Abstract
Background: The current risk stratification schemes for stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) are insufficient for an accurate assessment of stroke risk.
Aims: This study evaluates the association between the mechanical function of the left atrial appendage (LAA), as assessed by angiography, and the risk of stroke.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study to assess the mechanical function of the LAA by measuring the left atrial appendage ejection fraction (LAAEF) and grading the contrast retention (CR) using angiography.
Results: A total of 746 patients referred for a left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) procedure with (n=151; stroke group) or without (n=595; control group) a history of stroke were included in the analysis. LAAEF was significantly lower (14% [9-19] vs 20% [12-33]; p<0.001) and grade 3 CR was more common (66.9% vs 33.9%; p<0.001) in patients with a history of stroke. Multivariable analysis showed that CR was independently associated with stroke in patients with AF (grade 2 vs grade 1=7.29; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.84-21.65; p<0.001; grade 3 vs grade 1=16.45; 95% CI: 6.16-51.02; p<0.001). The receiver operating characteristics curve demonstrated that CR identified patients with stroke more accurately than the CHA2D-VASc score (C-statistic 0.712 vs 0.512; p<0.001), and the combination of CR and the CHA2DS2-VASc score provided the best performance (C-statistic 0.871 vs 0.829 [CHA2DS2-VASc score alone]; p=0.048)
Conclusions: Impaired mechanical function of the LAA, indicated by a low LAAEF and CR, is associated with a history of stroke in patients with AF. Assessment of CR using LAA angiography helps improve the stratification scheme for stroke risk prediction.
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a prevalent arrhythmia and a leading cause of ischaemic stroke, which affects over 35 million people worldwide1, and accounts for more than 15% of all strokes2. In the past decades, stroke prevention has become the cornerstone of AF treatment. Accordingly, an accurate assessment of individual thrombotic risk, which subsequently leads to different antithrombotic strategies, is critical. Currently, there are several scoring schemas for stroke risk stratification in AF patients, including CHADS2, CHA2DS2-VASc, R2CHADS2, Anticoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA), and the Age/Biomarker/Clinical history (ABC) scores34567. However, these schemas, based on different clinical risk factors or blood biomarkers, are mostly general markers of an unhealthy phenotype, which limits their predictive values for stroke in the specific population with AF. For example, the CHA2DS2-VASc scoring system, which is widely accepted and recommended by current guidelines as the most important tool for stroke prediction in AF, fails to identify a large number of high-risk patients with a suboptimal C-statistic value, ranging from 0.55 to 0.67, among various cohorts8. Despite being initially classified as low risk based on their CHA2DS2-VASc score, some patients sustain strokes9. Moreover, there is still uncertainty as to whether a patient with a single non-sex-related CHA2DS2-VASc risk factor carries a low or high stroke risk1011. These limitations emphasise the need to improve the risk stratification paradigm for thromboembolic (TE) events in patients with AF.
TE events in non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF) have been essentially attributed to the formation of thrombi in the left atrium (LA), with precisely over 90% of thrombus originating from the left atrial appendage (LAA)1213. Previous small sample studies revealed that the LA/LAA mechanical function is impaired in NVAF patients via multimodality imaging including transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE), and cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR)1415161718. Nevertheless, there are currently few reports regarding the mechanical function of LAA evaluated by angiography and its association with stroke in AF patients.
In this study, we established two angiographic parameters to measure the mechanical function of the LAA and investigated their relationship with stroke and other imaging parameters established for AF. More importantly, we explored their potential value in improving the risk stratification paradigm for stroke in AF patients.
Methods
Study population
We performed a cross-sectional study using a retrospectively enrolled database of patients referred to the Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine for left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) between September 2017 and August 2022. Of 770 consecutive patients with NVAF who underwent LAAO, 24 patients were excluded because of incomplete imaging exams. A total of 746 patients were included in the analysis, with (n=151; stroke group) or without (n=595; control group) a history of stroke before LAAO. All patients were comprehensively assessed for LAA mechanical function using both TOE and LAA angiography. Stroke was defined as a focal neurological deficit from a non-traumatic cause, lasting at least 24 hours and categorised as ischaemic (with or without haemorrhagic transformation). Patients with a history of haemorrhagic stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA) were assigned to the control group. The CHA2D-VASc score (which is the CHA2DS2-VASc score without the inclusion of stroke itself) is composed of the following clinical risk factors: congestive heart failure, hypertension, age, diabetes mellitus, vascular disease, and sex category (female). The Ethics Committee of the Shanghai Chest Hospital approved this study, and all the patients provided written consent.
Echocardiography
Before the LAAO procedure, all patients underwent TTE and TOE examinations using a Philips iE33 Matrix ultrasound system (Philips). The left atrial anteroposterior diameter (LAAPD) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were routinely examined with TTE; spontaneous echo contrast (SEC) and left atrial appendage peak emptying velocity (LAAPEV) were obtained with TOE according to the standards of the American Society of Echocardiography19.
