An 88-year-old diabetic man was admitted for progressive angina. Four years before, he required a bare metal stent (BMS) implantation in a severely calcified lesion at the ostium of the right coronary artery. Six months later he presented severe focal in-stent restenosis (ISR) which was treated with a new BMS. Urgent coronary angiography showed recurrent ISR (Figure 1A). Optical coherence tomography (OCT) revealed the classic “stent-sandwich” image with two well-expanded stents (Figure 1B). The tissue causing ISR was highly heterogeneous, suggestive of neoatherosclerosis (Figure 1B). After pre-treatment with 600 mg of clopidogrel, aggressive lesion dilation was performed. Then, a bioresorbable vascular scaffold (BVS) (3.5×12 mm) was implanted and post-dilated with a 3.75 mm non-compliant balloon at 26 bar. OCT revealed good results but with some persistent areas of BVS underexpansion (Figure 1C).
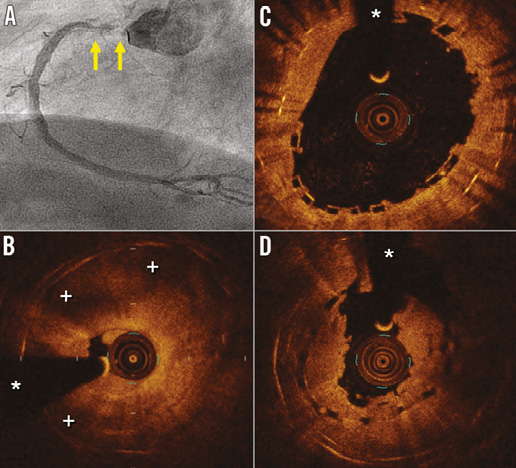
Figure 1. Angiographic and intravascular findings. A) Angiography showing recurrent severe in-stent restenosis of the proximal right coronary artery (arrows). B) Optical coherence tomography disclosing obstructive neoatherosclerosis with large lipidic areas (+). C) Optical coherence tomography image obtained immediately after BVS post-dilation. The black box appearance of the device is visualised over a double metal stent layer. D) Optical coherence tomography image at the time of BVS thrombosis. The obstructive thrombus is readily recognised but also a clear recoil of the BVS was detected (intra-scaffold minimal area: distal 5.3 mm2 [Δ=–1.5 mm2]; proximal 4 mm2 [Δ=–1.1 mm2]). (*) denotes wire artefact.
Thirty-six hours later, the patient experienced chest pain and the ECG revealed inferior ST-segment elevation. Angiography showed occlusion at the right coronary ostium. OCT disclosed a mixed thrombus obstructing the BVS (Figure 1D). Surprisingly, the BVS minimal lumen area was significantly reduced compared with results immediately after the procedure, demonstrating the occurrence of subacute BVS recoil (Moving image 1). Aggressive multiple balloon dilatations were performed and eventually a satisfactory final result was obtained.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
Moving image 1. BVS subacute thrombosis.

