Abstract
Background: Randomised controlled trials of ultrasound (US)-guided transfemoral access (TFA) for coronary procedures have shown mixed results.
Aims: We aimed to compare US-guided versus non-US-guided TFA from randomised data in an individual participant-level data (IPD) meta-analysis.
Methods: We completed a systematic review and an IPD meta-analysis of all randomised controlled trials comparing US-guided versus non-US-guided TFA for coronary procedures. We performed a one-stage mixed-model meta-analysis using the intention-to-treat population from included trials. The primary outcome was a composite of major vascular complications or major bleeding within 30 days.
Results: A total of 2,441 participants (1,208 US-guided, 1,233 non-US-guided) from 4 randomised clinical trials were included. The mean age was 65.5 years, 27.0% were female, and 34.5% underwent a percutaneous coronary intervention. The incidence of major vascular complications or major bleeding (34/1,208 [2.8%] vs 55/1,233 [4.5%]; odds ratio [OR] 0.61, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.39-0.94; p=0.026) was lower in the US-guided TFA group. In the prespecified subgroup of participants who received a vascular closure device, those randomised to US-guided TFA experienced a reduction in the primary outcome (2.1% vs 5.6%; OR 0.36, 95% CI: 0.19-0.69), while no benefit for US guidance was observed in the subgroup without vascular closure devices (4.1% vs 3.3%; OR 1.21, 95% CI: 0.65-2.26; interaction p=0.009).
Conclusions: In participants undergoing coronary procedures by TFA, US guidance decreased the composite outcome of major vascular complications or bleeding and may be especially helpful when using vascular closure devices.
Introduction
Compared with femoral access, radial access has been demonstrated to reduce bleeding and vascular complications in stable ischaemic heart disease and even mortality in acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)12. However, transfemoral access (TFA) is still essential for larger-bore procedures and in cases of radial access failure3. Careful placement of the femoral arterial access is mandatory, as cannulation above the inguinal ligament may result in retroperitoneal haemorrhage, while cannulation below the femoral bifurcation is associated with an increased risk of major vascular complications3. Ultrasound (US)-guided access has emerged as a potentially more efficacious alternative to non-US-guided access using traditional palpation and fluoroscopy. However, existing trials have shown mixed results, hence, more definitive data are required.
The use of US for TFA demonstrated promise in earlier trials, including the Femoral Arterial Access with Ultrasound Trial (FAUST)4. However, recent randomised controlled trials (RCTs) lacked the power to reach definitive conclusions due to the low rates of adverse clinical events567. Reflecting the small body of evidence and clinical inertia, two surveys of interventional cardiologists demonstrated that only 13-27% routinely used US for femoral access despite 88% answering that US was available in the catheterisation laboratory89.
Considering the low clinical uptake of US to guide TFA and the lack of adequately powered studies, we performed a systematic review, an individual participant-level data (IPD) meta-analysis of coronary RCTs, and a complementary aggregate-level meta-analysis of coronary and peripheral vascular disease (PVD) RCTs to determine the effect of US-guided TFA versus non-US-guided TFA on major vascular complications or major bleeding. We hypothesised that US-guided access would decrease complications as compared with non-US-guided access.
Methods
We registered the present meta-analysis in the PROSPERO international prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO CRD42023411468) and followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)-IPD guidelines10.
SEARCH STRATEGY AND RISK-OF-BIAS ASSESSMENT
We completed a systematic review of PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials from inception to 23 June 2022. We included all RCTs comparing US-guided TFA versus non-US-guided TFA for angiography in participants >18 years old. Supplementary Table 1 details our complete search strategy. We restricted our search to the English language and RCTs. Independently of our search strategy, we also hand-searched the bibliographies of the most recent relevant meta-analyses to identify other potentially eligible studies and accessed the Routine Ultrasound Guidance for Vascular Access for Cardiac Procedures (UNIVERSAL) trial data before publication5111213. Two independent authors performed the literature review (M. d’Entremont, S. Alrashidi) using the Covidence systematic review software (Veritas Health Innovation). No disputes required resolution with the senior author (S. Jolly). We assessed the studies for bias using the Cochrane Collaboration risk-of-bias tool to ensure that no studies included in the IPD meta-analysis were at a high risk of bias14.
STUDY ORGANISATION
A total of nine eligible trials were identified. Four of these nine trials consisted of participants undergoing retrograde TFA access for coronary procedures4567. The investigator groups of these four trials agreed to participate in the IPD meta-analysis.
