particular, the adoption of dissection and re-entry techniques (DART) has played a major role in improving the success rate of CTO PCI3. Despite encouraging procedural results, the intermediate- and long-term outcomes of patients treated by means of subintimal as opposed to intraplaque techniques remain a matter of debate. The initial variant of DART, the subintimal tracking and re-entry (STAR) technique, which resulted in an uncontrollable re-entry into the distal lumen, was invariably associated with extensive vascular injury, large intramural haematomas and side branch occlusion as well as prohibitive rates of in-stent restenosis (ISR) and reocclusion4. However, DART have evolved over time, aiming at minimising the extent of subintimal dissection and vascular injury. Contrary to initial reports, contemporary DART have shown comparable midterm clinical outcomes to intraplaque crossing techniques5,6,7,8,9,10. However, the majority of studies comparing the outcomes of these recanalisation modalities did not include a systematic angiographic follow-up5,7,8,10. The ongoing controversy regarding the use of DART is highlighted by the recent proposal of an alternative CTO crossing algorithm, which restricts upfront adoption of antegrade dissection and re-entry (ADR) techniques even in the presence of long (>20 mm) occlusions, favouring the use of antegrade wire escalation (AWE) instead11.
Against this background, the aim of this study was to compare the midterm clinical and angiographic outcomes of intraplaque as opposed to subintimal CTO recanalisation achieved by contemporary DART.
Methods
STUDY PATIENTS, ENDPOINTS AND DEFINITIONS
Consecutive patients undergoing successful CTO recanalisation between 2015 and 2018 at the German Heart Centre Munich were included in the Intracoronary Stenting and Angiographic Results– Chronic Total Occlusion (ISAR-CTO) registry. The study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki and the locally appointed ethics committee approved the study protocol. Informed consent was obtained for all patients prior to each scheduled procedure. Follow-up angiography was scheduled at 6-9 months after successful CTO recanalisation. Target lesion revascularisation (TLR) was performed according to the Academic Research Consortium (ARC) criteria12 in case of: i) ≥50% diameter stenosis (%DS) with accompanying signs or symptoms of myocardial ischaemia, or ii) ≥70%DS even in the absence of ischaemic signs or symptoms. Clinical follow-up up to 12 months was performed by office visit, phone contact or structured follow-up letter.
Lesion complexity was assessed by means of the J-CTO score. The recanalisation technique was categorised as intraplaque (AWE or retrograde wire escalation [RWE]), or subintimal (ADR or reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde tracking [rCART]). Use of dedicated instruments (CrossBoss™ catheter/Stingray™ LP system; Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) was also recorded. Dual antiplatelet therapy was prescribed for at least 12 months following CTO PCI.
The primary endpoint of the study was the cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), defined as a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction (MI) or TLR. The individual components of the primary endpoint were also assessed separately. The secondary endpoint was in-segment binary restenosis at surveillance angiography.
ANGIOGRAPHIC DATA ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS
Baseline, post-procedural and follow-up angiograms were recorded and assessed off-line in a core laboratory (ISAResearch Center, Munich, Germany). Details and definitions are provided in Supplementary Appendix 1.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous data are presented as mean±SD or median (interquartile range) and categorical data as observed frequencies or proportions (%). The normality of distribution of continuous data was assessed by means of the Shapiro-Wilk test. Data were analysed on a per-patient basis for clinical characteristics and on a per-lesion basis for the remaining calculations. For patient-level data, differences between groups were checked for significance using the Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test for continuous data or the chi-square test (or Fisher’s exact test when an expected cell value was <5) for categorical variables. For lesion-level data, differences between groups were checked for statistical significance using generalised estimating equations for non-normally distributed data in order to address intra-patient correlation in the case of patients undergoing multilesion intervention13. Clinical outcomes were assessed with the Kaplan-Meier method and hazard ratios (HR) with pertinent 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were calculated using the univariable Cox proportional hazards model. Independent predictors of MACE occurrence were analysed by means of multivariable Cox proportional hazards models accounting for clustering effect for patients with multilesion intervention, whereas generalised estimating equations were used for the identification of independent predictors of binary restenosis. The selection of variables for both multivariable models was performed using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression method14 after entering all clinical, procedural and angiographic parameters as candidates. All tests were two-sided and assessed at a significance level of 5%. Statistical analysis was performed using the R 3.6 Statistical Package (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Results
BASELINE CLINICAL AND PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS
A total of 473 successful CTO recanalisations (454 patients) were included. CTO recanalisation was achieved by means of intraplaque techniques in 403 (85.2%) and DART in 70 (14.8%) lesions.
