Abstract
BACKGROUND: Acute ischaemic stroke (AIS) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a rare, but debilitating, complication. However, contemporary data from real-world unselected patients are scarce.
AIMS: We aimed to explore the temporal trends, outcomes and variables associated with AIS as well as in-hospital all-cause mortality in a nationwide cohort.
METHODS: A retrospective analysis of healthcare records from 2006-2021 was implemented. Patients were stratified according to the occurrence of AIS in the setting of PCI. The temporal trends of AIS were analysed. A stepwise regression model was used to identify variables associated with AIS and in-hospital all-cause mortality.
RESULTS: A total of 4,910,430 PCIs were included for the current analysis. AIS occurred in 4,098 cases (0.08%). An incremental increase in the incidence of AIS after PCI from 0.03% to 0.14% per year was observed from 2006-2021. The strongest associations with AIS after PCI included carotid artery disease, medical history of stroke, atrial fibrillation, presentation with an ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) or non-STEMI and coronary thrombectomy. For patients with AIS, a higher in-hospital all-cause mortality (18.11% vs 3.29%; p<0.001) was documented. With regard to all-cause mortality, the strongest correlations in the stroke cohort were found for cardiogenic shock, dialysis and clinical presentation with a STEMI.
CONCLUSIONS: In an unselected nationwide cohort of patients hospitalised for PCI, a gradual increase in AIS incidence was noted. We identified several variables associated with AIS as well as with in-hospital mortality. Hereby, clinicians might identify the patient population at risk for a peri-interventional AIS as well as those at risk for an adverse in-hospital outcome after PCI.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) and its sequalae are associated with a relevant proportion of the global mortality risk attributed to cardiovascular deaths1. For revascularisation of CAD, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has become the most commonly utilised treatment method2. Also, a remarkable safety profile has been proven for the peri-interventional phase, including the in-hospital stay34. However, acute ischaemic strokes (AIS) with their inherent consequences can occur after a PCI procedure, leading to increased mortality rates both during early as well as later follow-up. In these cases, morbidity with subsequent speech and motor impairment is a devastating result of AIS, with a decreased quality of life in those affected567. Over the last years, single-centre and registry studies have investigated the characteristics of AIS after PCI58910111213. However, contemporary data with regard to AIS after PCI, including the most recent time frame with improved interventional techniques and tools, from nationwide registries are scarce101113. Moreover, data regarding variables associated with in-hospital mortality are lacking for patients with AIS after PCI.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to analyse the baseline characteristics, incidence, temporal trends, and variables associated with outcomes and AIS after PCI using an unselected all-comers nationwide sample of hospitalised patients from 2006-2021.
Methods
DATA AVAILABILITY
The data underlying this article were provided by the Federal Bureau of Statistics in Germany with permission. Data will be shared upon request to the corresponding author with permission of the German Federal Bureau of Statistics.
STUDY DESIGN
For the purpose of this study, data from the German Federal Bureau of Statistics were analysed. For the presented analysis, we included all patients ≥18 years of age hospitalised for a PCI procedure, who were admitted to an internal medicine or cardiology department, from 2006 to 2021. Information about baseline characteristics including demographics, classical cardiovascular risk factors, and prior medical history as well as the procedural characteristics of the index PCI were based on the World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases (10th revision of the German Modification [ICD-10-GM] and operation and procedure keys [OPS]). Subgroups were created according to the diagnosis of AIS versus no AIS during the in-hospital stay. Also, the length of the hospital stay and in-hospital mortality were ascertained. For the full set of ICD-10-GM and OPS codes used for the definitions of inclusion criteria, subgroups and comorbidities, see Supplementary Table 1.
ETHICS STATEMENT
This research adhered to the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. The researchers did not have direct access to patient information. Instead, access to completely anonymised summary findings from the research data centre of the German Federal Bureau of Statistics was given. As the data were routinely gathered as part of clinical practice, institutional review board approval and informed consent were not mandated by German law.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The data export was managed by the Federal Bureau of Statistics in Germany on the researchers’ behalf. The authors provided R codes for aggregated statistical analyses, which were then executed by the research data centre of the German Federal Bureau of Statistics. The aggregate data underwent consistency and secrecy checks by the German Federal Bureau of Statistics ahead of publication.
