Abstract
Background: Perioperative thromboembolism is the main consideration in carotid artery stenting (CAS). Precise evaluation of carotid plaque components is clinically important to reduce ischaemic complications since CAS mechanically pushes plaque outwards, which releases plaque debris into the bloodstream.
Aims: This study aimed to determine whether high lipid core plaque (LCP) assessed by catheter-based near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is associated with ipsilateral cerebral embolism by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging during CAS using a first-generation stent.
Methods: Carotid stenosis magnetic resonance (MR) T1-weighted plaque signal intensity ratio (T1W-SIR) followed by NIRS assessment at the time of CAS (using the carotid artery Wallstent) was performed in 117 consecutive patients.
Results: The maximum lipid core burden index (max-LCBI) at minimal luminal areas (MLA; max-LCBIMLA) and the max-LCBI for any 4 mm segment in a target lesion defined as max-LCBIarea were significantly higher for the post-procedural new ipsilateral diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI)-positive than negative patients (p<0.001 for all). There was a significant linear correlation between max-LCBIarea and the number of new emboli (r=0.544, p<0.0001). We also found that the second quantile (Q2) of T1W-SIRMLA had a significantly higher max-LCBIMLA and a higher incidence of DWI positivity than Q1 and Q3 (p<0.001 for all). Furthermore, max-LCBIMLA appeared to distinguish between patients with and without postoperative new ipsilateral DWI positivity (AUC 0.91, 95% CI: 0.86-0.96; p<0.0001).
Conclusions: High LCP assessed by NIRS is associated with cerebral embolism by diffusion-weighted imaging in CAS using a first-generation stent.
Introduction
Carotid artery stenting (CAS) has become a popular alternative to invasive carotid endarterectomy (CEA) in primary and secondary stroke prevention. Randomised trial evidence shows that CAS, despite being associated with an increased early embolic risk, is in the long term not inferior to CEA1. Indeed, one major concern with CAS using first-generation (single-layered) stents is incomplete plaque insulation, leading to plaque prolapse and an increased incidence of, in most cases minor, stroke1,2. Thus, evaluation of the carotid plaque composition may play a role in estimating the risk of embolic events during CAS3,4. Procedure-related multiple emboli may cause not only clinical strokes but also long-term cognitive dysfunction by subclinical embolic infarcts5. Silent brain infarcts on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are a recognised surrogate outcome measure for procedural stroke6. The composition of unstable plaque, including a lipid necrotic core and intraplaque haemorrhage (IPH), is commonly assessed using MRI7. Although a high volume of lipid core plaque (LCP) is the main risk factor for myocardial infarct during stent deployment8, unstable carotid plaques often contain IPH, and the increased risk of embolism during CAS might depend on the lipid component9. Recent catheter-based near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) can detect LCP in coronary arteries, and NIRS of a non-culprit vessel in patients with coronary artery disease predicts increased risk of cardiovascular events10,11. LCP has recently been detected in carotid arteries using NIRS12,13 and has confirmed histological validation14; however, its value in terms of CAS deployment remains unknown. The present study aimed to determine whether high LCP assessed by NIRS can define increased risk of embolic infarct by diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in CAS.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN
This prospective observational study was based on criteria of the STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) statement. This study analysed LCP assessed by NIRS during CAS at a single centre between 2017 and 2020.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
We prospectively recruited 117 consecutive patients who underwent CAS to treat internal carotid artery stenosis at our institute between April 2017 and March 2020. The inclusion criteria comprised >80% stenosis in asymptomatic lesions, and >50% stenosis in symptomatic lesions accompanied by ipsilateral acute cerebral infarction or transient ischaemic attack (TIA), and high risk for CEA according to the Stenting and Angioplasty with Protection in Patients at High Risk for Endarterectomy (SAPPHIRE) criteria15. Patients with carotid artery occlusion requiring thrombolysis or thrombectomy were excluded.
