
Abstract
Aims: Significant platelet activation after long stented coronary segments has been associated with periprocedural microvascular impairment and myonecrosis. In long lesions treated either with an everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold (BVS) or an everolimus-eluting stent (EES), we aimed to investigate (a) procedure-related microvascular impairment, and (b) the relationship of platelet activation with microvascular function and related myonecrosis.
Methods and results: Patients (n=66) undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in long lesions were randomised 1:1 to either BVS or EES. The primary endpoint was the difference between groups in changes of pressure-derived corrected index of microvascular resistance (cIMR) after PCI. Periprocedural myonecrosis was assessed by high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT), platelet reactivity by high-sensitivity adenosine diphosphate (hs-ADP)-induced platelet reactivity with the Multiplate Analyzer. Post-dilatation was more frequent in the BVS group, with consequent longer procedure time. A significant difference was observed between the two groups in the primary endpoint of ΔcIMR (p=0.04). hs-ADP was not different between the groups at different time points. hs-cTnT significantly increased after PCI, without difference between the groups.
Conclusions: In long lesions, BVS implantation is associated with significant acute reduction in IMR as compared with EES, with no significant interaction with platelet reactivity or periprocedural myonecrosis.
Introduction
Platelet activation significantly increases during the implantation of long coronary stents despite dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT)1. This is proportional to the extent of vascular damage induced by the coronary intervention and to the length of the stent, translating into periprocedural myocardial infarction (PMI)2. The stiffness of the metallic drug-eluting stent (DES) might in fact result in a distortion at the stented segment and an increased compliance at the contiguous segments (compliance mismatch)3. The latter has been associated with ring vortices at the inflow of the stent and rapid variations of wall shear stress that might potentially induce platelet activation and thrombus formation4,5.
Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) were developed to overcome the shortcomings of DES, providing transient scaffolding and local drug delivery, with potential restoration of vasomotion, cyclic strain, and shear stress6,7,8. In addition, BVS are less stiff than metallic stents9, and are not associated with increased compliance at the inflow segment, but rather with a decreased compliance at the outflow segment, resulting in lower compliance mismatch10. However, the higher scaffold thrombosis rate has tempered the initial enthusiasm for BVS11,12,13. It is not yet clear what the impact of BVS on microvascular function might be, especially in relation to platelet inhibition during and after PCI. Given the inherent flexibility, we hypothesised that the Absorb™ BVS (Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) might be associated with less platelet activation, thrombus formation and downstream microvascular impairment as compared with the XIENCE metallic EES (Abbott Vascular) in stable patients undergoing PCI of long coronary stenoses.
Methods
The PROcedure-related microvascular ACTIVation in long lEsions treated with bioresorbable vascular scaffold versus everolimus-eluting stent implantation (PROACTIVE) study was a prospective, randomised (1:1), open-label, superiority controlled trial (Figure 1) carried out at the Cardiovascular Research Center Aalst, OLV Hospital, Aalst, Belgium, between December 2013 and March 2017.
