Current transcatheter coronary sinus (CS) reducer technology is associated with significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life in patients with refractory angina1. However, its design and technology have some limitations, such as a “1-stop” deployment opportunity, limited device sizing, risk of dislodgement during balloon retrieval, and reliance on endothelialisation for its therapeutic effect23.
The A-Flux (VahatiCor) is a novel CS reducer made of a dense nitinol mesh (Figure 1A) with four different sizes (Figure 1B) that enable implantation of the device in the specific CS segment where the greatest therapeutic benefit is expected. Additionally, the A-Flux is partially recapturable and repositionable. Its delivery system (Figure 1C) allows a low, chronic outward deployment force that anchors the device without the risk of balloon-induced CS dissection or rupture. Its dense nitinol mesh immediately diverts flow, resulting in double the mass flow through its central waist compared to a conventional open-cell stent design (Figure 1D). The A-Flux is preloaded into a 10 Fr delivery system; however, its distal tapered nose cone achieves a smaller profile: the tip entry has a diameter of 1.27 mm (3.8 Fr), the taper length is 6 mm, and the widest part is only 2.8 mm (8.4 Fr). Additionally, once the A-Flux is delivered, the <3 mm diameter tapered nose cone can be retrieved through the 3 mm central waist in a gradual and controlled fashion because of its dedicated handle and delivery/retrieval control wheel. The currently available technology requires a 9 Fr guiding catheter; however, once this device is implanted with balloon inflation, the operator needs to retrieve a balloon that has been inflated and deflated, thus with an unpredictable size and configuration, through the narrow central waist (risking device dislodgement, embolisation, and displacement).
The first-in-human implantation of the A-Flux CS reducer was performed in a 67-year-old male patient with a history of severe coronary artery disease, with prior quadruple coronary artery bypass graft surgery in 2000. In 2015, he developed severe stable angina, with an angiogram revealing two occluded saphenous vein grafts to two marginals and a severe lesion in the left anterior descending artery (LAD) distal to the right mammary artery anastomosis. The left mammary graft to the 1st marginal was patent, providing retrograde filling to the marginals. Following percutaneous coronary intervention on the distal LAD, his symptoms improved, but angina recurred in 2023. A perfusion scan showed a low-normal left ventricular ejection fraction and severe ischaemia compromising 50% of the left ventricle. Repeat angiography identified two new LAD lesions deemed unsuitable for revascularisation. Despite maximally tolerated doses of beta blockers, long-acting nitrates, calcium channel blockers, and ranolazine, the patient was still experiencing Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) class 3 angina, necessitating frequent nitroglycerine use. Consequently, CS reduction therapy was considered for his refractory angina. The first-in-human implant was authorised by Health Canada, and the patient provided signed consent for this special access device and first-in-human procedure.
Under conscious sedation and via a right jugular access, the A-Flux implant was performed. The first step was cannulating the CS with a properly shaped 5 Fr or 6 Fr catheter (Barbeau, multipurpose). After CS injection and device sizing using fluoroscopy (Figure 1E, Moving image 1) and intravascular ultrasound (Figure 1F, Moving image 2), a CS wedge pressure assessment of potential treatment responsiveness was undertaken (Figure 1G, Moving image 3)4. This is an important step, since an acute increase in CS wedge pressure leads to a decrease in microvascular resistance and an increase in blood flow4; however, the pressure does not increase to the same extent in all patients. Indeed, patients with higher increases usually show better responsiveness to CS reduction therapy5. The optimal implantation site was identified distal to the bifurcation, and then, based on its size, a 9 mm A-Flux reducer was implanted (to guarantee a minimum of 30% vessel oversizing) (Figure 1H, Moving image 4) with final angiography showing a correct position without complications (Figure 1I, Moving image 5). At 1-month follow-up, the patient was in CCS class 1 with a significant improvement in his quality of life and no reported postprocedural use in nitroglycerine spray. The computed tomography image showed the A-Flux reducer in place (Figure 1J, Moving image 6), with its central waist still patent without fracture or thrombosis within the device (Figure 1K).