Two antiplatelet agents (aspirin 100 mg, clopidogrel 75 mg, or cilostazol 200 mg) and statins (rosuvastatin 5 mg/day, pitavastatin 4 mg/day, or atorvastatin 10 mg/day) were administered to all patients starting four weeks before CAS. Platelet function in all patients was analysed using the VerifyNow rapid platelet function assay (Accumetrics, San Diego, CA, USA) on the day before undergoing CAS.
Baseline clinical characteristics recorded for each patient included patient age, sex, history of risk factors, and preoperative medical conditions. Hyperlipidaemia was defined as serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥120 mg/dL. Patients with diabetes mellitus were included if they had been medically managed for at least two months without changes in their hypoglycaemic treatment regimens. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) was determined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Current smokers were defined as those who had smoked at least one cigarette per day during the month before CAS. All patients underwent preoperative MRI/angiography and duplex sonography, followed by digital subtraction angiography.
The institutional review board at our university approved the study protocol (Approval no. 1456). All patients provided written, informed consent to their participation in all CAS procedures and allowed access to their medical records for research purposes.
INTERVENTION
An activated clotting time of >275 s was maintained using intravenous heparin during CAS procedures under local anaesthesia. An 8 Fr guiding catheter was placed in the common carotid artery. A stenotic lesion was then crossed using a guidewire. Then a FilterWire EZ™ embolic protection device (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) was inserted distal to the lesion. The flow was reversed under proximal guiding balloon protection for severely stenotic and/or thrombus-containing lesions because of the high potential for distal embolism when an embolic protection filter passes through the stenotic lesion. The lesion was dilated using a 3 or 4 mm-diameter balloon, then a Wallstent™ (Boston Scientific) was deployed under distal filter protection. Angioplasty balloons with diameters ≤80% of the normal luminal diameter distal to the stenotic site were used for conservative balloon post-dilatation under distal filter protection, then removed when the procedure was completed16. A column of blood proximal to the filter was suctioned several times using an aspiration catheter if the slow-flow phenomenon was recognised. All procedural symptomatic ischaemic and haemorrhagic events, and the slow-flow phenomenon were recorded. Ipsilateral and contralateral stroke (<7-day and <30-day), cardiovascular events, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), and disease-specific mortality (DSM) for myocardial infarction and stroke within one month of CAS were also recorded during patient follow-up.
NIRS AND INTRAVASCULAR ULTRASOUND IMAGING
Both NIRS and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) were performed utilising a single 3.2 Fr rapid-exchange Dualpro™ IVUS+NIRS imaging catheter (Infraredx Inc., Burlington, MA, USA). Catheter retraction at 0.5 mm/s was automated, and raw spectra were acquired at 40 Hz (wavelengths, 1,180-2,500 nm), to produce images with data points spaced 0.1 mm apart every 1°. The fraction of yellow pixels obtained from an image map derived from the NIRS measurements (chemogram) was multiplied by 1,000 to compute the lipid core burden index (LCBI). Therefore, the 4 mm long segment, with the maximum LCBI (max-LCBI 4 mm) ranging from 0 to 1,000 and representing the percentage of lipid core in the investigated segment, was calculated by the Makoto™ intravascular imaging system (Infraredx). Lipid signals from regions of interest (ROI) were quantified using the following parameters: maximal LCBI for any 4 mm segment in a target lesion defined as max-LCBIarea, the maximal LCBI for a segment 2 mm proximal and distal from the site of a minimal luminal area (MLA) was defined as max-LCBIMLA, and lesion-LCBI was defined as LCBI when an entire plaque lesion defined by IVUS was included. The IVUS images were acquired via a 40 MHz transducer rotating at the same speed as the NIRS probe. Three NIRS-IVUS measurements were taken during CAS before balloon predilatation (baseline), after stent deployment, and after balloon post-dilatation. MLAs, plaque burden (PB), and calcifications were assessed using IVUS. Plaques at the MLA were defined as calcified when calcifications were visually evident.