Of the remaining five trials, one (Katircibasi et al, 2018) included a mix of coronary and PVD participants, while the other four (Dudeck et al, 2004; Gedikoglu et al, 2013; Slattery et al, 2015; and Stone et al, 2020) were limited to participants undergoing lower extremity PVD interventions1516171819. For these trials, one investigator group declined participation, and the other four could not be reached.
Authors participating in the IPD meta-analysis shared individual participant-level data as part of a collaborative effort. All data were merged at the Population Health Research Institute (Hamilton, ON, Canada). Data were reviewed for completeness and consistency, and differences were resolved by discussion within our collaborative study group. All four included trials were approved by their institutional ethics committees, and participants provided informed consent.
OUTCOMES
To decrease between-trial heterogeneity in the IPD meta-analysis, our collaborative group reclassified outcome data to create a uniform primary outcome across all trials. For our analysis, we defined the primary outcome as the composite of major vascular complications (femoral artery pseudoaneurysm, arteriovenous fistula, retroperitoneal bleed, large haematoma of more than 5 cm in diameter, or ischaemic limb requiring intervention or surgery) or major bleeding as defined by the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) type 3 or 5 at the end of follow-up, which was a maximum of 30 days20. As no BARC 5 bleeding was identified, major bleeding was subsequently defined as BARC 3. Secondary outcomes included the composite of major vascular complications, major bleeding or minor bleeding (defined as BARC 2 bleeding); major vascular complications alone; and major or minor bleeding alone. Other outcomes included the individual components of the major vascular complication outcome, the number of attempts, and the rates of venipuncture and successful common femoral artery cannulation. Of note, the Standard versus ultrasound-guided radial and femoral access in coronary angiography and intervention (SURF) trial did not capture common femoral artery cannulation and was excluded from the analysis of this specific outcome.
For the aggregate-level studies, major bleeding was compiled as reported by each individual trial, and a major vascular complication composite outcome, as described for the IPD meta-analysis, was also compiled by combining the individual components as reported by each trial.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
All analyses were performed by intention-to-treat, meaning all randomised participants were included in their initially allocated study group. We used a one-stage mixed-model meta-analytic method with a random-study effects (accounting for clustering at the trial level with a random intercept) and a fixed-treatment effect (fixed slope) as our primary prespecified analytic method21. The fixed-treatment effect modelling assumption was chosen because the participants in the IPD trials had similar baseline characteristics, were randomised to the same intervention, and the redefined outcomes were relatively homogenous21. Furthermore, the small number of trials and events led to non-convergence issues when attempting to model random slopes as a sensitivity analysis, confirming our decision to use fixed slopes22. To evaluate the totality of the data of coronary and PVD interventions and to explore potential selection bias, we also performed a two-stage fixed-effect and random-effects subgroup (IPD trials vs aggregate-level trials) meta-analysis for the primary composite outcome.
Prespecified subgroup analyses for this IPD were performed, including age (≥65 years vs <65 years), sex (female vs male), body mass index (≥30 kg/m2 vs <30 kg/m2), peripheral vascular disease (presence vs absence), PCI (yes vs no), operator experience (trainee/fellow vs attending/consultant), sheath size (≥7 Fr vs <7 Fr), and vascular closure device (VCD) use (yes vs no). These subgroups were identical to those prespecified in the UNIVERSAL trial. As post hoc exploratory analyses, we also completed subgroup analyses for heparin and glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa use. The Marquis-Gravel et al trial did not report VCD use and was subsequently excluded from the VCD subgroup analysis. Analyses were based on the primary composite outcome, and we tested for statistical interaction.
We subsequently performed several sensitivity analyses. We computed two-stage fixed-effect and random-effects meta-analyses for all secondary and procedural outcomes but not for the individual components of major vascular complications, as there were too few events. Heterogeneity was interpreted as per the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group23. To estimate the actual efficacy of the intervention, we completed an as-treated analysis. As a post hoc exploratory analysis, we used our primary analytic method to perform a leave-one-out analysis with the vascular closure device subgroups for the primary composite outcome.