For the current study, binary variables are presented as absolute numbers and percentages, while continuous variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD). For between-group comparisons, a 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was applied to continuous variables, and the χ² test was employed for binary variables. Stepwise logistic regressions were performed to determine the variables associated with stroke and with in-hospital mortality, separately. To identify variables which correlated with AIS, we used age and all binary variables with at least a 2% frequency in the stroke or the non-stroke subcohorts. For in-hospital mortality of the AIS cohort, age and all binary variables with at least a 2% frequency in this cohort were used. First, all variables were entered into univariable logistic regressions. Thereafter, all variables were used in a backward selection process. The goal was to find the model with the smallest Akaike information criterion. The statistical analyses codes were programmed at the University Heart & Vascular Center Hamburg using R statistical software, version 4.2.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing); the analyses were conducted at the Federal Bureau of Statistics in Wiesbaden.
Results
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
From 2006 to 2021, a total of 4,910,430 inpatient PCIs were carried out and were included in the current analysis. Of these, AIS was noted in 4,098 (0.08%) cases, whilst in 4,906,256 cases (99.92%), no AIS was documented. Patients with AIS were slightly older (70.90 vs 68.45 years; p<0.001) and more likely to be female (34.68% vs 28.63%; p<0.001) in contrast to those without AIS. With regard to classical cardiovascular risk factors, a higher prevalence of diabetes (36.12% vs 28.94%; p<0.001) was noted in AIS patients, whilst rates of arterial hypertension (61.27% vs 61.32%; p=0.966) did not differ between groups. Hyperlipoproteinaemia (HLP) and obesity were more common amongst individuals without AIS. Furthermore, in patients with AIS, a higher prevalence of comorbidities, such as history of stroke (3.95% vs 0.72%; p<0.001), atrial fibrillation (34.63% vs 17.81%; p<0.001) and carotid artery disease (10.05% vs 1.70%; p<0.001), was registered. A detailed description of baseline characteristics and classical cardiovascular risk factors as well as prior medical history can be found in Table 1.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients with and without periprocedural acute ischaemic stroke after percutaneous coronary intervention.
| Acute ischaemic stroke (n=4,098) | No acute ischaemic stroke (n=4,906,256) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 70.90±11.34 | 68.45±11.59 | <0.001 |
| Female sex | 1,421 (34.68) | 1,404,594 (28.63) | <0.001 |
| Classical CVRF | |||
| Diabetes | 1,480 (36.12) | 1,420,102 (28.94) | <0.001 |
| Arterial hypertension | 2,511 (61.27) | 3,008,456 (61.32) | 0.966 |
| HLP | 1,892 (46.17) | 2,610,917 (53.22) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 248 (6.05) | 487,026 (9.93) | <0.001 |
| Prior medical history | |||
| Myocardial infarction | 339 (8.27) | 565,768 (11.53) | <0.001 |
| Ischaemic CMP | 364 (8.88) | 302,545 (6.17) | <0.001 |
| Stroke | 162 (3.95) | 35,475 (0.72) | <0.001 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1,419 (34.63) | 874,023 (17.81) | <0.001 |
| Carotid artery disease | 412 (10.05) | 83,263 (1.70) | <0.001 |
| PAD | 367 (8.96) | 288,008 (5.87) | <0.001 |
| CKD | 798 (19.47) | 851,380 (17.35) | <0.001 |
| Dialysis-dependent CKD | 55 (6.89) | 54,304 (6.38) | 0.602 |
| Liver disease | 96 (2.34) | 62,652 (1.28) | <0.001 |
| COPD | 251 (6.12) | 294,975 (6.01) | 0.787 |
| Valve disease | 673 (16.42) | 500,293 (10.2) | <0.001 |
| Categorical variables are displayed as absolute numbers (%). Continuous variables are described by mean±standard deviation. CKD: chronic kidney disease; CMP: cardiomyopathy; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CVRF: cardiovascular risk factors; HLP: hyperlipoproteinaemia; PAD: peripheral artery disease | |||
INDICATION FOR PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION AND PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS
Overall, the indication for PCI was ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) in 18.97% of patients, and in 21.85% it was due to non-STEMI (NSTEMI). In patients with ischaemic stroke, a higher proportion of patients presented with a STEMI (27.40% vs 18.97%; p<0.001) or an NSTEMI (38.92% vs 21.84%; p<0.001) than those without AIS. Also, a significant difference in the presence of cardiogenic shock was noted between the 2 subgroups (9.83% vs 3.50%; p<0.001).
Concerning procedural characteristics, coronary thrombectomy was utilised significantly more often in the AIS cohort (5.51% vs 2.75%; p<0.001). The major proportion of patients underwent implantation of a coronary stent (overall: 88.81%), although it was significantly less frequent in individuals with AIS (84.21%) than those without (88.81%; p<0.001). The use of drug-coated balloons, cutting balloons and rotablation devices did not differ between groups. Details concerning the clinical presentation and procedural characteristics can be found in Table 2. Furthermore, cohort characteristics stratified according to presentation with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) or chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) are included in Supplementary Table 2.
