
Abstract
Aims: Blooming artefacts limit accurate coronary assessment by multislice computed tomography (MSCT) in metallic stents. We sought to investigate whether bioresorbable vascular scaffolds (BVS) could be better assessed by MSCT.
Methods and results: Among 400 patients in the randomised ABSORB Japan trial, a pre-specified MSCT substudy was performed in 98 patients (103 lesions) in the BVS arm and 49 patients (49 lesions) in the cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent (CoCr-EES) arm at 13 months prior to follow-up angiography. The assessability of BVS by MSCT was superior to that of CoCr-EES (94% versus 67%, p<0.001). Blooming artefacts were the main reason CoCr-EES could not be analysed (29%), while marker artefacts precluded analysis in 1.1% of BVS. In the CoCr-EES arm, non-assessable lesions were more prevalent in segments with 2.5 mm stents compared to 3.0 or 3.5 mm stents (75.0% versus 23.5%, p=0.01), while in the BVS arm image quality was good regardless of the diameter. The in-device minimal lumen diameter by MSCT was smaller than that by QCA with a difference of 0.61 mm in the CoCr-EES arm, vs. only 0.026 mm in the BVS arm.
Conclusions: The feasibility of MSCT assessment of BVS-treated lesions was greater than that for lesions with CoCr-EES.
Abbreviations
BVS: bioresorbable vascular scaffold(s)
CoCr-EES: cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent(s)
ID-TLR: ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation
MLD: minimal lumen diameter
MSCT: multislice computed tomography
QCA: quantitative coronary angiography
TIMI: Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction
TLF: target lesion failure
TV-MI: target vessel myocardial infarction
Introduction
Non-invasive assessment of coronary stenosis by multislice computed tomography (MSCT) has been clinically applicable for de novo lesions. However, the diagnostic accuracy in stented segments has been affected by blooming artefacts caused by the metallic stent struts. The assessablity of stenosis after coronary metallic stent implantation by MSCT ranges from 52% to 92%1-3. The recently developed everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold (BVS) is composed of a radiolucent poly-lactide backbone that does not induce blooming artefacts. One of the possible advantages of BVS over a metallic stent is the feasibility of MSCT assessment of coronary stenosis as an alternative to invasive coronary angiography during follow-up. Some previous studies have demonstrated that BVS did not preclude either qualitative or quantitative analysis by MSCT4,5. The presence of platinum markers on scaffold edges, however, may cause artefacts. There have been no previous prospective studies to compare the diagnostic accuracy of MSCT in BVS-treated segments with that in metallic stent-treated segments. Therefore, we sought to assess the diagnostic capability of MSCT in BVS as compared with metallic cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stents (CoCr-EES) in a prospective pre-specified MSCT substudy of the ABSORB Japan trial6.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN
The ABSORB Japan trial was a prospective, multicentre, randomised, single-blinded trial in which 400 patients were randomised in a 2:1 ratio to treatment with the Absorb™ BVS (Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) or a CoCr-EES (XIENCE PRIME®/Xpedition®; Abbott Vascular). Details of the study protocol have been reported previously6. In brief, key angiographic inclusion criteria included: reference diameter ≥2.5 mm-≤3.75 mm and lesion length ≤24 mm. Key angiographic exclusion criteria included: left main or ostial location; heavily calcified lesion and bifurcation lesion with side branch ≥2 mm in diameter. The sizes of the BVS available in the study were 2.5, 3.0, and 3.5 mm in diameter, and 8, 12, 18, and 28 mm in length. Treatment with the same size matrix was required for patients assigned to the CoCr-EES arm. A total of 28 MSCT sites with at least 64-slice scanners were preselected based on their willingness to participate in the substudy. Enrolment in the MSCT substudy was specified before randomisation. In the MSCT substudy, patients were scheduled to undergo CT angiography prior to invasive coronary angiography at 13 months. Standard CT acquisition techniques were used, which included using beta-blockers in patients with a fast heart rate and ensuring accurate tube voltage (100 to 120 kV) depending on patient size. Coronary angiography was performed using standard techniques by operators who were blinded to the MSCT results.
