Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with the development of atrial thrombi and the risk of embolisation. A detrimental manifestation after embolisation of these thrombi is ischaemic stroke, with 15-20% of all ischaemic strokes occurring in patients with AF1. The increased thromboembolic risk depends on various risk factors. Therefore, current guidelines recommend risk stratification by CHA2DS2-VASc score to estimate the need for oral anticoagulation (OAC) therapy in patients with AF2.
Several randomised controlled trials (RCTs) demonstrated a two-thirds reduction in the incidence of stroke using vitamin K antagonists (VKA) compared to placebo in patients with AF3. For several decades VKA treatment was the gold standard, until novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) were introduced, showing similar efficacy in thromboembolic risk reduction4. However, the use of (N)OACs still needs rigorous therapy compliance and carries a concomitant risk for bleeding complications. The fear of severe bleedings causes patients with AF to be undertreated. In patients with a contraindication for long-term OAC therapy, percutaneous left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) is an upcoming and promising alternative5.
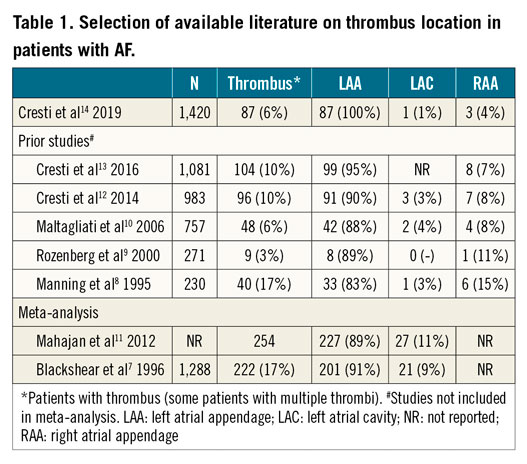
The origin of the thromboembolic risk in patients with AF has been thoroughly investigated for many decades. Blood stasis in the atria, resulting from atrial mechanical dysfunction during AF, causes a prothrombotic environment. Shear stress causing atrial myocardial damage during AF stimulates the expression of endothelial prothrombotic factors and activates inflammatory cells and platelets, forming the basis for thrombogenesis by Virchow’s triad6. The left atrial appendage (LAA) has been pointed out as the most frequent origin of thrombi in patients with non-valvular AF. The most cited meta-analysis presenting thrombus location in non-valvular AF patients observed a 91% prevalence of thrombi located in the LAA7. Table 1 illustrates a selection of earlier reports on this subject7,8,9,10,11,12,13.
In this issue of EuroIntervention, Cresti and colleagues present an observational study on the prevalence of extra-LAA thrombus in patients scheduled for electrical cardioversion (ECV)14.
A total of 1,420 patients (61% male, mean age 70±10 years) were enrolled. These patients had non-valvular AF or atrial flutter lasting >48 hours, did not use adequate anticoagulation and opted for transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) prior to ECV. In 87 patients a total of 91 thrombi were observed; LAA thrombus was present in all patients. In addition, right atrial appendage (RAA) thrombus was observed in three patients and in one patient in the left atrial cavity (LAC), resulting in a prevalence of extra-LAA thrombus of 4.6% in patients with thrombus. Patients with documented thrombi were more often affected by non-valvular AF (92% vs. 77%, p=<0.001) and had a higher CHA2DS2-VASc score (3.4 vs. 2.8, p=0.002) compared to patients without thrombi.
The authors should be congratulated for presenting these results in the largest group of non-valvular AF patients on this subject. Earlier reports included both valvular and non-valvular AF types with variable definitions, anticoagulation strategies were diverse and frequently not well reported and the RAA was not structurally assessed. The extra-LAA origin of thrombus of 4.6% in this study was lower compared to prior studies. This is an important finding in the current era where LAAC is emerging and extra-LAA thrombus occurrence might cast doubts on its effectiveness. The authors note that the low prevalence of extra-LAA thrombi may reinforce indications for LAAC. However, this should be considered carefully due to the highly selected patient population in the current study. Patients who qualify for LAAC tend to have higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores and higher prevalence of echocardiographic risk factors associated with developing thrombi. Aside from that, many patients treated by LAAC are affected by permanent AF, which was not present in this cohort at all.
The choice for LAAC is often the only alternative to no therapy at all, since current guidelines only recommend LAAC when (N)OAC is contraindicated. Therefore, a very low incidence of extra-LAA thrombus will most likely not influence decision making, as LAAC seems more attractive than no treatment at all. However, earlier described prevalence of extra-LAA thrombus may have contributed to the restricted indication recommendations for LAAC; the low prevalence in this study may encourage a different approach for selecting patients for LAAC. Of note, patients received various anticoagulants at the time of TOE. Although not meeting sufficient anticoagulation criteria, the use of these anticoagulants may have led to an underestimation of thrombus prevalence.
Multivariable analysis in this cohort showed heart failure, lower left ventricular ejection fraction and larger atrial volumes to be associated with atrial thrombus. Unfortunately, the authors do not report on results of other previously described echocardiographic risk factors, such as spontaneous echo contrast (SEC) or LAA outflow velocity, which might be a valuable contribution.
Although the risk for stroke is strongly associated with the occurrence of atrial thrombi, not all observed thrombi will embolise. Conversely, cardiac thrombi outside of the LAA may be transient in nature as they are swept away in the bloodstream and may only be seen by chance, as is seen in paradoxical emboli with a patent foramen ovale (PFO) or atrial septal defect (ASD), underestimating extra-LAA thrombus formation. Most extra-LAA thrombi were found in the RAA; very few data are currently available on its clinical consequences. Since no results on clinical outcomes were presented in this study, the clinical relevance remains uncertain. Furthermore, it should be noted that no inclusion period was described, and earlier publications of the same authors seem to be partly about the same cohort, which might give rise to publication bias. The higher prevalence of extra-LAA thrombus (~10%) in these studies is probably explained by not excluding valvular AF patients.
In summary, this study supports the fact that, in a selected population referred for LAAC, the risk of extra-LAA thrombus is low. Therefore, the implication is that LAAC in these patients may be very effective. Extra-LAA thrombus is associated with different clinical and echocardiographic findings and a more personalised approach seems reasonable. However, current risk stratification scores lack the inclusion of most echocardiographic characteristics associated with thrombus formation. When considering the eligibility for LAAC, the risk of extra-appendage thrombus should be assessed to enable better patient selection, and systemic therapy with (N)OAC remains the gold standard in patients who can tolerate it.
Conflict of interest statement
L. Boersma is a consultant for Boston Scientific and proctor for Abbott. M. Swaans reports proctoring fees for training/educational services to the Department of Cardiology from Boston Scientific, and personal fees from Abbott Vascular, Philips Healthcare and BioVentrix, Inc., outside the submitted work. M. Maarse has no conflicts of interest to declare.

