The optimal treatment of coronary lesions affecting circumflex (CX) or left anterior descending (LAD) ostia remains a subject of debate, as stent implantation is associated with competing risks of inadequate plaque coverage and excessive stent protrusion into the left main (LM)1.
We show an example of ostial CX stent implantation in a 54-year-old male patient presenting with acute coronary syndrome (Figure 1A, Figure 1B, Moving image 1A, Moving image 1B). After 1 year, the patient presented with chest pain. Regional wall motion abnormalities were reported on a stress echocardiogram, mainly of the septum and of the lateral wall of the left ventricle. Subsequent angiography showed a hazy stenosis at the level of the ostial LAD (Figure 1C, Moving image 2), which corresponded to tissue-covered stent struts protruding from the CX on optical coherence tomography (OCT) (Figure 1D, Moving image 3). A wire was passed into the LAD, and its position outside of the protruding CX stent strut contour was confirmed by OCT (Figure 1E), which allowed for the successful execution of the steps of double kissing crush (Figure 1F) to correct the initially unrecognised stent protrusion (Figure 1G, Figure 1H, Figure 1I). After careful CX rewiring, which can be challenging through the crushed tissue-covered struts, and the first kissing balloon inflation (KBI), a stent was implanted from the ostial LM into the proximal LAD, followed by proximal optimisation. Finally, a sequential high-pressure KBI was performed to optimise the result in both ostia and to centralise the tissue-covered metallic neocarina (Figure 1J, Figure 1K, Figure 1L, Moving image 4, Moving image 5) that remained, a consequence of the initial excessive CX stent protrusion into the LM.
Importantly, our decision-making was guided by intracoronary imaging: initially, to understand the causes of stent failure after a previous CX ostial stenting, and then to guide the treatment strategy for the removal of the protruding struts and tissue from the LAD ostium, ultimately, highlighting the need for better planning and standardisation of approaches to treat coronary lesions affecting CX or LAD ostia.
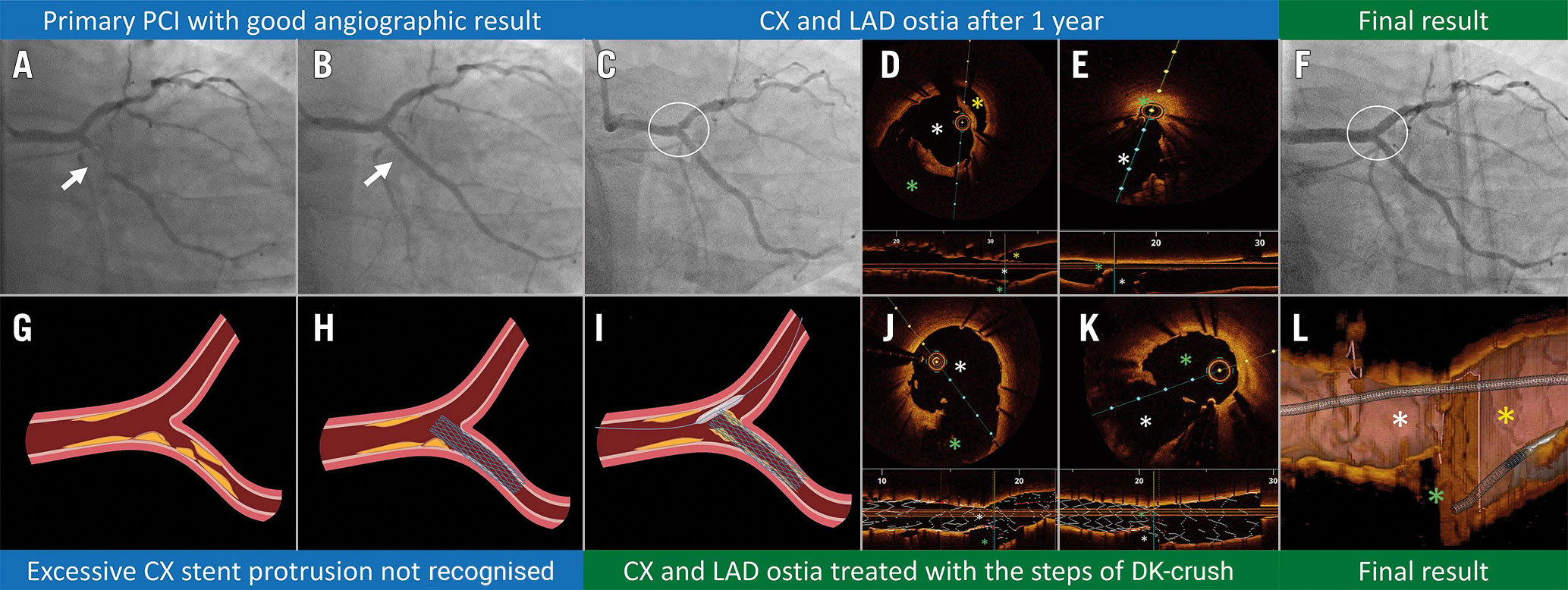
Figure 1. OCT-guided management of inadequate ostial CX stenting. A) Subtotal occlusion of the proximal CX. B) Primary PCI with stenting of the ostial CX and a good angiographic result. C) Hazy stenosis of ostial LAD, 1 year after the initial proximal CX stenting. D) Excessive CX stent strut protrusion (white asterisk) with the consequent gross malapposition in the left main (yellow asterisk) and the obstructed LAD ostium (green asterisk). E) Confirmation of the ostial LAD wire position (green asterisk) outside of the CX stent (white asterisk). F) Final angiographic result after the steps of DK-crush. G-I) Schematic representations corresponding to the angiographic findings in panels A-C. J) OCT pullback from the CX (white asterisk) corresponding to the baseline in (D), showing removal of tissue-covered struts from the ostial LAD (green asterisk). K) OCT pullback from the LAD corresponding to the baseline in (E), showing the luminal gain at the LAD ostium (green asterisk) with the preserved expansion of the stent at the CX ostium (white asterisk). L) 3D OCT reconstruction of the tissue-covered metallic neocarina, with yellow, white and green asterisks depicting left main, CX and LAD, respectively. This figure was created using BioRender Software. CX: circumflex artery; DK: double kissing; LAD: left anterior descending artery; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; 3D: three-dimensional
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report related to the submitted work. Outside of the submitted work, G. Stankovic reports speaker fees from Medtronic, Terumo, Abbott Vascular, and Boston Scientific. D. Milasinovic reports speaker fees from Abbott Vascular, Terumo, Boston Scientific, and Biosensors.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1A. Initial angiography.
Moving image 1B. Angiographic result following ostial CX stenting.
Moving image 2. Angiography at 1 year.
Moving image 3. OCT pullback from the CX showing tissue coverage of the excessively protruding stent struts.
Moving image 4. Angiographic result following double kissing crush left main stenting.
Moving image 5. OCT pullback from the CX following double kissing crush LM stenting.