LAAPEV was defined as a late diastolic positive outflow signal measured at the LAA orifice’s entry and was calculated as the average value of 5 consecutive cardiac cycles during the TOE examination20. SEC was defined as dynamic “smoke-like” echoes with a characteristic swirling motion in the LAA that could not be eliminated despite optimised gain settings21.
Mechanical function of the LAA according to angiography
Before LAA angiography, all patients received transseptal puncture with TOE guidance under general anaesthesia. LAA angiography was performed with a 6 Fr pigtail catheter at the distal end of the LAA in right anterior oblique (RAO) 30°+caudal (CAU) 20° projections. Fifteen ml of contrast medium were injected with a slow to fast injection speed through the pigtail catheter within 3 seconds, followed by a long cine angiography lasting at least 6 consecutive cardiac cycles to observe the filling and clearance of the contrast agent in the LAA.
We evaluated the mechanical function of the LAA based on two parameters obtained from the LAA angiography. First, we measured the LAA end-diastolic area (LAAEDA) and end-systolic area (LAAESA) with a picture archiving and communication system (PACS), as shown in Figure 1. We calculated the LAA ejection fraction (LAAEF) using the following formula: LAAEF=(LAAEDA− LAAESA)/LAAEDA*100%. Additionally, we assessed the degree of contrast retention (CR) in the LAA with PACS, based on long LAA cine angiography. The degree of CR was graded into 3 levels based on the clearance of contrast agent. Grade 1 represents complete clearance of contrast agent in the LAA within 3 cardiac cycles. Delayed clearance within 3 to 6 cardiac cycles is considered grade 2, and grade 3 indicates that the contrast agent is not completely cleared out from the LAA even at the end of the long LAA cine angiography (Central illustration), which reflects severely impaired LAA emptying function.
The measurement of LAAEF and grading of the CR degree were both performed by two independent physicians. If there was a significant difference between the results (defined as a difference >3% for LAAEF or a mismatch for the degree of CR), a third physician was required for confirmation.
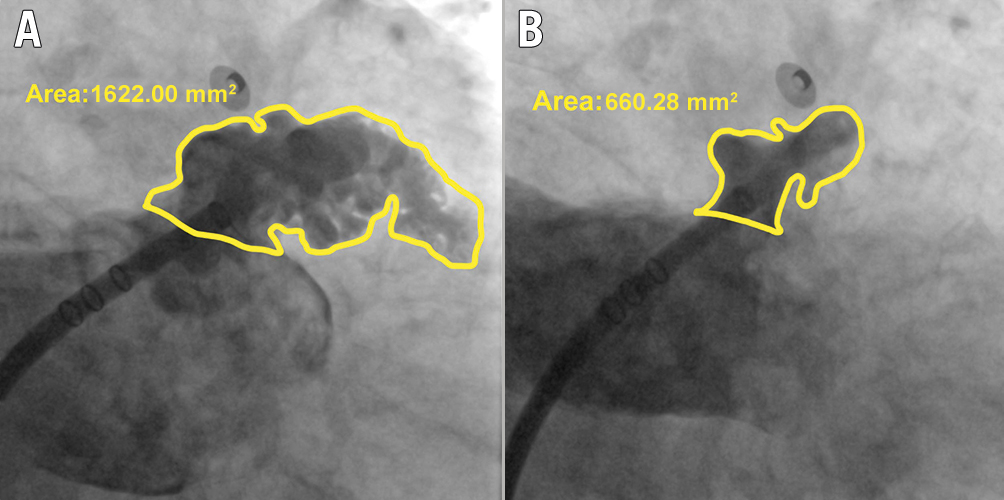
Figure 1. Measurement of LAAEF based on LAA angiography. A) The left atrial appendage end-diastolic area (LAAEDA), and B) the left atrial appendage end-systolic area (LAAESA). The LAAEF is calculated with the formula: LAAEF=(LAAEDA−LAAESA)/LAAEDA*100%. LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAEF: left atrial appendage ejection fraction
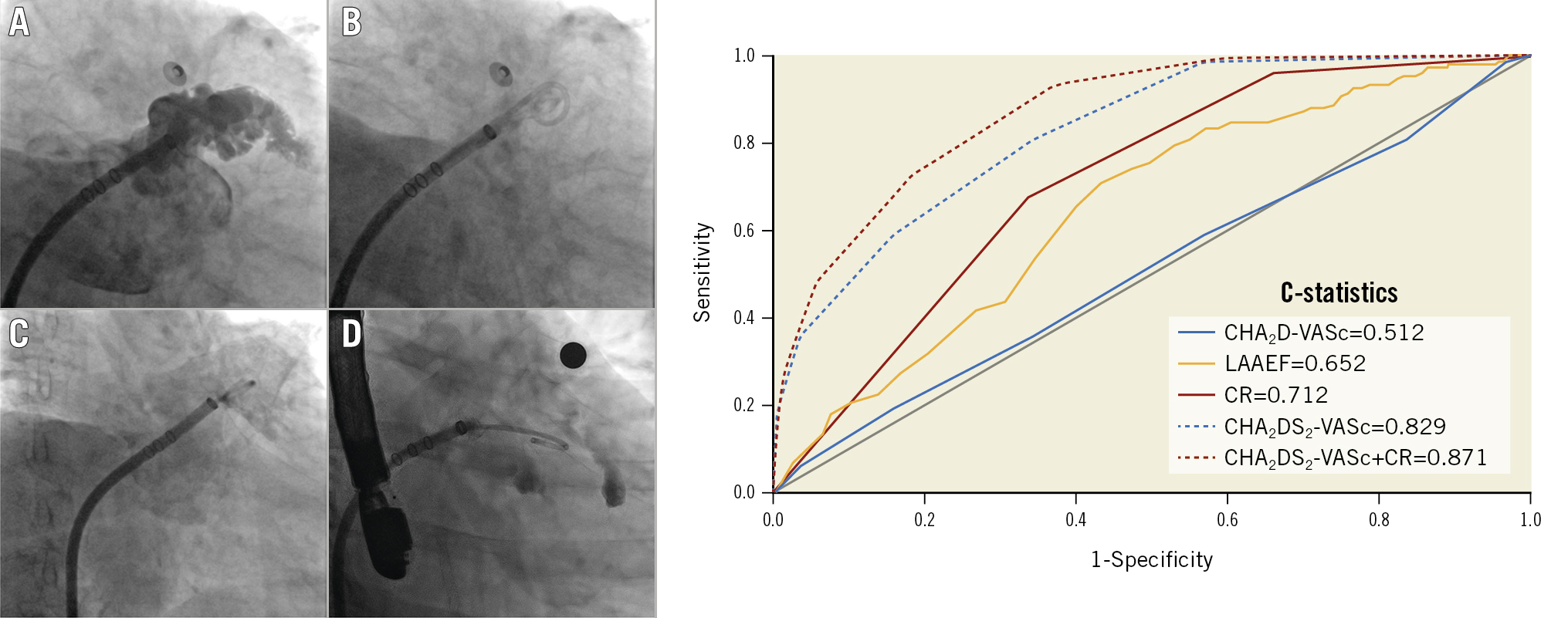