MRI PLAQUE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING
Plaques were also characterised by MRI using the MAGNETOM® Verio 3-T system (Siemens Healthineers, Forchheim, Germany). Two-dimensional T1-weighted (T1W) sequence images (FA:120, TR:600, TE:13) were acquired four weeks before CAS using black-blood double inversion recovery preparation and fat-saturation pulses. The signal intensity of the T1-weighted sequence was measured with the ROI drawn over carotid plaque, and the signal intensity ratio (T1W-SIR) of plaque relative to adjacent muscle was calculated. The SIR at the MLAs was defined as plaque SIRMLA and maximal SIR at all stenotic lesions was defined as plaque SIRarea. Three-dimensional time-of-flight (TOF) MR angiography (FA:19, TR:22, TE:3.69) was also carried out four weeks before CAS. A Cohen κ value of 0.76 indicated a high level of between-observer agreement for the presence of hyperintense signals in plaque on TOF magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) images4. Diffusion-weighted images were acquired using multisection, single-shot, spin-echo planar imaging from 18 to 24 hrs after the CAS procedure using a MAGNETOM Verio 3-T system. The imaging parameters comprised: echo duration, 100 ms; field of view, 23 cm; intersection gap, 1 mm; matrix, 96×128; section thickness, 5 mm. Experienced neuroradiologists who were blinded to the clinical information reviewed all DWI scans and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps acquired from the patients. Ischaemic lesions which arose due to procedure-related cerebral embolisms were defined as new ipsilateral hyperintense lesions on DWI. Each individual embolus was manually traced on individual MRI slices using Synapse Vincent software (Fujifilm Medical, Tokyo, Japan), which then incorporated slice thickness and interslice gap to calculate the volume of each infarct as well as their total volume.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