The primary endpoint of the substudy was assessability by MSCT. The institutional review board at each investigational site approved the trial protocol. All patients provided written informed consent.
MSCT IMAGE ANALYSIS
MSCT images were analysed at an independent core laboratory (Cardiocore Japan, Tokyo, Japan), blinded to the results of the coronary angiography. The image quality was evaluated by two observers. Images with distinct anatomic details and without noise or artefacts were rated as “excellent.” Images with clear anatomic details, but with mild or moderate increase in noise and/or artefacts not affecting the diagnostic ability, were rated as “good.” Images with a distinct increase in noise and/or artefacts affecting the diagnostic ability were rated as “poor.” The “excellent” and “good” image qualities were classified as assessable to diagnose restenosis3. In case of disagreement, a third observer’s opinion was taken.
The quantitative MSCT analysis was performed by a validated software (QAngio CT Research Edition 2.1; Medis medical imaging systems, Leiden, the Netherlands)7,8. Parameters such as minimal lumen diameter (MLD), lesion length, minimal lumen area were derived. The reference vessel diameter (RVD) was calculated as the average of the mean proximal and distal lumen diameters. The diameter stenosis (DS) was calculated as the reference minus the minimal lumen diameter as a percentage of the reference lumen diameter. Significant restenosis was defined as a diameter stenosis ≥50%.
QUANTITATIVE CORONARY ANGIOGRAPHY
Quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) was performed at an angiographic core laboratory (Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA), blinded to the MSCT results. The software used was QAngio XA 7.3 (Medis medical imaging systems). Binary restenosis was defined as a diameter stenosis ≥50%.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The full-analysis-set (FAS) population, defined as patients who received the assigned study device at the target lesion, was used on a per lesion basis for this MSCT substudy. For binary variables, counts and percentages were calculated, and the p-value based on Pearson’s χ2 test was used when Cochran’s rule was met9. Otherwise, Fisher’s exact test was used. For continuous variables, means and standard deviations were calculated, and t-tests were performed. A Bland-Altman plot of the MLD was displayed to evaluate the agreement between two different instruments/measurement techniques (MSCT and QCA). All statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.2 or higher (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
Results
PATIENT POPULATION
Of the 400 patients enrolled in the ABSORB Japan trial, the study population consisted of 147 patients with 152 lesions assigned to the MSCT substudy (98 patients with 103 lesions in the BVS arm, and 49 patients with 49 lesions in the CoCr-EES arm) (Figure 1). In the BVS arm, one patient did not receive the assigned study device and was excluded from the FAS analysis. Of the FAS population, CT coronary angiography was performed in 84 BVS patients with 88 lesions (87%) and in 42 CoCr-EES patients with 42 lesions (86%). One BVS patient who underwent target lesion revascularisation with a metallic stent prior to 13-month follow-up was excluded, which resulted in an analysis population consisting of 83 patients with 87 lesions in the BVS arm and 42 patients with 42 lesions in the CoCr-EES arm. Baseline reference vessel diameter was significantly larger in the CoCr-EES arm compared to the BVS arm (Table 1). There were no significant differences in the other baseline patient and lesion characteristics between the two arms.
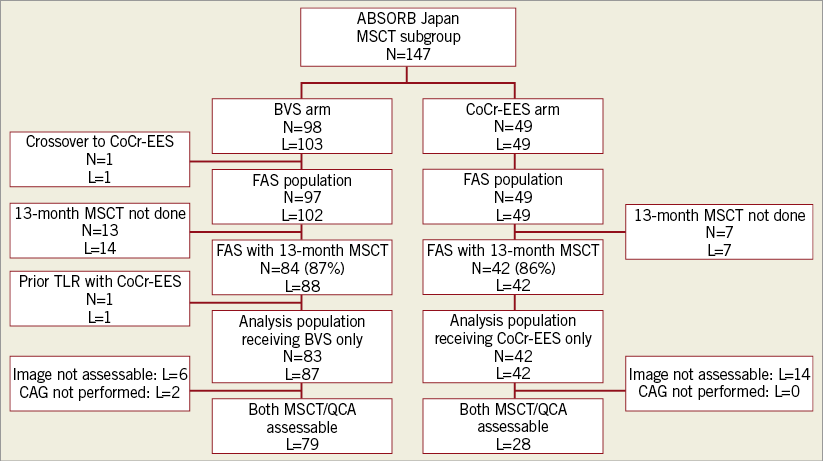
Figure 1. Patient flow chart. BVS: bioresorbable vascular scaffolds; CoCr-EES: cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stents; FAS: full-analysis-set; L: number of lesions; MSCT: multislice computed tomography; N: number of patients; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; TLR: target lesion revascularisation
QUALITATIVE MSCT DATA
CT scanners from all major manufacturers were used (Table 2). Except for the more frequent use of Discovery CT750HD (GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA) in the CoCr-EES arm, there were no differences in the types of scanners or parameters between the two arms.
