Introduction
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has recently emerged as a treatment option for high risk patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis and has now been performed in more than 20,000 patients. This article provides an overview on TAVI with a special focus on the technical aspects when using the transfemoral approach. The following is an introduction and summary of the complete unabridged version, supplemented with extensive moving imagery, which can be viewed at www.eurointervention.org.
Devices
Two devices are commercially available:
The balloon expandable Edwards SAPIEN XTTM transcatheter heart valve (ES; Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA USA) and the self-expanding Medtronic-CoreValve System (MCV; Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA).
Patient selection
The selection of candidates for TAVI should involve a heart team, that is to say, cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, imaging specialists, anaesthesiologists with experience in valve disease and other specialists such as geriatricians if necessary.
Today the technique should be restricted to patients with severe aortic stenosis leading to symptoms, either at high risk or contraindications for surgery as well as having sufficient life expectancy.
The next step is to evaluate the feasibility of TAVI using echocardiography, coronary angiography, aortography, peripheral angiography or MSCT.
Performing the procedure
The performance of TAVI should be restricted to high volume centres which have both cardiology and cardiac surgery departments with expertise in valvular heart disease.
The physicians involved in TAVI should have received specific training based on acquisition of basic, then advanced and finally device-specific skills. Anaesthesia personnel involved in the procedure should be senior cardiac anaesthesiologists. While overall there is now a trend towards simplification of the procedure from general anaesthesia to a full percutaneous approach under conscious sedation and loco-regional anaesthesia, the definite advantages of one approach over the other are not yet established.
Monitoring of the haemodynamic parameters throughout the procedure is crucial.
When anaesthesia and/or sedation is performed, vascular access for angiography and pacing is obtained on the opposite side to that chosen chosen for the TAVI approach.
Percutaneous access
Success of the percutaneous femoral approach requires the following of a meticulous procedure from artery puncture to closure.
Sheath insertion
When the percutaneous access device is in place, or the arterial cut-down performed, the aortic valve is crossed and a stiff exchange guidewire is placed in the apex of the LV.
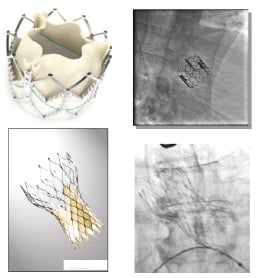
Figure 1. The Edwards SAPIEN XT transcatheter heart valve and the Medtronic CoreValve System.
Balloon valvuloplasty is performed to pre-dilate the native valve and also serve as a rehearsal for TAVI.
Valve delivery has specific aspects according to the device used.
As a general principle, an assessment, including aortography and TEE guidance if available is necessary after each modification of the position, before considering valve positioning as final.
Evaluation of the immediate results
Immediately after TAVI, haemodynamic status is assessed based on haemodynamics and aortography; echocardiography is performed to evaluate valve function and eliminate complications.
Management of complications
The best management of complications is based on:
1. Prevention by a comprehensive screening before TAVI;
2. Training of the team on techniques and materials required for bail-out procedures;
3. Anticipation of complications during the multidisciplinary evaluation before the procedure;
4. Fast identification of the complication and its cause;
5. Immediate availability of cardiac support and surgery if needed.
Tips to prevent or treat complications
Complication: Rupture/dissection of the arterial access
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– Careful screening, avoid borderline cases
– Suture sheath in place
– Watch out for sheath / catheter tip injury to arterial wall
– Abort procedure if resistance to sheath progression
– Systematic angiogram at time of sheath removal
– Cross over access available
– Occlusion balloon (30 mm) and covered stents (8-14 mm) available
Complication: Rupture/dissection of the aortic annulus during balloon valvuloplasty or valve implantation
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– Caution if huge aortic calcification,
– Adequate sizing of annulus diameter, avoid overestimation
– Careful post-implantation evaluation (TTE±TEE, CT Scan)
– Immediate surgical conversion available
Complication: Valve malposition
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– CoreValve “too low”: valve repositioning with the “lasso” technique, or valve in valve implantation
– CoreValve “too high”: secure the valve in a high position in the ascending aorta with a goose-neck catheter, then valve in valve implantation, or surgery
– SAPIEN “too low”: valve in valve implantation in a higher position, or surgery
– SAPIEN “too high”: if severe consequence (e.g.; aortic regurgitation), valve in valve implantation or surgery
Complication: Valve embolisation
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– Adequate sizing of annulus diameter, avoid underestimation
– Avoid valve malposition
– Remove delivery system before valve deployment (SAPIEN)
– Make sure of full balloon inflation during implantation (SAPIEN)
– Do not stop pacing prematurely (SAPIEN)
– Aortic embolisation: SAPIEN: pull back valve with semi-inflated balloon to a stable position, if possible in the descending aorta / CoreValve: pull back with a goose-neck catheter
– Ventricular embolisation: surgical conversion
Complication: Coronary occlusion
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– Careful screening for bulky calcification close to the left main, low-lying coronary ostia, shallow aortic root
– Angiogram during predilatation, to analyse motion of calcification and coronary artery patency.
– If no other option, protection wire in the LAD before valve delivery
– If occurs, PCI is the first option, circulatory assistance and surgical conversion may be discussed. With CoreValve, try to retract the system in the ascending aorta (see above)
Complication: Aortic regurgitation > grade 2
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– Careful analysis of its severity, mechanism (TEE/TTE) and haemodynamic consequences
– Severe para-prosthetic leak: post-dilatation if under-expansion, valve repositioning or valve in valve implantation if malposition
– Severe central leak: valve in valve implantation
Complication: Haemodynamic deterioration
Tips to avoid or treat the problem:
– Skilled cardiac anaesthesiologist present in the room
– Avoid hypovolaemia
– Maintain a systolic aortic pressure at 110-130 mmHg during the procedure
– Never start pacing if haemodynamics is unstable
– Let pressure recover between two pacing sequences
– If necessary, use vasopressors, not inotrops
– Echo check for immediate diagnosis
– Specific treatment of tamponade, arrhythmia
– Rarely, temporary circulatory assistance

