
Abstract
Aims: Our aim was to study the effectiveness of coronary stent implantation during the endovascular treatment (EVT) of acute basilar artery occlusion (BAO) with occlusion-underlying intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS).
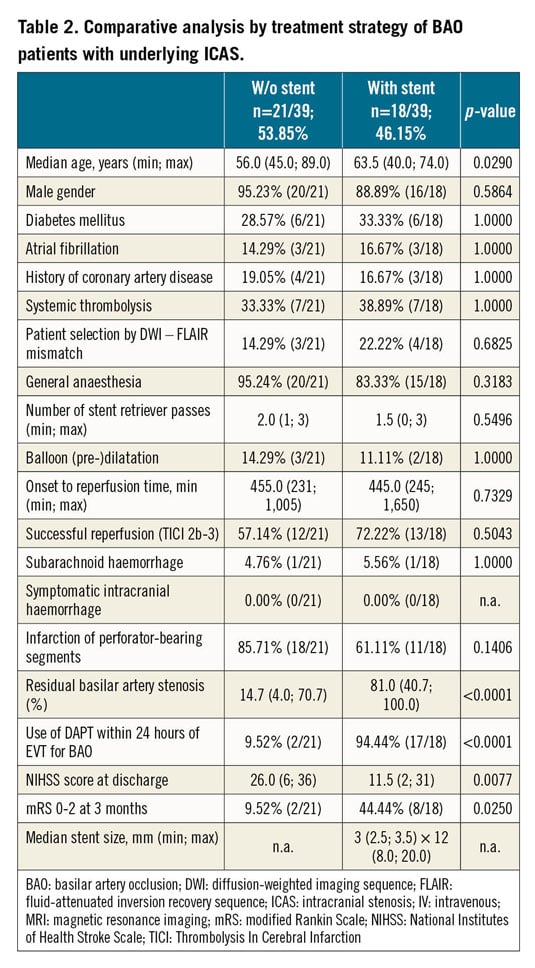
Methods and results: We retrospectively analysed 91 consecutive BAO patients who underwent EVT between February 2014 and January 2019 in a single, high-volume neurointerventional centre. We studied the effect of immediate coronary stent implantation on the clinical outcome of BAO with occlusion-underlying stenosis. BAO patients with underlying ICAS (n=41) were characterised by longer symptom-onset-to-reperfusion times (231 min vs 173 min, p=0.0020), lower TICI 2b-3 reperfusion rates (65.85% vs 90.00%, p=0.0084), and higher overall mortality (HR 2.021, p=0.0417) compared to the BAO cases without ICAS (n=50). The patients undergoing stenting (n=18) had lower residual basilar artery (BA) stenosis (14.7% vs 81.0%, p<0.0001), higher chance for functional recovery (OR 7.6, p=0.0250) and higher chance of survival (HR 4.163, p=0.0026) compared to the BAO-ICAS cases treated without coronary stents (n=21).
Conclusions: The immediate treatment of the occlusion-underlying stenosis with coronary stents and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) in BAO was associated with improved overall survival and better functional outcomes.
Introduction
The occlusion of the basilar artery (BA) generally leads to severe forms of ischaemic stroke with a natural history characterised by high mortality or persistent major disability1. Early observational studies have already demonstrated that successful reperfusion therapy significantly improves the outcome of acute basilar artery occlusion (BAO) in patients treated by local intra-arterial and by systemic intravenous thrombolysis (IVT)2. While recent advances in the endovascular treatment (EVT) of large vessel occlusions (LVO)3 have fundamentally changed the treatment guidelines of anterior circulation strokes4, the evidence-based approach to LVO in the posterior fossa is still controversial, with no clear recommendation on the optimal reperfusion strategy in these patients5. The currently available data on the safety and efficacy of mechanical thrombectomy (MT) in the posterior circulation come from non-randomised observational studies. Most authors agree that, despite its remarkable effectiveness6, MT in the posterior fossa is more prone to complications than similar procedures in the anterior circulation7. One likely explanation for this phenomenon is the higher prevalence of atherosclerotic disease in the posterior fossa, which was previously reported to be a very common cause of BAO8. The aim of our study was to analyse the clinical effectiveness of high radial force coronary stent implantation during the EVT of acute BAO with occlusion-underlying stenoses.