We calculated odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) with a significance level of p<0.05. We did not adjust for multiplicity. We assessed publication bias through a visual inspection of the funnel plot. List-wise deletion was used, as all variables had fewer than 1% missing data. Results were obtained using R, version 4.1.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Results
The PRISMA flowchart (Supplementary Figure 1) describes the selection of studies for the analysis. Of the 668 studies initially identified; 20 full-text studies were screened. After the exclusion of 11 studies, four studies were included in the IPD analysis, while five were used to perform an aggregate-level meta-analysis (Supplementary Table 2, Supplementary Table 3)45671516171819. In brief, 2,441 participants contributed to the IPD meta-analysis, of whom 1,208 were randomised to US-guided and 1,233 were randomised to non-US-guided TFA. The individual trials were the FAUST (n=1,004), the Marquis-Gravel et al (n=128), the SURF (n=688) and the UNIVERSAL (n=621) trials. The five predominantly PVD trials that contributed to the aggregate-level meta-analysis had a total study population of 1,994, of whom 985 were randomised to US-guided and 1,009 were randomised to non-US-guided TFA.
RISK-OF-BIAS EVALUATION
We summarised the risk of bias in Supplementary Table 4. Studies included in the IPD meta-analysis were all deemed to have “some concern” for bias; however, this was only because the operator could not be blinded to the intervention. For the aggregate-level studies, the Gedikoglu et al 2013 study was categorised as high risk for bias as the outcome was measured by the operator who performed the procedure. The funnel plot did not demonstrate significant asymmetry for the primary composite outcome (Supplementary Figure 2).
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
For trials included in the IPD meta-analysis, the mean age was 65.5 years, and 27% of participants were female (Table 1). A total of 12.1% had peripheral vascular disease, and 34.5% underwent PCI. Regarding procedural characteristics, 79.6% of access sites were fitted with a 6 Fr introducer, and 50.9% were closed with a VCD (Table 2).
For the trials included in the aggregate meta-analysis, the weighted mean age was 62.1 years, and 45.4% of the participants were female (Supplementary Table 2). Sheath sizes ranged from 4 to 7 Fr, and only two of the five trials used VCD.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics (by participant).
| Overall (n=2,441) | Ultrasound (n=1,208) | No ultrasound (n=1,233) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics and comorbidities | ||||
| Age, years | 65.5±13.2 | 65.3±13.3 | 65.8±13.1 | 0.29 |
| Female sex | 659 (27.0) | 326 (27.0) | 333 (27.0) | 0.98 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29.1±6.62 | 29.4±6.23 | 28.8±6.6 | 0.02 |
| Hypertension | 1,955 (80.1) | 960 (79.5) | 995 (80.8) | 0.43 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 1,900 (77.9) | 947 (78.4) | 953 (77.4) | 0.56 |
| Diabetes | 923 (37.8) | 467 (38.7) | 456 (37.0) | 0.40 |
| Current smoker | 675 (27.7) | 337 (27.9) | 338 (27.5) | 0.79 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 296 (12.1) | 161 (13.3) | 135 (11.0) | 0.07 |
| PCI performed during procedure | 841 (34.5) | 414 (34.3) | 427 (34.7) | 0.83 |
| Periprocedural medications | ||||
| Aspirin | 1,952 (80.0) | 950 (78.6) | 230 (81.3) | 0.10 |
| P2Y12 inhibitor | 1,222 (50.1) | 589 (48.8) | 633 (51.4) | 0.19 |
| Heparin1 | 1,240 (50.8) | 612 (50.7) | 628 (51.0) | 0.86 |
| Bivalirudin | 79 (3.2) | 39 (3.2) | 40 (3.2) | 0.98 |
| GPIIa/IIIb inhibitors | 91 (3.7) | 43 (3.6) | 48 (3.9) | 0.66 |
| Data are presented as mean±SD or n (%). Missing data for each variable <0.5%. 1 Heparin includes either low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin. BMI: body mass index; GP: glycoprotein; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; SD: standard deviation | ||||
Table 2. Procedural characteristics (by access).
