A 70-year-old male underwent transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve implantation using a 26 mm SAPIEN XT valve (Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA, USA). He received aspirin (100 mg/day) indefinitely and clopidogrel (75 mg/day) for one month. At six-month follow-up, the patient presented with recurrent symptoms of heart failure and angina. The echocardiogram depicted a severe transcatheter prosthesis stenosis, with a mean gradient of 48 mmHg. Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) showed thickened leaflets along with low-density images, suggestive of thrombus (Figure1A, Figure1B, Moving image 1, Moving image 2). Two-dimensional (2D) transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) also revealed echogenic images suggestive of thrombus surrounding the leaflets, which were more evident by 3D TEE (Online Figure 1A, Online Figure 1B, Moving image 3). Oral anticoagulation with coumadin was initiated and dual antiplatelet therapy was restarted. Three months later, repeat MDCT (Figure 1C, Figure 1D, Moving image 4, Moving image 5) and 2D and 3D TEE (Online Figure 1C, Online Figure 1D, Moving image 6) showed normal appearance of the prosthesis, with thin leaflets and a mean gradient of 6 mmHg. Lifelong anticoagulation was recommended.
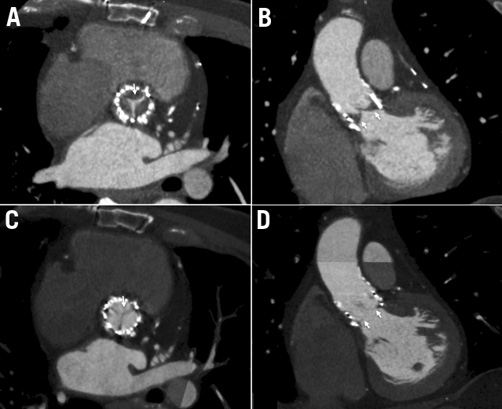
Figure 1. Axial (A) and coronal (B) MDCT planes showing thickened leaflets with low-density images suggestive of thrombus (arrows). At follow-up, normal appearance of the prosthesis, with thin leaflets (C & D).
Conflict of interest statement
F. S. de Brito Jr and M. Perin receive honoraria for speeches and proctoring from Medtronic and Edwards Lifesciences. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Online data supplement
Online Figure 1. Baseline 2D TEE (longitudinal and transversal planes) showing echogenic images suggestive of thrombus (arrows) inside the prosthesis (A). The thrombus image (arrow) became more evident by 3D TEE (B). Follow-up 2D (C) and 3D (D) TEE demonstrating disappearance of thrombus inside the prosthesis.
Moving image 1. Axial MDCT plane showing thickened leaflets with low-density images suggestive of thrombus.
Moving image 2. Coronal MDCT plane showing thickened leaflets with low-density images suggestive of thrombus.
Moving image 3. Baseline 2D TEE (longitudinal and transversal planes) showing echogenic images suggestive of thrombus inside the prosthesis.
Moving image 4. Axial MDCT plane showing normal appearance of the prosthesis at follow-up, with thin leaflets and absence of low-density images.
Moving image 5. Coronal MDCT plane showing normal appearance of the prosthesis at follow-up, with thin leaflets and absence of low-density images.
Moving image 6. Follow-up 2D TEE (longitudinal and transversal planes) demonstrating disappearance of thrombus inside the prosthesis.
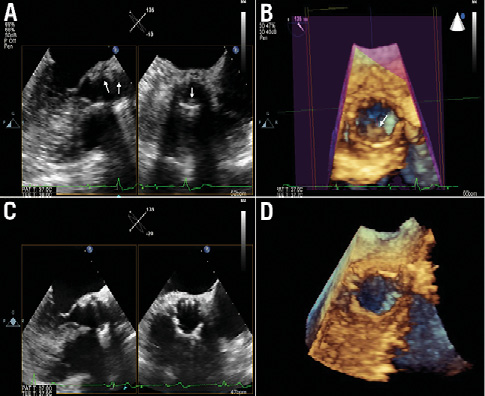
Online Figure 1. Baseline 2D TEE (longitudinal and transversal planes) showing echogenic images suggestive of thrombus (arrows) inside the prosthesis (A). The thrombus image (arrow) became more evident by 3D TEE (B). Follow-up 2D (C) and 3D (D) TEE demonstrating disappearance of thrombus inside the prosthesis.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1.
Moving image 2.
Moving image 3.
Moving image 4.
Moving image 5.
Moving image 6.