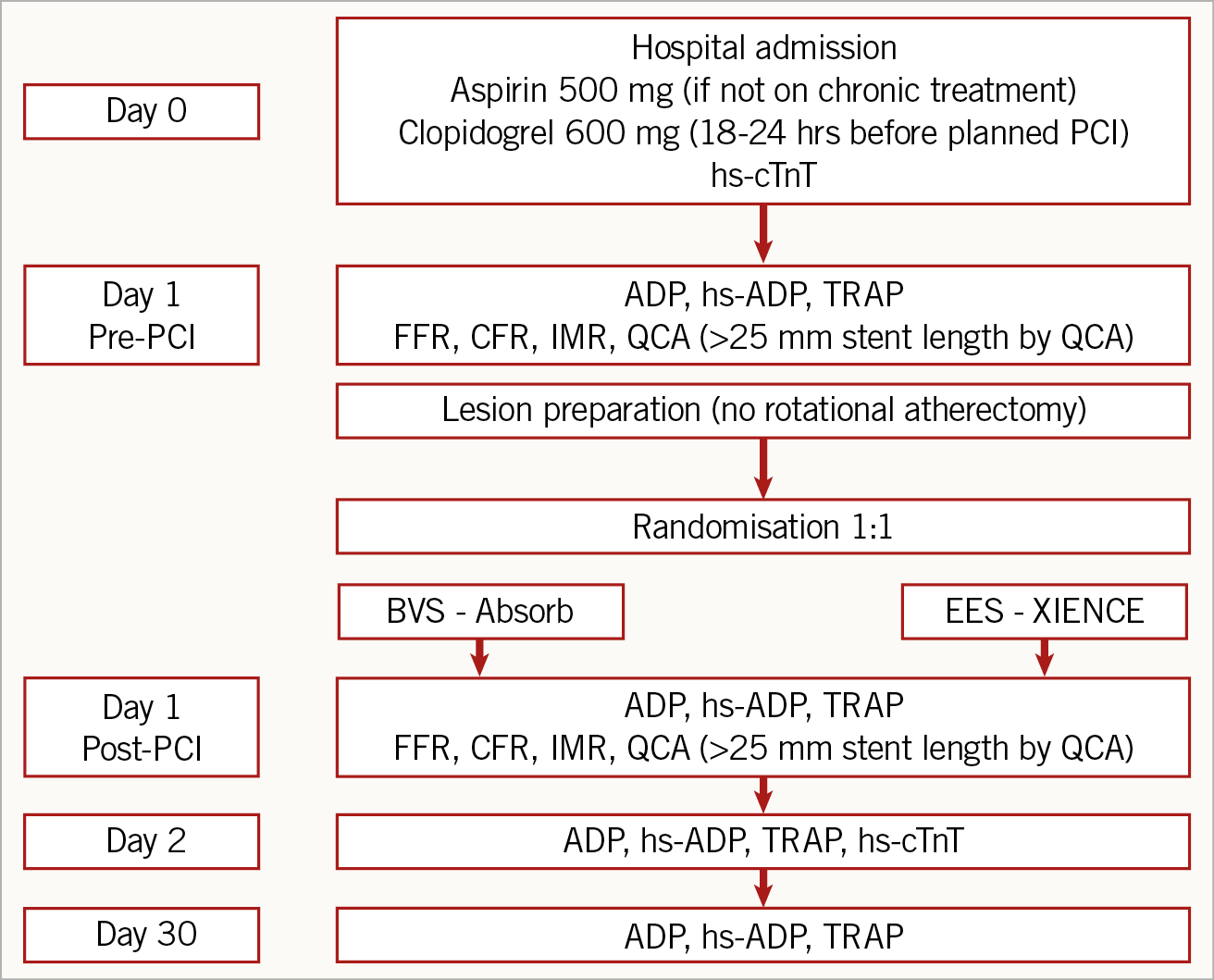
Figure 1. Study design. ADP: adenosine diphosphate; BVS: bioresorbable vascular scaffold; CFR: coronary flow reserve; EES: everolimus-eluting stent; FFR: fractional flow reserve; hs-ADP: high-sensitivity adenosine diphosphate; hs-cTnT: high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; IMR: index of microvascular resistance; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; TRAP: thrombin receptor-activated peptide
PATIENT POPULATION
We enrolled patients with stable coronary artery disease and long lesions (i.e., lesions to be treated with a stent ≥25 mm long) (Figure 1). The study protocol (Figure 1, Supplementary Appendix 1) was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee and all patients gave written informed consent for participation and data collection. Exclusion criteria are reported in Supplementary Appendix 1.
PLATELET FUNCTION ANALYSIS AND CORONARY PHYSIOLOGY INDICES
Details on platelet function analysis and coronary physiology indices can be found in Supplementary Appendix 1.