Table 2. Clinical presentation and procedural characteristics of patients with and without an acute ischaemic stroke after percutaneous coronary intervention.
| Acute ischaemic stroke (n=4,098) | No acute ischaemic stroke (n=4,906,256) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical presentation | |||
| STEMI | 1,123 (27.40) | 930,599 (18.97) | <0.001 |
| NSTEMI | 1,595 (38.92) | 1,071,391 (21.84) | <0.001 |
| UAP | 246 (6.00) | 734,145 (14.96) | <0.001 |
| Cardiogenic shock | 403 (9.83) | 171,821 (3.50) | <0.001 |
| PCI procedural characteristics | |||
| Stent implantation | 3,451 (84.21) | 4,357,211 (88.81) | <0.001 |
| DCB | 143 (3.49) | 188,185 (3.84) | 0.266 |
| CTO | 31 (0.76) | 59,110 (1.20) | 0.011 |
| Blade/cutting | 95 (2.32) | 107,324 (2.19) | 0.604 |
| Rotablation | 32 (0.78) | 40,063 (0.82) | 0.867 |
| Coronary thrombectomy | 226 (5.51) | 134,881 (2.75) | <0.001 |
| Categorical variables are displayed as absolute numbers (%). CTO: chronic total occlusion; DCB: drug-coated balloon; NSTEMI: non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; UAP: unstable angina pectoris | |||
TEMPORAL TRENDS OF ISCHAEMIC STROKE AFTER PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION
Between 2006 and 2021, a stepwise increase of AIS after PCI was observed (0.03% from 2006-2008, 0.05% from 2009-2011, 0.07% from 2012-2014, 0.09% from 2015-2017 and 0.14% from 2018-2021; p<0.001) (Supplementary Table 3). This was accompanied by an increasing age (66.72±11.22 years from 2006-2008, 67.58±11.46 years from 2009-2011, 68.3±11.6 years from 2012-2014, 68.98±11.61 years from 2015-2017 and 69.62±11.68 years from 2018-2021; p<0.001), an increasing cardiovascular risk factor burden (e.g., diabetes mellitus), and an increasing proportion of patients with comorbid disease (e.g., atrial fibrillation) in the overall cohort; the use of thrombectomy devices varied (0.83% from 2006-2008, 3.97% from 2009-2011, 5.28% from 2012-2014, 2.66% from 2015-2017 and 1.44% from 2018-2021; p<0.001). Baseline and procedural characteristics of the overall population stratified by year groups can be found in Supplementary Table 3. Of note, when analysing the yearly incidences of AIS after PCI, a sharp increase in AIS rates is noted in 2021 (0.25%), whereas a steady and gradual increase is documented from 2006 (0.03%) to 2020 (0.11%), as displayed in Figure 1.
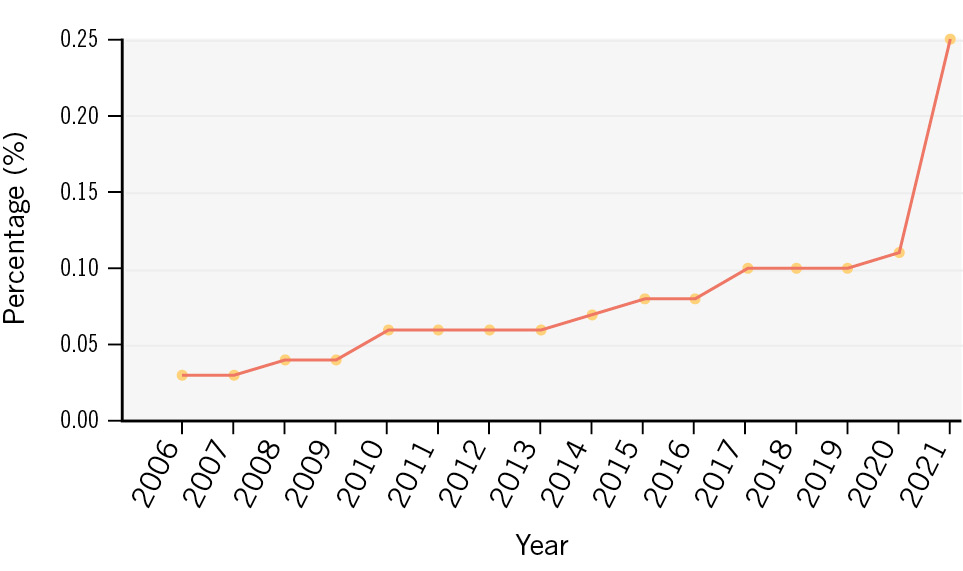
Figure 1. Temporal trends of acute ischaemic stroke in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.
