
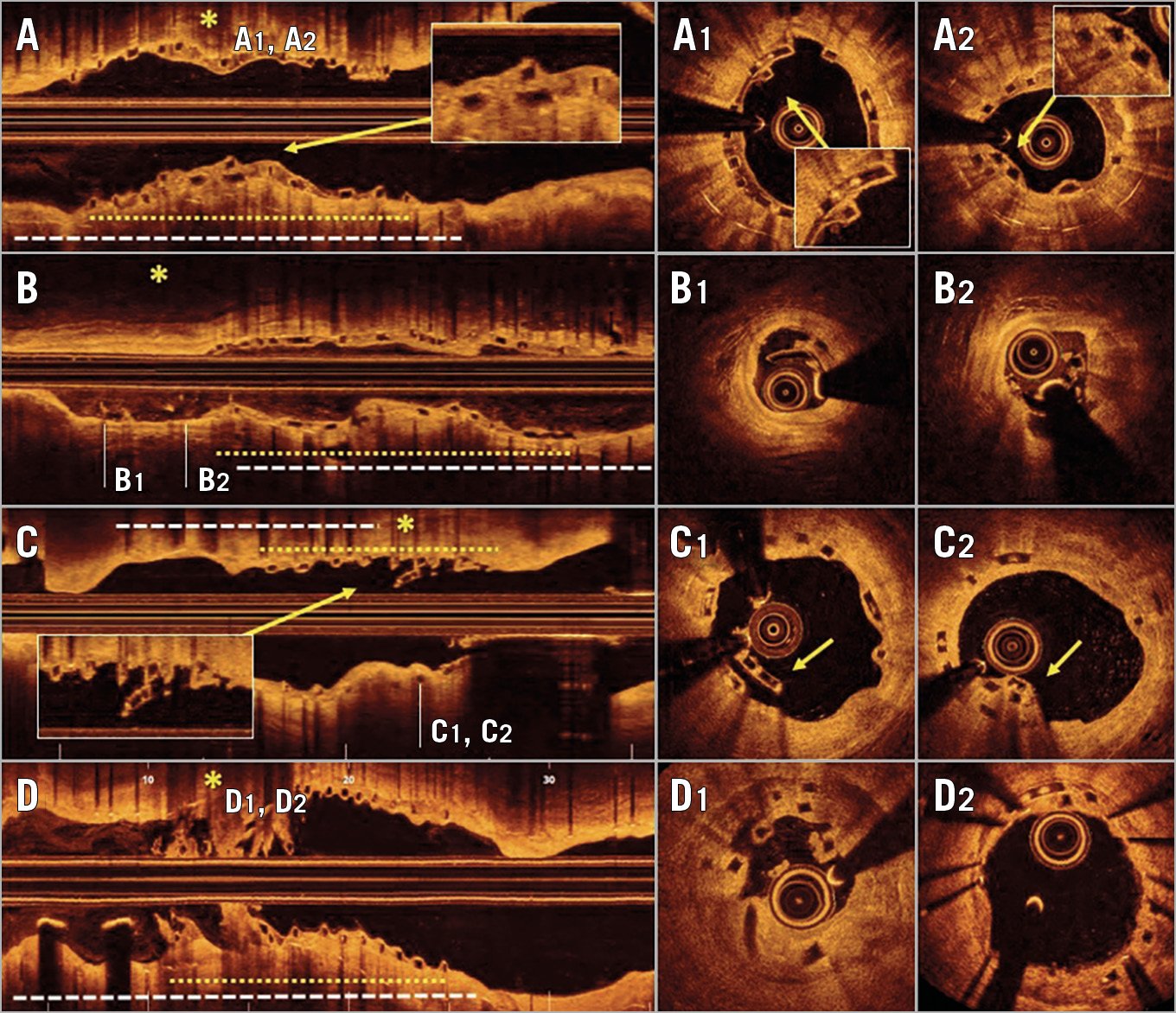
Figure 1. Optical coherence tomography images showing BVS dismantling. *: dismantling location; white dotted lines: metallic stent; yellow dotted lines: BVS.
Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) allow the treatment of coronary lesions by offering vascular support and antiproliferative drug release without the need to implant a permanent metal layer in the coronary vessel. A problem occasionally observed during follow-up is late fracture or late structural discontinuity1,2. Although severe BVS dismantling has been associated with an increased risk of late BVS thrombosis, the implications of this phenomenon still remain uncertain1,2. The use of BVS in patients with in-stent restenosis (ISR) has been demonstrated to be feasible, safe, and effective3. However, the implications of late BVS dismantling in patients treated for ISR currently remain unknown. We present the first series of patients presenting with late BVS fracture after treatment of ISR.
A) A 68-year-old man was admitted with ISR at the mid segment of the right coronary artery. A BVS was implanted (Supplementary Figure 1A),3. OCT follow-up, scheduled at six months, disclosed several areas with stacked struts (overlapping struts in close contact at the same angular sector) covered by neointimal tissue (Figure 1A, Figure 1A1, Figure 1A2).
B) A 72-year-old man who presented with ISR at a diagonal branch was treated with a BVS (Supplementary Figure 1B),3. Seven months later, OCT disclosed dismantling with structural disruption at the distal portion of the BVS (Figure 1B). In some cross-sections, isolated struts hanging at the centre of the lumen, with loss of circularity of the scaffold and without any contact with the vessel wall, were detected (Figure 1B, Figure 1B1, Figure 1B2).
C) A 61-year-old woman was admitted with ISR in the proximal right coronary artery that was treated with a BVS (Supplementary Figure 1C),3. One month later, the patient suffered a subacute thrombosis of a drug-eluting stent previously implanted in the posterior descending coronary artery. During the procedure, OCT revealed that the proximal BVS had a late fracture consisting of two rows of overhanging struts, not overlapping on each other, without contact with the vessel wall (Figure 1C, Figure 1C1). A conservative management of this segment was decided. After eight months, OCT revealed that the area previously showing BVS dismantling was fully covered by neointimal tissue (Figure 1C, Figure 1C2).
D) A 70-year-old man who presented with severe ISR in the right coronary artery was treated with a BVS (Supplementary Figure 1D). Seventeen months later, he was admitted with angina. OCT revealed images showing severe collapse and dismantling of BVS with associated intraluminal thrombus (Figure 1D, Figure 1D1). An everolimus-eluting stent was implanted with excellent results (Figure 1D, Figure 1D2).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