Methods
PATIENT SUBGROUPS
We analysed the data of consecutively treated stroke patients with occlusion of the BA (Table 1). All included cases were treated by MT over a five-year period at the National Institute of Clinical Neurosciences, Budapest, Hungary, a high-volume, interventional stroke centre with a catchment area which includes about three million inhabitants. We compared the data of patients with or without intracranial stenosis involving the BA; within the cohort with occlusion-underlying stenosis we compared the cases treated by coronary stent implantation or a conservative approach allowing only MT and balloon dilatation in some cases.
PROTOCOL FOR MT
All patients eligible for IVT received alteplase before EVT. Patients with a confirmed BAO on non-invasive imaging would proceed to EVT within 12 hours from symptom onset if the admission computed tomography (CT) scan did not indicate any suspicion of intracranial bleeding or extensive ischaemic hypodensity. Patients presenting beyond 12 hours and cases with unknown onset of symptoms underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); those who had diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) confirming fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) mismatch in the eloquent regions would be offered EVT. MT was performed according to standard protocols using predominantly 8 Fr balloon guide catheters (Cello™; ev3 Inc., Irvine, CA, USA), dedicated intracranial Transend® 14” guidewires with compatible Trevo® Pro 18” microcatheters (Stryker Neurovascular Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) and three different types of commercially available stent retriever – Solitaire™ (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA), Trevo (Stryker Neurovascular Inc.) and pRESET (Phenox GmbH, Bochum, Germany). The procedures were executed by five experienced neurointerventional specialists, each performing over 30 thrombectomies a year. The direct aspiration first pass technique was applied only in selected cases in the last two years of the study period using the SOFIA® aspiration catheter (MicroVention, a Terumo group company, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA). The procedures were performed predominantly under general anaesthesia.
STENTING OF THE BA
A subgroup of patients with significant occlusion-underlying stenosis underwent stent placement. Significant atherosclerotic stenosis was diagnosed based on the digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images: occlusion-underlying stenosis was defined as an estimated 50% or greater luminal narrowing at the site of the occlusion following MT, with the stenotic lesion persisting after the local administration of 1 mg nimodipine through the guide catheter (Figure 1).
