Introduction
Senile calcific aortic stenosis (AS) is a multifactorial degenerative disease which results in calcification of the aortic valve leaflets. A bridging pattern of calcium involving both the centre and bases of the leaflets is typical and causes progressive restriction of valve opening, yielding the clinical syndrome of symptomatic AS. The Leaflex™ device (Pi-Cardia, Rehovot, Israel) is designed to score calcium deposits on the aortic surface of calcified aortic valve leaflets. The scoring lines aim to segment restrictive deposits and thereby increase mobility, reducing the severity of AS without implantation of a bioprosthetic valve. The device has undergone extensive bench testing in a reconstructed excised human stenotic aortic valve model1 and was also tested intraoperatively2. The aim of this first-in-human study was to evaluate the safety, feasibility, and performance of aortic valve repair with the transfemoral Leaflex device.
Methods
We conducted a single-arm prospective first-in-man evaluation of the Leaflex device in six centres in Europe and Israel (Supplementary Appendix 1). Patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) for treatment of symptomatic severe AS were considered for the study. Eligibility criteria, an example computed tomography (CT) scan, and core labs are provided in Supplementary Appendix 2 and Supplementary Figure 1.
The scoring procedure is shown in Figure 1 and Moving image 1. The device components are described in Supplementary Appendix 3 and illustrated in Supplementary Figure 2. The Leaflex intervention was performed during the index TAVI procedure. General anaesthesia (GA) was recommended due to the requirement for transoesophageal echocardiography assessment of the acute performance of the system. A SENTINEL™ embolic protection device (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) was inserted from the right radial artery, as per recommendation. Femoral access was achieved through a 16 Fr arterial sheath in standard fashion. A stiff guidewire was placed in the left ventricle and the Leaflex system was introduced across the aortic valve. Following unsheathing and positioning of the device, scoring was performed with the intention of creating multiple scoring lines in different locations across the valve leaflets. Echocardiographic and valve haemodynamic measurements were performed before and after the Leaflex procedure. On completion of the Leaflex procedure, a standard TAVI was performed. Sheath removal and femoral closure was carried out as per standard procedure and patients were monitored in hospital for at least 24 hours. Clinical follow-up was mandated at one and three months. Post-procedural anticoagulation therapy was at the operator’s discretion. Endpoints, definitions and statistical analysis are described in Supplementary Appendix 4 and Supplementary Appendix 5.
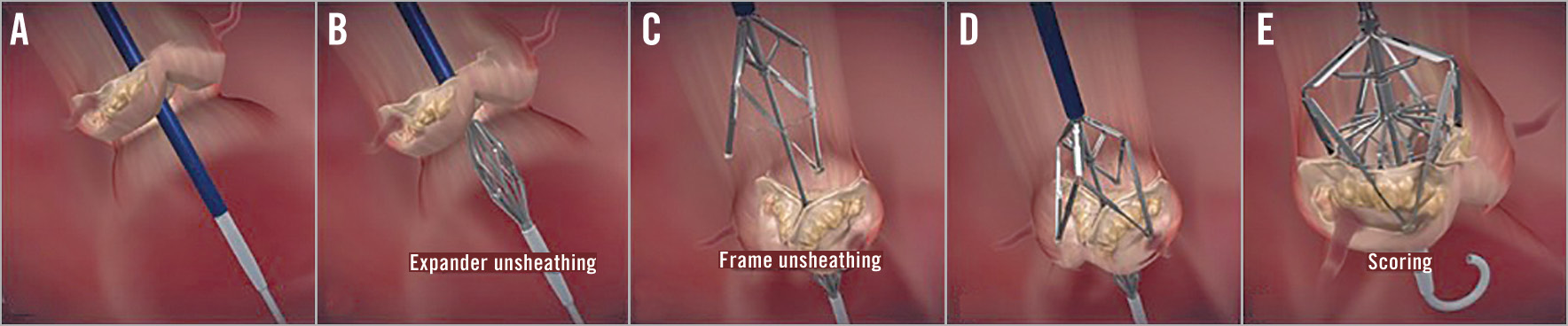
Figure 1. Mechanism of action. Scoring steps – Leaflex insertion and valve crossing (A), expander unsheathing below valve (B), frame unsheathing above valve (C), frame landing on valve (D), scoring (E).
The study protocol was approved by national regulatory authorities and local ethics committees, and all patients signed written informed consent for study participation.
Results
Sixteen patients were enrolled from May 2018 to April 2019. Demographics and baseline echocardiographic findings are shown in Supplementary Table 1. Fifteen procedures were performed under GA. The Leaflex procedure was followed by TAVI in 15 patients. In one patient, a guidewire perforation occurred, requiring surgical repair without subsequent TAVI.
In the first four cases, less than full expansion of the device with incomplete leaflet scoring was observed. This was caused by high friction forces between the internal shafts of the delivery system and required a design modification. Thereafter, successful scoring was achieved in all but one case, where initially the device could not be positioned on the valve due to anatomical reasons and had mechanical failure after resheathing.