STUDY ENDPOINTS
The primary endpoint of the PROACTIVE trial was the difference in the Δ corrected index of microvascular resistance (cIMR post-PCI – pre-PCI) between the two groups. Secondary endpoints were: a) immediate periprocedural (post-PCI – pre-PCI) variations in platelet reactivity assessed by hs-ADP; b) periprocedural myonecrosis as assessed by hs-cTnT at 24 hours between the two groups; c) changes at 30-day follow-up in hs-ADP between the two groups.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous variables are expressed as mean±SD or as median (interquartile range), as appropriate. Categorical variables are reported as frequencies and percentages. Normal distribution was evaluated with the Shapiro-Wilk test. Comparisons between continuous variables were performed using the Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney test. Repeated measurements on a single sample for platelet reactivity assessment were performed with the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Repeated measures two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess the effect interaction between treatment and time on continuous variables. Comparisons between categorical variables were evaluated using Fisher’s exact test or the Pearson chi-square test, as appropriate. Correlations between continuous variables were assessed using the Pearson correlation test. A sample size of 33 patients randomised per group was calculated to demonstrate the statistically significant superiority of the Absorb BVS versus the XIENCE EES in terms of post-PCI versus pre-PCI changes in cIMR. A power of 90% was estimated in order to detect a difference in means of 8.280 assuming a common standard deviation of 10.000, using a two-group t-test with a 0.025 one-sided significance level. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 6.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) and SPSS, Version 23.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) and p-values <0.05 (two-tailed) were considered significant.
Results
CLINICAL AND ANGIOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS
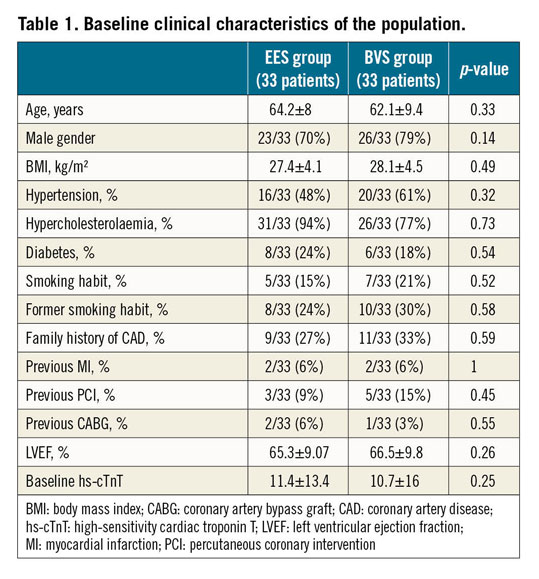
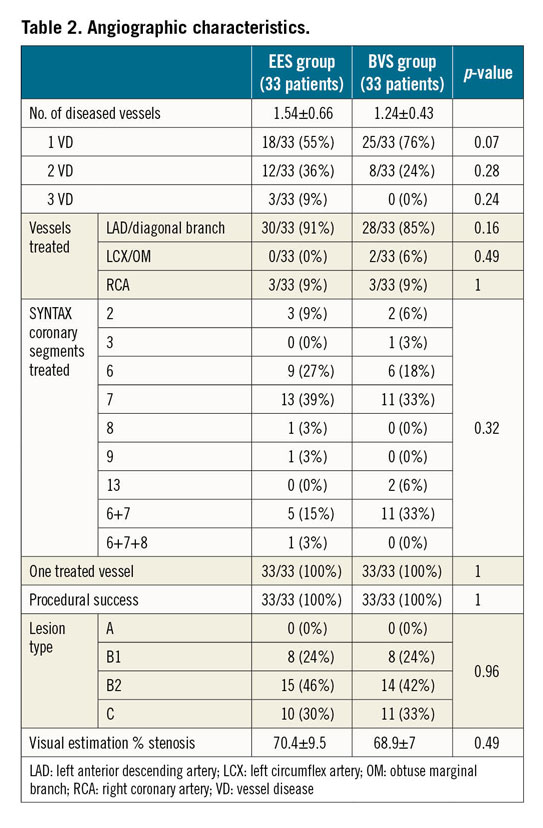
A total of 66 patients were enrolled in this trial, 33 randomised to the Absorb BVS, and 33 to the XIENCE Xpedition® or XIENCE Alpine™ EES (both Abbott Vascular). Baseline clinical characteristics were not different between the groups (Table 1). No in-hospital major adverse events occurred. No differences between the two groups in number of diseased vessels, vessels and SYNTAX segments treated as well as complexity of the lesions defined according to the ACC/AHA classification were observed (Table 2). Only one vessel per patient was treated and procedural success was reached in 100% of the patients.
PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS
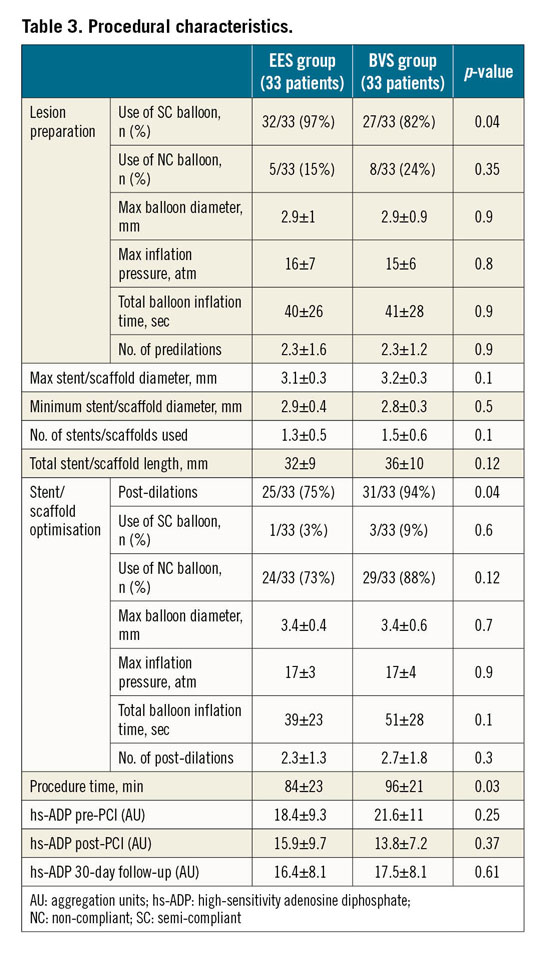
Procedural characteristics are shown in Table 3. Semi-compliant balloons were more frequent in patients treated with EES, although there were no differences between the groups in terms of lesion preparation, maximum and minimum stent/scaffold diameter, number of stents/scaffolds implanted per patient and total stent/scaffold length. As per protocol, post-dilatation was more frequent in patients treated with BVS, with longer procedure time. However, no differences between the two groups were observed regarding the use of semi-compliant and non-compliant balloons, maximal diameter balloons, maximal pressure and total balloon inflation times. Occlusion of small side branches (<2 mm) was evenly distributed in the two groups (7/33 in the BVS group versus 7/33 in the XIENCE EES group, p=1).
HAEMODYNAMIC CHARACTERISTICS AND CORONARY PHYSIOLOGY ASSESSMENTS
A significant difference in heart rate was observed between the two groups both pre and post PCI. No significant between-group differences were observed in fractional flow reserve (FFR), coronary flow reserve (CFR) and cIMR both before and after PCI (Table 4). However, a significant difference in cIMR was observed within the BVS group after PCI versus baseline (19±8 vs 24±12, p=0.04), but not in the EES group (21±9 vs 21±13, p=0.84) (Figure 2). A significant difference in the primary endpoint of ΔcIMR was observed between the two groups (EES group -0.3±13.6 vs BVS group –4.7±13.2; p=0.04) (Figure 3).