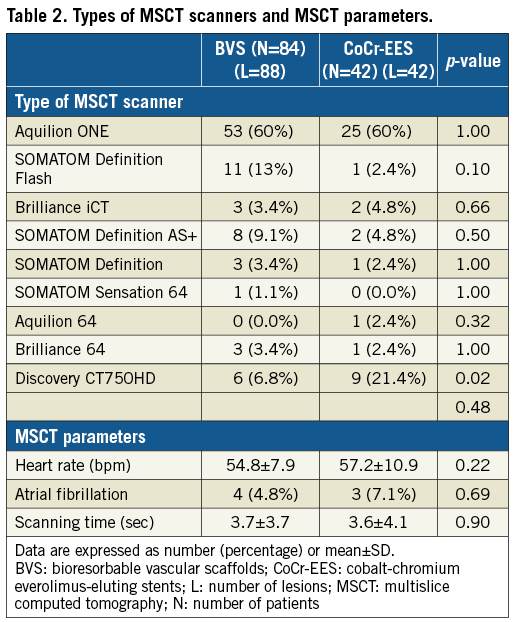
The assessability of coronary stenosis by MSCT was significantly higher in the BVS arm than in the CoCr-EES arm (94% versus 67%, p<0.0001) (Table 3). The metal artefact caused by stent struts contributed 29% to the poor image quality in the CoCr-EES arm. Typical non-assessable MSCT images are shown in Figure 2. In contrast, metal artefact caused by the edge markers of the BVS precluded the assessment in only 1.1% of the analysed lesions (p<0.0001). Representative non-assessable MSCT images due to metal artefact caused by the edge markers of the BVS are shown in Figure 3. Calcification, motion artefact and insufficient contrast in the lumen resulting in poor image quality were seen in similar frequencies in the BVS and CoCr-EES arms. Restenosis was not observed in the assessable segments either in the BVS arm or in the CoCr-EES arm.
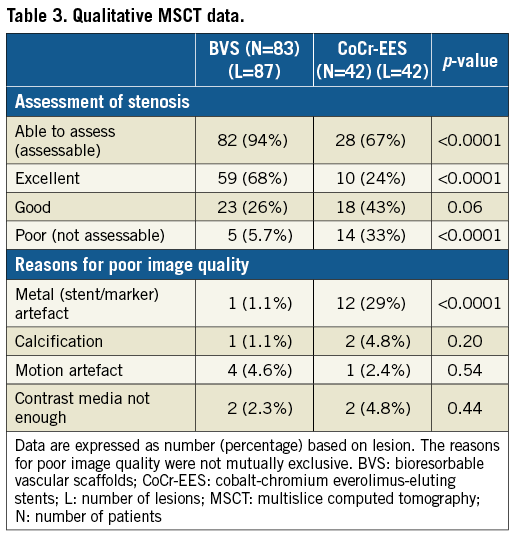
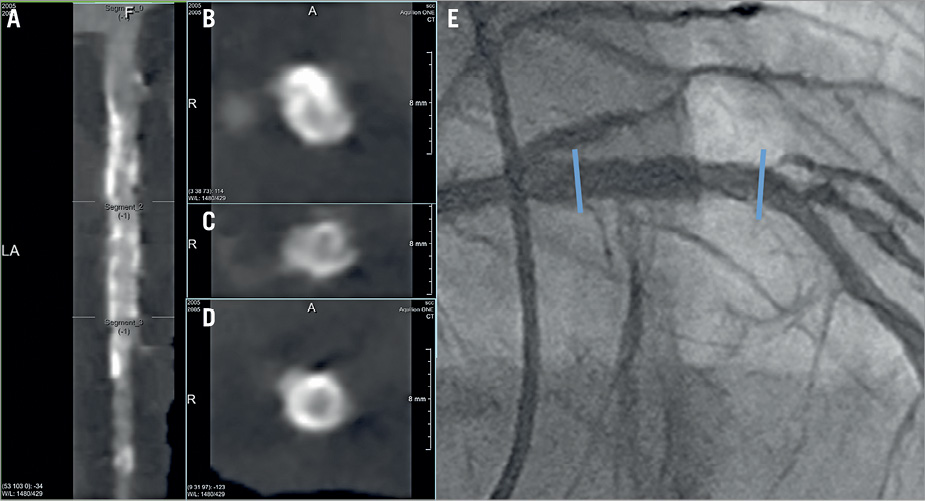
Figure 2. Non-assessable MSCT images in a patient with CoCr-EES implantation. A) Stretched curved planar reformation (CPR) image from MSCT in a patient with a 3.5×18 mm metallic CoCr-EES implantation in the proximal left anterior descending artery. B) Cross-sectional image of the proximal edge of the stent. C) Cross-sectional image of the mid portion of the stent. D) Cross-sectional image of the distal edge of the stent. E) Invasive coronary angiography performed at 13 months. The MSCT images were not assessable to determine the patency due to metal artefact, especially in the proximal half of the stent. Coronary angiography revealed no restenosis. The blue arrows indicate the edges of the stent. CoCr-EES: cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent; MSCT: multislice computed tomography
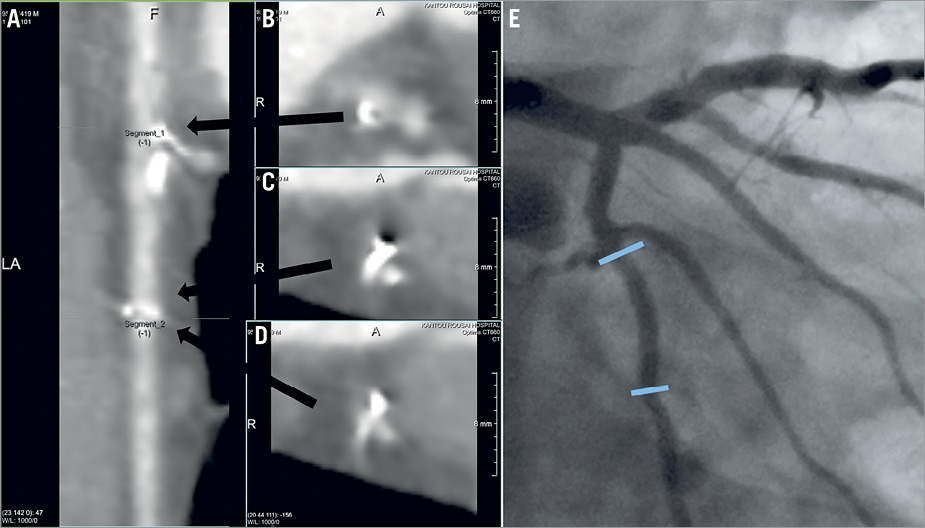
