
Bioresorbable scaffolds (BRS) were conceived and introduced into clinical practice with the objective of overcoming the limitations of newer-generation drug-eluting stents (DES), such as the risk of target lesion revascularisation and device thrombosis1. The drug-eluting poly-L-lactide acid-based bioresorbable vascular scaffold (BVS; Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was the first to be introduced onto the market in 2011, claiming late lumen enlargement and restoration of normal vasomotor response as potential advantages related to its transient scaffolding. These data were based on the first-in-man experience, which was the only evidence available at that time2,3.
In 2015, the Gauging coronary Healing with biOresorbable Scaffolding plaTforms in EUrope (GHOST-EU) registry was the first study to point out a higher than expected midterm scaffold thrombosis4. Since then, many meta-analyses, based on few clinical trials not powered for clinical endpoints, have questioned the safety profile of this device, either at midterm or at long-term follow-up. Specifically, at three-year follow-up, BVS were associated with a higher rate of target vessel myocardial infarction and scaffold thrombosis, when compared to newer-generation DES5-7. These unsatisfactory data resulted first in a restriction of BVS use to clinical trials only and later to a stop in sales of the device.
The scaffold thrombosis issue is seen as being of particular importance. It seems to have different causes according to the time of its occurrence8,9. With regard to early events, for example, implantation technique has been advocated as an important issue for its prevention. The PSP technique, which consists of adequate predilatation, sizing and post-dilatation, was seen as an important feature in order to reduce adverse events up to one-year follow-up10-12. However, when we move to very late events, it is unknown whether scaffold thrombosis is still related to implantation technique or whether other factors must be taken into account13.
Waiting for long-term data which may help to shed light on these very late events, there are still ABSORB real-world registries being published. In the present issue of EuroIntervention, BVS real-world data from the Swedish Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty Registry (SCAAR) and the German-Austrian ABSORB RegIstRy (GABI-R) are reported14,15.
The SCAAR registry is part of the Swedish Web-system for Enhancement and Development of Evidence-based care in Heart disease Evaluated According to Recommended Therapies (SWEDEHEART) registry, including all Swedish patients undergoing a diagnostic catheterisation or PCI procedure. Within this registry the authors compared the two-year outcomes of 460 patients (810 scaffolds) treated with BVS between October 2011 and August 2016 and of a control group of 38,097 patients (67,099 stents) treated with newer-generation DES in the same period14. The authors performed a main analysis in all the included patients (stent-level) and four additional sensitivity analyses including a propensity score matching, the details of which are not reported. They found an increased adjusted rate of scaffold thrombosis in the BVS group when compared to the DES (12 [1.5%] vs. 406 [0.6%]; HR 4.34, 95% CI: 2.35-8.45; p=0.001). Interestingly, about 83% of BVS thromboses may be explained by lack of compliance to dual antiplatelet therapy or implantation technique issues with BVS undersizing, which in one case needed a post-dilatation above the allowed limit (0.5 mm). Only three cases of very late scaffold thrombosis were noted and no specific details are given. Of note, despite most of the BVS operators having more than 10 years’ experience in PCI, about 66% of the thrombosed devices occurred within the first five BVS implanted by the same operator, implying a learning curve and, for the future, the need for an appropriate and specific experience in these devices and the PSP technique, regardless of personal experience with metallic stent implantation.
The GABI-R, also reported in this issue of EuroIntervention, is a prospective, observational, multicentre study (NCT02066623) of 3,231 consecutive patients undergoing BVS implantation at 92 sites between November 2013 and January 201615.
At six-month follow-up, the rates of MACE and TLF were 4.1% and 2.4%, respectively, with a definite/probable scaffold thrombosis rate of 1.4%. The authors performed an outcome analysis according to an optimal PSP technique, but they did not find any differences. In our opinion, however, this analysis could be misleading: when the authors instead analysed patients according to the time of inclusion, they found that later patients received a more accurate implantation technique with a higher rate of predilatation and post-dilatation and higher use of NC balloon than early patients, resulting in a lower six-month event rate. In the absence of prospective implantation protocol, operators usually perform extensive predilatation and high-pressure post-dilatation in lesions where the device expansion is suboptimal. If the patients were selected retrospectively according to protocol-defined implantation technique, the group could represent a biased population in terms of lesion complexity and clinical outcomes. A favourable role for the PSP technique cannot then be excluded.
A specific sub-analysis from GABI-R focusing on a cohort somehow more numerous than the one specified in the original paper (3,364 vs. 3,231 patients) tried to rule out the predictors of 24 clinically indicated target lesion revascularisations (cTLR)16.
