
Introduction
In this chapter of Tools and Techniques, the authors present an update on coronary guidewires for chronic total occlusions (CTO). The following is a summarised overview of guidewire selection. The complete, unabridged version with images is available online at: http//:www.pcronline.com/eurointervention/92nd_issue/216.
Coronary guidewires are fundamental to the interventional cardiologist. The wide selection of commercially available guidewires can sometimes be confusing, often leading to random choices being made. Previously in this series, Erglis1 elegantly strove to address this by outlining the salient features of workhorse wires. This update expands on the previous work but aims primarily to provide an overview of guidewire selection, specifically in the treatment of CTO. Recommendations concerning wire choices are described for: 1) access, 2) microchannel crossing, 3) direct penetration, 4) collateral crossing, 5) knuckling, 6) re-entering and 7) externalisation of the wire2.
Guidewire composition and characteristics
Coronary guidewire characteristics include torque control, trackability, steerability, flexibility, prolapse tendency, radiopacity/visibility, tactile feedback, crossing and support1. The basic composition of guidewires is well established (Figure 1, Table 1), and it is well known that there is a trade-off between lubricity and tactile response (Figure 2). In addition to the classic core-to-tip and shaping ribbon tip designs, coronary guidewires are becoming increasingly sophisticated as can be seen in the newer, composite “dual coil” cores from ASAHI Intecc (Aichi, Japan), where a rope coil wraps around the central core and then the whole wire is encased in a spring coil to aid torque transmission further. Moreover, newer wires may have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic coatings, e.g., a mainly hydrophilic coating for lubricity but a hydrophobic distal 1-2 cm tip for tactile feedback. Wire stiffness is measured as its tip load – the force (grams) to deflect the wire by 2 mm, when suspended 10 mm from its tip. In CTOs wire stiffness can be enhanced via a microcatheter or an “over-the-wire” balloon.
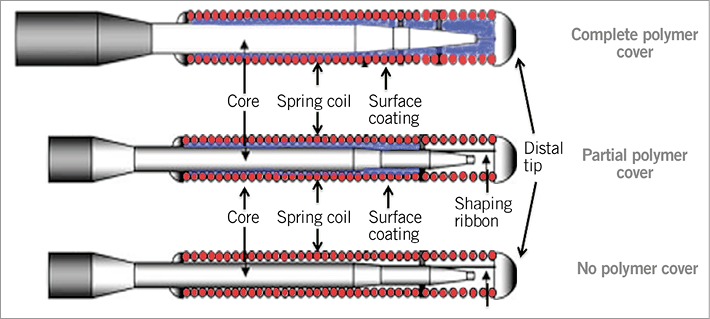
Figure 1. Schematic drawing of basic guidewire (polymer and non-polymer wires) design.
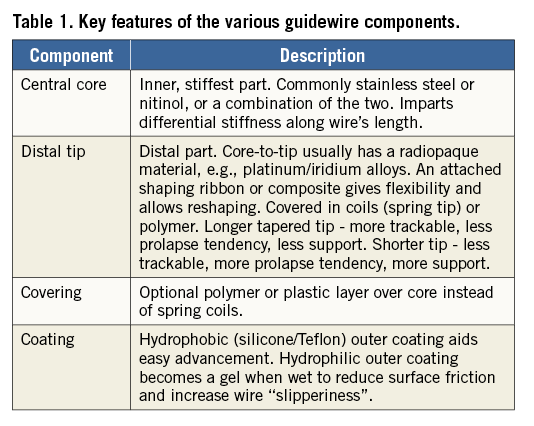
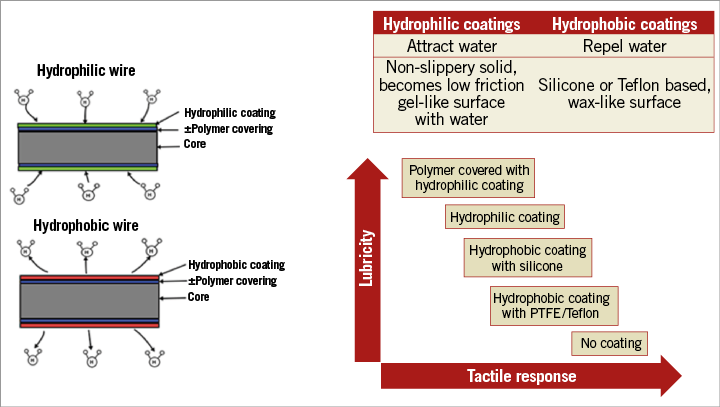
Figure 2. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic wires and coatings, and the relationship between lubricity and tactile response.