VARIABLES ASSOCIATED WITH ISCHAEMIC STROKE AFTER PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION
After applying the stepwise regression analysis, 23 variables were found to be associated with AIS. The full set of variables is included in the Central illustration. Variables with the strongest positive association with AIS included carotid artery disease (odds ratio [OR] 5.73, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 5.15-6.37; p<0.001), medical history of stroke (OR 3.37, 95% CI: 2.87-3.96; p<0.001) atrial fibrillation (OR 2.08, 95% CI: 1.94-2.23; p<0.001), presentation with STEMI (OR 2.26, 95% CI: 2.08-2.47; p<0.001) or NSTEMI (OR 2.66, 95% CI: 2.48-2.87; p<0.001), and coronary thrombectomy (OR 1.46, 95% CI: 1.27-1.67; p<0.001). In contrast, for HLP (OR 0.83, 95% CI: 0.78-0.89; p<0.001), obesity (OR 0.59, 95% CI: 0.52-0.68; p<0.001) and coronary stent implantation (OR 0.65, 95% CI: 0.60-0.71; p<0.001) an inverse association was noted. The outcomes of the univariable analysis are included in Supplementary Table 4. Also, variables associated with AIS according to presentation with ACS or CCS are displayed in Supplementary Table 5 and Supplementary Table 6 (for uni- and multivariable analysis, respectively).
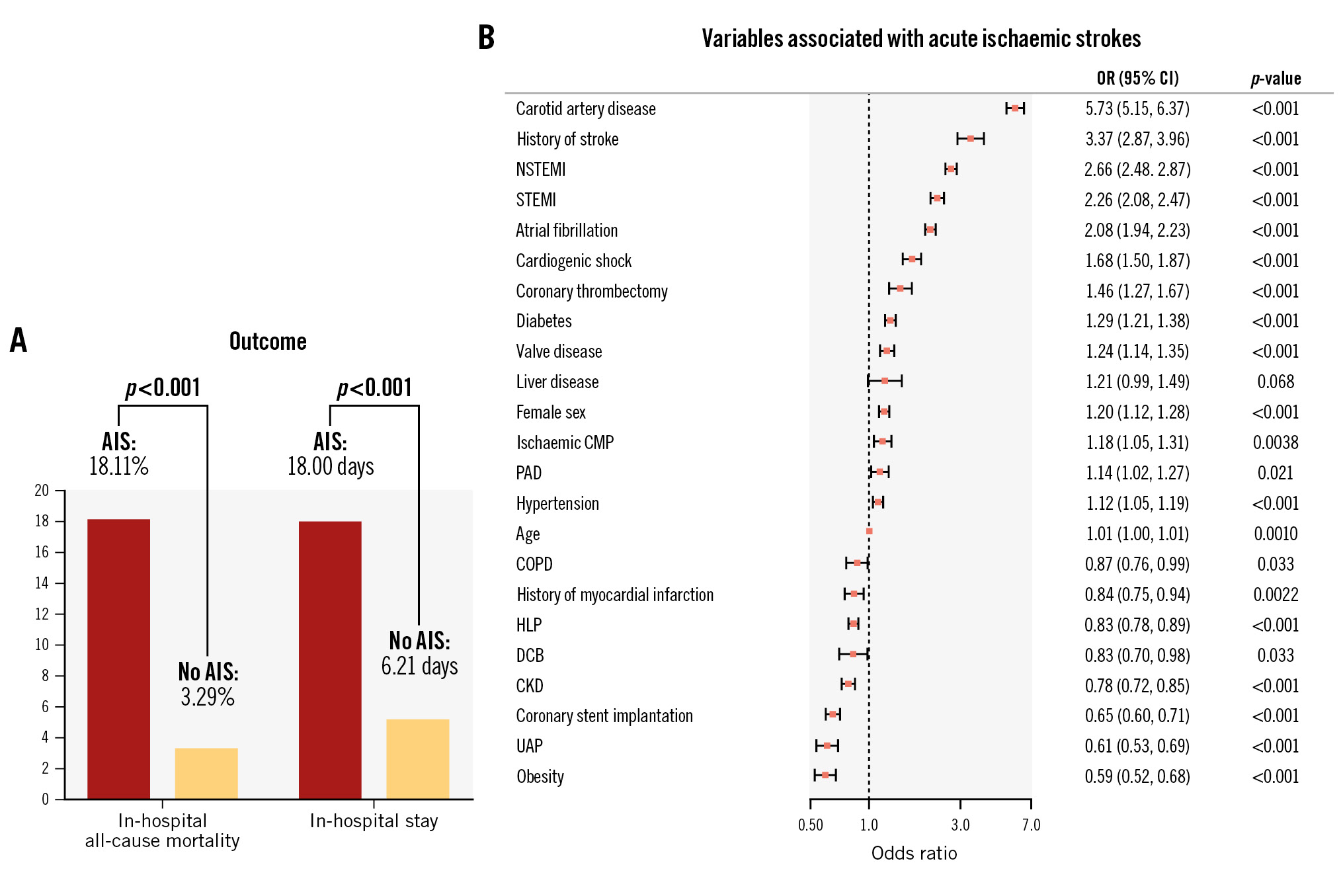
Central illustration. Acute ischaemic stroke in patients undergoing PCI. A) Visualisation of in-hospital all-cause mortality and in-hospital stay according to subgroup. B) Variables associated with acute ischaemic stroke in patients undergoing PCI after multivariable stepwise regression analysis. Odds ratios (OR) and the 95% confidence interval (95% CI) are given. AIS: acute ischaemic stroke; CKD: chronic kidney disease; CMP: cardiomyopathy; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DCB: drug-coated balloon; HLP: hyperlipoproteinaemia; NSTEMI: non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PAD: peripheral artery disease; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; UAP: unstable angina pectoris
RATES OF IN-HOSPITAL MORTALITY AND VARIABLES CORRELATED WITH IN-HOSPITAL DEATH IN PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHAEMIC STROKE AFTER PERCUTANEOUS CORONARY INTERVENTION
Patients hospitalised for PCI suffering from an AIS had a notably higher rate of in-hospital all-cause mortality (18.11% vs 3.29%; p<0.001) and a longer in-hospital stay (18.00±15.16 days vs 6.21±7.76 days; p<0.001) (Table 3) than patients without an AIS. We identified 13 variables which were associated with in-hospital mortality in the AIS cohort (see Figure 2 for the full set of associated variables). For example, cardiogenic shock (OR 6.62, 