The “black hole” phenomenon is described as a series of small anechogenic spherical images (50-300 µm) inside a late restenotic neointimal hyperplasia dorsal to sirolimus-coated stent struts implanted in failed intracoronary brachytherapy. This is seen in vein grafts or bare metal stent restenosis exclusively. Histologically, there is a hypocellular matrix with abundant proteoglycans areas, without mature elastin or collagen1.
A coronariography due to angina was performed in a 66-year-old diabetic female two months after a first sirolimus-stent restenosis on left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) treated with a paclitaxel-coated balloon. Optical coherence tomography showed severe restenosis associated with distal stent underexpansion and an atypical “black hole” phenomenon in proximal neointimal hyperplasia tissue: low reflective and big size elliptic areas (1-1.5 mm of large diameter) localised between the stent struts and next to the native vessel but separated from lumen (Figure 1, Moving image 1). Previous paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty could have promoted apoptosis, internal elastic lamina disruption, and decreased medial smooth muscle cells and collagen content2 which could explain the holes appearance since they are localised between the struts, where sirolimus activity is supposed to be lower.
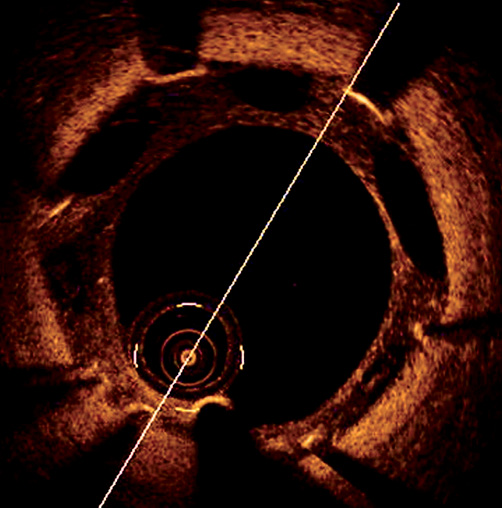
Figure 1. Optical coherence tomography of LAD sirolimus stent showing the atypical and large “black hole” phenomenon in a neointimal hyperplasia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Online data supplement
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. OCT pullback.