Central illustration. Assessment of LAA contrast retention and the ROC curve. Angiographic assessment of the mechanical function of the LAA by CR grading. A) Shows the end-diastolic image of contrast filling into the LAA; B) represents grade 1 CR (complete clearance of contrast agent); C) represents grade 2 CR (delayed clearance of contrast agent within 3 to 6 cardiac cycles), and D) represents grade 3 CR (the contrast agent stayed inside the LAA even at the end of the long LAA cine angiography). According to the ROC analysis on the right, the C-statistic for each parameter was as follows: CHA2D-VASc=0.512; LAAEF=0.652; CR=0.712; CHA2DS2-VASc=0.829; CHA2DS2-VASc+CR=0.871. CR identified patients with stroke more accurately than the CHA2D-VASc score (p<0.001) and LAAEF (p<0.001), and the combination of the CHA2DS2-VASc score and CR provided the best performance (p=0.048 compared to CHA2DS2-VASc alone). CR: contrast retention; LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAEF: left atrial appendage ejection fraction; ROC: receiver operating characteristics
Statistical analysis
Data for continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR) for non-normal data and were analysed with the Student’s t-test or analysis of variance (ANOVA). Categorical data are summarised as percentages and were compared using the Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons of participant’s characteristics according to the grade of LAA contrast retention. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to assess the effects of LAA mechanical function evaluated by angiography on the likelihood that the patient has a history of stroke. Results are presented as odds ratios (OR): Model 1: unadjusted; Model 2: adjusted for factors (1) significantly associated with the outcome – stroke and (2) closely related to the main parameter – CR, which include history of anticoagulation, heart failure, AF rhythm during the procedure, LAAPD, LVEF, LAAPEV and SEC; Model 3: adjusted for model 2+LAAEF. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the value of different parameters in risk stratification for stroke in AF patients. We performed Chi-squared statistics to compare two different values of C-statistics. A p-value<0.05 was considered significant, and all t-tests were 2-sided. Statistical analyses were performed with the use of R software, version 4.2.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Results
Patient characteristics
Of the 746 patients, 151 (20.2%) had a history of stroke and 595 (79.8%) did not. The median age of the cohort was 71 (interquartile range [IQR] 65-77) years, and 321 patients (43.0%) were female. All clinical characteristics were comparable between the 2 groups, except that more patients received oral anticoagulants in the stroke group (77.5% [stroke] vs 43.4% [control]; p<0.001). The median CHA2D-VASc score was 3 (IQR 2-4) for both groups, and the CHA2DS2-VASc score was 2 points higher for the stroke group.