| Overall (n=2,457) | Ultrasound (n=1,217) | No ultrasound (n=1,240) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator | ||||
| Fellow/trainee | 1,788 (72.8) | 879 (71.5) | 918 (74.1) | 0.15 |
| Attending/consultant | 668 (27.2) | 347 (28.5) | 321 (25.9) | |
| Overall (n=2,323) | Ultrasound (n=1,152) | No ultrasound (n=1,117) | p-value | |
| Introducer size1 | ||||
| 5 Fr | 117 (5.0) | 59 (5.1) | 58 (5.0) | 0.85 |
| 6 Fr | 1,850 (79.6) | 911 (79.1) | 939 (80.2) | 0.51 |
| 7 Fr | 166 (7.1) | 79 (6.9) | 87 (7.4) | 0.59 |
| 8 Fr | 18 (0.8) | 15 (1.3) | 3 (0.3) | 0.008 |
| Vascular closure device use1 | 1,181 (50.9) | 628 (54.6) | 553 (47.3) | 0.001 |
| Data are presented as n (%). Missing data for each variable <1 %. 1 The Marquis-Gravel et al study did not report exact introducer sizes (all either 5 or 6 Fr) or vascular closure device use and were excluded from these analyses. | ||||
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
In the IPD meta-analysis of the coronary trials, participants randomised to US-guided TFA compared with non-US-guided TFA had a significant decrease in the odds of experiencing the primary composite outcome of major bleeding or major vascular complications (34/1,208 [2.8%] vs 55/1,233 [4.5%], OR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.39-0.94; p=0.026) (Table 3). When including BARC 2 bleeding in the composite outcome, the effect estimate shifted slightly towards the null (OR 0.70, 95% CI: 0.49-1.01; p=0.06). Participants who were allocated to US-guided TFA experienced fewer major vascular complications (29/1,208 [2.4%] vs 49/1,233 (4.0%); OR 0.58, 95% CI: 0.36-0.93; p=0.023). While no significant differences between groups were observed for all bleeding outcomes separately, large haematomas were less frequent in the US-guided TFA group as compared with the non-US-guided TFA group (25/1,208 [2.1%] vs 45/1,233 [3.6%]; OR 0.54, 95% CI: 0.33-0.89; p=0.016). Lastly, the number of access attempts (1.42 vs 2.21, mean difference −0.78, 95% CI: −0.93 to −0.64; p<0.001) and the number of inadvertent venipunctures (64/1,217 [5.3%] vs 174/1,240 [14.1%]; OR 0.33, 95% CI: 0.25-0.46; p<0.001) were fewer in the US-guided TFA group compared with the non-US-guided TFA group.
In the subgroup of predominantly PVD trials with only aggregate-level data available, participants randomised to US-guided TFA seemed to experience less major vascular complications or major bleeding (13/985 [1.3%] vs 44/1009 [4.4%]; fixed-effect OR 0.30, 95% CI: 0.16-0.46; random-effects OR 0.35, 95% CI: 0.05-2.41) (Figure 1). When adding the individual participant-level data of the coronary trials, the effects estimates shifted slightly towards the null but remained in favour of the US-guided TFA group (47/2,193 [2.1%] vs 99/2,242 [4.4%], fixed-effect OR 0.47, 95% CI: 0.33-0.67; p<0.01; random-effects OR 0.49, 95% CI: 0.26-0.94; p=0.04; I2=41%; p=0.12). There was no evidence of interaction between subgroups (interaction p for fixed-effect=0.07; interaction p for random-effects=0.31).