Important considerations about the use of this device are as follows: the recommended antithrombotic regimen for patients with coronary stents is 80 mg of aspirin indefinitely and 75 mg of clopidogrel for at least 6 months (or longer as per physician discretion). The neck of the A-Flux allows the passage of certain leads, and it can also be dilated if needed (bailout scenario), although its therapeutic effect will be lost. Compared to currently available CS reducer technology, one of the potential drawbacks of the A-Flux could be the requirement of a stiff wire for its delivery. However, the use of a properly shaped 5 Fr or 6 Fr catheter (Barbeau, multipurpose) allows the safe delivery of the stiff wire within the CS. Although a theoretical risk of dislodgement exists with self-expanding technologies, this risk is reduced with controlled deployment and adequate oversizing. Depending on the selected size, the delivery system’s nose cone extends over the distal edge of the A-Flux CS reducer by 15-20 mm. However, this distal tip, with its tapered and flexible nose cone that becomes even softer at body temperature, could be advantageous compared to currently available technology. It allows for an easy transition to the maximum outer diameter that gradually tracks the guidewire so the device can reach planned targets, even in distal branches of the main CS. In addition, the nitinol mesh is a flexible alloy that allows the material to track within the outer sheath delivery system and to conform to the patient’s CS anatomy.
Although encouraging, these results are the first-in-human experience and, thus, are applicable only to this patient. Large prospective sham-controlled trials are needed to determine the efficacy of this new technology.
This first-in-human experience with the A-Flux CS reducer demonstrates periprocedural safety and feasibility with no complications, coupled with good short-term clinical results for treating refractory angina. Ongoing safety and feasibility studies involving the A-Flux device in patients with persistent angina and obstructive or non-obstructive coronary disease are underway.
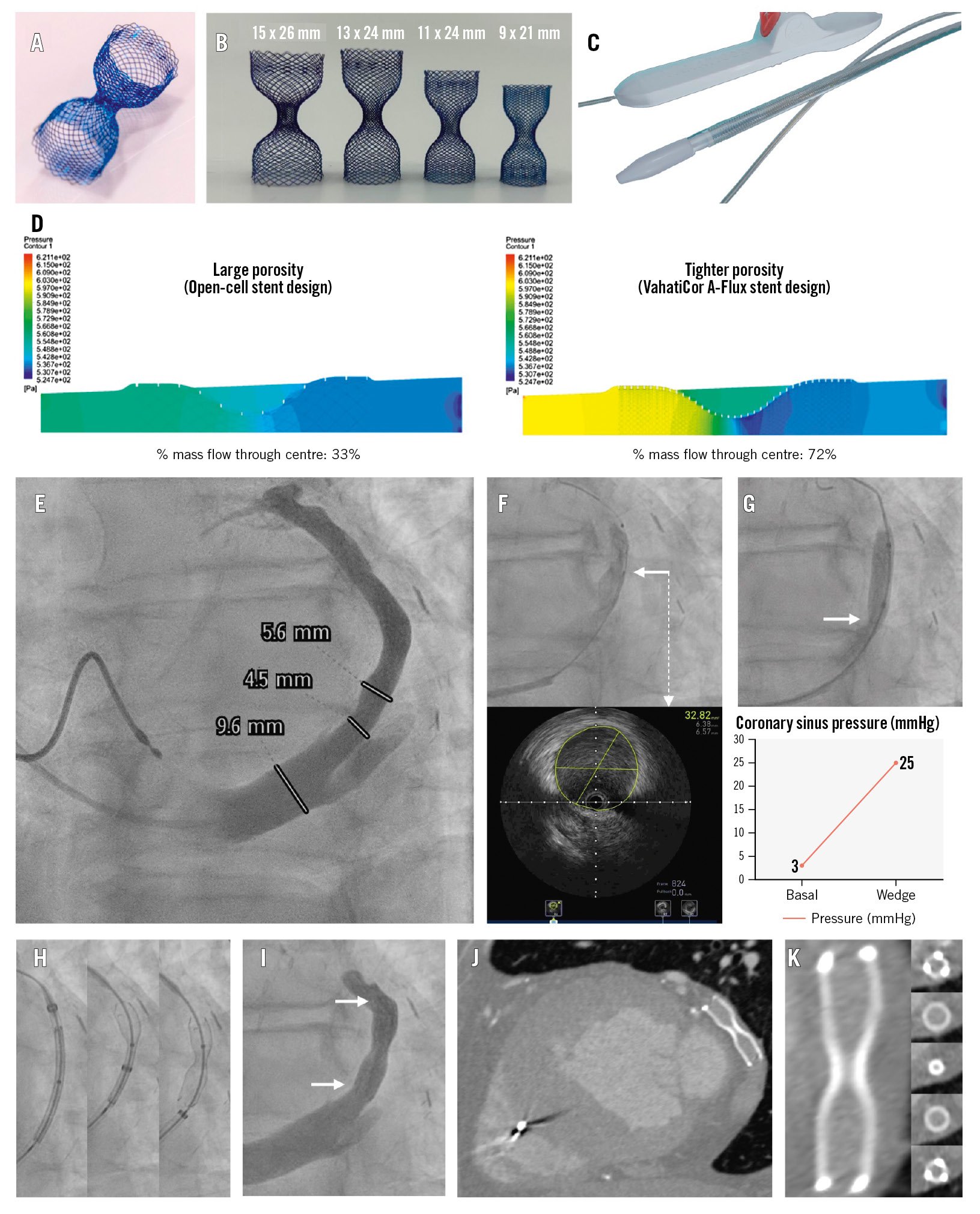