All data are presented as means±standard deviation. Between-group comparisons were assessed using Student’s tests, Fisher’s exact tests and the ANOVA test. Linear regression models were used to assess the relationship between two parameters. Differences were deemed statistically significant at p<0.05. The diagnostic values of LCBI determined by NIRS and plaque burden determined by IVUS were assessed by calculating the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC) for sensitivity versus 1-specificity to determine cut-offs for new ipsilateral DWI positivity after CAS. Univariate analysis was performed, and factors with a p-value <0.10 were included in the multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
STUDY POPULATION
Table 1 presents the clinical characteristics of the 117 enrolled patients (male, n=104; female, n=13; mean age, 75 years). The mean ages of the new ipsilateral DWI positive (n=39) and negative (n=78) groups were 77 (range, 52-90) and 75 (range, 59-89) years, respectively. Baseline characteristics, risk factors and medications did not significantly differ between the groups, but symptomatic lesions were significantly more frequent in the new ipsilateral DWI positive group than in the negative group (74% vs 53%, p=0.028) (Table 2). There were four ipsilateral strokes (<7 days) and 3 of 4 patients showed slow-flow phenomenon (Supplementary Table 1). Figure 1 shows two representative patients.
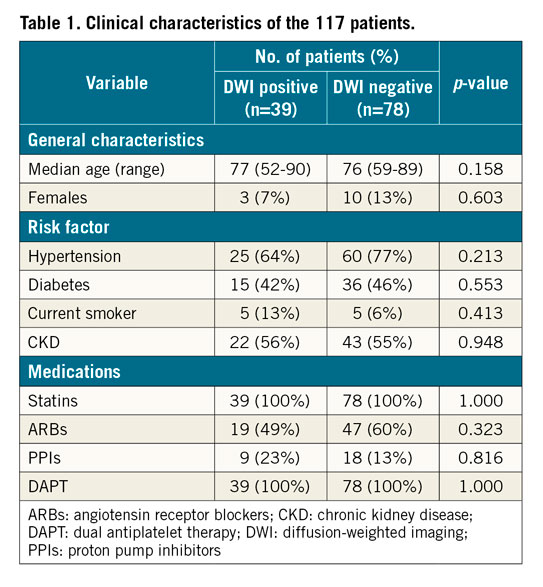
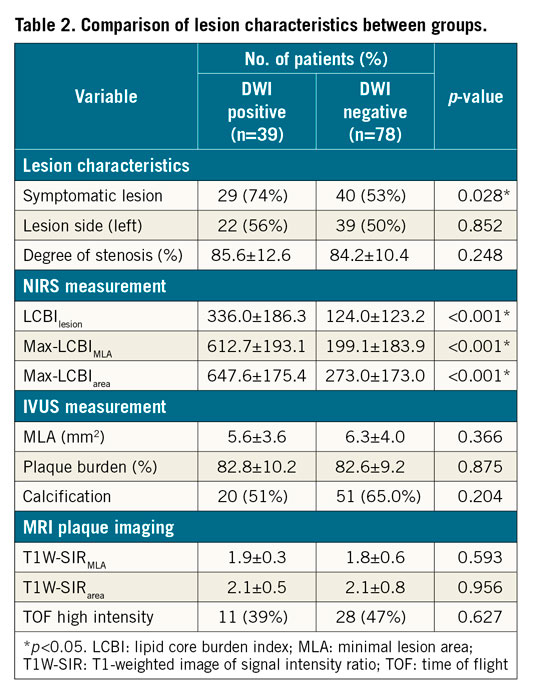
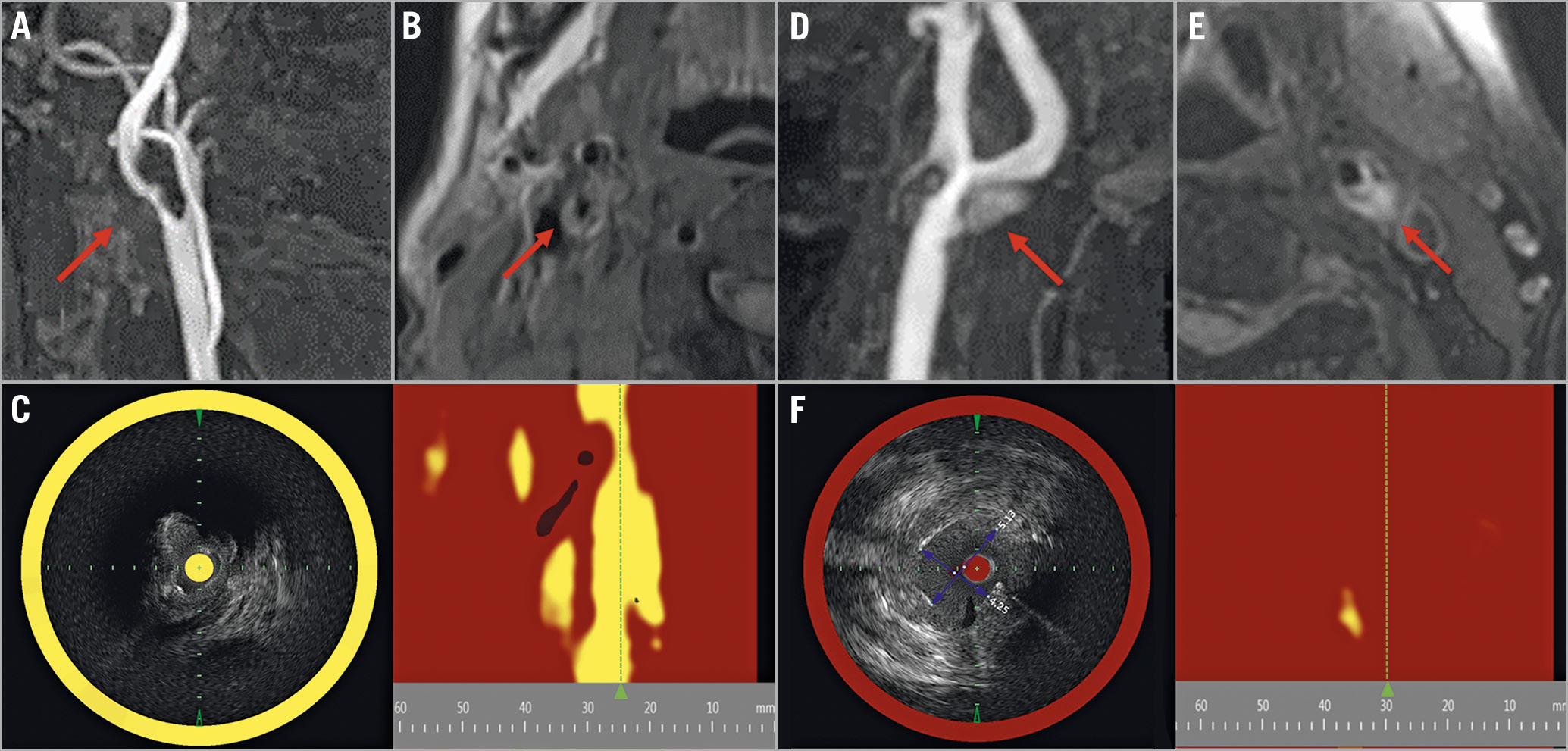
Figure 1. Findings from NIRS-IVUS and MRI of carotid plaques. A) Right symptomatic carotid stenosis in a 79-year-old man on TOF image (arrow). B) Plaque has slightly higher intensity on the T1-weighted image (arrow). C) NIRS-IVUS has a very high LCBI (961) at the MLA segment. This patient presented with embolic stroke and stent occlusion after