Based on the imaging results, there were no significant differences in LAAPD and LVEF between the groups. However, LAAPEV was slower (29 cm/s [IQR 20-39] vs 32 cm/s [IQR 22-40]; p=0.043) and SEC was more frequent (28.5% vs 14.3%; p<0.001) in the stroke group. According to the LAA angiography, LAAEF (14% [IQR 9-19] vs 20% [IQR 12-33]; p<0.001) was significantly lower in the stroke group because of a larger LAAESA (1,554 mm2 [IQR 1,202-2,026] vs 1,397 mm2 [IQR 1,019-1,822]; p<0.001). Furthermore, there was a significant difference in the distribution of the degree of LAA contrast retention between the 2 groups. Patients with a history of stroke had significantly less normal clearance (grade 1 CR) (4.0% vs 33.4%; p<0.001) and more notable retention (grade 3 CR) (66.9% vs 33.9%; p<0.001) compared to those without stroke (Figure 2). Table 1 summarises the patients’ clinical and imaging characteristics.
The median delay from stroke to LAA angiography was 6 months in our cohort, and, except for age, all other characteristics (including LAAEF and CR) were consistent between patients who had a stroke within and beyond 6 months before angiography. Additionally, a low LAAEF (14% [IQR 8-19] vs 20% [IQR 12-33], stroke within 6 months vs control; p<0.001; 14% [IQR 10-18] vs 20% [IQR 12-33], stroke beyond 6 months vs control; p<0.001) and grade 3 CR (70.5% vs 33.9%; p<0.001; 63.0% vs 33.9%; p<0.001) were consistently associated with a history of stroke, regardless of the time interval between stroke and angiography. However, the correlation between LAAPEV and stroke was not significant in either group (Supplementary Table 1).
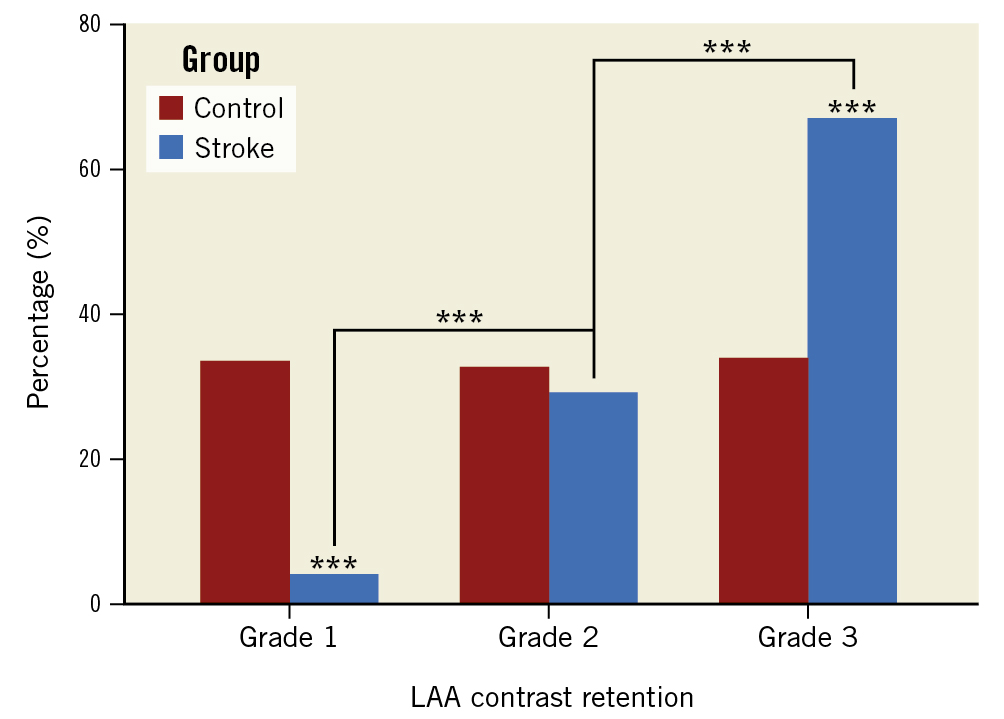
Figure 2. Patient distributions according to the grade of CR. Patient distributions according to the grade of CR are significantly different between the stroke and control groups, and there are more patients with grade 2 and grade 3 CR in the stroke group. ***p<0.001. CR: contrast retention; LAA: left atrial appendage
Table 1. Baseline characteristics.