Figure 3. Non-assessable MSCT images in a patient with BVS implantation. A) Stretched curved planar reformation (CPR) image from MSCT in a patient with a 3.0×18 mm BVS implantation in the mid portion of the left circumflex coronary artery. B) Cross-sectional image of the proximal edge of the scaffold. C) & D) Cross-sectional images of the distal edge of the scaffold. E) Invasive coronary angiography performed at 13 months. The MSCT images were not assessable to determine the patency due to metal artefact, especially in the distal edge of the scaffold. Coronary angiography revealed no restenosis. The blue arrows indicate the edges of the scaffold. BVS: bioresorbable vascular scaffold; MSCT: multislice computed tomography
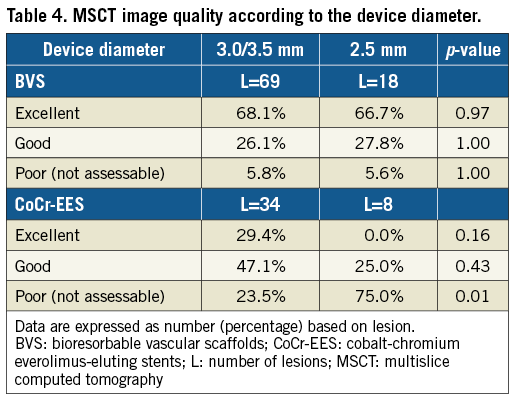
In the CoCr-EES arm, the non-assessable image rate was higher in the 2.5 mm stents compared to the 3.0/3.5 mm stents (75.0% versus 23.5%, respectively, p=0.01), whereas no difference was observed in the BVS arm between the 2.5 mm scaffolds and the 3.0/3.5 mm scaffolds (5.6% versus 5.8%, respectively, p=1.00) (Table 4). In the BVS group, the rate of non-assessable segments was 10.0% in 64-slice MSCT (one non-assessable segment in 10 segments), which is not statistically different from that in MSCT scanners greater than 64-slice (5.2% [four non-assessable segments in 77 segments], p=0.47). In the CoCr-EES group, the rate of non-assessable segments was 18.2% in 64-slice MSCT (two non-assessable segments in 11 segments), which is not different from that in MSCT scanners greater than 64-slice (38.7% [12 non-assessable segments in 31 segments], p=0.28). There was a statistical difference in the rate of non-assessable segments among the scanner types in the BVS arm (0% [0/52] in the one rotation type, 14.3% [2/14] in the dual source type, 14.3% [3/21] in the helical scan type, p=0.02); however, no difference was observed in the CoCr-EES arm (36% [9/25] in the one rotation type, 50% [1/2] in the dual source type, 26.7% [4/15] in the helical scan type, p=0.73). The presence of moderate to severe calcified lesions did not affect the rate of non-assessable segments either in the BVS arm (3.8% in the moderate to severe calcification vs. 6.6% in the none to mild calcification, p=1.00) or in the CoCr-EES arm (36.8% in the moderate to severe calcification vs. 30.4% in the none to mild calcification, p=0.66).