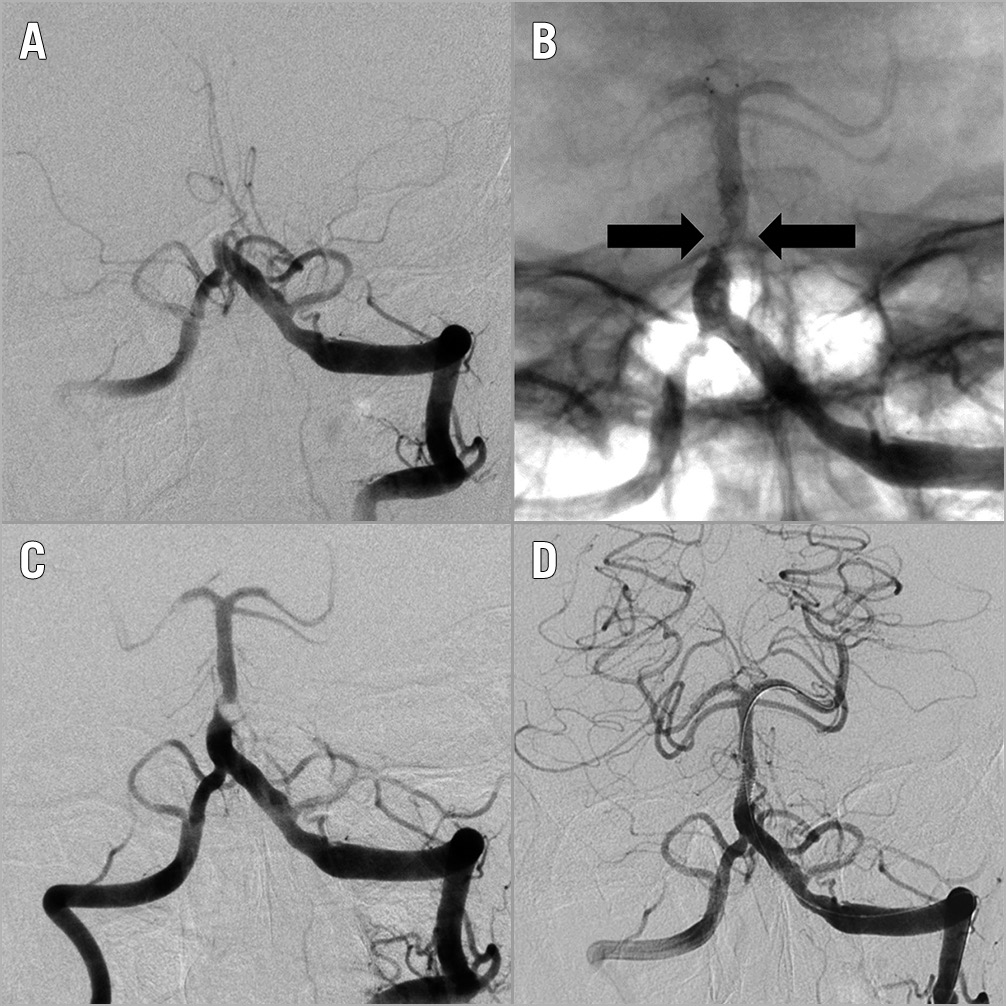
Figure 1. Stenting of the basilar artery. Occlusion of the basilar artery (A) with the unsheathed self-expanding stent retriever compressed (arrows) at the site of the occlusion (B), due to a flow-limiting, high-grade stenosis (C). Successful recanalisation of the occluded segment by balloon-expandable coronary stent (D).
The indication for stenting was left to the operator’s discretion. The currently available dedicated intracranial stents have questionable efficacy and no formal indication for the treatment of acute BAO; therefore, we decided to test the effectiveness of bare metal coronary stents (BMS) (Omega™; Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) in our patients. Stents were undersized by 0.5 mm to the estimated distal reference diameter of the BA in order to prevent edge dissection. The intended final diameter was reached applying overdilatation under roadmap control using pressures below the rated burst pressure (RBP) defined on the device label (Figure 1).
ANTITHROMBOTIC THERAPY
Patients who underwent stent placement received 70 IU/kg unfractionated heparin and 500 mg of IV aspirin during the procedure. If the post-procedural CT scan did not show any suspicion of bleeding, an additional 300 mg loading dose of clopidogrel was administered via a nasogastric tube. Patients without stenting received antithrombotic therapy according to the current treatment guidelines4: without confirmed indication for anticoagulation, they were given aspirin monotherapy and prophylactic low molecular weight heparin (LMWH). If extensive ischaemia or bleeding was detected on the control imaging, the antithrombotic therapy was withheld.
OUTCOME MEASURES
The symptom-onset-to-reperfusion time was defined as the interval between the time of onset of the acute symptoms that led to clinical diagnosis and the time of the angiographic run following the last procedural step of the intervention. When this time was unknown, the last time the patient was observed in a normal state was regarded as the onset. Intracerebral haemorrhages were classified according to the European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS) II criteria9.
BA angiography was obtained using at least two perpendicular projections. The vessels and stenoses were measured by a computerised quantitative analysis system (Advantage Workstation 4.6; General Electric, Chicago, IL, USA). Minimum lumen diameter, reference vessel diameter distal to the lesion and percent diameter stenosis were quantified before and after angioplasty (Figure 2A).