| Control, n=595 | Stroke, n=151 | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | |||
| Age, years | 71 (65-77) | 70 (64-77) | 0.634 |
| Female | 258 (43.4) | 64 (42.4) | 0.829 |
| Anticoagulation | 258 (43.4) | 117 (77.5) | <0.001 |
| Persistent AF | 412 (69.2) | 116 (76.8) | 0.067 |
| AF in procedure | 286 (48.1) | 93 (61.6) | 0.003 |
| Heart failure | 226 (38.0) | 53 (35.1) | 0.513 |
| Coronary artery/ vascular disease | 150 (25.2) | 48 (31.8) | 0.102 |
| Hypertension | 409 (68.7) | 106 (70.2) | 0.729 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 113 (19.0) | 33 (21.9) | 0.428 |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 3 (2-4) | 5 (4-6) | <0.001 |
| CHA2D-VASc | 3 (2-4) | 3 (2-4) | 0.645 |
| Imaging | |||
| LAAPD, mm | 44 (40-48) | 44 (41-48) | 0.081 |
| LVEF, % | 64 (60-65) | 64 (62-65) | 0.660 |
| LAAPEV, cm/s | 32 (22-40) | 29 (20-39) | 0.043 |
| SEC | 85 (14.3) | 43 (28.5) | <0.001 |
| LAAEDA, mm2 | 1,868 (1,486-2,278) | 1,883 (1,545-2,301) | 0.399 |
| LAAESA, mm2 | 1,397 (1,019-1,822) | 1,554 (1,202-2,026) | <0.001 |
| LAAEF, % | 20 (12-33) | 14 (9-19) | <0.001 |
| LAA contrast retention | |||
| Grade 1 | 199 (33.4) | 6 (4.0) | <0.001 |
| Grade 2 | 194 (32.6) | 44 (29.1) | 0.414 |
| Grade 3 | 202 (33.9) | 101 (66.9) | <0.001 |
| Data are presented as n (%) or median (interquartile range). AF: atrial fibrillation; LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAEDA: left atrial appendage end-diastolic area; LAAEF: left atrial appendage ejection fraction; LAAESA: left atrial appendage end-systolic area; LAAPD: left atrial anteroposterior diameter; LAAPEV: left atrial appendage peak emptying velocity; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; SEC: spontaneous echo contrast | |||
Correlations between LAA contrast retention and other parameters
Table 2 illustrates the patient demographics and imaging parameters based on the degree of CR. Substantial differences were observed between grade 1 and grade 2 CR in terms of patients with persistent AF, heart failure, stroke, AF during the procedure, CHA2DS2-VASc score and all imaging parameters. In contrast, only persistent AF (grade 2 vs grade 3, 76.9% vs 89.4%; p<0.001), LAAPEV (30 cm/s vs 25 cm/s; p<0.001) and LAAEF (17% vs 12%; p<0.001) showed a significant difference between grade 2 and grade 3 CR, with more patients with grade 3 CR taking anticoagulants (47.9% vs 59.7%; p<0.001). Figure 3 shows the distribution of LAAEF in different CR grades.
Table 2. Participants’ characteristics according to grade of LAA contrast retention.
| Grade 1, n=205 | Grade 2, n=238 | Grade 3, n=303 | p-value | p-value 1 | p-value 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical | ||||||
| Age, years | 70 (63-77) | 72 (66-77) | 71 (65-76) | 0.199 | ||
| Female | 93 (45.4) | 108 (45.4) | 121 (39.9) | 0.338 | ||
| Persistent AF | 74 (36.1) | 183 (76.9) | 271 (89.4) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Anticoagulation | 80 (39.0) | 114 (47.9) | 181 (59.7) | <0.001 | 0.225 | 0.024 |
| Heart failure | 45 (22.0) | 99 (41.6) | 135 (44.6) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Coronary artery/vascular disease | 52 (25.4) | 64 (26.9) | 82 (27.1) | 0.904 | ||
| Hypertension | 151 (73.7) | 157 (66.0) | 207 (68.3) | 0.205 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 39 (19.0) | 50 (21.0) | 57 (18.8) | 0.794 | ||
