
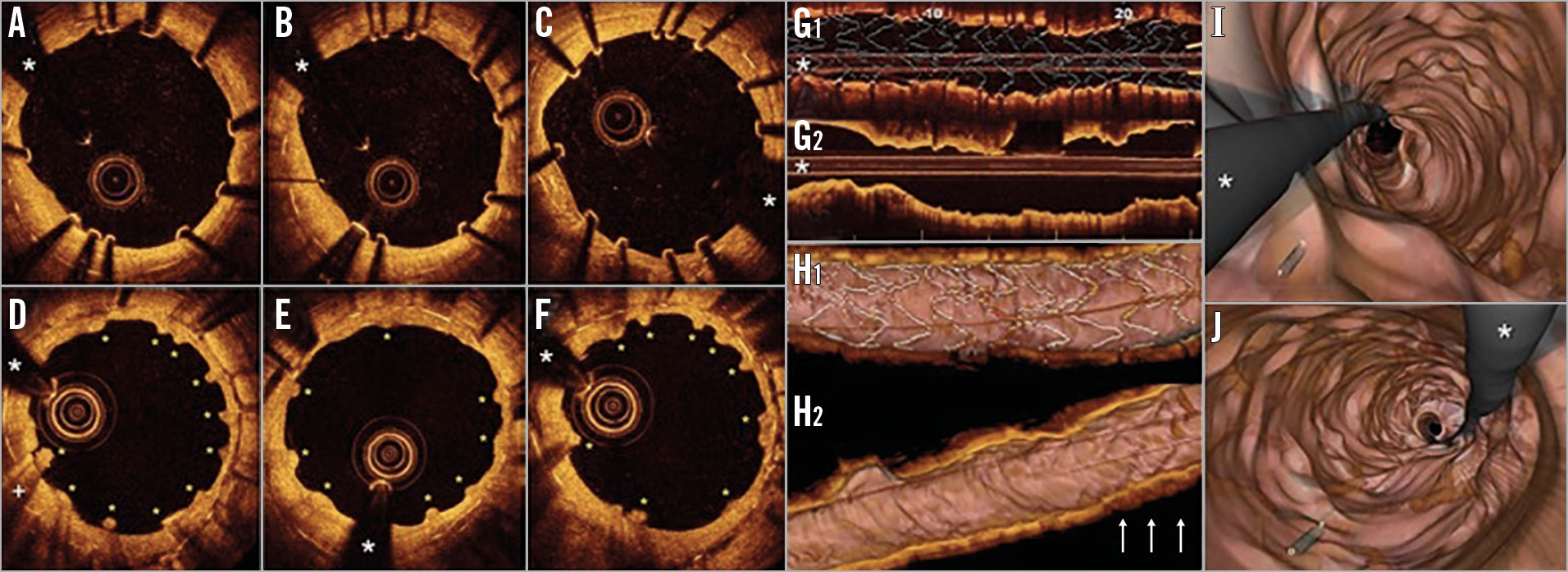
Figure 1. The distinct resorption pattern of bioabsorbable magnesium scaffolds. A) - C) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) images after bioabsorbable magnesium scaffold (MgS) implantation. The bright metallic MgS struts are clearly depicted. The previous metallic stent is also partially visualised as a double metal layer. D) - F) OCT findings at one-year follow-up. The inner metallic layer is no longer visible. Instead, multiple intimal “humps” (yellow asterisks) are recognised (these characteristic images were identified in 92% of the frames within the MgS). Very rarely (6% of frames), images consistent with small protruding thrombus casting dorsal shadow (D: +) were noticed. White asterisk: wire artefact. G) - J) OCT findings after stent implantation and one-year follow up. 2D longitudinal mode view showing the stent struts immediately after MgS implantation (G1) and at one year (G2). Images of multiple humps mimicking a “bumpy” neointima were visualised at the segment where the MgS was initially deployed. H1) 3D navigation view with stent struts depicted immediately after deployment, showing minimal malapposition (yellow-coded struts). H2) At one-year follow-up some areas (white arrows) displayed the “humps” as the fingerprint of the MgS which had “disappeared”. I) & J) Fly-through mode depicting the humps at one-year follow-up.
A 73-year-old man was admitted for pulmonary oedema. Eleven years before he had suffered a large inferior myocardial infarction treated with three long paclitaxel-eluting stents in the right coronary artery. One year ago, he presented with pulmonary oedema. Coronary angiography revealed two focal sites of in-stent restenosis (ISR) caused by neoatherosclerosis (calcified areas and lipid pools with neointima rupture) as demonstrated by optical coherence tomography (OCT). At that time two drug-eluting bioabsorbable magnesium scaffolds (MgS) were implanted (3.5×20 and 3.0×15 mm) at high pressure (20 bar) with excellent angiographic and OCT results (Figure 1A-Figure 1C). A double metal layer was visualised with the superficial MgS struts presenting as bright spots casting intense dorsal shadowing. Currently, coronary angiography shows persistence of good results at the segments treated with MgS. OCT demonstrated complete disappearance of the bright metallic signals of the MgS struts and a unique pattern of multiple “humps” causing a “bumpy” neointima appearance (Figure 1D-Figure 1F, Figure 1G-Figure 1J).
Currently, the use of either metallic drug-eluting stents (DES) or drug-eluting balloons is recommended for patients with ISR1. Recently, MgS provided a new alternative for coronary interventions with unique scaffolding and antiproliferative properties, yet eventually vanishing from the vessel wall2. Accordingly, MgS might emerge as a novel therapeutic modality for selected patients with ISR, avoiding an additional permanent metallic layer3. Although in our experience polymeric bioresorbable vascular scaffolds provide satisfactory outcomes in patients with ISR4, the first generation of these devices has been associated with a relatively high thrombosis risk. Further studies are required to critically evaluate the potential role of MgS in this challenging anatomic scenario.
Our current findings demonstrate, to the best of our knowledge for the first time, the complete disappearance from the vessel wall of the metallic struts of MgS at one-year follow-up in patients treated for ISR. At this time point, OCT disclosed a unique, previously unreported, pattern of neointimal healing. We speculate that these multiple humps causing a distinct “bumpy” neointimal pattern may be the fingerprint of previously covered MgS struts once they eventually vanish from the vessel wall. Although we have never seen this healing pattern with other stents1, further studies are required to confirm that the pattern is characteristic of this device. In addition, the extent of neointimal proliferation and coverage during the healing phase of the MgS (both on the struts and at the inter-strut spaces) may determine the formation of “bumpy” neointima but might also lead to other healing patterns.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