Table 3. Main outcomes (by participant and by access, see section titles).
| Ultrasound (n=1,208) | No ultrasound (n=1,233) | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome (by participant) | ||||
| Major vascular complications (femoral artery pseudoaneurysm, AV fistula, retroperitoneal bleed, large haematoma more than 5 cm in diameter, ischaemic limb requiring intervention or surgery) or BARC 3 bleeding | 34 (2.8) | 55 (4.5) | 0.61 (0.39-0.94) | 0.026 |
| Secondary outcome (by participant) | ||||
| Major vascular complications (femoral artery pseudoaneurysm, AV fistula, retroperitoneal bleed, large haematoma over 5 cm in diameter, ischaemic limb requiring intervention or surgery) or BARC 2 or 3 bleeding | 55 (4.6) | 76 (6.2) | 0.70 (0.49-1.01) | 0.06 |
| Major vascular complications (femoral artery pseudoaneurysm, AV fistula, retroperitoneal bleed, large haematoma more than 5 cm in diameter, ischaemic limb requiring intervention or surgery) | 29 (2.4) | 49 (4.0) | 0.58 (0.36-0.93) | 0.023 |
| BARC 2 or 3 bleeding | 42 (3.5) | 59 (4.8) | 0.70 (0.47-1.05) | 0.09 |
| BARC 3 bleeding | 9 (0.7) | 7 (0.6) | 1.32 (0.49-3.54) | 0.59 |
| BARC 2 bleeding | 36 (3.0) | 52 (4.2) | 0.68 (0.44-1.05) | 0.08 |
| Individual components of major vascular complications (by participant) | ||||
| Femoral artery pseudoaneurysm | 6 (0.5) | 7 (0.6) | 0.88 (0.30-2.58) | 0.81 |
| AV fistula | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0.0) | NA | NA |
| Retroperitoneal bleed | 2 (0.2) | 1 (0.1) | 2.04 (0.18-22.5) | 0.56 |
| Large haematoma of more than 5 cm in diameter | 25 (2.1) | 45 (3.6) | 0.54 (0.33-0.89) | 0.016 |
| Ischaemic limb requiring intervention or surgery | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.2) | NA | NA |
| Procedural outcomes (by access) | ||||
| US-guided (n=1,217) | Non-US-guided (n=1,240) | Odds ratio (95% CI) or mean difference (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Number of attempts | 1.42±0.74 | 2.21±1.85 | −0.78 (−0.93 to −0.64) | <0.001 |
| Venipuncture | 64 (5.3) | 174 (14.1) | 0.33 (0.25-0.46) | <0.001 |
| Common femoral artery cannulation (by access) | ||||
| US-guided (n=869) | Non-US-guided (n=856) | |||
| Successful common femoral artery cannulation1 | 758 (87.2) | 737 (86.1) | 1.10 (0.84-1.46) | 0.49 |