| Stroke | 6 (2.9) | 44 (18.5) | 101 (33.3) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AF in procedure | 46 (22.4) | 149 (62.6) | 184 (60.7) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 72 (65-80) | 75 (64-85) | 72 (64-81) | 0.096 | ||
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 3 (2-4) | 3 (2-5) | 3 (2-5) | <0.001 | 0.001 | 0.405 |
| CHA2D-VASc | 3 (2-4) | 3 (2-4) | 3 (2-4) | 0.178 | ||
| Imaging | ||||||
| LAAPD, mm | 40 (37-44) | 45 (41-48) | 46 (42-50) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.190 |
| LVEF, % | 64 (63-66) | 63 (60-65) | 63 (60-65) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 1.000 |
| LAAPEV, cm/s | 38 (30-47) | 30 (20-40) | 25 (18-36) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.003 |
| SEC | 7 (3.4) | 43 (18.1) | 78 (25.7) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.129 |
| LAAEDA, mm2 | 1,715 (1,377-2,124) | 1,897 (1,579-2,336) | 1,896 (1,486-2,403) | 0.002 | 0.003 | 1.000 |
| LAAESA, mm2 | 1,009 (736-1,310) | 1,525 (1,230-1,884) | 1,637 (1,280-2,114) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.077 |
| LAAEF, % | 39 (28-52) | 17 (13-24) | 12 (8-17) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| The significance is shown with p-value (Grade 1 vs Grade 2 vs Grade 3), p-value 1 (Grade 1 vs Grade 2) and p-value 2 (Grade 2 vs Grade 3). The Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons. Data are presented as n (%) or median (interquartile range). AF: atrial fibrillation; bpm: beats per minute; LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAEDA: left atrial appendage end-diastolic area; LAAEF, left atrial appendage ejection fraction; LAAESA, left atrial appendage end-systolic area; LAAPD: left atrial anteroposterior diameter; LAAPEV: left atrial appendage peak emptying velocity; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; SEC: spontaneous echo contrast | ||||||
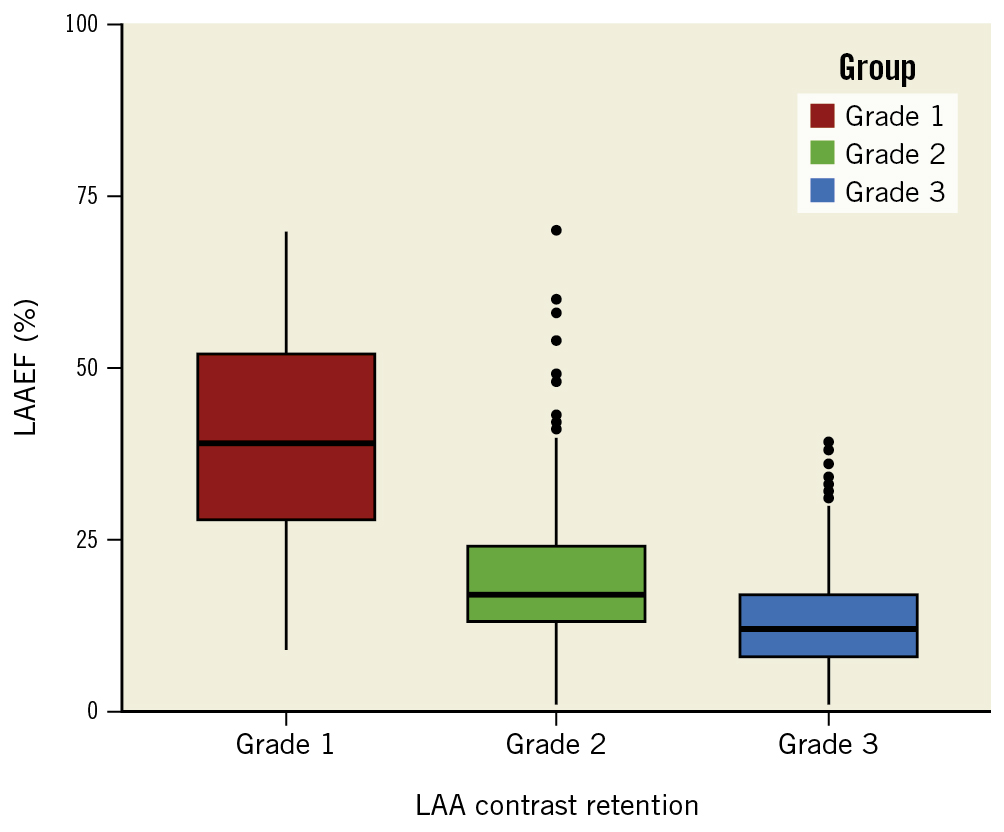
Figure 3. Correlation between LAAEF and CR. The boxplot shows the distribution of LAAEF in different CR grades. LAAEF became significantly lower as the degree of CR increased, which indicates a strong correlation between the two parameters. CR: contrast retention; LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAEF: left atrial appendage ejection fraction
Univariable and multivariable analyses
Table 3 lists the results of logistic regressions. Besides LAAEF and CR, univariate analysis identified the following potential risk factors for stroke: history of anticoagulation, AF rhythm during the procedure, LAAPD and SEC. According to the multivariate analysis, LAAEF (OR 0.96 [95% CI: 0.95-0.98; p<0.001]) and CR (grade 2 vs grade 1=6.82 [95% CI: 2.95-18.66; p<0.001], grade 3 vs grade 1=15.10 [95% CI: 6.69-40.74; p<0.001]) remained significantly associated with stroke after adjustment (Table 3, model 2). Given the multicollinearity between LAAEF and CR, we included variables in model 2 and LAAEF in a new multivariable model 3, of which the results showed that CR was independently associated with stroke in patients with AF (grade 2 vs grade 1=7.29, 95% CI: 2.84-21.65; p<0.001; grade 3 vs grade 1=16.45, 95% CI: 6.16-51.02; p<0.001).
Table 3. Univariate and multivariable analyses.