CAS. D) Left asymptomatic carotid stenosis in a 72-year-old man on TOF image (arrow). E) Plaque manifests as higher intensity than adjacent muscle on the T1-weighted image (arrow). F) NIRS-IVUS reveals very low LCBI (111) at the MLA segment. Embolic events did not occur after CAS in this patient. CAS: carotid artery stenting; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; LCBI: lipid core burden index; MLA: minimal lumen area; MRA: magnetic resonance angiography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; NIRS: near-infrared spectroscopy; TOF: time-of-flight
NIRS WITH IVUS ASSESSMENT FOR CAROTID PLAQUE
Details can be found in Supplementary Appendix 1 and Supplementary Table 2.
NIRS-DERIVED LCP AND NEW IPSILATERAL DWI POSITIVITY
A significant linear correlation was indicated between max-LCBIarea and the number of new emboli (r=0.544, p<0.0001) and between max-LCBIarea and the total volume of embolic lesions (r=0.473, p<0.0001) (Figure 2A, Figure 2B). There were significant differences in the number of new emboli and the total volume of emboli between the groups with max-LCBI <500 and ≥500 (0.7±2.7 vs 5.0±7.0, 0.9±3.6 mm3 vs 22.0±42.3 mm3, p<0.001 for both) (Figure 2C, Figure 2D),8. Analyses of ROC curves for max-LCBIMLA, max-LCBIarea, lesion-LCBI, and plaque burden showed that the max-LCBIMLA could be more useful to distinguish between patients with and without postoperative new ipsilateral DWI positivity (AUC 0.91, 0.89, 0.85, 0.50, sensitivity: 0.79, 0.79, 0.73, 0.29, specificity: 0.83, 0.81, 0.85, 0.78, 95% CI: 0.86-0.96, 0.84-0.95, 0.78-0.92, 0.39-0.62, p<0.0001, <0.0001, <0.0001, 0.95, respectively) (Figure 3). A max-LCBIMLA of ≥504 was the optimal cut-off for the risk of new ipsilateral DWI positivity. On multivariate logistic regression analysis, high LCP was the factor related to ipsilateral DWI-positive embolism (p<0.001, odds ratio 33.34, 95% CI: 8.68-128.03) (Supplementary Table 3).