We report echocardiographic and haemodynamic results in the patient cohort treated with the modified device, where scoring was performed as intended (N=11) (Table 1). In these cases, the mean aortic valve area (AVA) increased from 0.7±0.1 cm2 to 1.2±0.3 cm2 (p<0.001). Invasive measurements showed a relevant reduction of peak-to-peak pressure gradient (51±29 mmHg to 21±23 mmHg, p<0.001). Structural valve damage was not observed, and there was only one case with echocardiographically severe aortic regurgitation (AR), but none with haemodynamic effects (Supplementary Table 2, Supplementary Table 3). Figure 2 shows an example of the haemodynamic improvement and planimetry before and after a successful procedure. The median Leaflex procedure time (device insertion to removal) was 23 minutes.
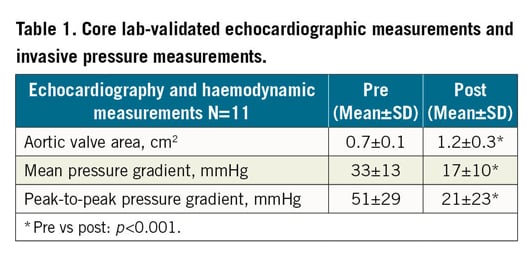
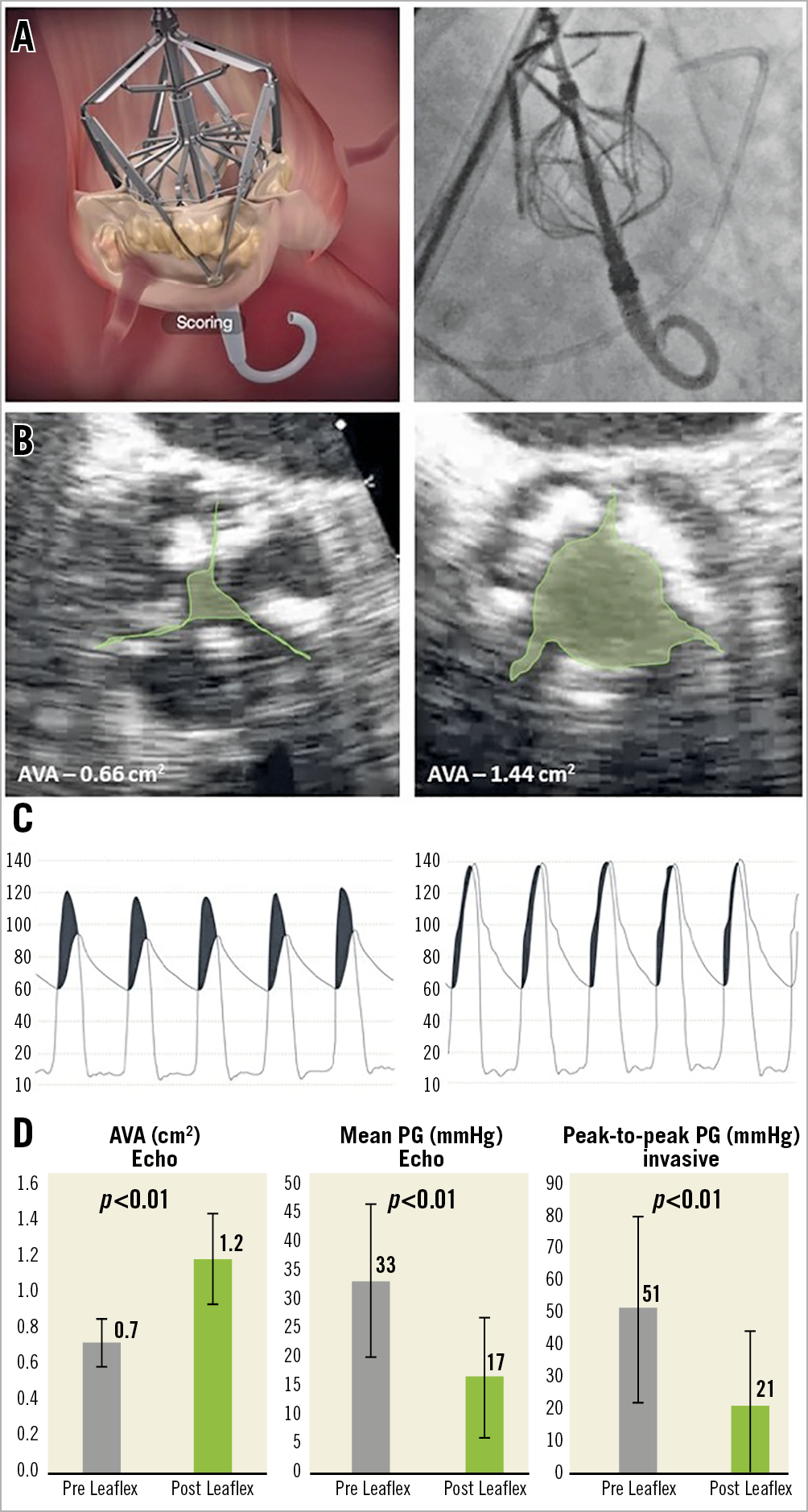
Figure 2. Procedure and effects on valve area and haemodynamics. A) The Leaflex Performer during scoring - animation (left) and fluoroscopy (right). B) Example of aortic valve area pre (left) and post (right) treatment. C) Example of invasive pressure measurement pre (left) and post (right) treatment. D) Echocardiography and invasive measurement study results (n=11): aortic valve area (left), transvalvular mean pressure gradient (centre) and transvalvular peak-to-peak pressure measurement (right) pre and post treatment with the Leaflex Performer.