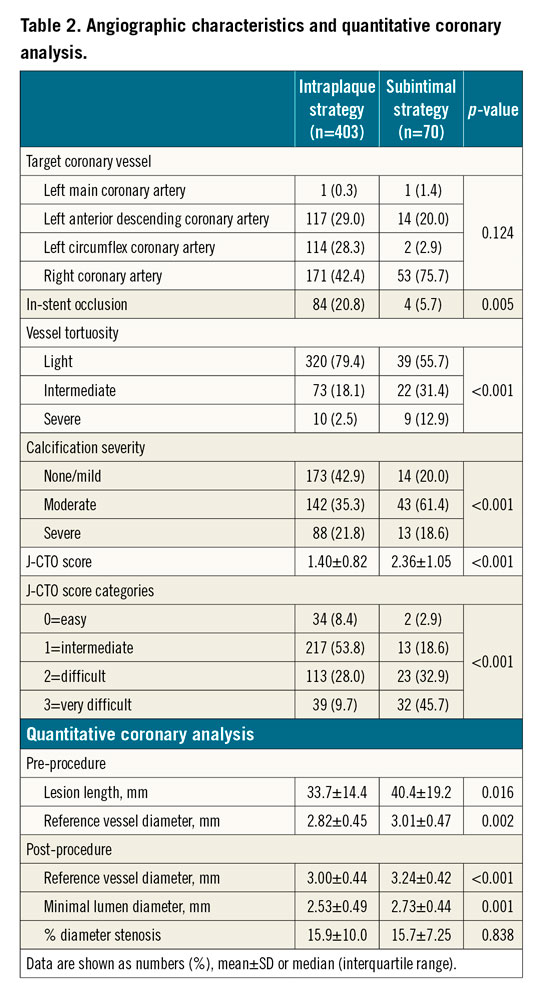
Baseline clinical and angiographic characteristics are summarised in Table 1 and Table 2. Aside from a significantly higher body mass index in the DART group, clinical characteristics were well balanced between the two groups. The right coronary artery was the most common CTO target vessel (47.4%). In-stent CTO was significantly more frequent (20.8% vs 5.7%; p=0.005) in the intraplaque recanalisation group. In line with previous CTO registries3, vessel tortuosity and J-CTO score were significantly higher in the subintimal recanalisation group (45.7% of this group having a J-CTO score ≥3).
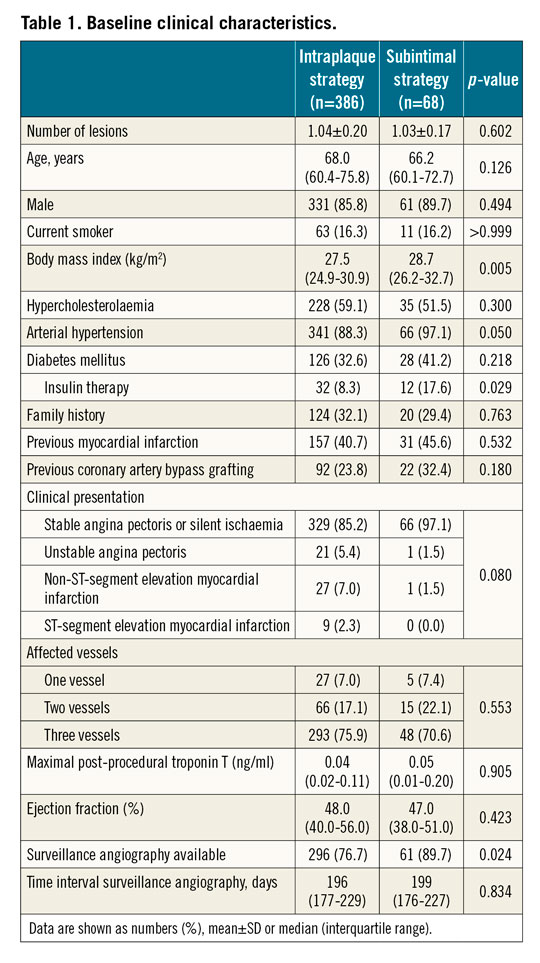
Procedural characteristics are shown in Table 3. An antegrade approach (AWE) was used in 96.8% of the intraplaque strategy group, while RWE was adopted in only 13 (3.2%) lesions of this group. Conversely, in the DART group, an ADR technique was used in 32 (45.7%) and an rCART in 38 (54.3%) lesions; the mode of dissection was wire-based in 29 (90.6%) and CrossBoss-based in 3 (9.4%) lesions, while mode of re-entry was wire-based in 12 (37.5%) and Stingray-based in 20 (62.5%) lesions of the ADR group (Figure 1). Finally, a rotablation procedure was performed in 36 (8.9%) and 3 (4.3%) lesions, respectively (p=0.815).