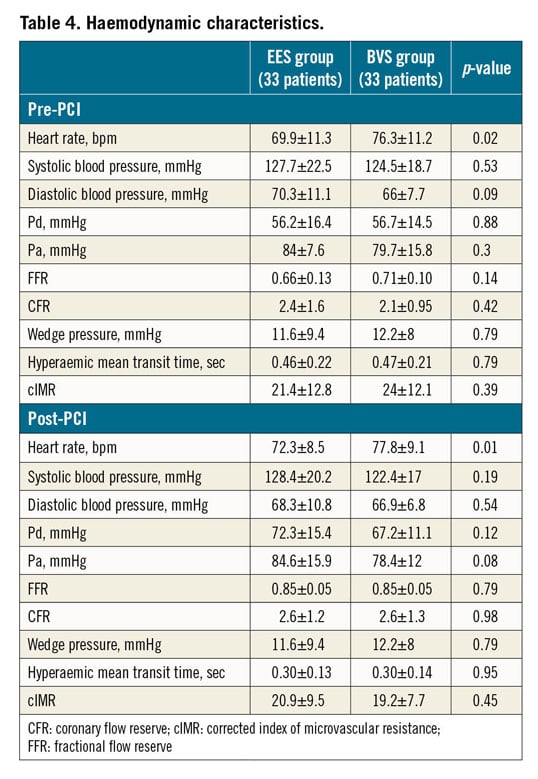
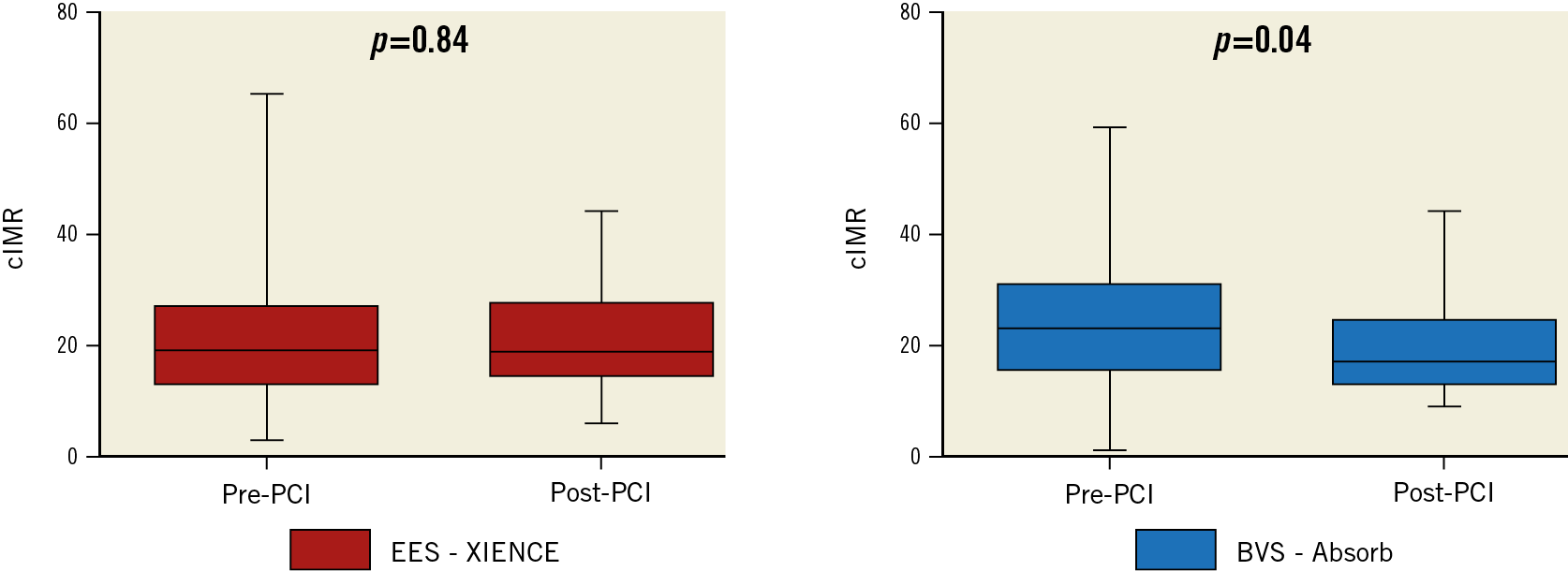
Figure 2. Changes in cIMR after PCI in the two groups. Left panel: patients treated with the XIENCE EES; right panel: patients treated with the Absorb BVS. cIMR: corrected index of microvascular resistance
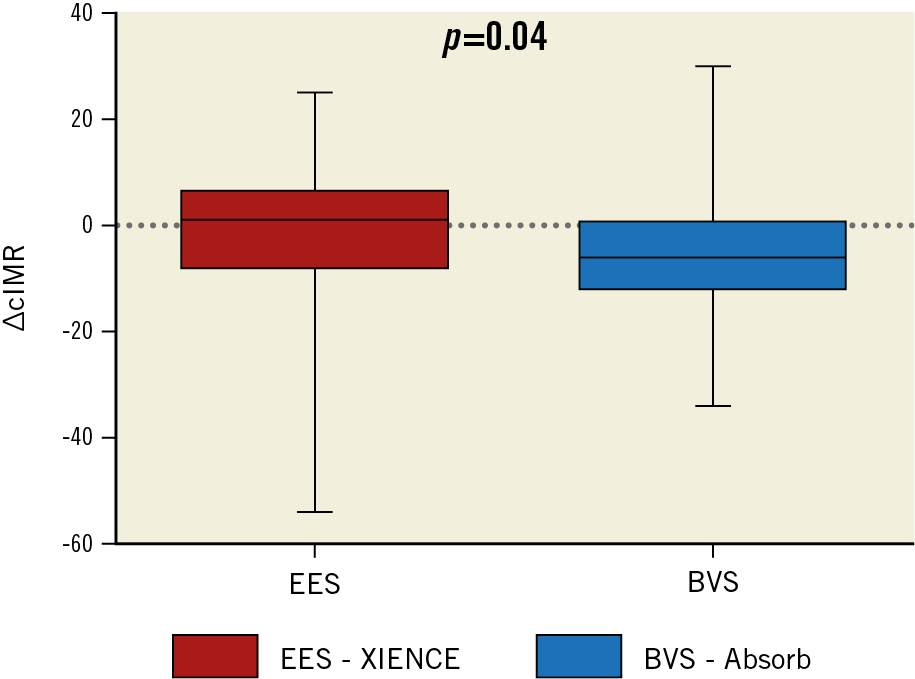
Figure 3. Difference between the two groups in ΔcIMR. Significant difference between the two groups in the primary endpoint, in favour of the BVS group. ΔcIMR: delta corrected index of microvascular resistance
PLATELET FUNCTION ANALYSIS AND PERIPROCEDURAL MYONECROSIS
Platelet function metrics were not different between the two groups at the different time points (Table 3, Supplementary Appendix 2). Likewise, myocardial biomarkers and periprocedural myonecrosis were not different between the two groups (Table 1, Figure 4, Supplementary Appendix 2).
