Vascular access site complications account for the majority of bleeding complications after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) and are associated with increased morbidity and mortality1. The marked decrease in vascular access site complications over recent years reflects a combination of accurate preprocedural computed tomographic mapping of the iliofemoral axis, refined technology of delivery catheters and vascular closure devices (VCD), sophisticated puncture techniques, and reliable bailout strategies built on the collective experience of the interventional community2.
We are in a process of streamlining, optimising and economising TAVI. Therefore, a systematic and versatile algorithm for large-bore vascular access closure that integrates a cascade of safety nets is of interest. The level of complexity of large-bore vascular access and closure is minimised by being broken down into individual steps amenable to standardisation (Figure 1). Procedural planning anticipates the risk of complications, without having one’s back against the wall. Computed tomography angiographic mapping of the access route considers the distance from the puncture site to the vessel wall, vessel diameter, tortuosity, distribution of calcifications, and the location of the femoral bifurcation relative to the head of the femur3. The contingency plan is not limited to the primary access route but also extends to the choice of the second (radial versus femoral ipsi-/contralateral) access route, allowing for a straightforward bailout intervention.
Vascular closure starts with the vessel puncture technique. An ultrasound-guided central vessel puncture at a 45-degree access angle provides the best starting point for successful VCD deployment. The use of micropuncture kits, featuring a particularly small needle, minimises trauma to surrounding tissues and is forgiving in the case of an inadvertent puncture at a suboptimal spot4. The puncture channel may be surgically prepared in patients with excessive fibrotic or scar tissue, in order to facilitate unhindered tightening of the suture knots. The choice of wire stiffness commensurate to the tortuosity of the vessel facilitates the advancement of the sheath. Smaller delivery catheters mitigate complications in standard anatomies, while pushing the boundaries of feasibility in patients with complex transfemoral access. At the same time, the diversification and maturation of alternative access routes has further refined the selection of suitable anatomies for a transfemoral arterial approach. The adverse effects of vascular access site complications are mediated by bleeding. The type, timing and dosage of periprocedural antithrombotic treatment (and the potential administration of protamine) may have implications on bleeding in patients with vascular complications. A multistep closure technique facilitates the early detection of vascular complications, providing the possibility of a timely intervention. Conceptually, suture-based and plug-based VCD are used in series rather than as alternatives to one another. Both types of VCD are challenging to deploy in severely calcified vessels, with a risk of incomplete apposition of the arteriotomy wall segments, needle failure, or suture tear. Hoping for the best and preparing for the worst-case scenario constitutes an appropriate attitude for vascular closure. Confidence in the practice of vascular preclosure may be negatively affected if we are unprepared. Bailout strategies in the event of bleeding include antegrade or retrograde covered stenting, depending on the tortuosity of the iliofemoral axis. Alternatively, balloon occlusion can halt the haemorrhage in preparation for surgical revision as a last resort.
In the present issue of EuroIntervention, Rosseel and colleagues present the findings from the MultiCLOSE observational study, which investigated the safety and efficacy of a stepwise algorithm for large-bore femoral artery access closure after TAVI5. The algorithm includes a cascade of safety nets such as ultrasound-guided arterial puncture, fluoroscopic documentation of the needle position at the arteriotomy site, leaving a 0.035-inch guidewire in situ after removal of the large-bore sheath, and insertion of a 6 Fr or 8 Fr sheath for ipsilateral angiographic control, followed by definite closure using a plug-based VCD in the majority of patients. In the MultiCLOSE study, only 4 out of 630 patients from 3 centres (0.6%) experienced a VARC-3 major vascular complication, and 14 patients had a minor vascular complication5.
In addition to its proven effectiveness, the MultiCLOSE algorithm5 is convincing because of its simplicity, time efficiency, and resourceful use of routinely used material. The utility of a structured approach to vascular access site management in TAVI may even be accentuated in more challenging anatomies that were excluded from the current study. Standardisation forms the basis of safe applicability and rapid adoption of TAVI across different settings. The systematic troubleshooting of vascular closure difficulties characterises resourceful TAVI programmes and translates into excellent clinical outcomes.