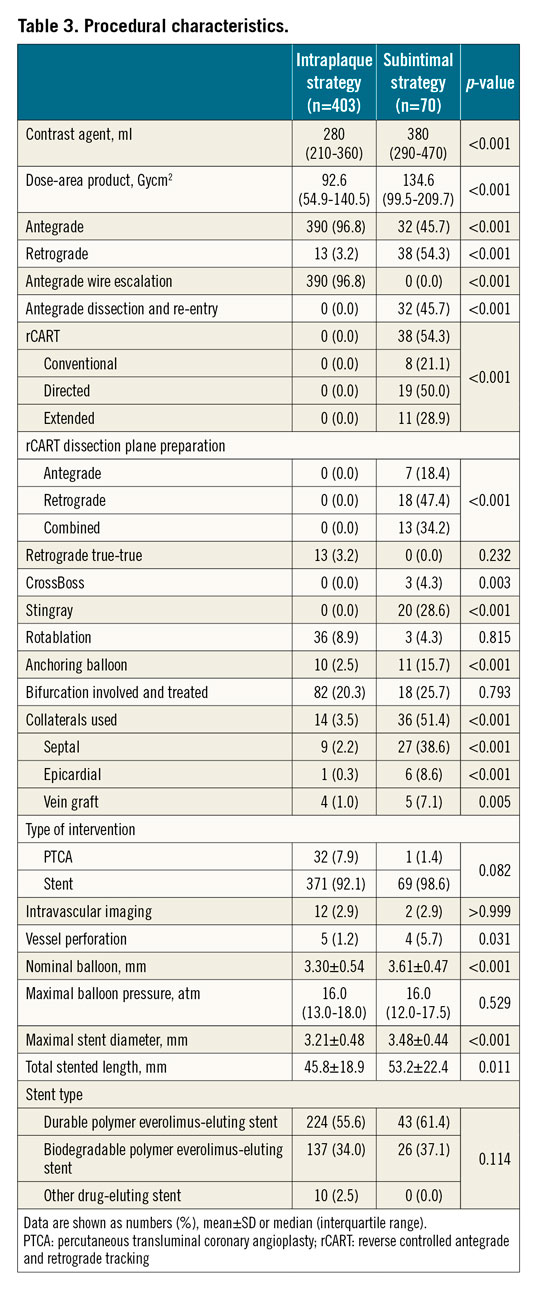
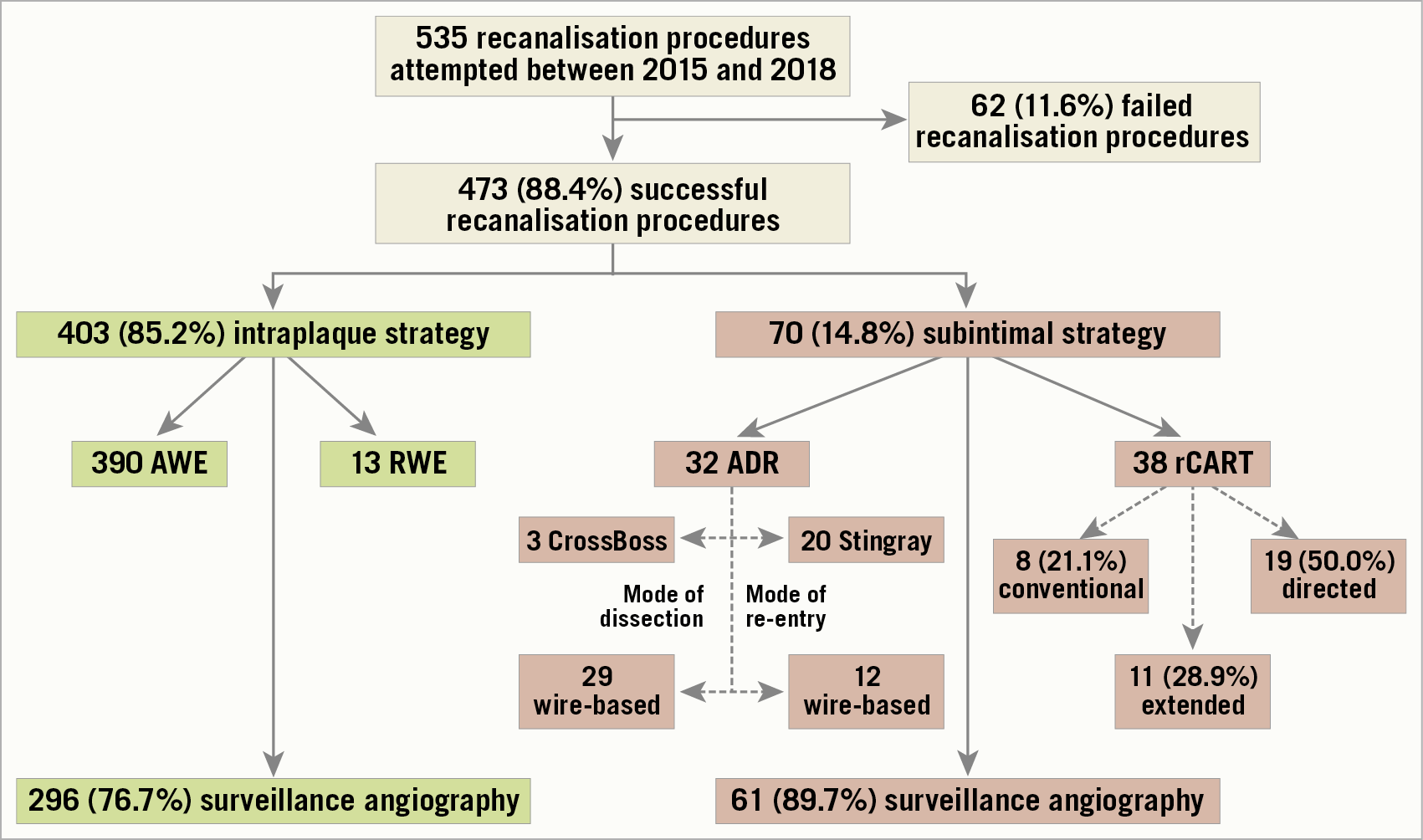
Figure 1. Overview of recanalisation procedures. ADR: antegrade dissection and re-entry; AWE: antegrade wire escalation; rCART: reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde tracking; RWE: retrograde wire escalation
Maximal stent diameter (3.48±0.44 vs 3.21±0.48 mm; p<0.001) and total stented length (53.2±22.4 vs 45.8±18.9 mm; p=0.011) were significantly higher in the DART group. There were no significant between-group differences in terms of stent type, while vessel perforation occurred more frequently (4 [5.7%] vs 5 [1.2%]; p<0.031) in the DART group. The DART group perforations were localised in an epicardial vessel in three cases, requiring the implantation