The time interval between MSCT and coronary angiography was 15.3±14.8 days. In the ABSORB Japan trial, there were six cases of angiographic in-device binary restenosis observed at 13-month angiographic follow-up (four in the BVS arm, and two in the CoCr-EES arm), of which only one patient in the CoCr-EES arm was assigned to the MSCT subgroup with non-assessable MSCT images. The angiographic core laboratory reported no angiographic restenosis in the segments assessable by MSCT. All the diagnoses made by the MSCT core laboratory in the assessable segments were in agreement with the diagnoses made by the angiographic core laboratory.
QUANTITATIVE DATA
Among the patients with assessable segments by MSCT, coronary angiography was not performed in two BVS patients (two lesions). As a result, paired quantitative MSCT and QCA data were available in 79 lesions in the BVS arm and in 28 lesions in the CoCr-EES arm for quantitative MSCT analysis (Figure 1). In the BVS arm, in-device MLD derived from MSCT (2.30±0.44 mm) was similar to that derived from QCA (2.28±0.45 mm). In the CoCr-EES arm, the in-device MLD by MSCT (2.01±0.39 mm) was smaller than that by QCA (2.62±0.45 mm). Bland-Altman analysis showed that MLD by MSCT was smaller than MLD by QCA with a difference of 0.61 mm in the CoCr-EES arm, while the difference was only 0.026 mm in the BVS arm (Figure 4A). Figure 5 shows an excellent image by MSCT in the CoCr-EES arm, which revealed no restenosis. The in-device MLD by MSCT (2.74 mm), however, was much smaller than that by QCA (3.12 mm). An excellent image by MSCT in the BVS arm is depicted in Figure 6, which shows no restenosis. The in-device MLD by MSCT (1.79 mm) was similar to that by QCA (1.795 mm). Bland-Altman analysis of the RVD (Figure 4B) showed that the difference between MSCT and QCA in the CoCr-EES arm (0.07 mm) was similar to that in the BVS arm (–0.12 mm). As a result, the difference in %DS in the CoCr EES (–18.7%) was greater than that in the BVS (–2.5%) (Figure 4C).