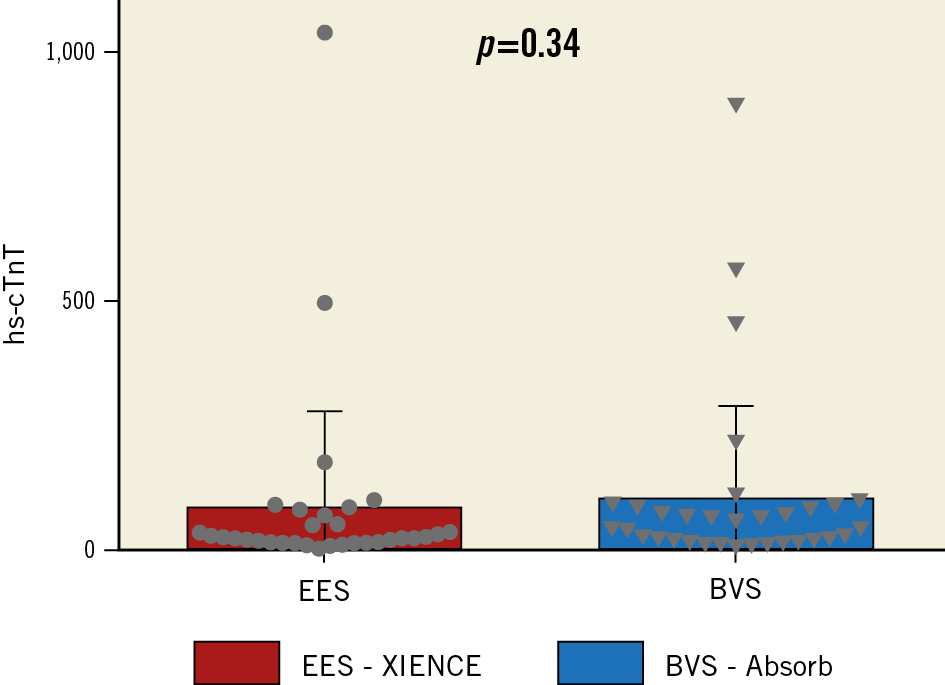
Figure 4. Difference in hs-cTnT post PCI between the two groups. Significant increase of hs-cTnT after PCI, without difference between the two groups. hs-cTnT: high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T
Discussion
In the PROACTIVE trial we found a significant reduction of cIMR after PCI in the BVS group but not in the EES group (p=0,04), therefore meeting the primary endpoint of significant between-group difference in ΔcIMR, in favour of the BVS group. In addition, we observed a significant platelet reactivity reduction after PCI with both EES and BVS implantation, without differences between the two groups at baseline, post PCI and at 30-day follow-up. Also, no difference in platelet reactivity over time up to 30-day follow-up was detected. Last, periprocedural myonecrosis after PCI of long coronary lesions was important with both BVS and EES, without significant variations in terms of ∆hs-cTnT between the two groups.
In designing the PROACTIVE trial, the assumption was made that metallic DES are associated with an increased compliance at the two contiguous segments of the stent implanted, generating a compliance mismatch. This translates into important ring vortices at the inflow of the stent and rapid variations of wall shear stress that might potentially induce platelet activation and thrombus formation10. The significant reduction of cIMR after BVS implantation, while it confirms previous findings14, might seem at odds with the available data in the literature suggesting increased thrombogenicity. To achieve a similar radial strength to that of an 80 µm metallic stent, the PLLA backbone of the 150 µm everolimus-eluting BVS is designed to have both thicker and wider struts7,9. On the one hand this translates into a significantly increased surface of contact between the BVS and vessel wall compared to second- and third-generation DES15,16,17, but on the other hand the increased strut thickness and width have been associated with more thrombogenicity in animal models18, also explaining the increased thrombogenicity of BVS in comparison with EES12,19.
How does one reconcile our findings with this evidence? We can speculate that the lower microvascular impairment after BVS implantation might be explained by the following. 1) As compared with EES implantation, the scaffold deployment is associated with a greater retention of atherothrombotic debris from the coronary plaques, preventing their embolisation distally in the microcirculation. 2) The potentially increased thrombogenicity of BVS is compensated for by a lower compliance mismatch, with a final neutral impact on the microvasculature. BVS implantation is not associated with an increase in compliance at the inflow segment, but conversely tended to decrease compliance at the outflow segment, therefore resulting in a potentially lower degree of compliance mismatch10. 3) The more accurate and prolonged vessel preparation and BVS optimisation with multiple balloon inflations might have resulted in a preconditioning of the microvasculature, possibly preventing an increase in resistance of the microcirculation20.