of single-layer polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stents and needle pericardiocentesis in two patients due to cardiac tamponade, and in a septal perforator in one case, managed conservatively. All patients were alive at 12 months and surveillance angiography was available for all of them; the recanalised vessel was patent in all cases and no TLR was required.
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Clinical events for the outcomes of interest are shown in Table 4. No significant differences in terms of the cumulative incidence of MACE (Figure 2) or the composite of death or MI (Central illustration, A) were present between the groups. J-CTO score categories did not impact on the risk of MACE, even when type of recanalisation technique was accounted for (Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Figure 2).
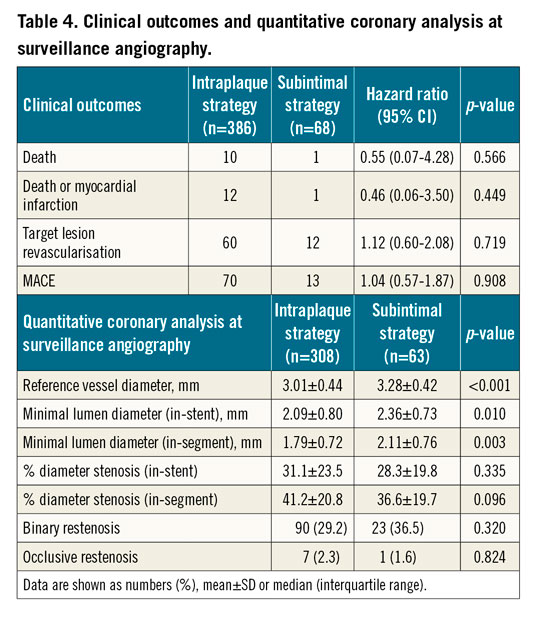
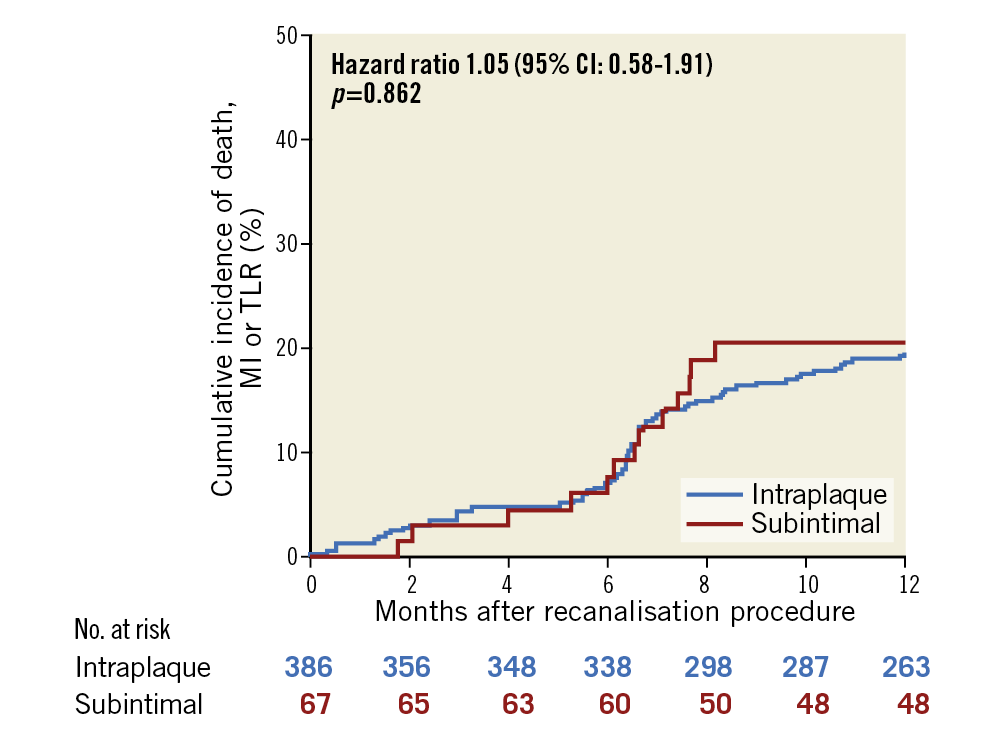
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence of major adverse cardiac events at 12-month follow-up according to recanalisation technique.
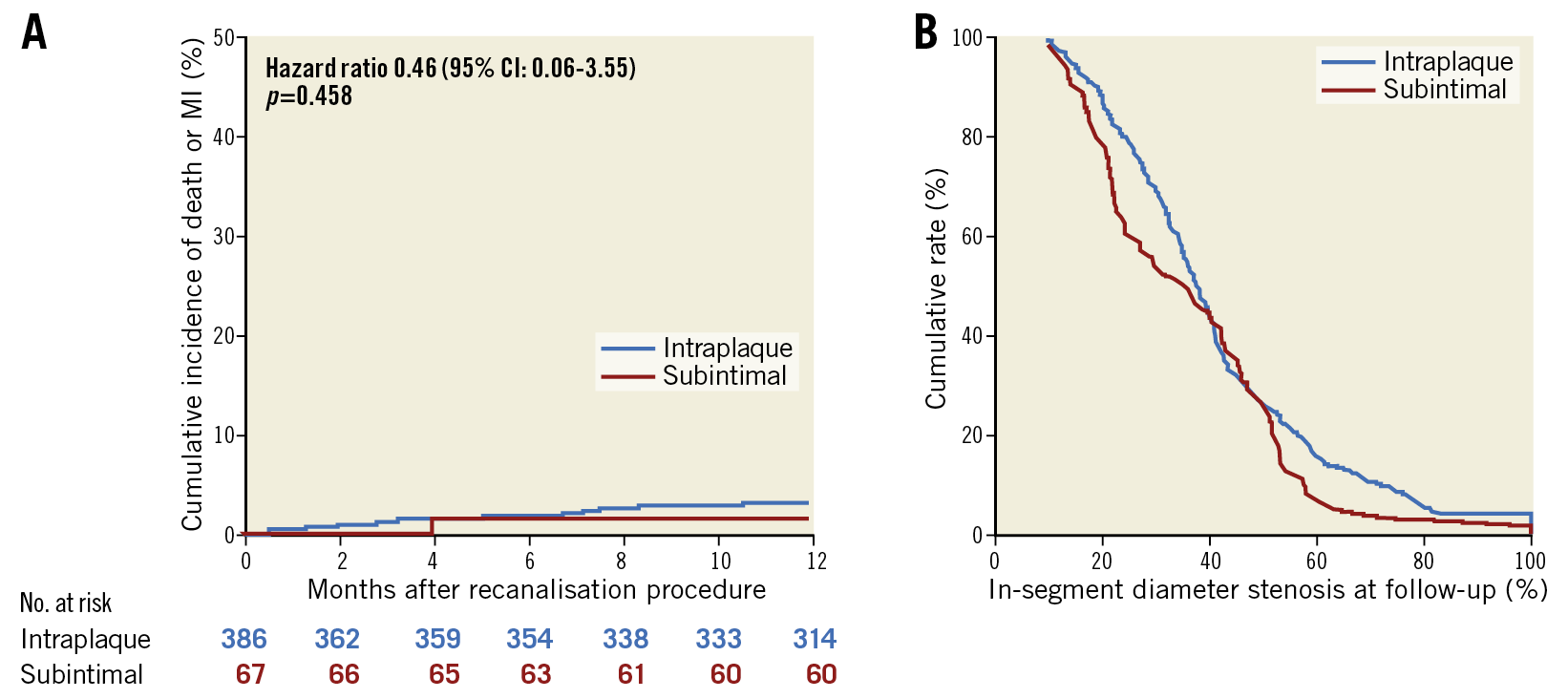
Central illustration. Clinical and angiographic outcomes according to CTO recanalisation technique. A) Cumulative incidence of all-cause death or myocardial infarction at 12-month follow-up according to recanalisation technique. B) Cumulative frequency distribution curves for in-segment percent diameter stenosis at angiographic follow-up according to recanalisation technique.
ANGIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES AND QUANTITATIVE CORONARY ANALYSIS
Surveillance angiography was available in a significantly higher proportion of patients in the DART group (61 [89.7%] vs 296 [76.7%]; p=0.024), while median clinical follow-up was comparable between the two groups (p=0.834). Preprocedural and post-procedural as well as follow-up QCA results are reported in Table 2 and Table 4, respectively. QCA measured lesion length (40.4±19.2 vs 33.7±14.4 mm; p=0.016) as well as reference vessel diameter (RVD) (3.01±0.47 vs 2.82±0.45 mm; p=0.002) were significantly higher in the DART subgroup.
QCA of surveillance angiography showed significantly higher RVD (3.28±0.42 vs 3.01±0.44 mm; p<0.001) as well as minimal lumen diameter (MLD) (2.36±0.73 vs 2.09±0.80 mm; p=0.010) in the DART group, while no significant differences in terms of in-stent %DS, in-segment %DS (Central illustration, B), or binary restenosis were present between the DART and intraplaque groups. TLR was performed in 12 (18.1%) and 60 (17.5%) (p=0.719) lesions in the DART and intraplaque groups, respectively; among patients undergoing TLR, only 34 (47.2%) were symptomatic. Importantly, the occurrence of occlusive ISR was low (1 [1.6%] vs 7 [2.3%]; p=0.824) and not different between the two groups.
PREDICTORS OF MACE AND BINARY RESTENOSIS
Two separate multivariable models were conducted to assess the potential independent role of variables selected by the LASSO regression method regarding the occurrence of MACE and binary restenosis. Baseline clinical, angiographic and procedural characteristics as well as baseline and follow-up QCA, according to MACE occurrence, are summarised in Supplementary Table 1-Supplementary Table 3. Besides recanalisation technique (subintimal vs intraplaque), the model for MACE included patient age and sex, previous coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), presentation with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), CAD family history, in-stent CTO and post-procedural %DS as independent variables. Among these, in-stent CTO (HR 1.72, 95% CI: 1.02-2.91, p=0.044) and post-procedural %DS (HR for 10% increment: 1.21, 95% CI: 1.00-1.46, p=0.049) independently correlated with MACE occurrence; all remaining variables, including recanalisation technique, did not independently correlate with MACE at 12-month follow-up (p>0.130 for all variables) (Figure 3A). Besides recanalisation technique (subintimal vs intraplaque), the model for binary restenosis included patient age and sex, previous CABG, previous PCI, right coronary artery (RCA) CTO, in-stent CTO, maximal balloon pressure and post-procedural %DS as independent variables. Among these, in-stent CTO (OR 1.94, 95% CI: 1.05-3.59, p=0.036), RCA CTO (OR 0.56, 95% CI: 0.33-0.94, p=0.029) and previous CABG (OR 1.78, 95% CI: 1.02-3.13, p=0.043) independently correlated with the presence of binary restenosis; all remaining variables, including recanalisation technique, did not independently correlate with the presence of binary restenosis at surveillance angiography (p>0.077 for all variables) (Figure 3B).