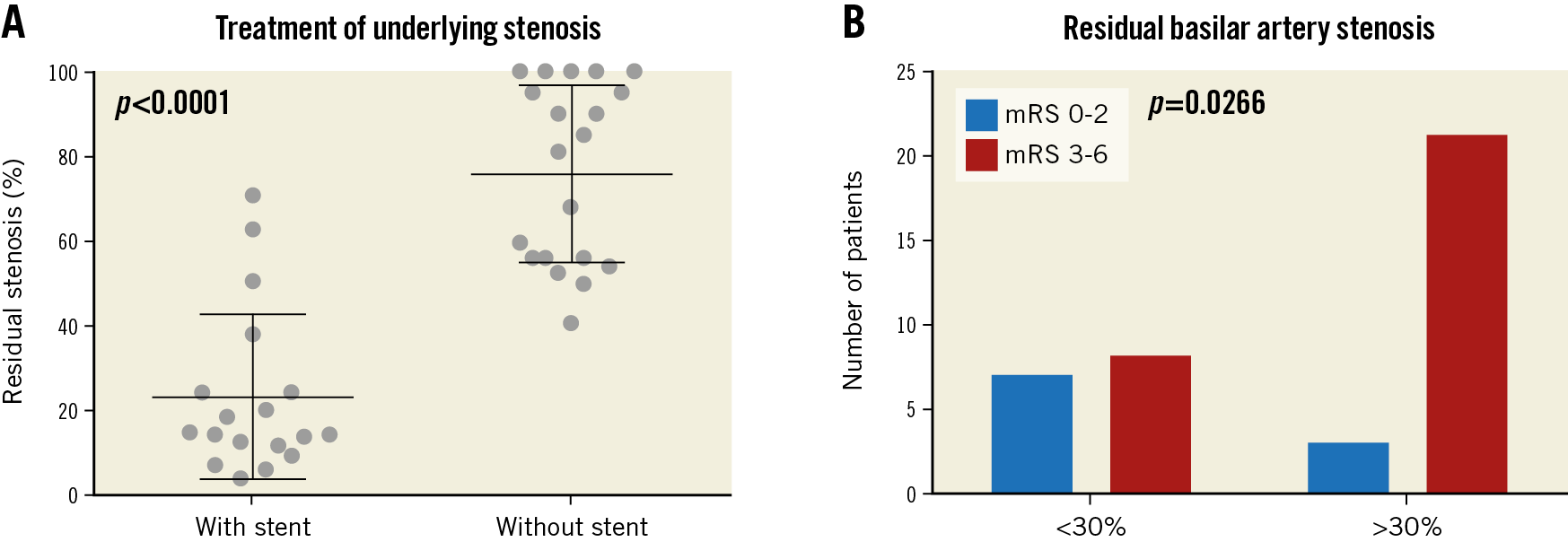
Figure 2. Residual stenosis following stenting. Significantly lower (p<0.0001) residual BA stenosis was measured after stent implantation (A). Error bars represent the means with standard deviation. Lower residual stenosis was associated with improved functional outcome (p=0.0266) (B).
Reperfusion status was also evaluated on the final angiogram by the operators using the modified Thrombolysis In Cerebral Infarction (m-TICI) scale. Successful reperfusion was defined as an m-TICI grade of 2b-310.
Clinical outcome was assessed 90 days after treatment with the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) score11 by certified stroke neurologists on outpatient visits. When patients were unable to attend the outpatient clinic, outcomes were assessed in telephone interviews. The long-term all-cause mortality data were provided by the National Health Insurance Database.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Descriptive statistics for continuous measures are given as the mean with standard deviation or as the median with minimum and maximum values. For discrete data, count (n/N) and percentages (%) are equally tabulated. The Mann-Whitney U test and Fisher’s exact test were used to compare clinical and imaging findings of the different patient cohorts, as appropriate. Survival probabilities were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method; differences were assessed by the log-rank test. All tests were two-tailed with a confidence interval of 95%; statistical significance was confirmed when p-values were <0.05. Calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism 6 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). All procedures and investigations were performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki, following approval of the institutional ethics committee of the National Institute of Clinical Neurosciences.
Results
OVERALL SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF EVT IN BAO
Altogether 92 cases of BAO were treated with EVT in our centre between January 2014 and February 2019. One patient was lost to follow-up and was therefore excluded from our study. One patient underwent two clinically successful thrombectomies with a six-month time difference. Ninety-one cases were included in our analysis (98.9%, 91/92), with a median mortality follow-up time of 83 days (minimum: 1; maximum: 1,050).