Our results are corroborated by recent data obtained in 60 patients randomised to either Absorb BVS or XIENCE PRIME® DES implantation where myocardial blood flow (MBF) and CFR over three years were assessed non-invasively by positron emission tomography (PET) perfusion imaging. No differences in PET-derived absolute myocardial perfusion were observed between the BVS and DES groups at one-month follow-up21, suggesting that BVS implantation is safe without major consequences in the short term with regard to myocardial perfusion. Similarly, in our trial the scaffold implantation did not affect the microcirculation. Although the initial one-year lower angina rates with BVS implantation of the ABSORB II trial22 were not confirmed in the ABSORB III trial, we can hypothesise that our findings of missing microvascular resistance increase after PCI with BVS might contribute to an improvement of angina-related symptoms, as observed in the ABSORB IV trial23. The significant reduction in platelet reactivity with both BVS and EES is another interesting finding of the PROACTIVE trial. The significant reduction of hs-ADP in both groups, in fact, without differences at baseline, post PCI and 30-day follow-up, confirm the results of previous studies supporting the notion that, in patients with adequate response to DAPT, the thrombogenicity of the Absorb BVS is not affected by on-treatment platelet reactivity but is mainly due to a suboptimal vessel sizing and procedural technique at the time of its implantation24,25.
Finally, the periprocedural myonecrosis was notable in both groups, as expected by the complexity of PCI of long lesions, without significant difference in terms of ∆hs-cTnT between the EES and BVS groups. As is known, the most common mechanisms of myocardial injury during PCI are distal embolisation and side branch occlusion26. In our trial, the discrepancy between the reduction of cIMR and the significant increase of hs-cTnT after BVS implantation could be explained by the fact that, although BVS implantation is associated with a high retention of atherothrombotic debris, because of thicker, wider struts as compared with DES, it is also related to an important rate of small side branch occlusion. Our results are in line with a post hoc analysis of the ABSORB II trial, where no differences in the incidence of cardiac biomarker rise and PMI were found between the two groups27.
Limitations
First, enrolment in the PROACTIVE trial was restricted to patients with long lesions. Our findings may not be generalisable to patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and more complex disease. Second, patients enrolled in the PROACTIVE trial were all treated with clopidogrel. Therefore, we cannot conclude that the same impact of Absorb BVS implantation on microcirculation, platelet reactivity and periprocedural myonecrosis can be obtained in patients treated with more potent P2Y12 inhibitors. Third, our trial was not powered for clinical endpoints. Fourth, heart rate was significantly higher in patients randomised to BVS as compared with EES. Nevertheless, this latter finding has no impact on our results considering that one of the advantages of the IMR is that it is obtained by measuring the mean transit time and the distal coronary pressure during minimal and stable microvascular resistance (i.e., during stable hyperaemia with IV adenosine infusion). In this condition, IMR has previously been shown to be independent from heart rate. Fifth, in the BVS group, procedure time was significantly higher as compared with the DES group. Transient early dynamic changes possibly occurring during PCI in the microcirculation might therefore not have been detected. Sixth, plaque features of coronary stenosis (e.g., plaque burden and minimal lumen area) as assessed by intravascular imaging have been demonstrated to be independently associated with FFR28. In our patients, we did not perform intravascular imaging and are not able to provide any further insight on the possible association between plaque features and IMR findings.
Conclusions
In long lesions, BVS implantation is associated with a significant reduction in cIMR as compared with EES. The limited acute impact of BVS on the microcirculation effect is associated with an optimal periprocedural and short-term platelet inhibition, without significant difference in periprocedural myonecrosis as compared with patients treated with EES.
|
Impact on daily practice The first generation of the Absorb BVS did not live up to its promise because of higher events due to greater scaffold thrombosis. However, we found a limited acute impact of BVS on the microcirculation, with lower periprocedural and short-term platelet inhibition. While refinements are warranted in the upcoming generations of the Absorb BVS in terms of reduction of the strut profile and vessel wall coverage area, our findings are reassuring on the acute impact of these devices on the microcirculation, suggesting that changes in the antiplatelet regimen of patients undergoing BVS are not needed. |
Funding
The Cardiovascular Research Center Aalst received an unrestricted grant from Abbott Vascular.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Pellicano has been supported by a research grant provided by the CardioPath PhD program. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