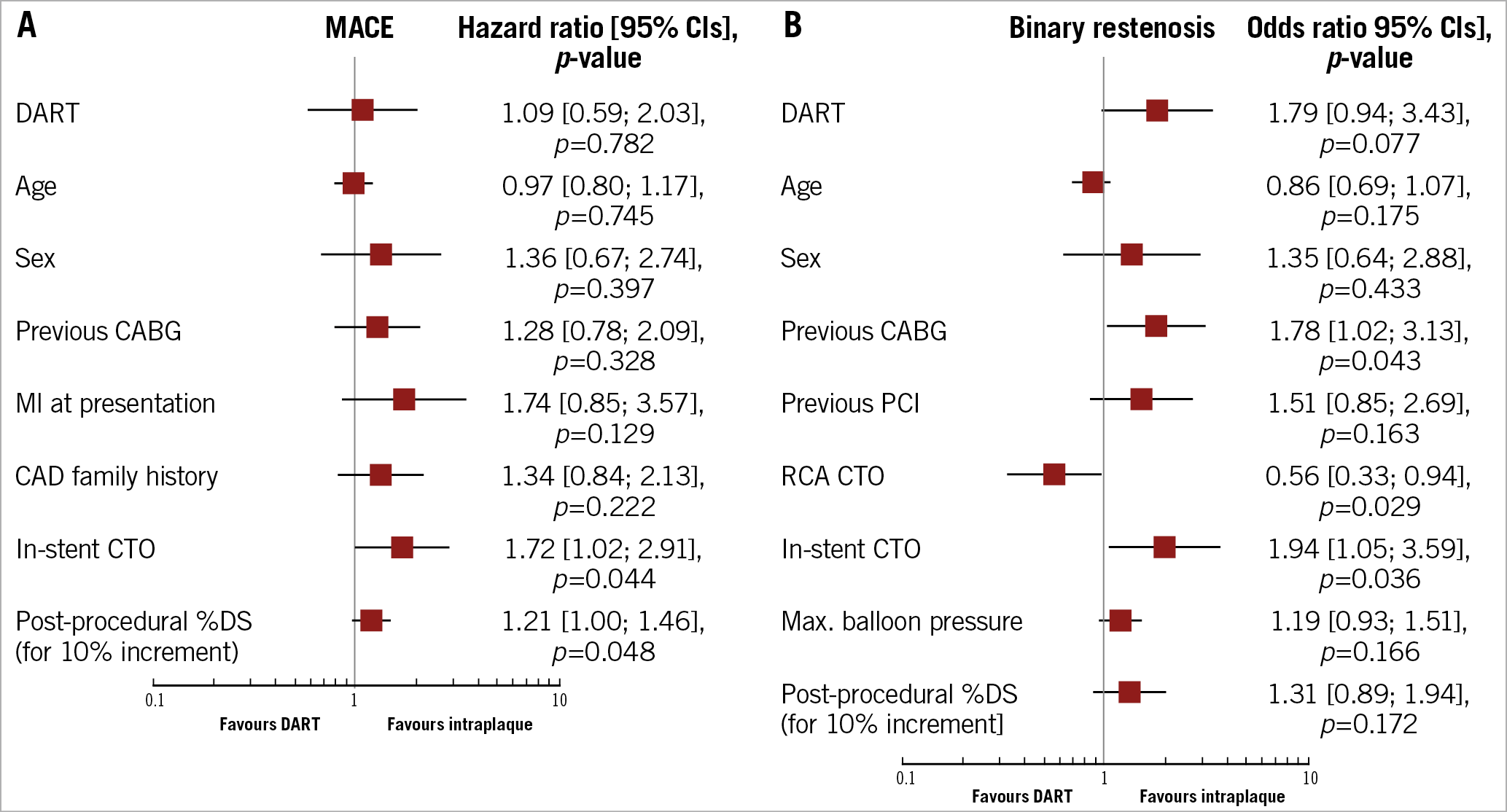
Figure 3. Multivariable analysis for predictors of MACE and binary restenosis. A) Plot of hazard ratios associated with MACE. B) Plot of odds ratios associated with binary restenosis. The squares indicate the point estimate and the left and right ends of the lines the 95% CI. 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting; CAD: coronary artery disease; CTO: chronic total occlusion; DART: dissection and re-entry technique; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; MI: myocardial infarction; %DS: percent diameter stenosis; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
Discussion
The main findings of the present study can be summarised as follows: i) use of contemporary DART is associated with similar midterm clinical and angiographic outcomes compared to intraplaque recanalisation techniques; ii) there was no independent correlation between recanalisation technique (subintimal vs intraplaque) and MACE occurrence or in-segment binary restenosis at follow-up; iii) contrary to previous reports applying extensive DART, the rate of occlusive restenosis was low and comparable in both recanalisation strategies; iv) despite similar angiographic outcomes, the overall incidences of binary restenosis and TLR were not negligible in both CTO recanalisation groups; and v) approximately half of the patients undergoing TLR were asymptomatic at the time of angiographic follow-up.