Choosing the right wires for CTOs
There are four ways in which a CTO can be approached2 - wire escalation techniques, whereby the guidewire is manipulated through the occlusion usually with a microcatheter. Wires with different properties are used at different stages throughout the procedure. This can be either from an antegrade or from a retrograde approach (antegrade wire escalation [AWE] or retrograde wire escalation [RWE]). When wire-based strategies are unlikely to be successful (usually in more complex long occlusions) then dissection techniques can be employed. The operator deliberately uses a guidewire or dedicated equipment (CrossBoss™; Boston Scientific, Fremont, CA, USA) to dissect through or around the occlusion with the aim of re-entering the vessel distal to the CTO either with a standard guidewire (Subintimal Tracking and Reentry [STAR]3 or Limited Antegrade Subintimal Tracking [LAST]2) or with specific equipment (Stingray™ balloon and Stingray™ guidewire; Boston Scientific). Retrograde dissection re-entry (RDR or reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde subintimal tracking [reverse CART]) is the fourth method. Once retrograde access is achieved, dissection is performed. When antegrade and retrograde equipment is overlapping, a balloon is used to connect the spaces and allow the guidewire to be manoeuvred through.
With these techniques in mind, guidewires can then be classified according to their role in the various techniques.
1. Access – to access the proximal cap, or a side branch, to anchor a balloon or a retrograde collateral channel and to allow delivery of a microcatheter or balloon.
2. Microchannel crossing – to find micro connections through a CTO which are not appreciated angiographically.
3. Direct penetration – to puncture and steer the penetrative wire or a different wire through the CTO segment and enter into the distal lumen. This is now referred to as antegrade wire escalation.
4. Collateral crossing (CC) – via septal or epicardial vessels which are usually small, often tortuous and easy to damage.
5. Knuckling – the deliberate advancement of a wire which has been intentionally prolapsed.
6. Re-entering – a penetrative wire (e.g., Confianza; ASAHI Intecc) is used to attempt a directed re-entry into the true lumen as close to the distal cap as possible. The Stingray balloon as part of the BridgePoint family of devices (Boston Scientific) can also facilitate this.
7. Externalisation – use of a long wire through a retrograde microcatheter, into the antegrade guide catheter and out of the antegrade guide hub.
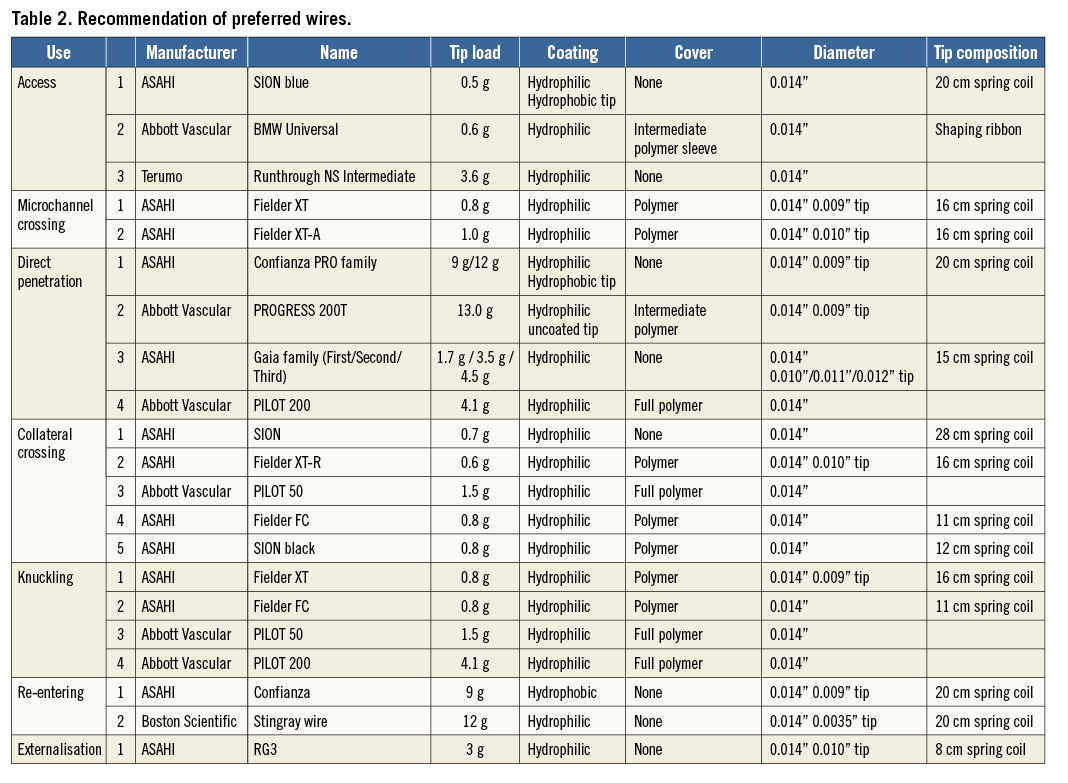
Suggested recommendations of preferred wires for each CTO technique are given in Table 2.
Conclusion
Guidewire characteristics are determined by their composition and design, and a large range of different wires is commercially available. The treatment of CTOs by PCI is complex, and the selection of guidewires according to their specific properties needs to be tailored to the lesion in question and is vital to procedural success. We have summarised the core characteristics of the guidewires which are required in each step, with suggestions for individual wire selection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