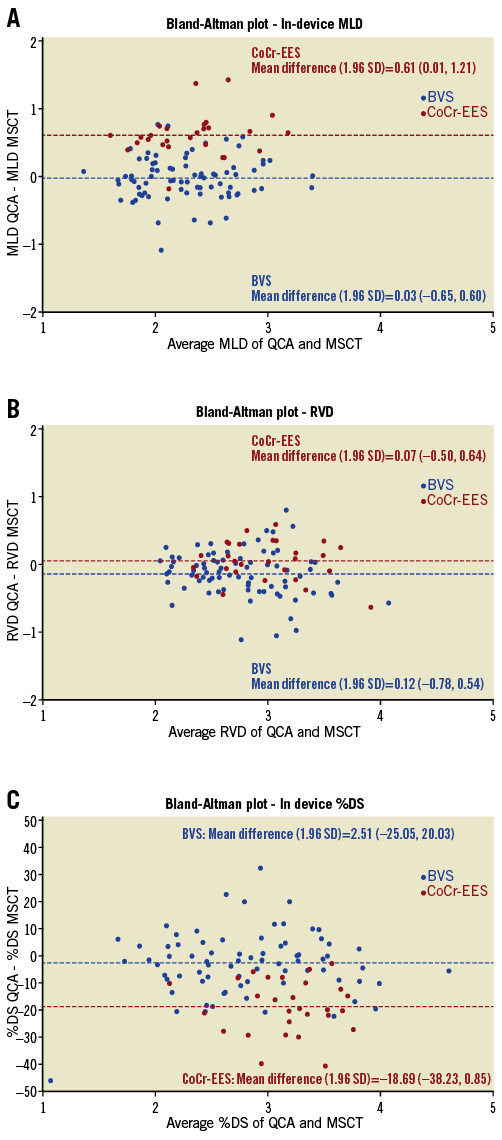
Figure 4. Comparison of QCA and MSCT parameters A) Bland-Altman plot of the difference in the in-device minimal lumen diameter between QCA and MSCT. B) Bland-Altman plot of the difference in the reference vessel diameter between QCA and MSCT. C) Bland-Altman plot of the difference in the in-device percent diameter stenosis between QCA and MSCT. Red and blue dots indicate the CoCr-EES and BVS arm, respectively. BVS: bioresorbable vascular scaffolds; CoCr-EES: cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stents; MLD: minimal lumen diameter; MSCT: multislice computed tomography; %DS: percent diameter stenosis; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; RVD: reference vessel diameter
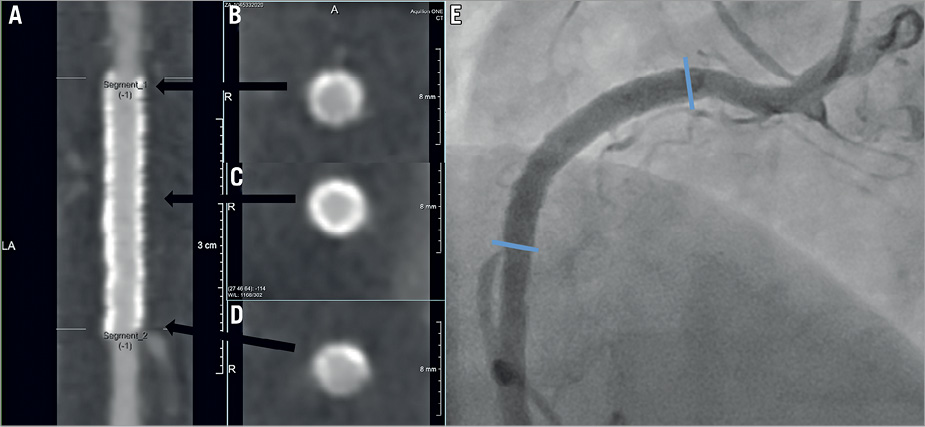
Figure 5. Assessable MSCT images in a patient with CoCr-EES implantation. A) Stretched curved planar reformation (CPR) image from MSCT in a patient with a 3.5×28 mm metallic CoCr-EES implantation in the proximal right coronary artery. B) Cross-sectional image of the proximal edge of the stent. C) Cross-sectional image of the mid portion of the stent. D) Cross-sectional image of the distal edge of the stent. E) Invasive coronary angiography performed at 13 months. The blue arrows indicate the edges of the stent. Both MSCT and coronary angiography images revealed no restenosis. CoCr-EES: cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent; MSCT: multislice computed tomography
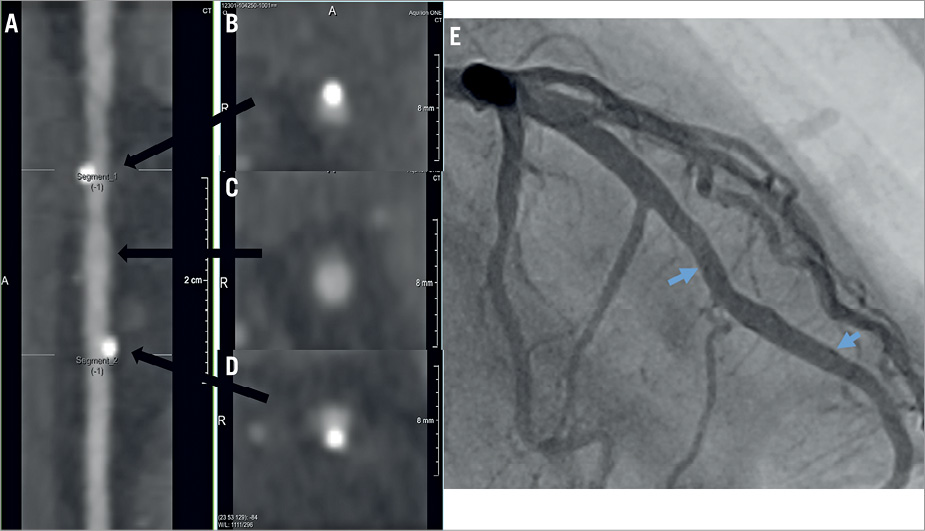
Figure 6. Assessable MSCT images in a patient with BVS implantation. A) Stretched curved planar reformation (CPR) image from MSCT in a patient with a 3.0×18 mm BVS implantation in the mid portion of the left anterior descending coronary artery. B) Cross-sectional image of the proximal edge of the scaffold. C) Cross-sectional image of the mid portion of the scaffold. D) Cross-sectional image of the distal edge of the scaffold. E) Invasive coronary angiography performed at 13 months. The blue arrows indicate the edges of the scaffold. Both MSCT and coronary angiography images revealed no restenosis. BVS: bioresorbable vascular scaffold; MSCT: multislice computed tomography