95% CI: 5.23-8.83; p<0.001), dialysis (OR 3.19, 95% CI: 1.76-5.81; p<0.001) and clinical presentation with STEMI (OR 2.65, 95% CI: 2.11-3.33; p<0.001) or NSTEMI (OR 1.47, 95% CI: 1.18-1.83; p<0.001) were amongst the strongest variables associated with in-hospital death. Moreover, for some variables, an inverse association with in-hospital all-cause mortality was documented, namely arterial hypertension (OR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.65-0.93; p=0.0055), HLP (OR 0.51, 95% CI: 0.42-0.61; p<0.001) and coronary stent implantation (OR 0.67, 95% CI: 0.53-0.85; p=0.0010). Univariable analysis is included in Supplementary Table 7. Variables associated with in-hospital mortality after AIS according to presentation with an ACS or CCS are displayed in Supplementary Table 8 and Supplementary Table 9 (for uni- and multivariable analysis, respectively).
Table 3. In-hospital outcome of patients with and without an acute ischaemic stroke after percutaneous coronary intervention.
| Acute ischaemic stroke (n=4,098) | No acute ischaemic stroke (n=4,906,256) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length of in-hospital stay, days | 18.00±15.16 | 6.21±7.76 | <0.001 |
| In-hospital all-cause mortality | 742 (18.11) | 161,273 (3.29) | <0.001 |
| Categorical variables are displayed as absolute numbers (%). Continuous variables are described by mean±standard deviation. | |||
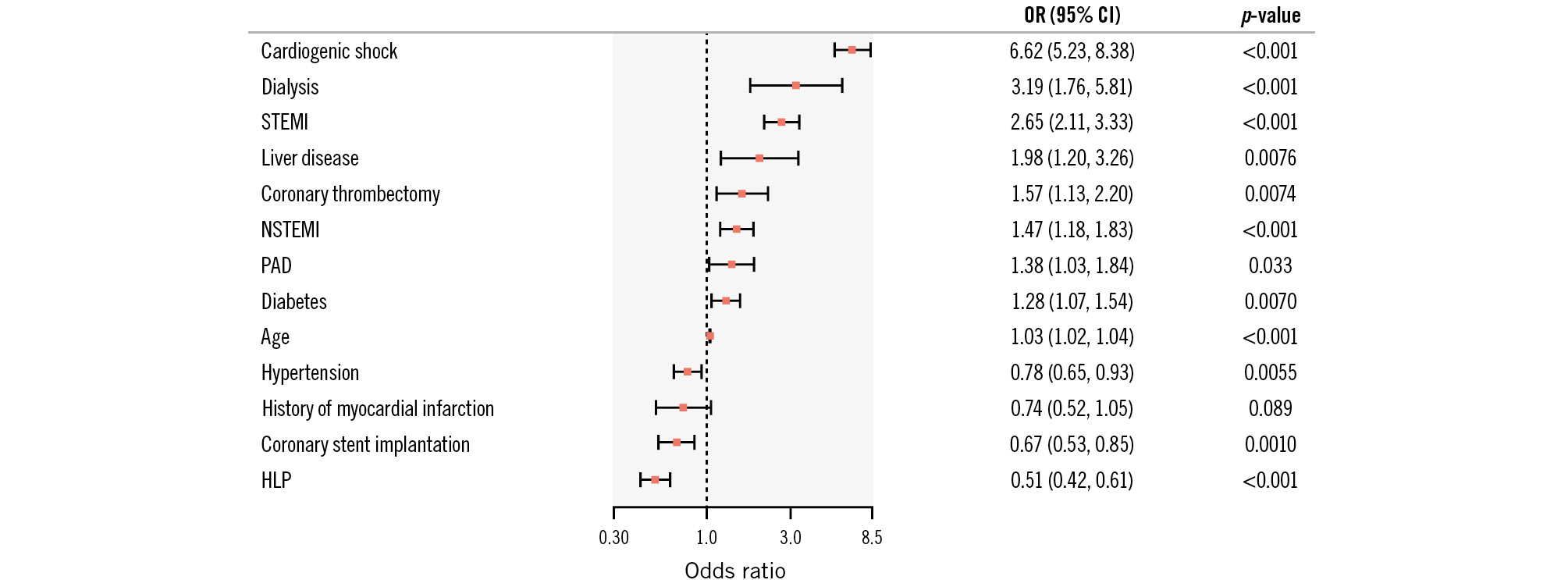
Figure 2. Variables associated with in-hospital mortality in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention with acute ischaemic stroke after multivariable stepwise regression analysis. Odds ratios (OR) and the 95% confidence interval (95% CI) are given. HLP: hyperlipoproteinaemia; NSTEMI: non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PAD: peripheral artery disease; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Discussion
In this nationwide cohort including nearly 5 million PCI procedures and spanning 16 years, we report the following main findings:
1) Whilst we noted an overall low rate of AIS events of 0.08%, an increase in the prevalence of AIS after PCI from 0.03% to 0.14% in the time period from 2006 to 2021 was documented.
2) We identified carotid artery disease, history of stroke, atrial fibrillation, clinical presentation with myocardial infarction and coronary thrombectomy amongst the strongest independently associated variables with stroke in individuals hospitalised for PCI.
3) When AIS occurred after PCI, it was associated with a significantly longer in-hospital stay and a nearly 6-fold increase in in-hospital all-cause mortality.