In three patients, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) was performed post TAVI for bioprosthesis optimisation. Moderate paravalvular leak (PVL) post TAVI was observed in two patients. Four patients received new permanent pacemaker implantation following TAVI (days 0, 2, 4 and 86 post procedure). In two of these patients a new conduction disturbance occurred after the Leaflex procedure.
One patient suffered a wire-related ventricular perforation. This occurred following uneventful positioning and three complete scorings. Pericardiocentesis and fluid resuscitation was instigated. The patient underwent emergency sternotomy with surgical repair of perforation/tear in the left ventricle (LV).
There were two disabling strokes, both attributed to prolonged procedures with protracted periods of hypotension due to complications. The first patient suffered a stroke after surgical conversion following LV guidewire perforation. The second patient had a prolonged procedure, with a period of hypotension caused by a failure in the external (sheathing) tube which prevented sheathing of the frame. It was eventually sheathed by the introducer and successfully removed. One patient died of an unrelated syndrome with diarrhoea and fever 16 days post procedure, after initial successful discharge from hospital.
Discussion
This study confirms that, among patients with severe calcific AS, the Leaflex procedure is feasible and leaflet scoring can improve valve haemodynamics and increase AVA. In most cases, treatment with the Leaflex led to a change of AS classification from severe to moderate.
In the current study, the modified Leaflex device increased the mean valve area from 0.7±0.1 cm2 to 1.2±0.3 cm2. This treatment effect is much larger than that reported for BAV3. While BAV results in an overstretching of the valve apparatus, considerable recoil reduces the gain early after the procedure, limiting the clinical benefit4. In contrast, the Leaflex approach leads to a more predictable and larger increase in the effective valve area, which has the potential to deliver a more significant and sustained clinical benefit. This feasibility study was designed in the context of a TAVI, and hence the direct clinical effect of the increased valve area could not be measured. However, the valve area achieved with the Leaflex would normally render patients free of exertional symptoms5.
We did not observe any echocardiographic evidence of leaflet damage and, importantly, did not observe acute severe AR with haemodynamic effects. This is significant, as persisting severe AR following wire removal would limit a stand-alone approach in individual cases, similar to BAV. These data confirm bench tests on excised human stenotic aortic valves which documented a targeted interruption of the calcium deposits on the leaflets without tissue damage to the ventricular surface of the leaflets1. In two patients stroke occurred. These events were attributed to prolonged procedures with protracted periods of hypotension due to complications, rather than direct embolic events. The number of patients treated is small and does not allow an estimate of the true complication rate of the procedure.
In this very first transfemoral experience, several technical challenges that required device design iteration were encountered. With increasing experience and further device iteration, the procedure has the potential to become an important tool in the management of AS. Additional sizes will enable treatment of a wider range of annulus diameters, as well as more robust scoring leading to potentially higher, more consistent improvement in AVA. Potential future indications could include the treatment of patients with moderate AS to avoid or postpone the requirement for aortic valve replacement (AVR). Large prospective clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of a stand-alone Leaflex procedure are clearly required and are in the development phase.
Limitations
Due to the small sample size we cannot draw definitive conclusions regarding the technology. The included patients were highly selected and the generalisability of the results is unclear. The procedure is presently limited by a single device size, which contributed to the prolonged recruitment. Echocardiographic assessment following the Leaflex procedure was limited by the presence of the guidewire.
Conclusion
The current study suggests that a non-implant repair of severely stenotic aortic valve leaflets with the Leaflex device is feasible and can improve valve haemodynamics. The initial experience was limited by technical problems. Further studies are needed and will aim to establish the clinical safety, efficacy, and durability of the results. This procedure has the potential to provide a treatment alternative for patients without current treatment options.
|
Impact on daily practice An alternative approach to provide a reliable valve repair procedure that restores aortic valve mobility and renders patients asymptomatic would complement existing therapies. |
Funding
A. Baumbach is supported by the Barts NIHR Biomedical Research Centre.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Baumbach reports personal fees from MicroPort, Sinomed, Abbott Vascular, and AstraZeneca, outside the submitted work. D. Mylotte reports grants and personal fees from Medtronic, personal fees from Boston Scientific and MicroPort, outside the submitted work. D. Hildick-Smith reports consultancy (stock options) from Pi-Cardia. M. Jonas reports personal fees from Pi-Cardia, outside the submitted work, and being a consultant to Pi-Cardia. R. Halevi, Y. Kislev, and L. Plotnikov are Pi-Cardia employees. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. The Leaflex Performer animation.