Figure 1. The A-Flux coronary sinus reducer system, first-in-human implantation procedure, and follow-up results. A) The A-Flux coronary sinus (CS) reducer is made of dense nitinol with a tight porosity, allowing immediate funnel function. B) Four different sizes of the device (9 mm device for CS of 6.4-7.6 mm, 11 mm device for CS of 7.7-9.2 mm, 13 mm device for CS of 9.1-10.9 mm, 15 mm device for CS of 10.4-12.5 mm), all with a 3 mm central waist. C) The single-operator delivery system allows partial recapture and repositioning. D) Computational fluid dynamics testing demonstrating a doubling in mass flow through the central waist compared to a conventional open-cell stent design. E) Pre-implant coronary sinus injection to assess anatomy and dimensions. F) Coronary sinus size evaluation by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS; requires a peripheral IVUS catheter) showing the IVUS catheter position (white arrow) in the top image and the IVUS image at that segment (white dashed arrow). G) Assessment of the coronary sinus wedge pressure rise as a predictor of coronary sinus reducer therapy responsiveness with balloon occlusion of the coronary sinus (top) to measure its wedge pressure, which showed an increase of 22 mmHg (bottom); white arrow showing adequate CS occlusion. H) A-Flux coronary sinus reducer deployment steps; the reducer is recapturable until 50% of the deployment has been completed (central image). I) Post-deployment final angiography showing correct device position and patency without CS dissection (white arrows showing both ends of the device). J) A 1-month follow-up computed tomography angiography (CTA) showed the A-Flux in its original deployed position. K) CTA reconstruction of the A-Flux reducer showing its central waist permeability without any fracture or device thrombosis.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Caroline Gravel and Maxime Tremblay for their invaluable contribution.
Conflict of interest statement
R. Puri and O. Abdul-Jawad Altisent have equity in VahatiCor. F. Giannini is a consultant for VahatiCor. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Initial coronary sinus angiography and fluoroscopic measurements.
Moving image 2. Intravascular ultrasound pullback inside the coronary sinus.
Moving image 3. Coronary sinus balloon occlusion for measuring its wedge pressure.
Moving image 4. A-Flux first-in-human implantation.
Moving image 5. Final post-deployment angiography.
Moving image 6. Follow-up computed tomography angiography reconstruction of the A-Flux coronary sinus reducer.