4) Also, we documented several variables which were associated with in-hospital mortality after AIS; amongst them were cardiogenic shock, dialysis and clinical presentation with either STEMI or NSTEMI as an indication for PCI.
Over the last decade, several registries have documented varying incidences of post-PCI AIS. The rate reported in our current analysis (0.08% peri-interventional AIS after PCI) is comparable to the 0.1% reported in the British Cardiovascular Intervention Society (BCIS) database, which represents the closest comparator to our cohort that is available in the literature with regard to the rates of AIS after PCI13. Other studies have reported higher rates of AIS, ranging from 0.6-1.6%89101112131415. This might be due to the different time frames investigated, as the most recent large-scale cohort only reports up to the year 2017.
We report a continuously increasing trend of PCI-associated AIS from 2006 to 2021, with the lowest rates of 0.03% from 2006-2008 and the highest rates of 0.14% documented in the most recent time period, from 2018-2021. This growing number of periprocedural AIS after PCI may be explained by a parallel increase in age, cardiovascular risk factors, temporally increased use of coronary thrombectomy devices, and NSTEMI presentation in our cohort10. Thus, during the recorded time frame, an increasingly elderly and comorbid population with an increasing burden of comorbidities and procedural complexity was documented, potentially leading to the increase in AIS for patients hospitalised for a PCI.
In the current dataset, a steady increase of AIS was noted from 2006-2020, with a sharp and substantial rise in AIS rates in 2021. One hypothesis which could, at least partially, explain this surprising finding might be the COVID-19 pandemic. For example, in a publication by Qureshi and colleagues, amongst 8,162 hospitalised COVID patients, a total of 1.3% suffered an AIS16. Of note, AIS occurred most commonly in the presence of other cardiovascular risk factors/comorbidities (hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia, atrial fibrillation, and congestive heart failure). Hence, as the investigated cohort represents a population with prevalent cardiovascular disease (i.e., CAD) and in whom a large proportion of patients display cardiovascular risk factors, the documented sharp increase could be attributable to this finding. Moreover, a COVID-19 infection has been described as a trigger for arterial thrombosis, including stroke, for up to 49 weeks after the initial diagnosis in a large-scale nationwide cohort analysis, which may have led to the steep increase of the AIS rate in 202117.