Systemic thrombolysis was used in 45.05% (41/91) of the cases; 83.52% (76/91) of all procedures were performed under general anaesthesia. Successful reperfusion (TICI 2b-3 flow) was achieved in 79.12% (72/91). The median symptom-onset-to-reperfusion time was 398 (173; 1,650) minutes. Subarachnoid haemorrhage was documented in 7.69% (7/91); symptomatic intracranial haemorrhage was diagnosed in 2.20% (2/91).
By three months, 32.22% (29/90) of the treated patients reached functional independence (mRS 0 to 2). The mortality rate at three-month follow-up was 32.22% (29/90).
COMPARISON OF PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND EVT OUTCOME IN BAO WITH OR WITHOUT ICAS
Significant occlusion-underlying stenosis was documented in 45.05% (41/91) of the treated cases. BAO patients with occlusion-underlying stenosis (n=41) were characterised by male predominance (92.68% vs 50.00% p=0.0001), and a higher frequency of proximal BA segment occlusions (51.22% vs 26.00%, p=0.0171) according to the Archer-Horenstein classification12. BAO cases without ICAS (n=50) had higher median CHA2DS2-VASc scores (3 vs 2, p=0.0231)13, supporting the presumed embolic origin of the occlusions in this subgroup.
The BAO patients with occlusion-underlying stenosis had an increased risk of all-cause mortality (HR 2.021, p=0.0417) compared to the patients without stenosis. All available validated predictive factors of EVT outcome in the posterior circulation were analysed (Table 1). Significant difference was found in two parameters: the symptom-onset-to-reperfusion times were significantly higher (451.0 min vs 375.0 min, p=0.0020), and the rate of successful reperfusion (65.85% vs 90.00%, p=0.0084) was significantly lower in the BAO patients with ICAS. Importantly, we found no significant difference in the rate of haemorrhagic complications.
SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF STENTING OF THE OCCLUSION-UNDERLYING STENOSIS IN BAO
Among the 41 patients presenting with occlusion-underlying stenosis, 18 underwent coronary stent implantation with early post-procedural administration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT). The decision to stent was based entirely on operator preference; no randomisation was performed. The delivery of coronary stents was successful in all attempted cases (Table 2).
In two BAO patients, the operator decided to implant low radial force self-expanding stent devices, originally developed for the treatment of wide-necked aneurysms. Due to the fundamentally different implantation technique and device structure, these two cases were excluded from our analysis.
Despite the lack of randomisation, among the baseline characteristics compared in our retrospective analysis, we found a significant difference only in the age of the BAO-ICAS subjects: stented patients were slightly older (63.5 vs 56.0 years; p=0.0290). The symptom-onset-to-reperfusion times, the number of stent retriever passes, the frequency of intracranial bleeding complications, the rate of perforator segment-related infarcts and even the end-procedure TICI 2b-3 reperfusion rates of the two treatment strategies were statistically non-different.
Despite the largely similar baseline and procedural characteristics of the patient groups, we found remarkable difference in the effectiveness of the treatment strategies. The patients undergoing stenting (n=18) had significantly lower residual basilar artery stenosis compared to the patients treated without stents (14.7% vs 81.0%, p<0.0001) (Figure 2B). They equally presented better National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) scores at discharge (11.5 vs 26.0, p=0.0057) (Figure 3A) and improved three-month functional status (3-month mRS 0-2: 44.4% vs 9.5%; OR 7.6, p=0.0250) (Figure 3B). More importantly, the stented cohort, which was also characterised by higher periprocedural use of DAPT (94.44% [17/18] vs 9.52% [2/21], p<0.0001), had a lower rate of overall mortality (HR 4.163, p=0.0026) (Figure 4).