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted | Adjusted | ||||
| OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | OR (95% CI) | p-value | |
| CHA2D-VASc | 1.04 (0.92-1.18) | 0.484 | ||||
| AF type (persistent) | 1.47 (0.98-2.26) | 0.069 | ||||
| Anticoagulation | 4.49 (3.00-6.89) | <0.001 | ||||
| Heart failure | 0.88 (0.61-1.28) | 0.513 | ||||
| AF in procedure | 1.73 (1.21-2.51) | 0.003 | ||||
| LAAPD | 1.04 (1.01-1.06) | 0.013 | ||||
| LVEF | 1.01 (0.98-1.04) | 0.489 | ||||
| LAAPEV | 0.99 (0.98-1.00) | 0.067 | ||||
| SEC | 2.39 (1.56-3.63) | <0.001 | ||||
| LAAEF | 0.96 (0.94-0.97) | <0.001 | 0.96 (0.95-0.98) | <0.001 | ||
| LAA CR (2 vs 1) | 7.50 (3.36-20.00) | <0.001 | 6.82 (2.95-18.66) | <0.001 | 7.29 (2.84-21.65) | <0.001 |
| LAA CR (3 vs 1) | 17.17 (8.00-44.74) | <0.001 | 15.10 (6.69-40.74) | <0.001 | 16.45 (6.16-51.02) | <0.001 |
| Model 1: Unadjusted. Model 2: Adjusted for history of anticoagulation, heart failure, AF in procedure, LAAPD, LVEF, LAAPEV, and SEC. Model 3: Adjusted for Model 2+LAAEF. Bias-corrected bootstrap 95% confidence interval. AF: atrial fibrillation; CI: confidence interval; CR: contrast retention; LAA: left atrial appendage; LAAEF: left atrial appendage ejection fraction; LAAPD: left atrial anteroposterior diameter; LAAPEV: left atrial appendage peak emptying velocity; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; OR: odds ratio; SEC: spontaneous echo contrast | ||||||
Risk stratification for stroke
According to the results of the ROC analysis, CR identified patients with stroke more accurately than the CHA2D-VASc score (C-statistic 0.712 vs 0.512; p<0.001) or LAAEF (C-statistic 0.712 vs 0.652; p<0.001). Furthermore, the combination of CR and CHA2DS2-VASc score provided better performance in risk stratification for stroke than CHA2DS2-VASc alone (C-statistic 0.871 vs 0.829; p=0.048) (Central illustration).
Discussion
In this cross-sectional study, we comprehensively assessed the mechanical function of the LAA by measuring the LAAEF and LAA contrast retention under angiography. We introduced a reasonable and convenient method of LAAEF measurement and divided the degree of LAA contrast retention into 3 levels. The results demonstrated that low LAAEF and occurrence of LAA contrast retention were closely associated with a history of stroke in AF patients. More importantly, we found that assessment of LAA contrast retention under angiography significantly improves the risk stratification for stroke in patients with AF.
Currently, the CHA2DS2-VASc scoring schema is widely accepted and is recommended as the most important tool for stroke risk stratification in AF, but its predictive value is still far from satisfactory because of its clinical nature8. Of note, some patients with low risk scores (0-1 point) according to CHA2DS2-VASc scoring stratification, who were not recommended for oral anticoagulation treatment by current guidelines, did, however, encounter stroke922. In other words, the CHA2DS2-VASc risk-scoring schema underestimates the risk of thromboembolism in some patients with few clinical risk factors. In fact, when assessing the independent effect of all potential risk factors on TE occurrence in multivariate analysis, female gender was the only significant associated factor4. In the present study, we found that patients with or without a history of stroke had a similar CHA2D-VASc score (CHA2DS2-VASc score not including stroke itself), and the C-statistic value was 0.512 (i.e., a discriminating power not better than chance), indicating that general clinical factors may not be sufficient for risk stratification of stroke in AF patients.
The mechanism of stroke associated with AF, which mainly results from the detachment of thrombus in the LAA, differs from that caused by traditional plaque formation in cerebral arteries. Quantitative evaluation of LAA function via imaging modalities has shown superior abilities in identifying stroke compared to general clinical risk factors. Among various imaging parameters, SEC and LAAPEV are the two representative indicators of LAA thrombus formation and TE events in patients with AF23. For example, a decreased LAAPEV <20 cm/s was correlated with LAA thrombosis and stroke according to recent studies242526. Several other parameters have also shown potential for identifying LAA thrombus and stroke. Ono et al measured the LAAEF using TOE in 260 consecutive patients with NVAF. The results showed that LAAEF was an independent determinant of LAA thrombus in the subgroup of 140 patients with a low CHADS2 score, and an LAAEF value of 21% was the optimal cut-off value for predicting LAA thrombus, which indicates that AF patients with a reduced LAA contractile fraction (LAAEF ≤21%) require strong anticoagulant therapy to avoid TE events regardless of a low CHADS2 score (≤1)14. Besides echocardiography, the incidence of LA mechanical dyssynchrony, measured by the standard deviation of the time to the peak longitudinal strain (SD-TPS) under cardiac magnetic resonance, also identified patients with stroke more accurately than the CHA2DS2-VASc score alone according to a cross-sectional study of 246 patients16. All these studies support that there are major limitations of the current risk stratification for stroke based on the general clinical characteristics in patients with AF, and impairment of the LAA mechanical function may play a critical role in the incidence of TE events. However, there are few reports regarding the evaluation of LAA function using angiography. In addition, the association between LAA mechanical function and stroke in patients with AF needs to be validated in larger populations.