| Data are presented as mean±SD or n (%). Missing data for each variable <1%. 1 The SURF trial was excluded from analysis, as this outcome was not reliably measured. AV: arteriovenous; BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; CI: confidence interval; NA: not applicable; SD: standard deviation; US: ultrasound | ||||
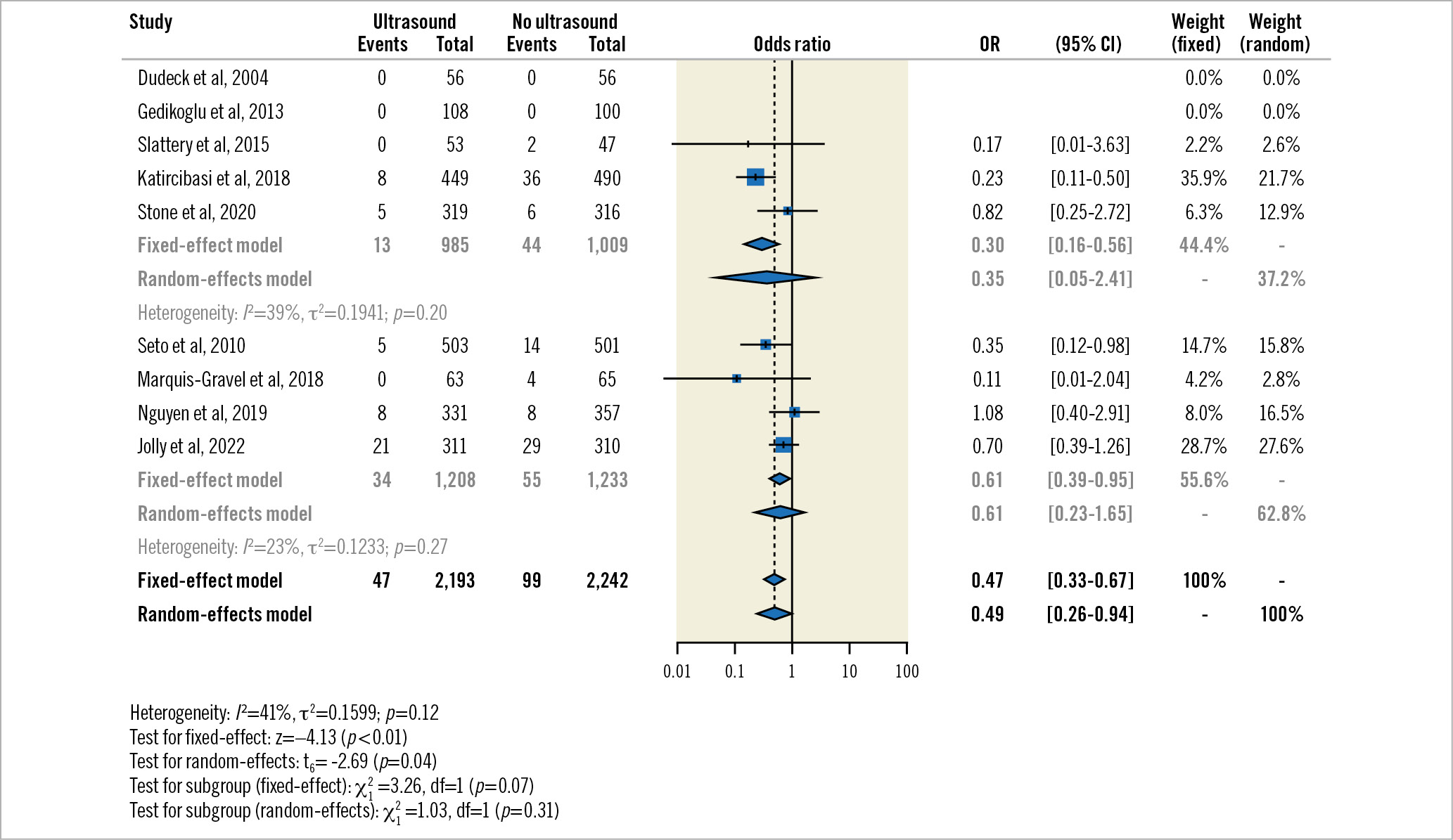
Figure 1. Two-stage fixed-effect and random-effects subgroup meta-analysis for the primary composite outcome by aggregate-level studies (predominantly peripheral vascular disease) and individual participant data studies (exclusively coronary). CI: confidence interval; OR: odds ratio
IPD SUBGROUP ANALYSES
In the subgroup of participants who received a VCD, those randomised to US-guided TFA compared with non-US-guided TFA experienced a reduction in major bleeding or major vascular complications (13/624 [2.1%] vs 31/550 [5.6%], OR 0.36, 95% CI: 0.19-0.69) (Figure 2). In participants who did not receive a VCD, there was no difference between the US-guided TFA and non-US-guided TFA groups, but there was significant interaction (21/517 [4.1%] vs 20/611 [3.3%], OR 1.21, 95% CI: 0.65-2.26; interaction p=0.009). While the UNIVERSAL trial had the most influence on the VCD subgroup analysis, the effect estimates of all trials had similar patterns (Supplementary Figure 3). The effect of US guidance remained consistent across all other subgroups, including for heparin and GPIIb/IIIa inhibitor use (Supplementary Table 5). Participants undergoing PCI, those who had larger sheaths, those who had VCD and those who underwent TFA by the attending/consultant group had a numerically higher percentage of complications.
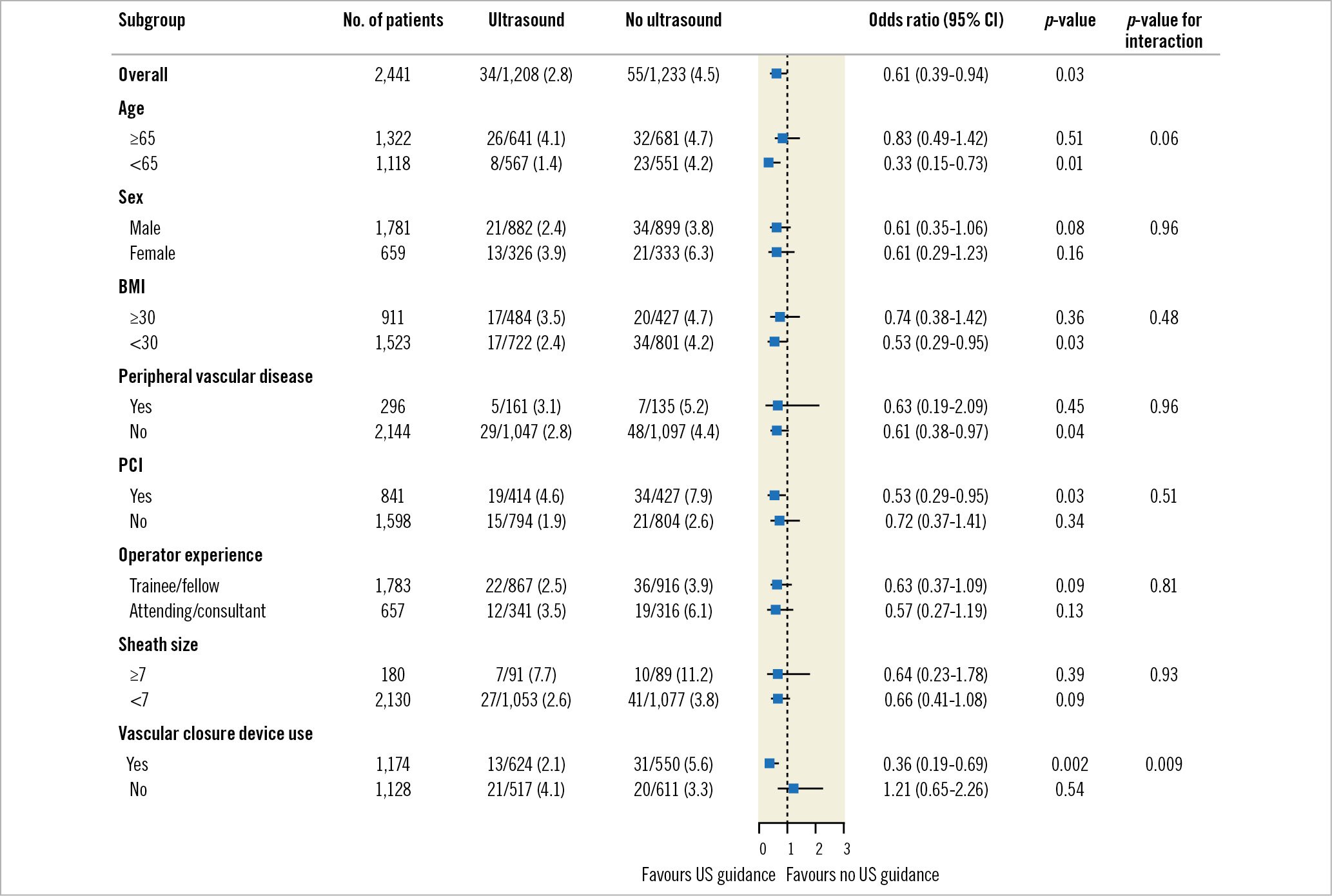
Figure 2. Subgroup analysis for the primary composite outcome. BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; US: ultrasound
SENSITIVITY ANALYSES
For the IPD coronary trials, the two-stage fixed-effect meta-analysis for the primary composite outcome gave similar results as our one-stage mixed model, favouring US-guided TFA (OR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.39-0.95; p=0.03; I2=23%; p=0.27) (Supplementary Figure 4). The effect estimates of the other two-step fixed-effect and random-effects sensitivity analyses were generally consistent with our primary one-stage mixed-model analysis, with the caveat that the 95% CIs of the random-effects estimates were wider (Supplementary Figure 4-Supplementary Figure 11).