By using a multivariate model, which may be overfitted by taking into account more than the recommended one variable per 10 events, the authors found that implanted BVS length was the only independent predictor of cTLR. As more lesions in different vessels were treated in those patients with cTLR, BVS length may be the result of different BVS implanted in different vessels and not necessarily of long lesions treated.
Overall, many important messages can be extrapolated from these three analyses. As compared to randomised clinical trials that contribute to evidence-based medicine, registries represent “real-world” clinical practice, where a technology is used in an all-comer population by an all-comer interventional cardiology community. Both registries agree that BVS, for the time being, is not an all-comer technology that can be used by all-comer interventional cardiologists. Once again, BVS appeared to be a “less forgiving” device as compared to metallic stents, as any issue with DAPT adherence and implantation protocol may represent the basis for future adverse events10,17. In this sense, waiting for BRS technological improvement, selection of the proper patient/lesion to be treated with a refined implantation technique, together with appropriate DAPT are important to consider when a BRS is going to be implanted (Figure 1).
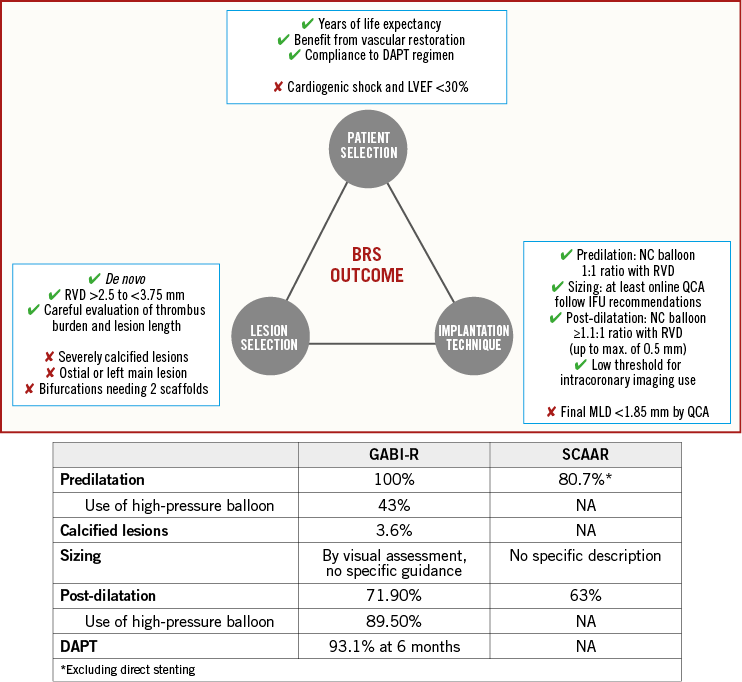
Figure 1. Predictors of BRS outcome. In the top panel, possible predictors of BRS outcome are illustrated, based on available data. The bottom panel shows a comparison between GABI-R and SCAAR results in terms of some of these predictors. BRS: bioresorbable scaffold; IFU: instructions for use; MLD: minimum lumen diameter; NC: non-compliant; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; RVD: reference vessel diameter
Last but not least, it should be noted that these registries have very limited additional value to the data already known, given their inherent registry nature, lack of a randomised control group or a follow-up as long as complete BVS resorption. As an interventional cardiology community, we should be focused either on data from other BRS devices currently on the market, which are unfortunately very limited, or on high-quality very long-term data. In this regard, very long-term follow-up of those randomised clinical trials, powered for clinical endpoints, such as ABSORB III and IV, are much needed. In theory, the device could reveal its clinical benefit after the completion of bioresorption (~3 years) by liberating the vessel from the metallic cage and restoring the physiological functions of the coronary artery18. As the primary outcomes of the ABSORB IV trial have recently changed to landmark TLF at 3-7 years, from its original endpoint of landmark TLF at 1-5 years (https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02173379), very long-term clinical outcomes beyond three years are warranted to judge the potential of this technology. Whether or not the Absorb could exhibit clinical benefit in the post-bioresorption period would be of paramount importance, not only for the Absorb but also for all future iterations of bioresorbable scaffolds. Along the same lines, very long-term outcomes from these registries are also important and will be complementary to the data stemming from randomised clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Brugaletta reports receiving a research grant to his institution from AstraZeneca, and speaker’s fees from Abbott Vascular and Boston Scientific. Y. Onuma was a member of the advisory board of Abbott Vascular. L. Ortega-Paz has no conflicts of interest to declare.