In the present study, 746 consecutive patients who received an LAAO procedure for prevention of stroke were enrolled. To our knowledge, this is the largest sample to date regarding the association between LAA mechanical function and stroke in AF patients using angiography. To comprehensively evaluate the mechanical function of the LAA, we first analysed the two representative echocardiographic parameters – SEC and LAAPEV − using TOE. In line with previous studies, our results indicate that the presence of SEC is more common and LAAPEV is slower in patients with a history of stroke. However, the association between LAAPEV and stroke did not reach significance according to univariate analysis. This may be because LAAPEV only measures the flow velocity at the ostium of the LAA, while the flow velocity at the distal end is usually much slower and more prone to thrombosis.
Compared with these echocardiographic parameters, angiography can mimic the dynamic process of blood flow into and out of the LAA through injection of the contrast agent in a long cine record, making it an intuitive and accurate way to assess the LAA emptying function and the degree of blood stasis inside the LAA. For the first time, we proposed a comprehensive and convenient method to evaluate the LAA function by measuring the LAAEF and grading contrast retention under angiography in a large sample of patients. According to the results, patients with a history of stroke are more likely to have low LAAEF, mostly due to a larger end-systolic area of the LAA. By dividing the degree of contrast retention into 3 levels, we found a significantly higher percentage of grade 3 CR in patients with a stroke history, indicating that a low LAAEF and grade 3 CR are both sensitive markers of impaired mechanical function of the LAA and stroke. It is noteworthy that the proportions of grade 2 CR are comparable between the 2 groups, indicating that delayed clearance of contrast agent is not rare in patients with AF. Although patients with grade 2 and grade 3 CR had similar clinical and imaging characteristics, stroke events were much more common in grade 3 CR, which highlights the value of severe contrast retention (grade 3 CR) in identifying stroke.
Univariate and multivariable analyses indicate that contrast retention in the LAA under angiography (both grade 2 and grade 3 CR) is independently associated with stroke, with grade 3 CR posing a 15-fold greater risk than grade 1. ROC analysis results suggest that CR is significantly better than both the CHA2D-VASc score and LAAEF in risk stratification of stroke in AF patients. Combining CR and the CHA2DS2-VASc score yields the best performance, which demonstrates the additional information that CR may provide beyond clinical risk factors. Moreover, the median delay between stroke and LAA angiography was 6 months in our cohort. Regardless of the time interval, patients with stroke consistently had a lower LAAEF and more notable CR, indicating that these angiographic parameters are associated with the risk of stroke for a long period and may have good prognostic value.
Two recent studies with small samples also analysed the results of LAA angiography in patients who underwent an LAAO procedure and found that patients with CR in the LAA have a higher risk of LAA thrombosis and cardioembolic stroke2728. In fact, compared with other parameters including the LAAPEV, SEC and LAAEF, the underlying mechanism of CR is possibly an integration of specific LAA morphology, physiology and haemodynamics, which makes it a unique and comprehensive way to assess the mechanical function of LAA and reflect the possibility of TE events. In addition, the angiographic method of mechanical function assessment with the LAAEF and CR is quite convenient to perform, with a one-time injection, and it can be conducted at the same time as any intervention inside the left atrium, including catheter ablation, which shows great potential in distinguishing high-risk from low-risk individuals during such procedures.
Limitations
The present study is a single-centre, retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of patients referred for an LAAO procedure with considerably high CHA2DS2-VASc scores rather than the general AF patients. Therefore, there is a non-negligible chance of selection bias. It is important to note that prior stroke was not used as a risk factor but was rather evaluated more akin to an outcome variable in our cross-sectional study. However, it should be noted that LAA angiography was performed after the stroke occurred. Thus, patient characteristics and anticoagulation treatment during the procedure may not be the same as they were at the time of stroke. Furthermore, instead of using software and algorithms, the assessment of LAAEF and CR was performed manually using PACS according to the medical record system in a retrospective manner; it is possible that inappropriate judgements were made. For the LAAEF calculation, we measured the LAAESA and LAAEDA from only 1 angiographic angulation (primarily the 30°/20° RAO/CAU view), which could introduce potential errors due to the large variety of LAA anatomies. Future prospective trials are needed to validate our conclusions.
Conclusions
Impaired mechanical function of the LAA indicated by a low LAAEF and CR is associated with a history of stroke in patients with AF. Assessment of CR using LAA angiography helps improve the stratification scheme for stroke risk prediction.
Impact on daily practice
Current risk stratification schemes for stroke based on clinical risk factors are suboptimal in patients with atrial fibrillation. Impaired mechanical function of the LAA, indicated by a low LAAEF and CR under angiography, is associated with a history of stroke. Combining CR with the CHA2DS2-VASc score is valuable in refining risk stratification for stroke in patients with AF.
Acknowledgements
We thank Bin Liu for helping with data collection and Ming Zhang for valuable advice on statistical analysis.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 82170247 and 82200557), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (grant number: 19ZR1449600) and the Three-year action plan project to promote clinical skills and clinical innovation ability of Shanghai municipal hospitals (grant number: SHDC2020CR1039B).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