For the IPD as-treated analysis, 25 participants crossed over from non-US-guided to US-guided, while 18 participants crossed over from US-guided to non-US-guided. As demonstrated in Supplementary Table 6, the effects estimate for the primary composite outcome result is similar to the result of the intention-to-treat analysis, with a slight shift of the effects estimates and 95% CI away from the null (34/1,215 [2.8%] vs 55/1,226 [4.5%], OR 0.60, 95% CI: 0.39-0.92; p=0.02).
Discussion
Our IPD meta-analysis, including 2,441 participants from four trials, sheds additional insights on the efficacy of US-guided TFA compared with non-US-guided TFA for coronary procedures. We demonstrated that US-guided TFA decreased the incidence of the composite of major bleeding or major vascular complications, major vascular complications alone, the number of access attempts and inadvertent venipunctures. US-guided TFA may be particularly beneficial in participants receiving VCDs. These data provide strong evidence of the potential benefits for interventional cardiologists of using routine US-guided TFA.
TFA vascular complications and major bleeding during percutaneous coronary interventions are associated with increased morbidity and mortality24. Our aggregate-level subgroup meta-analysis combining IPD from coronary trials and aggregate-level data from predominantly PVD trials is consistent with a previous meta-analysis5. Our IPD findings are confirmatory in the interventional cardiology study population. While there was no statistically significant interaction between the coronary and predominantly PVD subgroups, the notable difference between effects estimates may suggest intrinsic differences between the subgroup study populations. Even with the lack of statistical interaction for the PVD subgroup in the IPD trials, we hypothesise that US guidance may be even more beneficial in heavily diseased and calcified femoral arteries − frequently seen in the PVD population undergoing revascularisation.
The two-step analyses using the IPD coronary trials demonstrate that our findings are somewhat sensitive to our modelling assumptions, as shown by the wide confidence intervals produced by the random-effects analysis. However, the low heterogeneity for the primary composite outcome supports our prespecified fixed-effect modelling assumption25. On the other hand, the two-step analysis combining the aggregate-level and IPD trials strongly suggests a benefit for US guidance, regardless of the modelling assumption. This analysis suggests that if all coronary and PVD trials had been combined in an IPD meta-analysis, the effects estimates would have been even more pronounced, arguing against a spurious significant result caused by selection bias for our IPD analysis.