Due to the subsequent morbidity and mortality of AIS, interventional cardiologists should aim to prevent a periprocedural stroke at all times, and strategies have been recommended on how to accomplish this18. Multiple variables including carotid artery disease, medical history of stroke, atrial fibrillation, clinical presentation with myocardial infarction, and coronary thrombectomy were recognised to be associated with peri-interventional AIS. Some of these factors, such as coronary thrombectomy, emergent PCI, and carotid artery disease, are unsurprisingly associated with AIS and have been described before1011131920. Randomised controlled trials investigating coronary thrombectomy for emergent PCI in STEMI patients have also shown an excess stroke rate in individuals treated by thrombectomy2122. Moreover, this is underscored by our finding that coronary thrombectomy was independently associated with stroke after PCI, which corroborated previous data from the BCIS cohort and others1013. Interestingly, the rates of coronary thrombectomy decreased in our dataset after the above-named trial results, with regard to stroke incidence during routine coronary thrombectomy, were published, potentially due to a heightened awareness of operators regarding this specific complication. It must therefore be noted that the documented increase in AIS is not solely explainable via the utilisation of coronary thrombectomy devices. It is plausible that the increase in the burden of comorbidities as well as the complexity of interventional procedures may contribute to the increased rates of AIS.
Of note, some disease entities, such as HLP, obesity, chronic kidney disease and a prior myocardial infarction, were linked to a decreased risk of stroke in our analysis. However, in this patient population, secondary pharmacological preventive measures such as antiplatelet treatment and lipid-lowering medication are commonly implemented. Thus, one hypothesis could be that these individuals have a lower risk of AIS due to the standard preventive measures (e.g., due to statin-induced plaque stabilisation or the antithrombotic effects of antiplatelet medications) commonly prescribed in this population. However, no data with regard to medication were available for the current analysis. Also, stent implantation was similarly associated with a decreased risk for incident AIS. From an interventional viewpoint, the implantation of a stent can be viewed as a successful PCI, thus associated with successful lesion preparation and stent deployment, which could be correlated with a lower risk of AIS. Nevertheless, these findings warrant confirmation and exploration in subsequent studies, as they may be attributable to chance.
When AIS occurs, it is a debilitating complication for the affected individual. In our analysis, we demonstrate a significantly longer hospital stay (3-fold longer) and notably higher rates of in-hospital mortality (a nearly 6-fold increase) in individuals with AIS compared to those without. Recent large populations demonstrated an up to 10-fold increase in mortality, depending on the initial clinical indication for PCI (e.g., 23.5% mortality in STEMI patients with AIS, 9.5% in NSTEMI patients with AIS and 11.6% in patients with chronic coronary disease)10. Compared with non-PCI patients with an AIS undergoing best medical therapy, thrombolysis and/or mechanical thrombectomy, our reported mortality rates are comparable2324252627.
Of note, in our large-scale analysis, we describe variables that were independently associated with incident all-cause mortality in patients with AIS after PCI. In particular, the most strongly associated variables were cardiogenic shock, dialysis and clinical presentation with STEMI. This emphasises that, next to comorbidities, the initial clinical presentation for the PCI seems to influence outcomes in this vulnerable patient population. In contrast, previous data with regard to the predictors of early mortality after an ischaemic stroke identified clinical parameters − such as the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score, which was not available for the current analysis − as the most important variables associated with mortality27. Interestingly, a recent single-centre study of patients with an acute ischaemic stroke documented that cardiovascular complications (including acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, and cardiac arrest) had the strongest correlation with in-hospital mortality in female stroke patients28. Overall, the identification of cardiogenic shock and STEMI amongst the most relevant variables that correlated with mortality showcases that, for this vulnerable patient population, cardiovascular disease states like myocardial infarction have the most impact on these patients’ outcomes. Hence, in addition to the established treatment options for AIS, it is imperative to devise an optimised strategy for addressing cardiovascular comorbidities in order to enhance overall outcomes.
