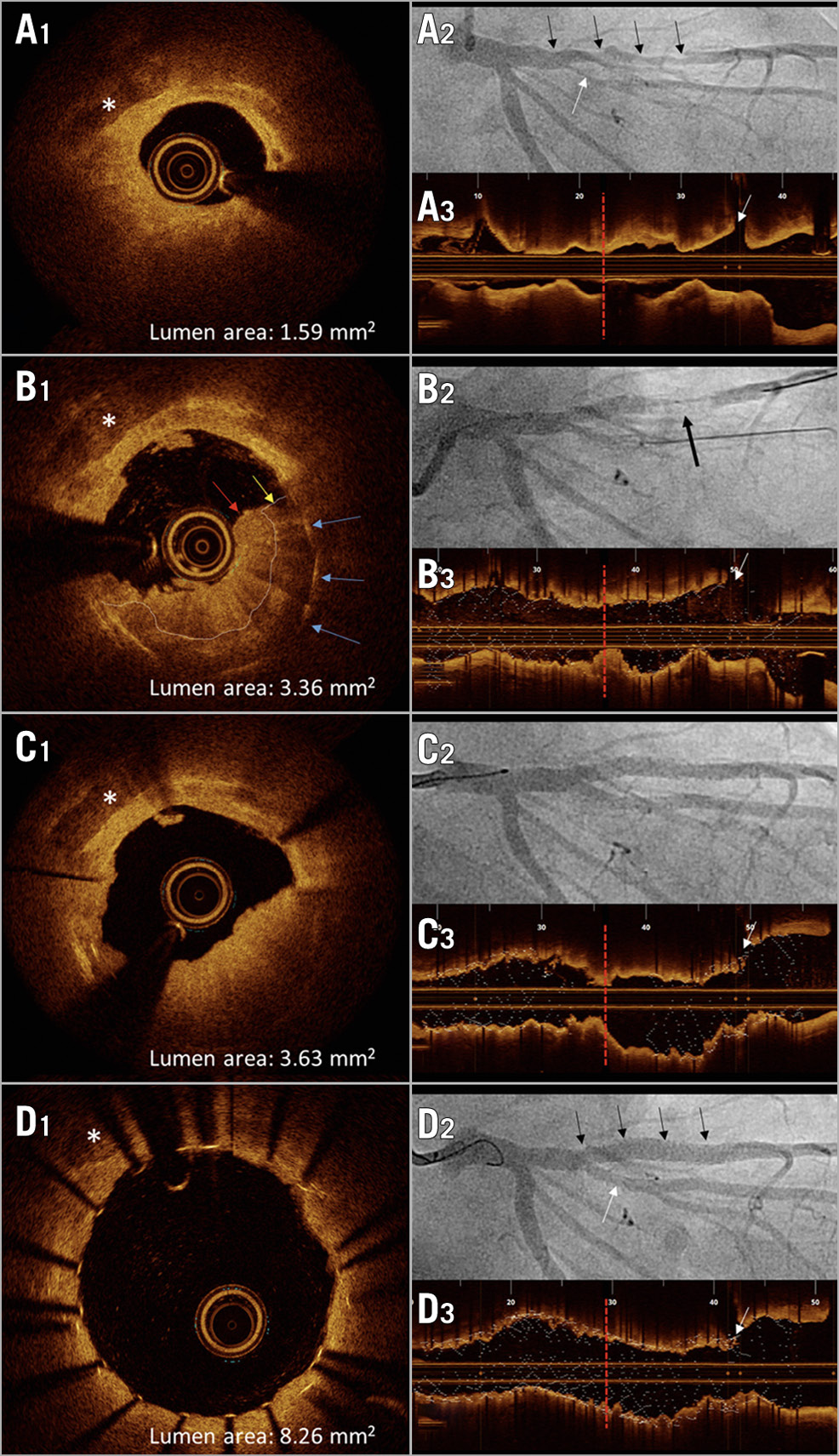
Figure 1. Stent thrombosis due to atheromatous protrusion after stenting. Left: cross-sectional OCT images (A1-D1; *=calcification) at four stages. Right: corresponding coronary angiographies (A2-D2; black arrows=LAD; white arrows=diagonal branch) and longitudinal OCT views of LAD (A3-D3; red vertical bars indicate site of stent thrombosis and correspond to site of OCT cross-sections; white arrows=diagonal branch). A1-A3. Pre-interventional OCT/angiography: circumferential, predominantly lipid-rich plaque (A1). B1-B3. OCT/angiography of stent thrombosis (arrow in B2): OCT (B1) shows thrombus (red arrow) attached to atheromatous protrusion (yellow arrow), blue arrows=buried stent struts. C1-C3. OCT/angiography two days later: residual stenosis due to protruding mass (C1). D1-D3. Final OCT/angiography: protruding material successfully compressed by additional stent, achieving good lumen area.
Preprocedural optical coherence tomography (OCT) of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) in a 58-year-old man with unstable angina due to a stenosis involving the LAD and first diagonal branch detected underlying mixed plaque, partially containing lipid in a circumferential distribution distal to the first diagonal branch (Figure 1A1-Figure 1A3). Bifurcational percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with side branch stenting (double-kissing mini-crush: 2.0×18 mm zotarolimus-eluting-stent [ZES] in diagonal branch, 2.25×38 mm ZES in the LAD with post-dilation using 3.0x20 mm and 3.5×8 mm non-compliant balloons) was performed after loading with ticagrelor (180 mg) and cumulative administration of 15,000 IU of heparin to achieve an activated clotting time >250 seconds. At the end of the procedure, acute stent thrombosis (ST) occurred in the LAD stent distal to the bifurcation (Figure 1B1-Figure 1B3). OCT excluded underexpansion or malapposition as possible causes for ST but showed fresh thrombus on top of protruding signal-rich tissue, suggestive of atheromatous material at the site of maximal preprocedural lipid burden (Figure 1B1). Acute ST was treated with post-dilation and administration of a GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor for 48 hours. Planned re-angiography with OCT two days later showed persisting protrusion with a consequently insufficient lumen area of 3.63 mm2 (Figure 1C1-Figure 1C3). Strategies to treat this finding were discussed. We proceeded with implantation of an additional stent (3.0×12 mm ZES) within the previously implanted stent, which resulted in excellent compression of the protruding material, achieving a lumen area of 8.26 mm2 (Figure 1D1-Figure 1D3).
OCT-detected irregular protrusion is more likely to be found after stenting of lesions with high lipid content and is an independent predictor for device-oriented clinical endpoints. Strategies to avoid acute ST include early administration of GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors or cangrelor, if bleeding risk allows. Implantation of a second stent to compress the protruding material to prevent further distal embolisation and in-stent restenosis has not yet been described but may be helpful in selected cases with extensive protrusion.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Häner has received a travel grant from Bayer. L. Räber has received research grants from Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, HeartFlow, Sanofi, and Regeneron, and speaker honoraria from Abbott Vascular, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biotronik, CSL Behring, Sanofi, Regeneron, Vifor and Occlutech. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