Increased adoption of DART has revolutionised the field of CTO PCI and played a fundamental role in achieving the high procedural success rates reported in contemporary CTO registries3. Despite their indisputable merits in terms of acute procedural success, the intermediate- and long-term outcomes of patients treated by means of subintimal techniques continue to engender significant controversy. Contrary to initial studies4 applying extensive dissection techniques, recent reports5,6,7,8,9,10,15 using limited DART have shown comparable midterm clinical outcomes with intraplaque recanalisation techniques. Although reassuring, these studies5,7,8,10 did not include a systematic angiographic follow-up; indeed, the number of studies comparing the outcomes of such recanalisation strategies which included surveillance angiography is extremely limited. This is particularly important, since patient clinical status following CTO recanalisation is determined not only by persisting patency of the recanalised vessel, but also by dynamic changes in collateral vessel supply, which, in case of restenosis/reocclusion, can recover to pre-recanalisation levels16. The results of the present registry, which, together with the CONSISTENT CTO study17, represent the largest data sets comparing contemporary DART and intraplaque recanalisation in terms of both clinical and angiographic outcomes to date, confirm the safety of contemporary DART with a low cumulative incidence of the composite of death and MI up to 12 months following CTO recanalisation with no significant differences between the two recanalisation strategies.
The absence of significant differences in terms of in-stent/in-segment %DS or rates of binary restenosis at surveillance angiography as well as of TLR between the two recanalisation techniques in our study confirms the sustained efficacy of modern DART. Rates of binary restenosis (29.2% and 36.5%) and TLR (17.5% and 18.1%) in our study were lower compared to those reported in the ACE-CTO study (46% and 37%, respectively)18 and tended to be higher than those reported in the recent CONSISTENT CTO (14.5% as well as 10.9% and 3.7%, respectively)17 and PRISON IV studies (8.0% and 2.1% as well as 10.5% and 4.0%, respectively)19; differences in CTO lesion complexity could explain some of the discrepancies in angiographic outcomes between studies. In view of the high complexity of the lesion subset being recanalised by means of DART in our patient collective (J-CTO score ≥3 in 45.7% of this subgroup), confirmation of comparable angiographic outcomes between the two groups is a remarkable finding, which confirms the sustained efficacy of contemporary DART.
Despite similar angiographic outcomes, the incidences of binary restenosis and TLR were not negligible in both CTO recanalisation groups. The overall TLR rate in the present study is higher than that reported in studies of non-CTO PCI with surveillance angiography20. In the light of the high lesion complexity and lesion length in the present data set, this finding is not unexpected and in line with previous reports following CTO recanalisation procedures18. However, contrary to previous studies applying extensive dissection techniques (STAR), the rate of occlusive restenosis following limited DART in our study was extremely low and comparable to intraplaque recanalisation. The low prevalence of symptoms (47.2%) in the patient subgroup undergoing TLR in our study shows that, in the specific setting of CTO recanalisation, failure to perform a systematic angiographic follow-up may significantly underestimate the occurrence of restenosis/reocclusion.
Finally, another important aspect which may impact significantly on the safety of recanalisation procedures is that of stent healing patterns. Clinical studies using intravascular optical coherence tomography have displayed somewhat conflicting results regarding rates of uncovered and malapposed struts in drug-eluting stents (DES) implanted in CTO lesions17,21 and the influence of recanalisation technique (intraplaque vs DART) on such intravascular imaging findings. Further investigation will be important in clarifying this issue since both stent coverage and apposition have been linked to the occurrence of stent thrombosis.
Study limitations
Some limitations should be considered when interpreting the results of the present report. First, despite being one of the largest studies to compare both clinical and angiographic findings of intraplaque as opposed to subintimal CTO recanalisation, this is a single-centre study. Second, no systematic intravascular imaging was performed following initial vessel wiring and the possibility of small subintimal wire trajectories in the intraplaque group cannot be ruled out. Third, since the study period preceded the ARC-2 consensus document, repeat PCI on surveillance angiography was performed according to the initial ARC criteria and physiological evaluation was not used to guide TLR procedures.
Conclusions
Besides their indisputable role in achieving high procedural success rates, contemporary DART display comparable midterm clinical as well as angiographic outcomes compared to intraplaque recanalisation techniques. Contrary to previous reports applying extensive DART, the rate of occlusive restenosis was low and comparable in both recanalisation strategies. However, irrespective of the recanalisation technique being used, the overall TLR rate following CTO recanalisation remains higher than that reported for non-CTO PCI. This finding, coupled with the absence of symptoms in a considerable proportion of patients undergoing TLR at surveillance angiography, underlines the necessity of a close clinical follow-up and eventually myocardial perfusion imaging as a means of detecting and treating ISR.
|
Impact on daily practice Use of contemporary DART is associated with similar midterm clinical and angiographic outcomes compared to intraplaque recanalisation techniques. Contrary to initial reports applying extensive DART, the rate of occlusive restenosis was low and comparable in both recanalisation strategies. However, regardless of the recanalisation technique being used, the overall incidences of binary restenosis and TLR following CTO recanalisation remain higher than those reported for non-CTO PCI. |
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to the present work.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