Limitations
Whilst the current study represents a nationwide analysis of AIS in hospitalised PCI patients, some limitations must be considered. Datasets were included in the current analysis based on standardised codes (both ICD-10-GM and OPS codes). However, the treating physician chose the utilised code based on clinical interpretation and available information, thus leading to a subjective confounding effect. Also, further baseline characteristics such as medications and vascular access site for PCI are not available for this dataset. Moreover, the precise temporal reconstruction of the in-hospital course (i.e., exact temporal association of PCI and AIS, including the differentiation of very early periprocedural or delayed AIS several days after PCI) is limited using ICD-10-GM and OPS codes. We aimed to account for this bias by only including patients who were initially admitted to an internal medicine or cardiology department. Nonetheless, residual confounding cannot be completely excluded, i.e., select patients might have undergone PCI after AIS. Also, the severity of stroke, affected cerebral territories, chosen treatment for AIS and other cerebrovascular accident entities, such as haemorrhagic stroke, were not available or were out of the scope of the current analysis and should be examined in future investigations. In addition, whilst in-hospital mortality is reported for all patients, further follow-up data, causes of death as well as other endpoints, including morbidity and quality of life, and data on AIS events in outpatient PCIs are not accessible. Lastly, since this analysis was based on federal data from Germany only, generalisability to other regions is limited.
Conclusions
AIS represents a debilitating and increasingly prevalent complication for patients hospitalised for PCI. In the current investigation, we describe this in a large-scale contemporary dataset including nearly 5 million PCIs from Germany over a timespan of 16 years. Moreover, we identify several variables associated with in-hospital mortality as well as AIS, which could enable clinicians to identify patients at risk for an adverse outcome and periprocedural ischaemic cerebral events after PCI, thereby facilitating tailored counselling of patients with specific risk profiles and predicting their likelihood for AIS after PCI. This might help to take measures aimed at the prevention of AIS and the subsequent morbidity and mortality in this vulnerable patient population.
Impact on daily practice
Acute ischaemic stroke (AIS) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a rare, but catastrophic, complication. In an analysis spanning 16 years, from 2006-2021, investigating 4.9 million PCI procedures, we describe an increasing trend in AIS after percutaneous revascularisation of coronary arteries. Moreover, we identified variables which were independently associated with AIS and in-hospital mortality, enabling clinicians to recognise patients at risk for an adverse in-hospital course after PCI and enabling personalised informed consent of patients with regard to their individual stroke risk.
Acknowledgements
Used RDC of the Federal Statistical Office and Statistical Offices of the Federal States, DOIs:10.21242/23141.2006.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2007.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2008.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2009.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2010.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2011.00.00. 1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2012.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2013.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2014.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2015.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2016.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2017.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2018.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2019.00.00.1.1.1; 10.21242/23141.2020.00.00.1.1.0; 10.21242/23141.2021.00.00.1.1.0, own calculations.
Funding
This study was funded by the University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg, Germany. B. Bay is supported by a grant from the German Heart Foundation (grant number S/06/23).
Conflict of interest statement
P.M. Becher received funding from the German Research Foundation; and received speaker fees from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim, all outside this submitted work. B. Schrage reports speaker fees from Abbott, Abiomed, and AstraZeneca; and research funding from Abiomed, the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung, and the German Research Foundation, outside of the submitted work. G. Thomalla reports honoraria as a consultant or lecturer from Acandis, Alexion, Amarin, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, and Stryker, all outside of the submitted work. S. Blankenberg received honoraria for lectures from Abbott, Abbott Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Amgen, Medtronic, Pfizer, Roche, Siemens Diagnostics, Siemens, and Thermo Fisher; and as a member of advisory boards and for consulting for Bayer, Novartis, and Thermo Fisher, outside of the submitted work. P. Clemmensen has previously or currently been involved in research contracts, consulting, speaker bureaus, or received research and educational grants from Abbott, Acarix AB, AstraZeneca, Aventis, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Evolva, Fibrex, Janssen, Merck, Myogen, Medtronic, Mitsubishi Pharma, The Medicines Company, Nycomed, Organon, Pfizer, Pharmacia, Regado, Sanofi, Searle, and Servier, all outside of the submitted work. F.J. Brunner reports grants from Daiichi Sankyo, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi; non-financial support from Abbott, Asahi Intecc, and Inari Medical; and personal fees from Amgen and Novartis, outside of the submitted work. C. Waldeyer reports lecture and consulting fees from Amgen, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi, and AstraZeneca, all outside of the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.Impact on daily practiceAcute ischaemic stroke (AIS) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a rare, but catastrophic, complication. In an analysis spanning 16 years, from 2006-2021, investigating 4.9 million PCI procedures, we describe an increasing trend in AIS after percutaneous revascularisation of coronary arteries. Moreover, we identified variables which were independently associated with AIS and in-hospital mortality, enabling clinicians to recognise patients at risk for an adverse in-hospital course after PCI and enabling personalised informed consent of patients with regard to their individual stroke risk.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