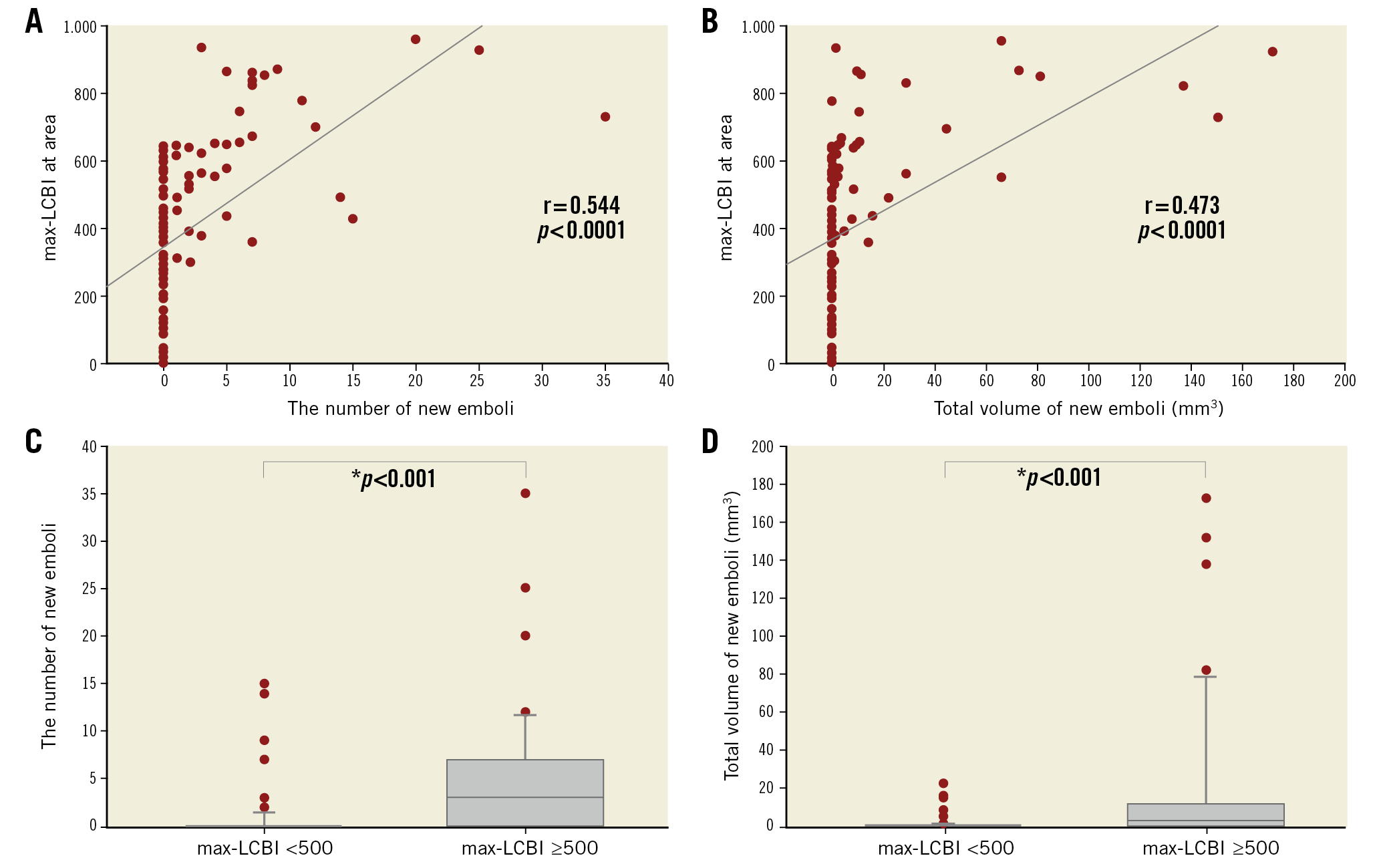
Figure 2. Relationship between new ipsilateral emboli and LCBI. A significant linear correlation was indicated between max-LCBIarea and the number of new emboli (A) and between max-LCBIarea and total volume of the embolic lesion (B). There were significant differences in the number of new emboli (C) and total volume of emboli (D) between the groups with max-LCBI <500 and ≥500.