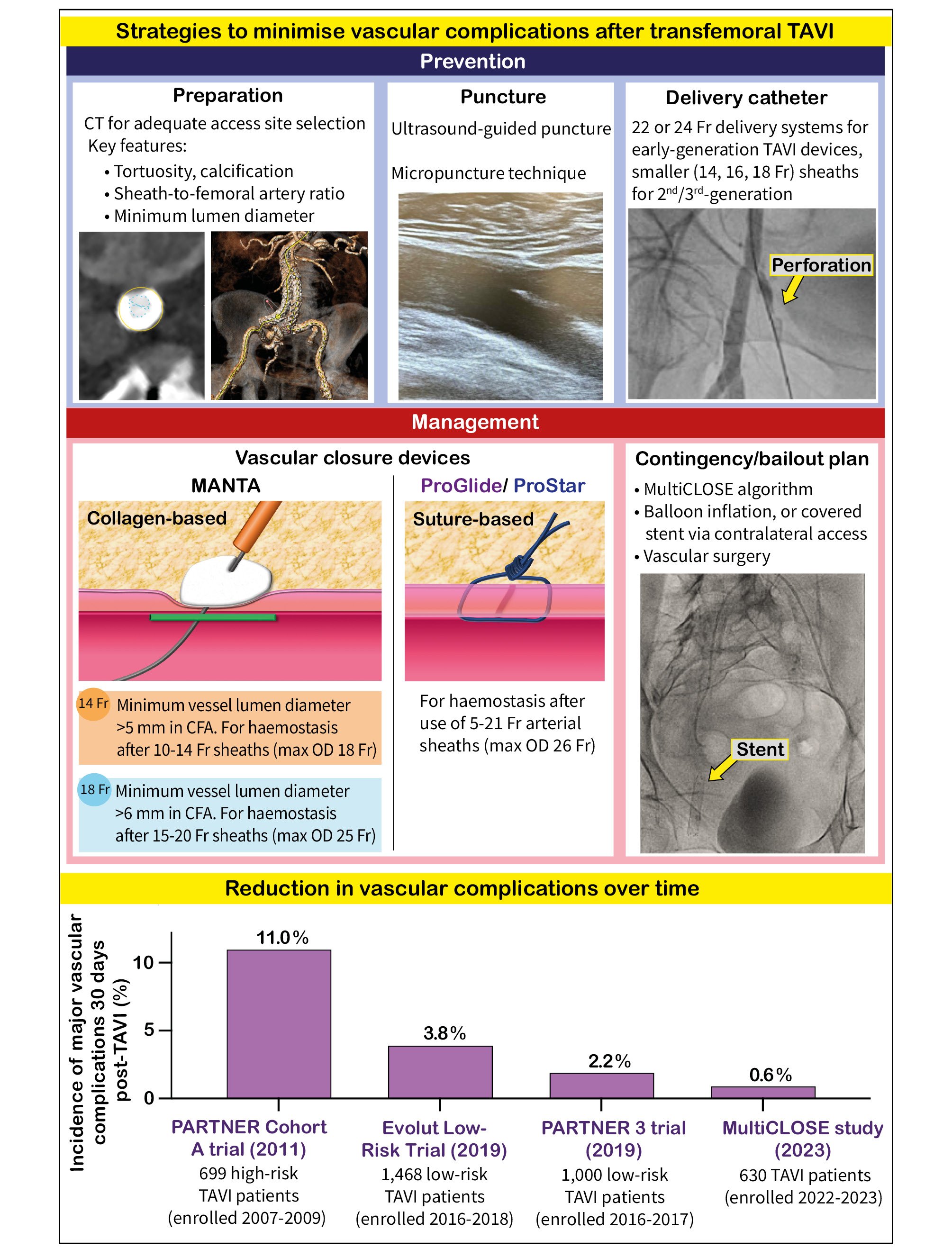
Figure 1. Strategies to reduce vascular access site complications after TAVI and data showing the reduction in vascular complications over time. CFA: common femoral artery; CT: computed tomography; max: maximum; OD: outer diameter; PARTNER: Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valves; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Conflict of interest statement
T. Pilgrim reports research, travel or educational grants to the institution without personal remuneration from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, and ATsens; and speaker fees and consultancy fees to the institution from Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott, Medtronic, Biosensors, and Highlife. A. Maznyczka is an EAPCI international structural fellow; her fellowship is funded by Edwards Lifesciences through EAPCI and not directly from Edwards Lifesciences.