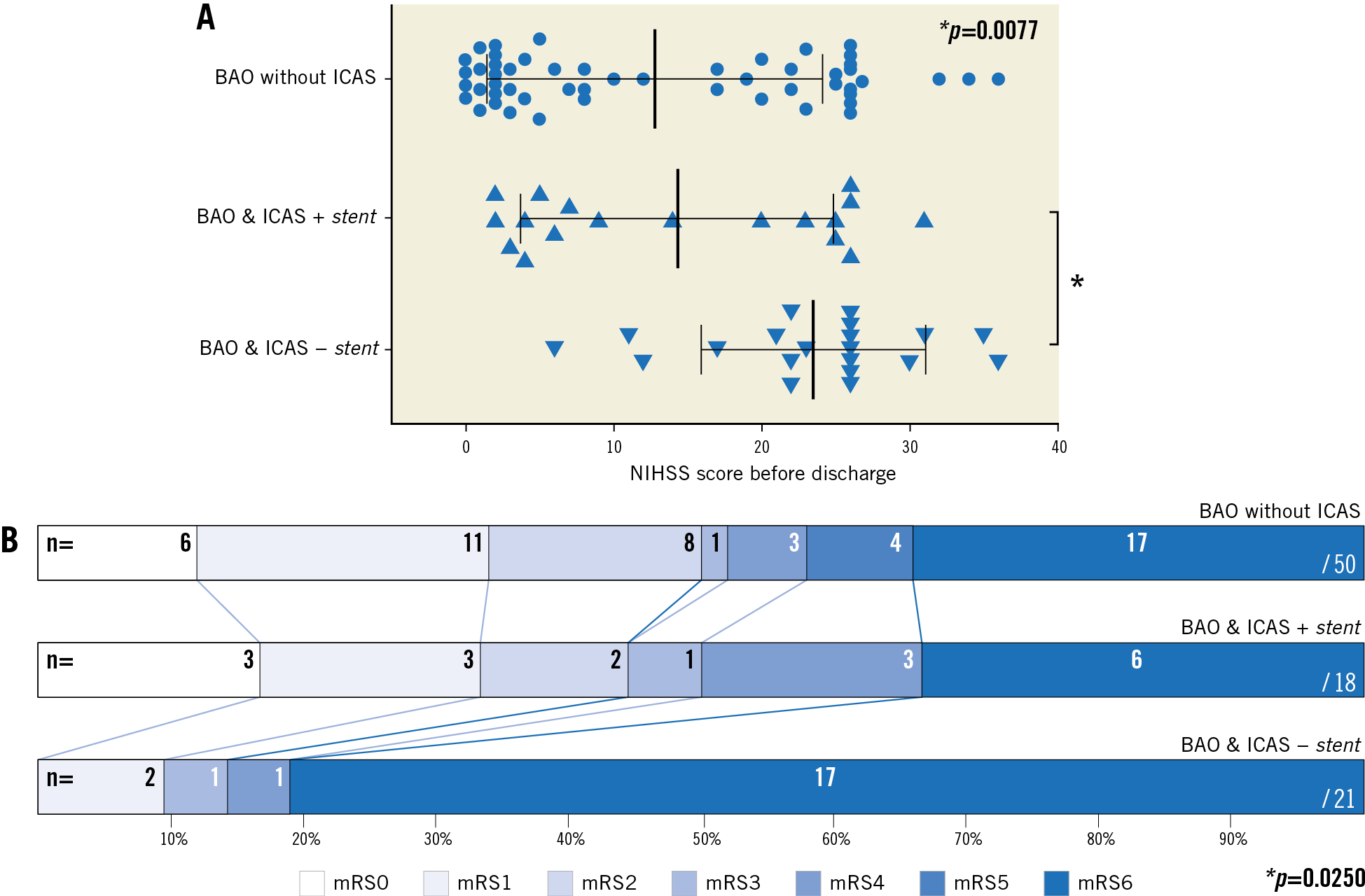
Figure 3. Functional outcomes following stent implantation. A) The last National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale values are shown for each patient before discharge. The star (*) indicates the significantly (p=0.0077) worse discharge status of the BAO patients with stenosis treated without stenting. Bars represent the means with standard deviation. B) The horizontal bars represent the distribution of modified Rankin Scale values of the three patient groups at three-month follow-up. The star (*) highlights the significantly (p=0.0250) worse functional outcome of ICAS patients treated without stents.