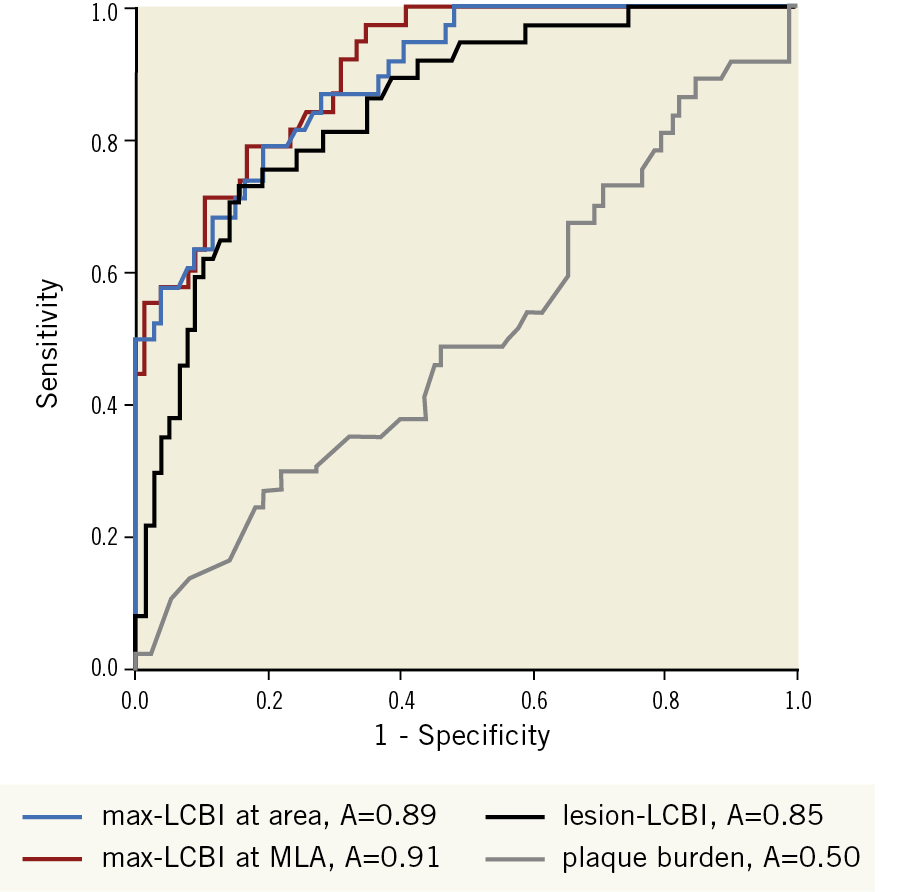
Figure 3. Accuracy of max-LCBI and plaque burden to detect new ipsilateral emboli after CAS assessed using ROC curves. Pairwise comparisons show significantly greater AUC for max-LCBIMLA (red line), max-LCBIarea (blue line), and lesion-LCBI (black line) than plaque burden (grey line). AUC: area under the ROC curve; CAS: carotid artery stenting; ROC: receiver operating characteristic
Discussion
The high LCP measured by NIRS was a crucial factor with which to define increased risk of ipsilateral embolic infarct during CAS, and max-LCBIarea ≥504 was the optimal cut-off for the risk of ipsilateral embolism. A significant linear correlation was indicated between max-LCBIarea and the number of new emboli, and the high LCP group also had a significantly higher frequency of new ipsilateral DWI positivity than the low LCP group. This first comparison with MRI showed that NIRS could identify a relationship between carotid plaque characteristics and risk of ipsilateral cerebral embolism associated with CAS. The strength of the present study is that it clearly shows an association between the carotid high LCP by NIRS and cerebral DWI-positive embolism in neuroprotected CAS using a single-layer stent.