While the UNIVERSAL trial was neutral for its primary composite outcome of major vascular complications or major bleeding, a prespecified analysis suggested that US use was associated with a decreased risk of complications in participants receiving a VCD26. US guidance reduced the number of access attempts and the number of venipunctures. VCDs will only close one puncture site compared with manual compression, which may decrease bleeding from multiple arterial and venous puncture sites. Furthermore, US guidance may allow the operator to sidestep particularly diseased or calcified areas of the common femoral artery, resulting in a safer deployment of VCDs. Our similar finding in a much larger study population corroborates the previous hypothesis and may prompt interventionalists to be especially diligent in performing US-guided TFA for patients scheduled to have a VCD. Other interesting subgroup findings included the numerically higher risk of complications in participants undergoing PCI, those who were fitted with larger sheaths, those who had VCDs and participants undergoing TFA performed by the attending/consultant group compared with the trainee/fellow group. We hypothesise that the attending/consultant group may have chosen to participate in more complex cases in higher-risk participants, such as participants undergoing complex PCI requiring larger sheaths and VCDs.
For several reasons, limiting femoral vascular complications is a growing consideration in interventional cardiology. First, operators may become less familiar with recognising and managing femoral complications as the use of radial access increases27. Secondly, large-bore access in patients requiring chronic total occlusion percutaneous coronary intervention, percutaneous valve therapies, and mechanical circulation support is also increasing. Accordingly, recent observational studies demonstrated an association between US-guided TFA and fewer vascular complications and bleeding in transcatheter aortic valve replacement and chronic total occlusion PCI patients compared with non-US-guided TFA2829. Optimising techniques to obtain safe femoral access remains a paramount objective in interventional cardiology and will become more important as percutaneous procedures develop.
It is important to note that US-guided femoral access does not supplant transradial access as the preferred approach when feasible. The transradial approach has demonstrated reduced vascular access complications for stable patients and a mortality benefit in acute coronary syndrome patients2. Our data are complementary in improving the safety of vascular access to patients, and we advocate for systematic US-guided TFA training in the core interventional cardiology curriculum.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, the limitations of our IPD meta-analysis are inherently related to the limitations of the original trials. A large proportion of the primary composite outcome was composed of large haematomas. While these are associated with patient discomfort and increased costs, they may not be associated with increased mortality30. However, a study including only the more severe adverse events, such as retroperitoneal bleeds or ischaemic limbs, would require a much larger sample size to be powered to detect clinically significant differences. Second, regarding our subgroup analysis, as VCD use was a post-randomisation variable, US guidance may have biased the choice to use a VCD. Third, subgroup analyses should be considered hypothesis-generating and interpreted cautiously. Fourth, 72.8% of TFA were obtained by fellows and trainees who may have been on a steeper slope of their respective US-guided TFA learning curves than the attending physicians. This may have biased the results towards the null, and the benefits of US-guided TFA may be greater in more experienced hands. Lastly, significant findings must be interpreted with the caveat that we did not adjust for multiplicity.
Conclusions
Our IPD meta-analysis demonstrates that US-guided TFA, compared with non-US-guided TFA, is associated with a decreased risk of major bleeding or major vascular complications for coronary procedures. Furthermore, US-guided TFA may be particularly useful in preventing vascular complications in patients receiving VCDs. Based on these data, interventional cardiologists should consider using routine US guidance as part of their femoral access practice.
Impact on daily practice
While worldwide ultrasound use is increasing for transfemoral access in coronary procedures, definitive data are lacking. We performed a systematic review and individual participant-level data meta-analysis, which included four randomised controlled trials (n=2,441), demonstrating that ultrasound-guided transfemoral access significantly decreases major bleeding or vascular complications (34/1208 [2.8%] vs 55/1,233 [4.5%]; odds ratio 0.61, 95% confidence interval: 0.39-0.94; p=0.026) and may be particularly beneficial in patients receiving a vascular closure device. Interventional cardiologists should consider using ultrasound guidance as part of their femoral access practice.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Seto reports receiving grants or contracts from Arena Medical, Philips, and ACIST; payment or honoraria for speakers’ bureaus from Janssen, Terumo, Getinge, and GE HealthCare; consulting fees from Medtronic and Medicure; and reports having equity in Frond Medical. S. Jolly reports receiving grants or contracts from Boston Scientific; and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing, or educational events from Penumbra. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