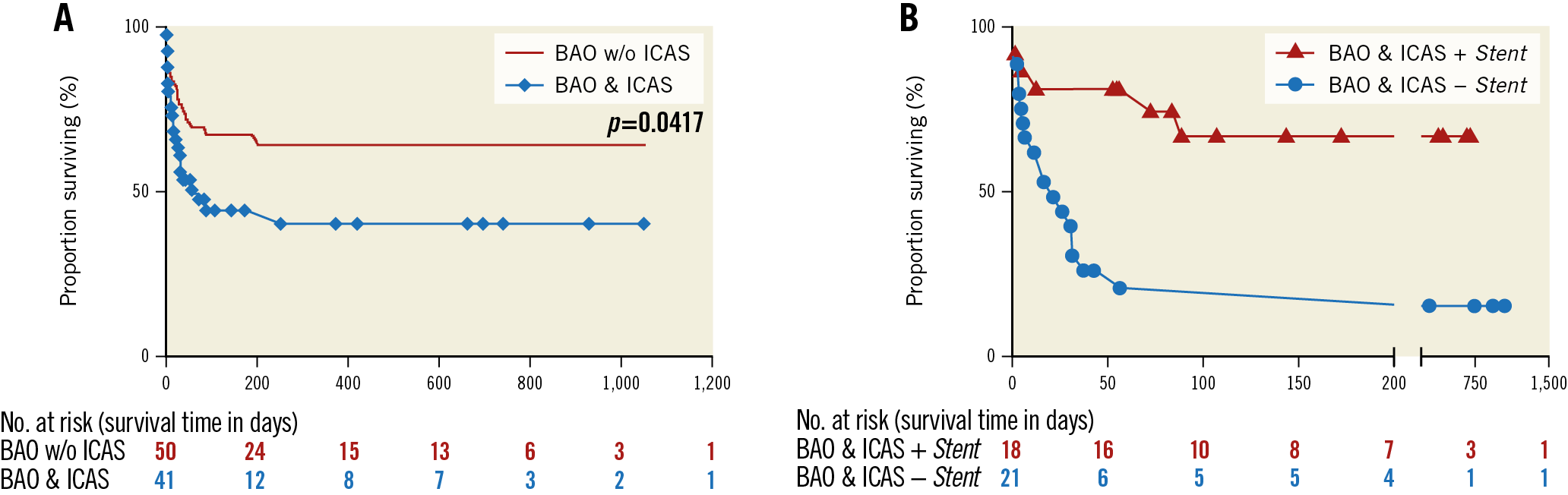
Figure 4. Overall survival of patients following EVT for BAO. A) The survival curve shows different overall survival for the BAO patients with (blue curve with diamonds) or without (red line) ICAS (p=0.0417). B) The survival of BAO-ICAS patients treated with or without stenting is shown separately: stented patients (curve with triangles) had better overall survival (p=0.0026). The tables under each survival curve show the number of patients at risk for each time interval.
Discussion
We report the outcome data of 91 consecutive cases of BAO undergoing EVT, with a 32.2% rate of good functional outcome and a 32.2% rate of mortality at three-month follow-up in a single high-volume centre. Our results are statistically non-different from the data published in the largest available meta-analysis including 312 patients treated by MT for BAO, regarding the safety and efficacy of the procedures14.
We detected occlusion-underlying stenosis of the BA in 45.05% (41/91) of the cases, with a significant impact on the prognosis of the patients undergoing MT (Figure 4). The reason for the difference in outcome was probably the significantly higher onset-to-reperfusion time and the significantly worse quality of reperfusion in the patients with ICAS, which can both be attributed to the technical difficulties of revascularisation in the presence of atherosclerotic plaques. According to our findings, specific rescue treatments are necessary to neutralise the negative effect of the occlusion-underlying stenosis in the BA. While at first our observations seem contradictory to the previously published data on the outcome of EVT in BAO patients with ICAS, the procedural differences between the studies can well explain the different conclusions. Lee at al found an equally high clinical success rate of EVT in BAO patients with or without ICAS; however, in the majority of their 15 ICAS cases (8/15), they used early aggressive treatment with the application of stents and DAPT, and almost all ICAS patients (13/15) underwent at least balloon angioplasty of the occlusion-underlying stenosis following MT15. Similar to these findings, the early aggressive therapy in our stented subgroup also resulted in a comparable treatment efficacy to the MT performed in BAO patients without ICAS.