LIPID CORE OF PLAQUE ASSESSED BY NIRS AND CAS HIGH-RISK PLAQUE
The main concern during CAS is to avoid embolic infarct. Unlike CEA, CAS mechanically pushes plaque outwards, which could release plaque debris into the bloodstream. Therefore, precise evaluation of carotid plaque components is clinically important to reduce ischaemic complications. In the present study, values for max-LCBIarea were significantly higher than those of max-LCBIMLA in all lesions, which indicates that the MLA is not always the site of the worst lipid-rich plaque characteristics. These results are consistent with previous reports12,17. IPH is one of the most dangerous features because it is significantly associated with clinical ipsilateral cerebrovascular events. However, not all plaque with IPH is associated with embolism3,18. Indeed, MRI and several other techniques can detect and differentiate LCP from IPH19,20. However, conventional MRI has limited ability to measure the volumes of these components. A catheter-based NIRS system has recently been validated for the automated identification of LCP in coronary arteries21,22,23,24. Recent coronary studies have found that max-LCBI >400 determined by NIRS can accurately distinguish culprit from non-culprit segments within arteries of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (MI)21. Percutaneous coronary intervention of lesions with large and small (max-LCBI ≥500 and <500, respectively) lipid cores determined by NIRS is associated with 50% and 4.2% risk, respectively, of periprocedural MI8,25. The detection of LCP by NIRS has been validated basically in vessels with a diameter <3.5 mm, and the NIRS-IVUS technology had not been histologically validated in larger vessels; however, we have currently proved that max-LCBI assessed by NIRS showed a significant positive linear correlation with histological evaluations in carotid lesions14. Here, we found that a high LCP measured by NIRS is a crucial factor for defining increased risk of embolic infarct in CAS and that a max-LCBIarea ≥504 was the optimal cut-off for the risk of ipsilateral embolism. Our results are consistent with those of previous coronary studies. Although the closed-cell design carotid artery Wallstent was used in the present study, recent optical coherence tomography assessments proved that the incidence of plaque prolapse of second-generation stents was lower than that of standard closed-cell stents26,27. The incidence of plaque prolapse of the single-layer stents (including closed-cell) is substantial, and only significantly reduced with two overlapped closed-cell stents26. The dual-layer carotid artery stent constitutes a second generation, where the MicroNet® mesh-covered stent (InspireMD, Tel Aviv, Israel) has demonstrated superiority versus the Roadsaver® stent (Terumo Corp., Tokyo, Japan)27. In contrast, an increased occupation ratio of IPH is more closely associated with the development of microembolic signals than the occupation ratio of LCP during CEA28,29. These results indicate that lipid-predominant plaque could be an embolic risk factor during CAS and that IPH-predominant plaque could be an embolic risk factor during CEA. If high embolic risk could be considered by NIRS as a high LCP in the clinical context, mesh-covered or dual-layer carotid stents could be deployed30, double filtration devices could be applied, and treatment strategies could be changed from CAS to CEA.
LIPID CORE OF PLAQUE ASSESSED BY NIRS AND INTRAPLAQUE HAEMORRHAGE
Details can be found in Supplementary Appendix 2.
Limitations
The small sample assessed at a single institution limited the statistical power and might have introduced bias into patient selection, data collection, and clinical outcomes. Therefore, the present results cannot be translated directly into clinical decision making. The other limitation is the lack of analysis of embolism parameters including the mean, total volume of LCPs, the length of LCPs, and the lack of 30-day imaging analysis. Although plaque evaluation by catheter-based NIRS is a relatively invasive imaging technique, it could be an additional modality to discriminate LCP at high risk for cerebral embolism by diffusion-weighted imaging during CAS. Standard closed-cell stents were used with a distal filter embolic protection device in the present study; however, usage of second-generation stents under flow reversal with Mo.Ma™ (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and transcarotid artery revascularisation (TCAR) could further reduce the incidence of new ipsilateral emboli31,32,33. Further work is needed to confirm whether optimised plaque insulation with new-generation (double-layer) carotid stents abolishes the association between the NIRS highly lipidic plaque characteristics and periprocedural cerebral embolism in neuroprotected CAS.
Conclusions
High LCP assessed by NIRS is associated with cerebral embolism by diffusion-weighted imaging in CAS.
|
Impact on daily practice Large lipid core detected by NIRS was associated with an increased risk of cerebral embolism using a first-generation (single-layer) stent. This risk might be mitigated by selecting a second-generation (such as MicroNet-covered) carotid artery stent rather than a single-layer stent and strengthening the peri-CAS hypolipidaemic and antithrombotic therapy. |
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