Discussion
The key findings of this MSCT substudy are the following: 1) assessability of coronary stenosis by MSCT was better in the BVS-treated lesions than in the CoCr-EES-treated lesions, mainly due to less blooming artefact caused by metal; 2) the device diameter had an influence on the assessability of coronary stenosis in the CoCr-EES-treated lesions, but not in the BVS-treated lesions; 3) the quantitative difference in the measurement of in-device MLD was 0.61 mm between MSCT and QCA in the CoCr-EES arm, but only a small difference (0.026 mm) was observed in the BVS arm.
The high diagnostic accuracy of MSCT to detect coronary de novo lesions has been demonstrated in prospective studies in comparison with coronary angiography10. However, there has been no prospective multicentre study with independent core laboratory analysis to investigate the diagnostic performance of MSCT to detect restenosis following coronary metallic stent implantation. The assessment of coronary stenosis in the stented segment is more difficult than in the native coronary artery, mainly due to blooming artefacts caused by metal. In fact, a relatively low MSCT assessability ranging from 52% to 92%1-3 has been reported for stented lesions in previous studies. Therefore, the appropriate use criteria for cardiac computed tomography11 assume a cautious attitude to the assessment of stented segments. Only a prior left main coronary stent with a stent diameter ≥3 mm is rated as appropriate. The other segment with a stent diameter ≥3 mm is classified as uncertain. Further, a stent diameter <3 mm is classified as inappropriate. The assessability of the CoCr-EES-treated lesions in the present study was 66.7%, which was within the range of those reported in previous studies1-3. The main reason for the non-assessable images was stent artefact in 29% of the lesions. Our finding that poor image quality (not assessable) was more prevalent in the segments treated with a 2.5 mm stent compared to those treated with a 3.0/3.5 mm stent supports the appropriate use criteria.