While the difference in outcomes in our study was driven mainly by the high mortality of the stenotic patients treated without stenting and DAPT, the optimal treatment of occlusion-underlying stenosis in BAO is still unclear. The choice of antiplatelet therapy seems to have crucial importance even in the very early phase following MT in BAO patients with ICAS. In their recent non-randomised comparison, Kang et al reported that the use of tirofiban combined with bail-out balloon angioplasty resulted in similar rates of successful reperfusion to the upfront angioplasty strategy with or without stent implantation6. However, the current guidelines do not allow the use of GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors in stroke patients treated with previous IVT4; therefore, alternative strategies need to be considered in a large proportion of cases. We found no difference in the bleeding rates among the different subgroups studied. Our findings suggest that the early use of DAPT was safe in most patients, irrespective of the previous application of thrombolytics. However, the optimal duration of DAPT is difficult to define, considering the potentially devastating consequences of an eventual stent thrombosis.
The indication for stenting in the BA is highly debated, as the optimal medical therapy (OMT) with aspirin and clopidogrel alone provided superior safety and treatment efficacy in the context of symptomatic stenosis, compared to the combined use of DAPT and self-expanding Wingspan stents (Stryker Neurovascular Inc.) in the SAMMPRIS randomised trial16. Similar results were published following the early termination of the Vitesse Intracranial Stent Study for Ischemic Stroke Therapy (VISSIT) study, favouring OMT over the use of the balloon-expandable Pharos™ Vitesse™ Neurovascular Stent System (Johnson & Johnson, New Brunswick, NJ, USA)17. However, following the publication of the SAMMPRIS and the VISSIT trials, several questions were raised concerning the study designs, device selection and trial execution. It is also important to note that acute BAO patients were excluded from both studies. According to all available observational data, the risk of adverse outcome is much higher in case of BAO than in non-occlusive BA stenosis; the direct effect of mechanical thrombectomy on the diseased wall of the BA is likely even to increase the thrombogenicity of the occlusion-underlying plaques, leading to an even more elevated risk of thrombotic vessel closure, similar to the effect of plain old balloon dilatation during coronary interventions. We took the high bleeding risk, the tortuous vascular anatomy and the generally short lesion length into account when choosing to implant bare metal coronary stents in our patients. Our choice was proven safe, as we found no excess in bleeding complications or perforator segment-related infarcts, similar to the previous publications using this off-label technique in the treatment of symptomatic ICAS18. Moreover, our work is the first analysis to show that coronary stent implantation in BAO was not only effective in increasing the final lumen at the occlusion site, but was also associated with improved neurological outcome and better survival. As the patients with less than 30% residual stenosis had a significantly higher chance of functional recovery, we assume that the therapeutic effect in the stented cohort resulted mainly from the more complete restoration of blood flow in the BA, while the early administration of DAPT probably also contributed to the clinical benefit.
Interestingly, the end-procedure TICI 2b-3 reperfusion rates of the ICAS patients treated with or without stenting were not significantly different; however, this anatomy-based scale focuses mainly on side branch occlusions and does not account for the potential flow limitation caused by stenotic vascular segments. Based on our findings, a dedicated scoring system should be developed for the assessment of reperfusion therapy in the posterior circulation due to the unique pathophysiologic characteristics of this vascular territory.
Limitations
We recognise that the retrospective design, the lack of randomisation and the uneven patient flow during our observational period are all important limitations of our study.
Conclusions
The large difference in outcomes observed in our study implies that BAO patients with ICAS need specific interventions. Randomised trials should be conducted in the future to determine the optimal treatment strategy.
|
Impact on daily practice Coronary stent implantation over the occlusion-underlying stenosis following MT in acute BAO significantly increases the final lumen of the basilar artery. It may equally improve the functional outcome and overall survival of the treated patients. |
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