In contrast, the assessability of coronary stenosis in the BVS arm was 94.3%, which is significantly higher compared to the CoCr-EES arm. The edge marker artefact precluded analysis in only 1.1% of the lesions. Given the fact that the BVS is not completely resorbed until approximately three years and the MSCT was performed at 13 months in the present study, the MSCT assessment is not confounded by the presence of a scaffold during its process of absorption. The only possibility to induce metal artefact is the platinum markers in the scaffold edges. This could be a reason for the lack of difference in the image quality between the segments treated with a 3.0/3.5 mm scaffold and those treated with a 2.5 mm scaffold.
In terms of quantitative analysis, MSCT systematically underestimated in-device MLD compared to QCA in the CoCr-EES arm. The lumen contours in the MSCT images might have been delineated more inside than those in the QCA images due to blooming artefacts of metallic struts. In contrast, a good agreement for the in-device MLD between MSCT and QCA was observed in the BVS group with a difference of only 0.026 mm. Thus, the BVS would be much more suitable for quantitative MSCT analysis as compared with the metallic stent. There was a good agreement for the RVD in both the BVS and CoCr-EES groups. Metallic struts did not affect the quantitative MSCT analysis in reference segments.
Limitations
The MSCT substudy was not powered to detect the significant difference of the assessability between the two arms. The study was performed in a preselected population, comprising 28 participating sites using nine types of MSCT, ranging from 64 to 320 slices. Although the standard MSCT acquisition technique was used, the variety of CT scanners might have influenced the results. The allocation of study device could not be blinded by the core lab analysts due to vastly different CTA imaging profiles. In addition, heavy calcification proximal to or within the target lesion was one of the angiographic exclusion criteria per the ABSORB Japan study protocol and hence the results could not be extrapolated for heavily calcified lesions. Lastly, reference vessel diameter at baseline was significantly larger in the CoCr-EES arm; however, considering the fact that a larger vessel is advantageous for MSCT assessment, the difference had a low impact on the conclusion that the feasibility of MSCT assessment in BVS was greater than in CoCr-EES.
Conclusions
In this pre-specified randomised MSCT substudy, the non-invasive MSCT assessment of BVS-treated lesions is more feasible than that of metallic stent-treated lesions. However, the present study did not include restenosis; thus, it remains uncertain whether MSCT could detect BVS restenosis.
| Impact on daily practice The MSCT substudy of the ABSORB Japan trial is the first prospective randomised comparison of the diagnostic capability of MSCT between two coronary devices. The assessability of BVS by MSCT was superior to that of metallic stents. To avoid unnecessary invasive coronary angiography, the feasibility of MSCT assessment following BVS implantation would benefit patients. |
Guest Editor
This paper was guest edited by Daniele Andreini, MD, PhD, FESC, FSCCT; Cardiovascular CT Unit, Centro Cardiologico Monzino, IRCCS, Milan, and Department of Clinical Sciences and Community Health, Cardiovascular Section, University of Milan, Milan, Italy.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Satoru Kishi, Dr Masahiko Asami, Dr Nahoko Kato, core laboratory staff, and investigators of the study for their valuable contributions.
Funding
This study was sponsored by Abbott Vascular. The sponsor was involved in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, and writing of this report.
Conflict of interest statement
K. Tanabe is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular Japan, and receives honoraria for lectures from Abbott Vascular Japan and Toshiba. J. Popma is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular. K. Kozuma is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular Japan. P.W. Serruys is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular. Y. Onuma is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular Japan. S. Ying is an employee of Abbott Vascular. H. Kusano is an employee of Abbott Vascular. G. Stone is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular and is a consultant to Reva Corp. T. Kimura is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. The Guest Editor has no conflicts of interest to declare.

